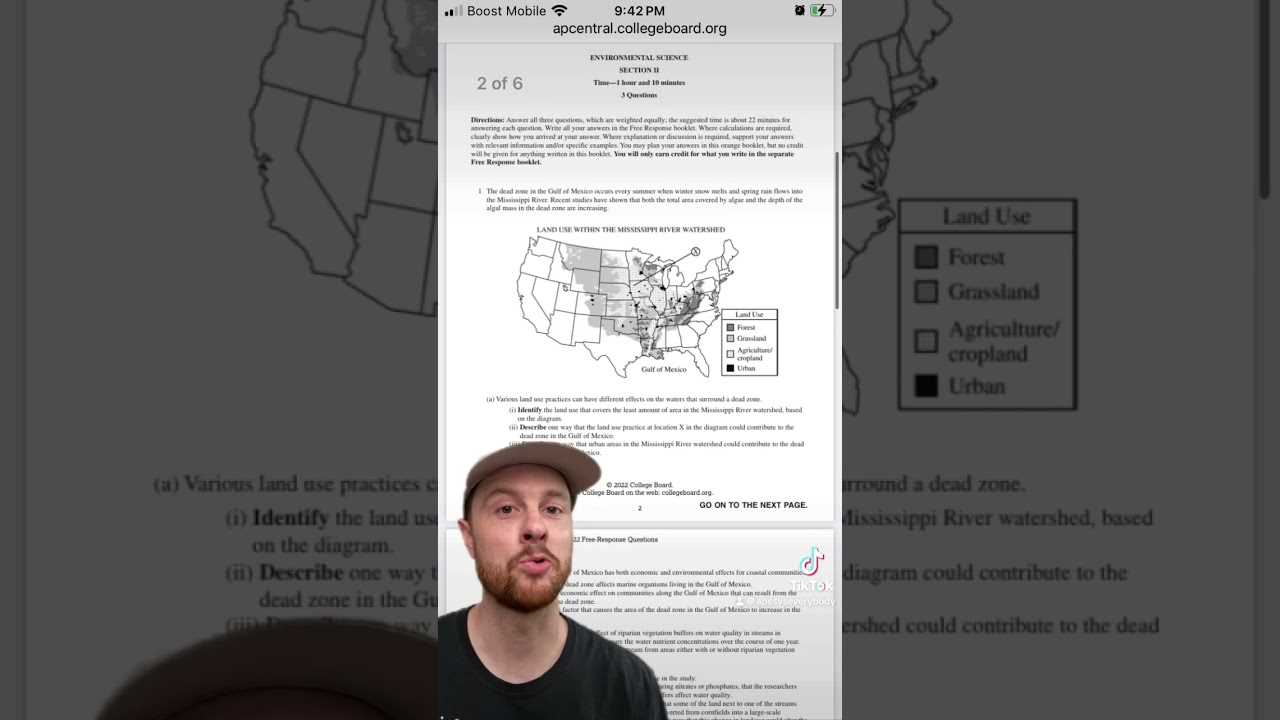
Preparing for environmental science assessments requires a strong understanding of key concepts and the ability to apply this knowledge under timed conditions. The test format challenges students to think critically, analyze various scenarios, and demonstrate their grasp of complex environmental topics. A comprehensive approach is essential for success, combining knowledge, strategy, and effective response techniques.
One of the most critical components of these assessments is the written portion, where students must formulate clear, concise responses. These questions test not only factual knowledge but also the ability to synthesize information and present logical, well-structured arguments. Mastering this part of the test involves practice, familiarity with common question types, and developing a methodical approach to problem-solving.
In this guide, we will explore strategies and tips to excel in these types of written questions. You will find insights into managing your time, understanding what examiners look for in responses, and practicing with realistic examples to enhance your readiness. A well-prepared student can approach these tasks with confidence, knowing they can apply their knowledge effectively in any situation.
Environmental Science Test Review and Solutions
In any rigorous assessment, understanding the format and structure of questions is key to success. Environmental science tests often include written tasks that require you to demonstrate not only factual knowledge but also analytical thinking and the ability to draw connections between concepts. These tasks are designed to challenge your ability to apply what you’ve learned in practical, real-world situations.
To excel, it’s essential to break down each question systematically, identifying the key points and structuring your response logically. Providing clear, well-supported arguments is critical, as is addressing every aspect of the question fully. Practicing with similar questions can help you refine your approach, ensuring that you are prepared for any scenario that may arise during the actual assessment.
This section delves into key strategies for tackling these types of written tasks, offering practical solutions and tips for approaching complex questions with confidence. By applying these methods, you can significantly improve your performance and demonstrate a strong grasp of environmental principles and issues.
Overview of Environmental Science Assessment
The environmental science assessment is designed to evaluate students’ understanding of key ecological concepts, issues, and practical applications. The test includes a variety of question types that assess both theoretical knowledge and the ability to apply this knowledge in real-world contexts. The questions are structured to challenge your critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, requiring you to consider complex environmental challenges from multiple perspectives.
Structure of the Test

The assessment typically consists of multiple sections, each focusing on different aspects of environmental science. This includes both multiple-choice questions and written responses that test your ability to synthesize information and present it in a coherent manner. The written tasks often involve analyzing case studies, evaluating data, and formulating solutions to hypothetical environmental problems. These sections are designed to simulate the types of challenges you might encounter in professional environmental work.
Key Areas of Focus
Important areas covered in the test include ecosystems, biodiversity, sustainability, human impact on the environment, and environmental policies. The questions aim to assess your depth of knowledge in these areas, as well as your ability to apply scientific principles to real-world environmental issues. Success in the assessment requires not only memorization but also a clear understanding of how to use that knowledge to address complex, interconnected problems.
Understanding the Written Response Format

The written response section of an environmental science assessment is designed to test your ability to think critically and communicate your understanding clearly. Unlike multiple-choice questions, these tasks require you to craft detailed, well-organized responses that demonstrate your knowledge and reasoning. The questions typically involve real-world scenarios or case studies that require careful analysis and the application of environmental concepts.
These types of questions are often structured to assess a range of skills, from explaining scientific principles to evaluating environmental policies or proposing solutions to specific issues. You are expected to provide evidence-based answers that reflect both depth and clarity. The key to success in this section is the ability to present your ideas logically and to address each part of the question thoroughly.
Key Concepts Tested in Environmental Science
The assessment of environmental science knowledge focuses on a broad range of key concepts that span ecological, social, and scientific disciplines. These concepts aim to evaluate your understanding of the natural world, human impact on ecosystems, and the ways in which environmental issues are addressed. Students are tested on their ability to comprehend and apply fundamental ideas such as energy flow, biodiversity, sustainability, and the interdependence of living and non-living systems.
Topics commonly covered include the principles of environmental conservation, climate change, pollution, and the management of natural resources. Understanding the complex relationships between human activities and environmental health is essential, as is the ability to evaluate and propose solutions to pressing ecological challenges. Mastery of these concepts is critical for success in this section of the assessment.
How to Tackle Written Response Tasks Efficiently
Successfully addressing written response questions requires a strategic approach to ensure that all aspects of the task are covered in a clear and organized manner. These questions test both your knowledge and your ability to communicate your thoughts logically. To excel, it’s important to manage your time effectively, structure your response thoughtfully, and focus on providing detailed, evidence-based explanations.
- Read the Question Carefully: Begin by thoroughly understanding what the question asks. Pay attention to any keywords or phrases that indicate what kind of response is required, such as “explain,” “describe,” or “analyze.”
- Break the Question into Parts: Many questions have multiple components. Break them down and tackle each one individually to ensure you address every aspect of the prompt.
- Plan Your Response: Take a few moments to outline your answer before writing. Organize your ideas logically, ensuring that your response flows from one point to the next.
- Use Clear Examples: Whenever possible, support your points with relevant examples. This helps demonstrate your understanding of the topic and strengthens your argument.
- Stay Focused and Concise: Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from your main points. Aim to be as clear and direct as possible while providing sufficient explanation.
By following these steps, you can approach written tasks with confidence, ensuring that your responses are well-structured, complete, and relevant to the question at hand.
Common Mistakes in Written Responses
When answering written questions in an environmental science assessment, it’s easy to make mistakes that can affect the clarity and quality of your response. These errors often stem from misunderstanding the prompt, lack of detail, or failure to address the question fully. Recognizing common mistakes can help you avoid them and improve the effectiveness of your answers.
Failure to Address All Parts of the Question
- Incomplete Responses: One of the most common errors is not answering all parts of the question. Many prompts contain multiple components that require separate explanations. Ensure you break down the question and address each part distinctly.
- Overlooking Keywords: Words like “describe,” “compare,” or “evaluate” are crucial to understanding the expected response. Misinterpreting these terms can lead to incomplete or off-target answers.
Lack of Detail and Support
- Generalized Statements: Vague answers that don’t include specific details or examples weaken your response. Always provide evidence or relevant data to back up your points.
- Missing Connections: Failure to link your examples or explanations to the core concept of the question can make your answer seem disconnected. Ensure that every point you make ties back to the main idea.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking the time to carefully craft your responses, you can improve the quality of your written answers and ensure they fully meet the expectations of the assessment.
Time Management for Environmental Science Assessments
Effective time management is crucial when tackling an environmental science assessment, especially when the test includes both multiple-choice and written response sections. Properly allocating your time ensures you can give thoughtful attention to each part of the test, avoid rushing through questions, and complete everything within the allotted time frame. With the right approach, you can maximize your performance without feeling overwhelmed.
Strategies for Managing Your Time
- Read the Instructions Carefully: Begin by reading through the instructions and all the questions. This will help you understand the scope of the test and allow you to plan accordingly.
- Allocate Time for Each Section: Divide your time between multiple-choice questions and written responses. Typically, you should spend more time on the written tasks, but don’t neglect the other sections.
- Set Time Limits for Each Question: Set a rough time limit for each question or section. This will help you avoid spending too much time on any one question at the expense of others.
Tips for Maintaining Focus
- Work Efficiently: Answer easier questions first to build confidence and gain quick points. Save more challenging questions for later, ensuring you have enough time to think them through carefully.
- Stay Calm and Focused: If you get stuck on a question, don’t panic. Move on to the next one and come back later if you have time. Staying calm will help you think more clearly and manage your time better.
- Use Extra Time Wisely: If you finish early, use any remaining time to review your answers, especially the written responses. This ensures that you didn’t miss anything and that your answers are as strong as possible.
By following these strategies, you can optimize your time during the test, ensuring that you complete all sections thoughtfully and thoroughly.
Effective Study Strategies for Environmental Science Assessments
Preparing for an environmental science assessment requires a combination of structured study techniques, time management, and consistent review. By focusing on the key topics, using active learning strategies, and regularly testing your knowledge, you can improve your understanding of complex concepts and perform well during the test. The following strategies will help you maximize your study sessions and ensure you’re well-prepared.
Focus on Key Concepts and Topics
- Prioritize Core Topics: Start by identifying the most important concepts, such as ecosystems, energy flow, climate change, and sustainability. Review these topics thoroughly, as they are frequently tested.
- Break Down Complex Information: Divide large topics into smaller, more manageable sections. For example, when studying the nitrogen cycle, focus on understanding each stage before looking at the cycle as a whole.
- Create Visual Aids: Use diagrams, mind maps, and flow charts to visualize complex processes. Visual learning helps reinforce key concepts and improves recall during the test.
Active Learning and Practice

- Engage with Practice Questions: Practice answering questions under timed conditions. This will help you familiarize yourself with the types of questions asked and refine your ability to provide clear, concise responses.
- Teach What You’ve Learned: One of the best ways to reinforce your understanding is by explaining concepts to someone else. Teaching forces you to organize your thoughts and identify any gaps in your knowledge.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards for key terms, definitions, and concepts. Reviewing these regularly can help you reinforce important information and improve recall.
By integrating these strategies into your study routine, you can enhance your knowledge retention, sharpen your problem-solving skills, and be fully prepared for the environmental science assessment.
Breaking Down Environmental Science Written Questions
When approaching complex written questions in an environmental science assessment, it’s important to break down the prompt into manageable parts. Understanding how to interpret and respond effectively can greatly improve the clarity and quality of your answers. By analyzing the structure and requirements of the question, you can ensure that each part is addressed thoroughly and thoughtfully.
Here’s a guide on how to approach these types of written questions:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Read the Prompt Carefully | Before you start writing, read the entire question to ensure you understand what is being asked. Look for specific instructions, such as “explain,” “describe,” or “compare,” which indicate the type of response expected. |
| 2. Break Down the Question | Identify each component of the question. Is it asking for an explanation, analysis, or application? Make sure you understand each part so that you can provide a complete response. |
| 3. Organize Your Thoughts | Before starting your response, jot down key points you want to cover. This helps to structure your answer and ensures that you don’t miss any important details. |
| 4. Provide Evidence and Examples | Support your answers with relevant examples, data, or real-world applications. This strengthens your response and demonstrates a deeper understanding of the material. |
| 5. Review Your Response | Once you’ve written your answer, take a moment to review it. Make sure you’ve addressed all aspects of the question and that your response is clear and concise. |
By following this systematic approach, you can ensure that you effectively break down and respond to written questions, improving both the quality and completeness of your answers.
How to Answer Environmental Science Questions
When tackling questions in environmental science, it’s crucial to approach them methodically to provide clear and concise responses. Whether you’re asked to describe, analyze, or explain, understanding the question’s intent is key. A well-structured answer not only demonstrates your knowledge but also reflects your ability to apply that knowledge in real-world contexts.
Step-by-Step Approach to Answering Questions

- Read the Question Carefully: Before starting your response, ensure you fully understand what the question is asking. Look for keywords like “define,” “analyze,” “compare,” or “explain” to determine the type of answer expected.
- Plan Your Response: Jot down key points or ideas that you want to include in your answer. Organizing your thoughts will help you avoid missing important details and ensure a logical flow.
- Provide Relevant Information: Ensure that your response includes facts, theories, and examples that are directly related to the question. Providing specific details helps strengthen your argument and demonstrate your understanding.
Tips for Effective Responses
- Be Clear and Concise: Environmental science questions often require detailed explanations, but it’s important to avoid unnecessary information. Stick to the main points and explain them clearly.
- Support with Evidence: Whenever possible, back up your statements with data or examples from scientific studies, real-world scenarios, or case studies. This not only strengthens your answer but also shows that you can connect theory to practice.
- Review Your Answer: After writing your response, take a moment to read through it. Make sure it’s well-organized, answers all parts of the question, and is free of errors.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your responses are both comprehensive and well-structured, showcasing your knowledge and analytical skills in environmental science.
Practice Test Tips for Environmental Science Assessments
Preparing for a comprehensive environmental science assessment requires not only understanding the material but also being strategic in how you approach the test. It’s essential to focus on both content knowledge and effective test-taking strategies. The more you practice, the more confident you’ll feel when facing the actual test. Here are some key tips to help you maximize your performance during these types of evaluations.
Effective Preparation Strategies
- Review Core Concepts: Start by revisiting the foundational concepts that are commonly tested. Focus on the most critical topics such as ecosystems, biodiversity, environmental policy, and sustainable practices.
- Practice Time Management: During practice tests, simulate real test conditions by timing yourself. This helps you build time management skills and ensures that you won’t rush through sections during the actual assessment.
- Understand Question Formats: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the questions. Many environmental science assessments include both multiple-choice and open-ended questions, so practicing both types will prepare you for all formats.
Test-Taking Techniques
- Read Carefully: Ensure you fully understand the question before answering. Often, questions include multiple parts, and missing a detail can lead to incomplete answers.
- Focus on Key Points: For open-ended questions, prioritize addressing the main points first. Organize your thoughts clearly, and ensure each part of the question is answered fully.
- Review Your Responses: If time allows, review your answers before submitting. This gives you a chance to correct any mistakes and ensure your responses are as clear and accurate as possible.
By integrating these preparation and test-taking strategies into your study routine, you’ll be better equipped to perform well on your environmental science assessments, ensuring you demonstrate a solid understanding of the material and effective time management skills.
Improving Your Written Response Skills
Writing strong, clear, and concise responses to open-ended questions is a key skill for success in any assessment. To excel in these types of tasks, it is important to not only understand the material but also to practice the art of communicating complex ideas effectively. Developing your writing skills can make a significant difference in how well you convey your knowledge and reasoning, especially when time is limited.
Structure Your Responses Clearly

- Start with a Strong Introduction: Begin each response by addressing the question directly. Provide a brief overview of the main points you will discuss, setting a clear direction for your answer.
- Use Paragraphs Effectively: Organize your thoughts into clear, separate paragraphs. Each paragraph should focus on one main idea, making your response easier to follow and more coherent.
- Provide Evidence: Support your points with relevant facts, examples, or concepts. This demonstrates a deeper understanding and strengthens the credibility of your response.
Polish Your Writing for Clarity

- Avoid Overly Complex Language: While it’s important to demonstrate your knowledge, using overly complex or technical language can confuse the reader. Aim for clarity and simplicity in your explanations.
- Use Transition Words: Employ words like “for example,” “therefore,” and “in conclusion” to help guide the reader through your response and show the connections between ideas.
- Stay on Topic: Avoid straying from the question at hand. Each part of your response should directly address the prompt, without unnecessary tangents or irrelevant details.
By practicing these techniques, you can refine your ability to write thoughtful, well-structured responses that clearly convey your knowledge. Regular practice will help you build confidence and improve the quality of your written answers, ultimately boosting your performance in assessments that require written responses.
Understanding Scoring Criteria for Assessments
To perform well in any test that includes written responses, it’s essential to understand how your answers are evaluated. Knowing the criteria used to assess your work can help you focus on the most important aspects of your response, ensuring you meet the expectations set by the scoring guidelines. Understanding the scoring process will not only help you in planning your answers but also allow you to improve your approach to future assessments.
The scoring system often evaluates several key components: the clarity of your argument, the accuracy and relevance of the information provided, and the depth of your analysis. Each of these areas contributes to the overall quality of your response and determines the score you receive. To earn the highest marks, it’s crucial to provide a thorough, well-organized, and well-supported answer that directly addresses the question.
Key Components of Scoring
- Clarity and Organization: Responses that are clearly organized with logical progression tend to score higher. Use structured paragraphs, with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion, to help readers follow your argument.
- Relevance and Accuracy: Providing accurate information that directly addresses the prompt is critical. Avoid including irrelevant facts or details that do not contribute to answering the question.
- Depth of Analysis: A well-thought-out response that goes beyond surface-level answers and offers detailed explanations or examples demonstrates deeper understanding and is rewarded with higher scores.
Maximizing Your Score
- Address All Parts of the Question: Many questions contain multiple parts. Be sure to answer each part completely to avoid losing points for missing information.
- Be Concise But Thorough: While it’s important to be detailed, avoid unnecessary repetition. Get straight to the point and make every sentence count.
- Support Your Answer with Examples: Whenever possible, use specific examples to support your points. Real-world examples or key concepts from the course can enhance the quality of your response.
By familiarizing yourself with the scoring criteria and applying these strategies, you can improve the quality of your responses and maximize your performance in assessments that require written responses. Understanding what evaluators are looking for will help you tailor your answers to meet their expectations more effectively.
Common Topics Covered in Written Assessments
Written assessments often include questions on a broad range of topics designed to test the depth of your knowledge and understanding. These questions typically cover key areas that reflect the core concepts of the subject matter. The topics may range from basic definitions and principles to more complex applications, requiring students to demonstrate critical thinking and the ability to analyze various scenarios.
To perform well, it’s important to be familiar with the common themes that are regularly tested. By understanding these topics, you can focus your study efforts on the most relevant areas, ensuring that you are well-prepared for any type of question that may arise.
Commonly Covered Topics
- Environmental Systems: Questions may cover ecosystems, biogeochemical cycles, energy flow, and the interdependence of living organisms. Understanding how various systems interact and function is crucial for these types of questions.
- Human Impact on the Environment: Topics related to pollution, deforestation, climate change, and resource depletion are often addressed. These questions assess how human activities affect natural systems and what measures can be taken to mitigate these impacts.
- Sustainability and Conservation: These questions focus on practices that promote environmental sustainability, conservation efforts, and the management of natural resources. Be prepared to discuss strategies for reducing waste, conserving energy, and protecting biodiversity.
- Environmental Policy and Economics: Questions on this topic often involve discussions of laws, regulations, and economic factors that influence environmental decision-making. Understanding the role of policy in shaping environmental outcomes is key.
- Environmental Ethics and Values: Some questions explore the ethical dimensions of environmental issues, asking students to evaluate the moral implications of human actions and policies in relation to the natural world.
Preparing for These Topics
- Review Key Concepts: Make sure you understand the fundamental principles behind each topic. This includes understanding definitions, processes, and theories relevant to environmental science.
- Use Real-World Examples: Support your responses with examples from current events or case studies. Demonstrating how theory applies to real-world situations can strengthen your answers.
- Understand the Interconnections: Many of the topics covered in these questions are interconnected. Be prepared to explain how different environmental issues relate to one another, such as how climate change can impact biodiversity or water resources.
Familiarity with these common topics will give you a significant advantage in written assessments. Focus your preparation on understanding the underlying concepts and be ready to apply them in various scenarios. The more knowledgeable and prepared you are, the better you will be able to handle the questions that come your way.
Key Environmental Issues to Review

Environmental challenges are among the most pressing concerns of the modern world, with significant impacts on ecosystems, human health, and global economies. To address these challenges effectively, it is essential to have a solid understanding of the key issues that are shaping the planet’s future. These issues range from the depletion of natural resources to the loss of biodiversity, and they require thoughtful consideration and action at local, national, and global levels. Understanding these topics is critical for developing sustainable solutions that will benefit both the environment and society.
Critical Environmental Concerns
- Climate Change: The global increase in temperatures due to human activities is causing shifts in weather patterns, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems. The scientific understanding of climate change and its far-reaching effects is essential for developing mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- Deforestation: The destruction of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban expansion contributes to habitat loss, disrupts carbon sequestration, and accelerates climate change. Protecting and restoring forests is key to maintaining biodiversity and combating global warming.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution continue to threaten human health and the environment. From industrial waste to plastic contamination, understanding the sources and impacts of pollution is crucial for reducing environmental damage and promoting cleaner practices.
- Overconsumption of Resources: Unsustainable extraction and use of natural resources, including water, minerals, and fossil fuels, are depleting the planet’s reserves and causing environmental degradation. Sustainable resource management is vital for ensuring long-term environmental health.
Emerging Issues to Monitor
- Biodiversity Loss: The rapid extinction of species due to human activities, habitat destruction, and climate change is weakening ecosystems and threatening the planet’s biological richness. Conservation efforts to protect endangered species and habitats are essential for preserving ecological balance.
- Ocean Health: Oceans are facing multiple threats, including acidification, overfishing, and pollution. Protecting marine ecosystems is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and the health of the planet.
- Waste Management: The increasing volume of waste, particularly plastic, is overwhelming landfills and polluting ecosystems. Effective waste management, including recycling, composting, and waste reduction, is critical for reducing environmental impacts.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Industrial farming practices contribute to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. Transitioning to more sustainable agricultural practices is necessary for ensuring food security while protecting the environment.
By reviewing these key environmental issues, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges facing our planet. This knowledge is essential for developing informed, sustainable solutions that promote environmental protection and foster a healthier future for all.
Resources for Further APES Preparation

To effectively prepare for environmental science assessments, utilizing a variety of resources can significantly enhance understanding and performance. These materials range from online tools and textbooks to practice questions and study guides. Each resource serves to reinforce knowledge, improve critical thinking skills, and offer opportunities for self-assessment. By exploring different types of study aids, learners can tailor their preparation to their specific needs and learning styles.
Study Materials and Tools
| Resource Type | Description | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| Textbooks | Comprehensive textbooks cover foundational topics in environmental science, offering in-depth explanations, diagrams, and examples. | Use to build a strong conceptual understanding and review key topics such as ecology, climate change, and sustainability. |
| Online Practice Questions | Interactive platforms offer a variety of practice questions, including multiple-choice and short-answer formats, mirroring real assessments. | Use to test knowledge, identify weak areas, and practice applying concepts in timed conditions. |
| Study Guides | Concise guides provide summaries of important concepts, vocabulary, and formulas, often with tips for answering questions effectively. | Use as quick reference material for focused revision before assessments. |
| Video Lectures | Educational videos from platforms like YouTube or online courses offer visual explanations and real-world examples of environmental issues. | Watch videos to gain different perspectives, deepen understanding, and reinforce complex topics. |
Additional Resources
- Environmental Science Podcasts: Listening to expert discussions on environmental issues can help reinforce concept