Understanding the correct application of specific expressions is a crucial step in becoming proficient in a new language. These linguistic elements often carry nuanced meanings that can significantly impact how your sentences are interpreted. Mastering them not only improves clarity but also boosts confidence in communication.
In this guide, we’ll explore the rules, contexts, and common applications of two essential components used in various situations. You’ll learn how to differentiate their usage effectively, ensuring your language skills are precise and natural.
By focusing on real-life scenarios and practical examples, this section aims to simplify complex ideas. With detailed explanations and tips, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding to excel in your learning journey.
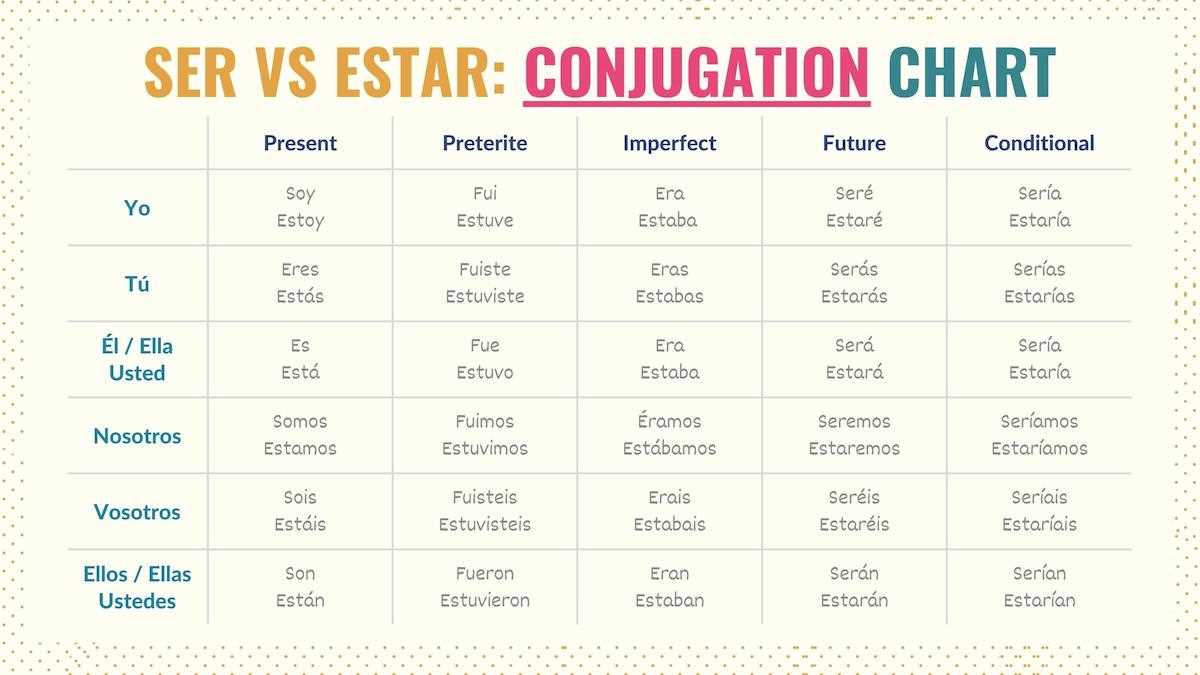
Understanding the Differences Between Ser and Estar
In language learning, choosing the correct expression to describe identity or temporary states can be challenging. These terms often depend on subtle contextual cues, making it essential to grasp their distinct roles to communicate effectively.
Key Concepts for Effective Usage
To apply these terms correctly, focus on the nature of the description. Some phrases emphasize inherent qualities, while others highlight temporary or situational aspects. Recognizing these contrasts can significantly improve your sentence construction.
- Expressions tied to lasting attributes often reflect qualities that define something or someone.
- Temporary conditions, on the other hand, indicate a state or situation subject to change.
- Context plays a crucial role, particularly in phrases involving time, place, or emotions.
Examples to Clarify the Usage
- Use descriptive terms for personality traits, professions, or physical attributes when referring to long-term characteristics.
- For fluctuating moods, health, or current activities, choose expressions that align with momentary circumstances.
- In cases involving location, differentiate whether permanence or transience is implied.
By understanding these principles, you can ensure your communication is clear and accurately conveys the intended message.
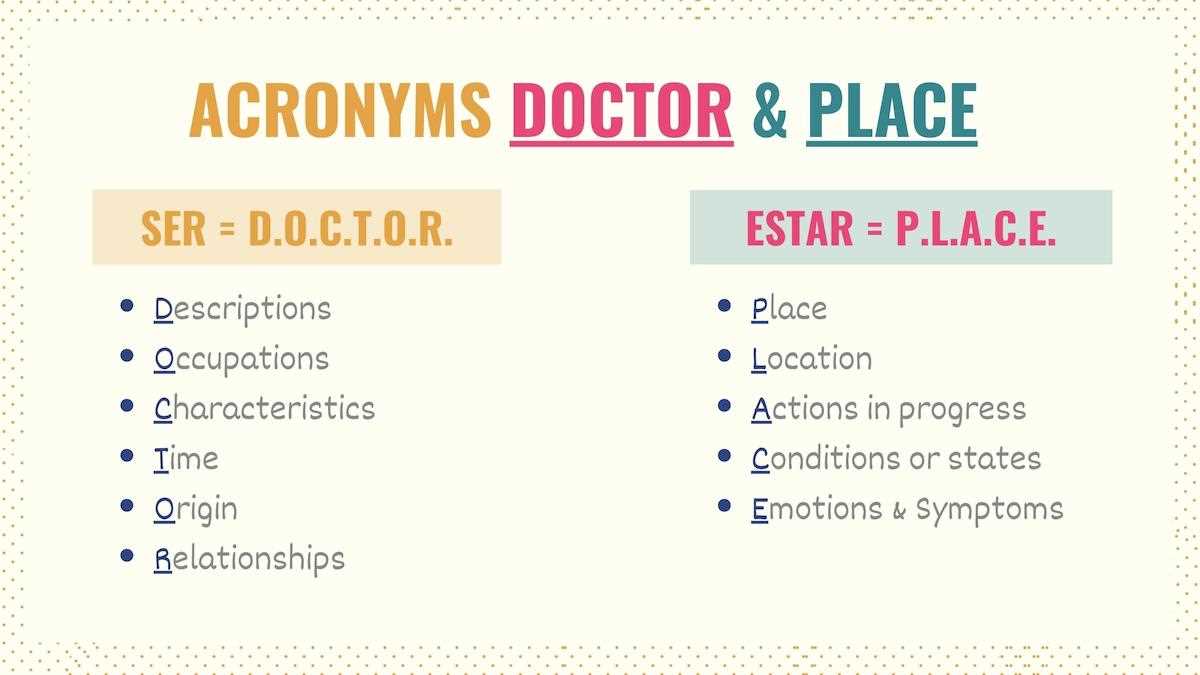
Key Rules for Using Ser in Sentences
Choosing the right expressions to describe qualities or attributes requires a clear understanding of their purpose. Some terms focus on defining permanent aspects or essential characteristics, helping to convey precise meanings in your communication.
Permanent Traits: When referring to features that define identity, such as professions, nationalities, or inherent qualities, the appropriate term emphasizes unchanging attributes. For instance, describing someone’s occupation or origin often relies on this form.
Time and Events: Expressions that mark time, dates, or locations of scheduled activities also follow this rule. These contexts highlight aspects that are set or defined rather than variable.
By mastering these principles, learners can create sentences that accurately convey the intended message, ensuring clarity in both spoken and written forms.
When to Choose Estar Over Ser
Using the correct form to describe temporary or situational states requires attention to context. Certain expressions emphasize moments, transitions, or changing conditions, making them essential for accurate and natural communication.
These terms are commonly applied in contexts that reflect momentary states, such as emotions, actions in progress, or conditions subject to change. Understanding these scenarios can help avoid common errors.
| Context | Example |
|---|---|
| Emotional States | Used to describe feelings like happiness, sadness, or excitement. |
| Physical Conditions | Helpful for indicating health, fatigue, or other temporary conditions. |
| Ongoing Actions | Paired with specific verb forms to describe activities happening at the moment. |
| Location | Used to specify where someone or something is at a given time. |
By focusing on these key areas, learners can confidently use expressions that reflect transitory situations and align with the intended meaning.
Common Mistakes with Ser and Estar
Distinguishing between terms used to describe identity or conditions can be challenging for learners. Misunderstanding their contexts often leads to errors, making communication unclear or less effective. Identifying these common pitfalls is essential for improving accuracy.
Mixing Permanent and Temporary Descriptions
A frequent error involves using the wrong expression to describe either enduring traits or momentary states. For instance, applying a term meant for lasting characteristics to a short-term condition can lead to confusion. Always consider whether the aspect being described is constant or subject to change.
Confusion in Location Contexts
Another common issue arises when describing locations. While one form is used for fixed or permanent settings, the other applies to temporary placements. Mixing these up can lead to sentences that misrepresent the intended meaning, particularly when discussing events or current whereabouts.
By focusing on the specific rules and scenarios for each term, learners can avoid these mistakes and communicate more effectively.
Practical Tips for Remembering Usage
Mastering the application of specific expressions in a new language requires strategies that simplify learning and improve recall. By using practical methods, learners can confidently navigate between similar terms and apply them correctly in various contexts.
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Associate with Keywords | Create mental links between phrases and their typical uses, such as stability for one term and change for another. |
| Practice with Context | Use flashcards or apps that provide real-world scenarios to reinforce proper application. |
| Visual Aids | Draw diagrams or use color coding to differentiate terms based on their function. |
| Memorize Common Phrases | Learn examples that illustrate correct usage to internalize patterns. |
Incorporating these tips into your study routine can make the process more intuitive and enhance your ability to use these expressions naturally in communication.
Answer Key for Exam 1 Explained
Understanding the correct responses to practice questions is essential for reinforcing learning. This section provides clarity on why certain choices are accurate and others may be misleading, helping to clarify the reasoning behind each decision.
Each response in the exercise follows specific rules, focusing on the correct application of expressions based on their respective contexts. By reviewing these explanations, learners can deepen their understanding of when and why particular terms are used over others.
The purpose of this explanation is to ensure that learners grasp the fundamental differences between the options, enhancing their ability to use these terms confidently in various situations.
Breaking Down Exam 1 Questions
In this section, we will analyze each question from the practice test to better understand the reasoning behind the correct choices. Breaking down the questions helps clarify which concepts are being tested and why certain terms are more appropriate than others in specific scenarios.
By thoroughly examining the structure of each question, learners can identify patterns and contextual clues that will guide their decision-making process in future exercises. This breakdown aims to reinforce the key principles and help learners improve their understanding of the material.
Example 1: In a question asking about an ongoing action, the correct term should reflect a temporary, changing situation. Understanding this distinction ensures accurate responses when dealing with dynamic circumstances.
Example 2: When asked to describe a permanent trait or characteristic, learners must recognize the proper expression for stability over time. Grasping this concept will help avoid confusion when talking about inherent qualities.
How Context Determines Ser or Estar
Understanding the nuances between different expressions in the language relies heavily on context. The meaning of a sentence can change based on the situation in which it is used, requiring the selection of one term over another. Recognizing these subtle differences is key to mastering the language.
Context of Permanence vs. Change
When describing characteristics that remain constant over time, one expression is more appropriate, while for actions or states that are temporary or in progress, a different term should be used. These distinctions are often subtle, but context can make the difference clear.
Emotional and Physical States
Another important factor to consider is the distinction between describing emotional or physical states that are temporary versus those that reflect a more lasting condition. The context of the sentence helps clarify which word fits the situation accurately.
Example 1: Describing someone’s nationality or profession indicates a permanent trait, so the appropriate term should reflect this stability.
Example 2: Talking about someone’s current mood or location, on the other hand, suggests a transient situation that requires the other expression.
Learning Ser and Estar Through Examples
One of the most effective ways to grasp the difference between these two terms is by examining real-life examples. By seeing how each expression is used in context, learners can better understand the underlying principles that guide their correct usage.
In this section, we will look at several examples that highlight the differences in meaning and usage. These examples will help clarify when to choose one term over the other, based on the nature of the situation being described.
Example 1: “She is a doctor.” In this case, the term reflects a permanent attribute of the subject, as a profession is typically stable and enduring.
Example 2: “He is tired.” Here, the term refers to a temporary condition, as tiredness is something that can change over time.
Example 3: “They are in the park.” The location of the subject is a momentary situation, which calls for the expression that indicates a temporary state or position.
Through these examples, learners can begin to intuitively differentiate when to use each expression, based on whether the described trait or state is permanent or transient.
Strategies for Success in Ser vs Estar Tests
To excel in tests that assess the understanding of these two expressions, it’s important to adopt certain strategies that focus on comprehension and application. By approaching the material methodically, students can build a solid foundation and confidently navigate questions that test their knowledge of usage rules.
Focus on Key Concepts
Before tackling practice exercises or tests, ensure that the fundamental concepts are clear. This includes understanding the distinctions between permanent and temporary states, as well as the types of situations where each expression is commonly used.
Practice Regularly
Frequent practice is essential to internalize the differences. Engaging with various examples will help reinforce the correct usage and make it easier to recall during tests.
- Use flashcards: Create a set of flashcards with different scenarios to test your knowledge and recall of when to use each term.
- Complete practice tests: Take mock tests that simulate exam conditions. This will help you build familiarity with the types of questions that may appear.
- Review common mistakes: Analyze mistakes you’ve made in previous tests to understand why they happened and prevent them from reoccurring.
By applying these strategies, students can increase their chances of success and improve their understanding of how to use these expressions in different contexts.
Real-Life Scenarios to Practice Ser and Estar
Applying the right expression in everyday situations helps reinforce the understanding of its usage. By immersing yourself in real-life scenarios, you can get a better grasp of how each form functions in different contexts. These practical examples make learning more relatable and can aid in remembering when to use each term correctly.
Everyday Situations to Practice
Here are a few common scenarios where these expressions are typically used. Try to determine which form fits best in each case:
- Describing someone’s occupation: “My father is a doctor.” (Use the form for permanent states)
- Talking about location: “The keys are on the table.” (Use the form for temporary situations or locations)
- Expressing emotions: “She is happy today.” (Use the form for temporary feelings or states)
- Indicating time or date: “It is 5 PM.” (Use the form for unchanging facts)
- Describing physical characteristics: “He is tall.” (Use the form for permanent traits)
Interactive Exercises
Putting yourself into these scenarios will not only improve your understanding but also make your learning experience more dynamic. Here are some interactive exercises to practice:
- Role-playing: Pair up with a partner and role-play everyday conversations, focusing on when to use each term.
- Journal writing: Write daily journal entries that describe your current emotions, routines, or any changes in your life. Practice alternating between the forms.
- Observation: Pay attention to conversations in your environment, TV shows, or books, and try to identify which form is being used and why.
By practicing with these real-life scenarios, you will strengthen your ability to correctly apply these expressions in both casual and formal settings.
Understanding Ser and Estar in Descriptions
When describing people, places, and things, choosing the right expression is essential for conveying accurate information. These expressions allow you to describe permanent qualities, like someone’s nationality or physical characteristics, as well as temporary states, such as mood or location. Understanding the distinction between these two forms will help you create clear and precise descriptions in various contexts.
Describing Permanent Qualities
In some cases, the characteristics you describe are stable and unchanging. These include:
- Physical traits: For instance, describing someone as tall, short, or having brown hair. These are lasting qualities.
- Profession: When talking about someone’s job or occupation, it is something that doesn’t change frequently.
- Origin: Nationality or where a person or object comes from is another example of something permanent.
Describing Temporary States
Other times, you describe conditions or feelings that fluctuate. These include:
- Emotions: Feelings like happiness, sadness, or surprise are temporary states that change over time.
- Location: Describing where someone or something is situated at the moment, as locations can change.
- Health: Temporary illnesses or fatigue are examples of states that may not last long.
By recognizing whether you are describing something that is permanent or temporary, you can confidently choose the right expression to complete your description accurately.
The Role of Ser and Estar in Time Phrases
Time expressions play a crucial role in determining the right structure to use when talking about specific moments or durations. The way time is presented in a sentence can depend on whether you are referring to something that is fixed and unchanging, or something that is temporary and subject to change. Understanding how different forms are used in time-related phrases is key to speaking clearly and correctly.
Indicating Fixed Moments in Time
When referring to time that is constant or unchanging, such as dates or seasons, you typically use the structure that signifies permanence. This expression is used to give specific information about the current time or a known time frame. Examples include:
- Days of the week: “It is Monday” refers to a fixed moment in time.
- Calendar dates: “Today is the 25th” implies a set day.
- Seasons: “It is summer” refers to a recurring, unchanging season.
Describing Temporary Time States
In contrast, when referring to a temporary state related to time, such as the momentary occurrence of an event or feeling, another form is used. This conveys something that is not fixed and can change with time. Examples include:
- Current activity or action: “I am studying now” refers to something happening in the present, which is temporary.
- Temporary conditions: “It is raining today” describes a passing state.
- Age: “She is 25 years old” reflects an ongoing but changing aspect of time.
By recognizing whether the time phrase reflects something fixed or transient, you can accurately convey the intended meaning and maintain proper grammar in context.
Ser and Estar in Expressions of Location
Location phrases are an essential aspect of language, helping to convey where something or someone is situated at a given moment. Understanding the difference in how to express locations is important, as it can refer to either a permanent position or a temporary one. The use of different forms helps clarify the nature of the location being described, whether it is fixed or changeable.
Indicating Permanent Locations
When referring to a permanent, unchanging location, the expression used conveys a sense of stability or established position. These situations often describe the inherent or long-term places where things or people are located. Examples include:
- Building locations: “The bank is on the corner” refers to a fixed, permanent place.
- Geographical locations: “Madrid is in Spain” indicates a consistent and established location.
- National or regional placement: “She is from Italy” shows an unchanging place of origin.
Indicating Temporary Locations
In contrast, when describing temporary locations that are subject to change, another form is used. This highlights a state or position that is not fixed, often referring to movements or temporary situations. Examples include:
- Current position or placement: “I am at the park” refers to a place one is temporarily at.
- Movements: “They are in the car” reflects a temporary location during travel.
- Temporary situations: “He is staying at a friend’s house” highlights a short-term living arrangement.
By distinguishing between permanent and temporary locations, speakers can communicate more accurately and with greater clarity about the nature of the position or place in question.
How to Master Ser and Estar Quickly
Mastering the use of two essential verbs that express different states and qualities in Spanish can be a challenge. However, with focused practice and understanding of their distinct contexts, you can quickly become proficient. By recognizing patterns, applying strategies, and immersing yourself in real-world examples, you can grasp their usage with confidence.
Key Strategies for Quick Mastery
To accelerate your learning, here are some key strategies to keep in mind:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Practice Contextual Usage | Understand the differences in context–whether the situation is permanent or temporary, or referring to a characteristic or a state. |
| Use Mnemonics | Create memory aids to remember when each verb is used, such as associating one verb with conditions and the other with locations or identities. |
| Real-Life Application | Immerse yourself in the language by reading, listening, and conversing. The more you practice in real-world situations, the faster you will grasp the nuances. |
| Consistent Review | Regularly review your knowledge by testing yourself with sentences and examples, reinforcing your understanding. |
By using these strategies, you’ll not only memorize the differences but also improve your fluency in recognizing when each verb should be used. With practice, you’ll be able to apply them quickly and accurately in your conversations and writing.
Why Ser and Estar Confuse Beginners
For language learners, especially those just starting with Spanish, mastering the use of two specific verbs that convey different meanings can be a challenging task. These verbs seem similar, but their applications vary depending on context, which is what often leads to confusion. The key lies in understanding the subtleties between permanent states, temporary conditions, and specific situations, all of which require different verbs. Let’s explore why this distinction is difficult for many newcomers to the language.
Key Reasons for the Confusion
- Different Contexts for Usage: These verbs are often used to describe things that might seem similar, like appearance or condition, but their meaning changes based on whether something is permanent or temporary.
- Overlapping Meanings: Some situations may seem to fit both verbs, making it hard to decide which one to use. For example, describing a person’s mood or location can involve either verb depending on the situation.
- Complex Grammar Rules: The rules for when to use each verb can be complex. While one verb might be used for identity or profession, the other is used for health or emotional states. Understanding the rules often requires memorization and practice.
- Native Language Influence: Learners’ native languages may not have a direct equivalent for these two verbs, making it difficult to apply the correct one instinctively in Spanish.
Despite these challenges, with consistent practice and exposure to real-life situations, learners can begin to identify when each verb should be used. Over time, this knowledge will become second nature, making it easier to speak and understand Spanish with confidence.