
Understanding how to uncover critical details and interpret information is vital in many professional fields. This discipline combines logical reasoning, technical expertise, and attention to detail, offering a unique approach to solving complex puzzles. By mastering these principles, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to draw meaningful conclusions from collected data.
From uncovering hidden patterns to piecing together fragments of evidence, these methods play a crucial role in diverse applications. Whether it involves examining physical materials or analyzing subtle traces left behind, the process requires a balance of precision and creativity. By diving deeper into these practices, learners gain insight into the essential tools and strategies used in professional problem-solving scenarios.
This guide aims to provide clear, practical insights into core principles and methodologies. By working through real-world examples and engaging with thought-provoking exercises, readers can strengthen their skills and improve their confidence in tackling challenging scenarios. With the right approach, these tools can empower anyone to achieve remarkable results in their field.
Understanding the Basics of Forensic Science
Exploring the methods used to uncover hidden truths and analyze critical details provides a foundation for problem-solving in complex scenarios. This discipline combines systematic observation, careful analysis, and technical skill to identify connections and draw accurate conclusions.
Key Elements of Evidence Examination
- Observation: Careful assessment of materials and surroundings to detect significant details.
- Collection: Ensuring that physical traces are preserved for accurate evaluation.
- Documentation: Creating records of findings to support clarity and reproducibility.
Common Methods in Analytical Processes
- Trace Analysis: Examining small particles or residues to understand their origins.
- Comparative Techniques: Matching samples to establish links between sources.
- Technological Tools: Using advanced devices to enhance precision and reliability.
Mastering these basic steps allows professionals to build a strong understanding of how to approach and solve complex cases effectively. Through consistent practice and study, learners can refine their ability to interpret data and identify meaningful patterns.
Key Disciplines in Forensic Analysis
Modern techniques for examining evidence rely on specialized areas of expertise. Each field focuses on a specific type of material or data, ensuring precise and reliable outcomes. By dividing responsibilities among these disciplines, professionals can tackle diverse challenges with greater accuracy.
One critical area involves the study of physical remains to uncover details about identity or cause. Another discipline centers around chemical testing, which identifies substances and their properties. Digital tools also play a significant role, offering insights into electronic traces that might otherwise go unnoticed. Together, these approaches create a comprehensive framework for understanding and solving complex scenarios.
The combination of expertise in different fields ensures that every detail, no matter how small, contributes to the overall picture. These methods not only enhance the accuracy of findings but also provide a deeper understanding of the events or materials under examination.
The Role of Forensics in Modern Investigations
Technological advancements and meticulous methodologies have transformed how evidence is interpreted. These tools allow experts to uncover crucial details, bridging gaps in complex cases. The ability to analyze diverse materials and draw connections has become essential for resolving uncertainties and providing clarity.
Key Contributions: The integration of specialized techniques helps identify relationships between events, trace origins, and confirm authenticity. By examining physical and digital traces, experts can reconstruct scenarios, offering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Modern practices not only enhance accuracy but also ensure that findings are supported by objective data. This approach strengthens decision-making processes, providing a solid foundation for addressing challenges effectively.
Essential Techniques in Crime Scene Processing
Effectively examining a location where an event occurred requires careful planning and precise execution. Each step, from initial observation to final documentation, plays a critical role in ensuring all relevant details are preserved and analyzed. These techniques help create a clear and accurate picture of what transpired.
The process begins with securing the area to prevent contamination or loss of crucial evidence. Detailed documentation follows, including photographs, sketches, and written records to capture the scene comprehensively. Every item is meticulously collected, labeled, and stored to maintain integrity during later analysis.
Consistency in applying these methods ensures reliability and accuracy. The ability to gather and preserve even the smallest traces can significantly impact understanding, making these techniques indispensable for solving complex cases.
Forensic Biology and DNA Evidence Explained
The study of biological materials plays a pivotal role in understanding events and identifying individuals. Techniques for analyzing genetic information have revolutionized the ability to connect evidence to specific sources, offering unmatched precision and reliability.
One of the most critical aspects is the extraction and amplification of genetic material, ensuring even trace amounts can be examined. These sequences provide unique identifiers, making it possible to establish connections with a high degree of certainty. Additionally, analyzing biological traces such as hair, fluids, or skin cells helps reconstruct actions and timelines.
Applications: From confirming identities to excluding possibilities, these methods are crucial for resolving uncertainties. The meticulous handling and interpretation of this type of evidence ensure accuracy and maintain its value in broader analyses.
The Importance of Trace Evidence Analysis

Even the smallest particles can provide valuable insights into an event or interaction. Analyzing minute traces left behind during an incident can reveal critical details about the people, objects, or actions involved. This technique often helps bridge gaps in understanding and can turn seemingly insignificant items into key pieces of the puzzle.
Common Types of Trace Evidence
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fibers | Small threads or particles from clothing, carpets, or other materials. |
| Hair | Can provide DNA or other identifying features such as root characteristics. |
| Glass | Fragments may be linked to a location or point of impact. |
| Pollen | Helps establish the geographic area or season of an event. |
| Soil | Can match a suspect or item to a specific location based on its composition. |
Why Trace Evidence Matters
The analysis of trace materials is crucial in connecting suspects, victims, or scenes. By identifying these tiny but telling pieces of evidence, investigators can create links that otherwise might not be apparent. It provides an additional layer of certainty, often confirming or disproving theories with remarkable accuracy.
How Forensic Chemistry Solves Crimes
In criminal cases, the identification and analysis of substances can uncover critical clues that lead to resolutions. By applying chemical techniques to various materials, experts can determine the presence of specific compounds, identify unknown substances, and understand the interactions between different elements found at crime scenes.
One key application involves the analysis of bodily fluids, drugs, explosives, and toxins. By isolating and examining these substances, experts can link them to suspects, victims, or locations. The chemical composition of a sample can reveal its origin, purity, or how it was used, providing important evidence to confirm or challenge hypotheses about the crime.
In addition, chemical tests can detect residues or traces that might not be visible to the naked eye, helping to establish a timeline or reconstruct events. This approach not only supports other evidence but often provides the missing piece needed to solve complex cases.
Insights into Ballistics and Firearm Analysis
Understanding the behavior of projectiles and the tools used to launch them is key to resolving cases involving firearms. By examining ballistic evidence, experts can provide crucial details about the weapon used, the trajectory of the shot, and even the location of the shooter. These insights help reconstruct events and establish timelines with precision.
Key Elements in Firearm Analysis
- Tool Mark Examination: Identifying unique markings on bullets and shell casings left by the firearm’s barrel or firing pin.
- Trajectory Analysis: Mapping the path a projectile took to determine shooting angles and distances.
- Firearm Identification: Matching a bullet or casing to a specific gun based on unique identifiers.
Applications of Ballistics in Criminal Cases
- Linking Crimes: Ballistics evidence can tie a suspect to multiple crime scenes by matching projectiles to a specific weapon.
- Determining Intent: The nature of the shot (e.g., distance, angle) can reveal whether it was deliberate or accidental.
- Establishing Self-Defense: Trajectory analysis can help prove if the position of the shooter aligns with a self-defense claim.
The analysis of firearms and projectiles is an invaluable tool in uncovering the truth, offering a detailed perspective that other forms of evidence may not provide.
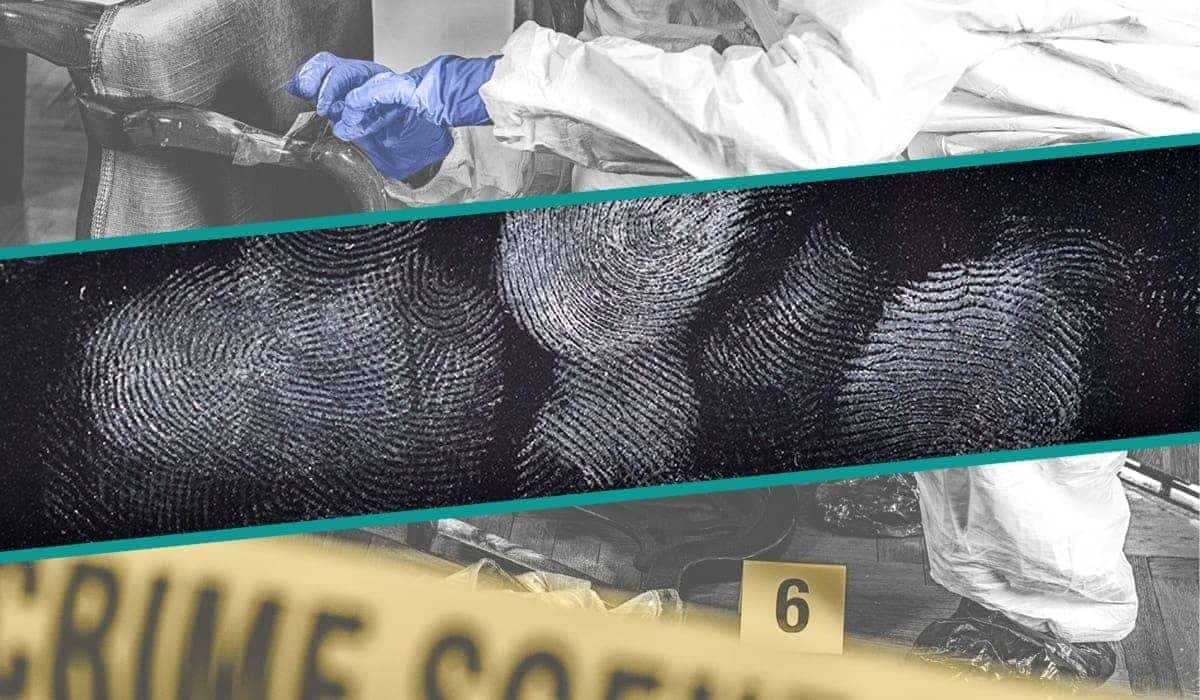
Uncovering Truth with Fingerprint Identification

Fingerprint identification has become one of the most reliable methods for identifying individuals based on unique physical characteristics. The distinct patterns on fingertips, formed by ridges and lines, serve as a permanent identifier for each person. This technique is invaluable for linking individuals to specific locations, objects, or events.
Every fingerprint is unique, which means no two individuals share the same pattern, making this form of identification highly precise. By carefully collecting and analyzing these prints left behind at crime scenes, investigators can establish connections between suspects and criminal activities. Even partial prints, when properly examined, can provide vital information and contribute to solving complex cases.
Key Aspects of Fingerprint Identification:
- Individuality: Each person has a distinct fingerprint pattern, making it one of the most effective forms of personal identification.
- Reliability: The unique nature of fingerprints ensures their high accuracy in matching individuals to specific events or places.
- Wide Reach: Fingerprint identification is applicable in various contexts, including criminal investigations, security checks, and identity verification.
With its high degree of certainty, fingerprint identification plays a critical role in uncovering the truth, helping to bring clarity to situations that would otherwise remain unresolved.
The Science Behind Document Examination
Document examination involves a detailed analysis of written materials to determine their authenticity, origin, or potential alteration. This process examines various features of a document, including the ink, paper, handwriting, and printing methods. The goal is to uncover critical details that can either confirm or disprove the legitimacy of the document in question.
Experts in this field use advanced techniques to study the physical properties of documents. By examining aspects such as ink composition, paper fibers, and ink marks, they can identify whether a document is genuine or has been manipulated. Additionally, analyzing handwriting or signatures helps to detect forgery or trace the document back to its creator.
Core Elements in Document Examination:
- Ink Analysis: The study of ink types and their chemical composition can reveal when a document was created or modified.
- Paper Analysis: The structure and composition of paper can be examined to trace the origin of a document or determine its age.
- Handwriting Comparison: Comparing handwriting styles can confirm the authorship of a document or detect alterations.
By employing these methods, professionals can provide crucial insights into the authenticity of a document, supporting legal proceedings or resolving disputes.
Understanding Digital Forensics and Cyber Investigations
In today’s interconnected world, understanding digital evidence has become essential in solving a wide array of crimes. From tracking down cybercriminals to uncovering hidden data, experts use specialized methods to examine electronic devices, networks, and storage systems to gather critical information. This discipline involves the recovery, preservation, and analysis of digital traces left behind by criminals, aiding in both criminal justice and corporate security.
Key Techniques in Digital Evidence Recovery
Recovering digital evidence is a meticulous process that requires skill and the use of sophisticated tools. Whether dealing with hard drives, smartphones, or cloud storage, investigators follow strict protocols to avoid compromising evidence. The process typically involves:
- Data Recovery: Using specialized software to retrieve deleted or damaged files from storage devices.
- Network Monitoring: Analyzing network traffic to trace unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
- File Forensics: Examining files and metadata to identify modifications, timestamps, and other clues that could indicate tampering.
Legal Considerations in Digital Evidence Handling
Handling digital evidence requires an understanding of legal boundaries. It’s essential that investigators ensure the proper chain of custody and follow applicable laws to maintain the integrity of the evidence. Any mishandling can lead to compromised findings and legal challenges.
Ultimately, the combination of technical expertise and legal knowledge in digital analysis plays a crucial role in uncovering the truth behind cybercrimes, protecting individuals and organizations from digital threats.
Psychological Profiling in Criminal Investigations
Understanding the mind of a criminal is a vital aspect of solving many types of crimes. Psychological profiling is a technique used to analyze behavioral patterns, motives, and psychological traits of suspects, which can provide law enforcement with a clearer picture of the individual behind the crime. This approach helps narrow down suspects and predict future actions, making it an essential tool in criminal cases, especially when traditional evidence is scarce.
Key Aspects of Psychological Profiling
Psychological profiling involves several key elements that help in constructing a criminal’s profile. Some of the primary aspects include:
- Behavioral Patterns: Analyzing the method and sequence of actions taken during the crime to determine characteristics of the perpetrator.
- Motivation: Understanding the reasons behind a crime, whether driven by revenge, lust, financial gain, or another psychological factor.
- Personality Traits: Assessing the psychological makeup, including traits such as aggression, narcissism, or obsession, to predict the behavior of the criminal.
Applications in Solving Crimes
Profiling can significantly enhance law enforcement’s ability to identify and apprehend criminals. By analyzing past cases and identifying patterns in behavior, psychologists can help investigators target the most likely suspects. In some cases, profiling has led to breakthroughs, particularly in serial crimes, where the perpetrator’s behavior is repetitive and revealing.
Ultimately, psychological profiling is a valuable tool that, when combined with other investigative techniques, aids in creating a comprehensive approach to solving complex criminal cases.
The Legal Impact of Forensic Testimony
Expert testimony plays a crucial role in the courtroom, providing judges and juries with the specialized knowledge needed to understand complex evidence. When professionals testify regarding specific types of evidence–such as biological samples, weapon analysis, or digital data–they offer insights that can significantly influence the outcome of a trial. The credibility and clarity of their testimony can either strengthen or weaken the case, making it an essential aspect of the legal process.
Influence on Trial Outcomes

In many cases, expert testimony can be the deciding factor in determining the guilt or innocence of a defendant. This testimony can clarify technical details, such as the identification of substances or the analysis of physical evidence, making them more understandable for the jury. When presented effectively, such testimony can lead to a conviction or acquittal by helping the jury make more informed decisions.
Challenges to Credibility
While expert testimony can have a significant impact, it is not without its challenges. Inaccurate or unreliable testimony can undermine the case, leading to appeals or wrongful convictions. It is essential for professionals to adhere to established protocols and standards to maintain the integrity of their testimony. Additionally, opposing counsel may challenge the qualifications or methods of the expert, further complicating the legal process.
Ultimately, the role of expert witnesses in the courtroom is vital for ensuring that the legal system is equipped with the necessary expertise to make fair and informed decisions. The accuracy and trustworthiness of their testimony can determine the course of justice in criminal cases.
Advancements in Forensic Technology Tools
Recent developments in technological tools have dramatically improved the way evidence is analyzed and understood in legal contexts. These innovations offer new ways to collect, preserve, and interpret data, providing professionals with more efficient and accurate methods to solve complex cases. As these tools evolve, they continue to revolutionize how investigations are conducted and contribute to the accuracy of legal proceedings.
Key Technological Innovations
- DNA Sequencing: Advances in DNA testing methods allow for faster, more accurate identification of individuals based on genetic material. This has helped solve cold cases and exonerate the wrongly convicted.
- Digital Evidence Analysis: New software tools allow investigators to retrieve deleted files, track digital footprints, and analyze communications, making digital investigations more comprehensive and efficient.
- 3D Imaging: Three-dimensional imaging techniques are increasingly used to reconstruct crime scenes or accidents with precision, providing a clearer visual understanding for courts.
- Mobile Device Forensics: The latest tools can extract data from mobile devices, including encrypted messages, location data, and call logs, aiding investigations involving smartphones and tablets.
Impact on Investigation Processes
- Speed: New technologies significantly reduce the time needed to analyze evidence, allowing for faster case resolution.
- Accuracy: With more advanced tools, investigators can conduct more precise analyses, improving the quality of evidence presented in court.
- Collaboration: These tools also facilitate collaboration between different jurisdictions and departments, enhancing the overall efficiency of case handling.
As new technologies continue to emerge, their integration into investigations holds the promise of more effective, transparent, and equitable legal proceedings. These advancements empower experts to make discoveries that would have been difficult or impossible with older methods, ensuring that justice is served in an increasingly digital world.
Common Challenges in Evidence Collection

Collecting reliable evidence is crucial for solving cases, but the process often encounters several hurdles that can affect the quality and integrity of the material gathered. From contamination risks to improper handling, these challenges can undermine the entire investigative process. Addressing these obstacles is vital to ensuring that evidence can be effectively used in legal proceedings.
Handling and Contamination Risks

- Cross-Contamination: Evidence can be easily contaminated if not properly secured, leading to mixed samples or inaccurate conclusions. This can be especially problematic in cases involving DNA or biological materials.
- Environmental Factors: Weather conditions or the location of the scene can compromise evidence, such as rain washing away important traces or sunlight affecting the preservation of certain materials.
- Human Error: Mistakes made by those handling the evidence–whether through negligence or lack of training–can lead to the loss or mishandling of critical items.
Challenges in Evidence Preservation
- Degradation: Some types of evidence, like biological samples or digital data, can degrade over time if not stored properly, making it difficult to analyze later on.
- Chain of Custody: Maintaining a documented chain of custody is essential to demonstrate that the evidence has not been altered or tampered with. Any breaks in this chain can cast doubt on the authenticity of the evidence in court.
Despite these challenges, continued advancements in protocols and technology are helping to address these concerns, improving the reliability of evidence collection. Proper training, rigorous procedures, and the use of innovative tools can help minimize the risks and ensure that evidence remains valid and useful for solving cases.
Tips for Analyzing Investigation Activity Sheets
When working with investigation-related materials, it’s important to approach the analysis systematically. Properly reviewing and interpreting the information provided can lead to more accurate conclusions and better decision-making. Here are some essential tips to guide your process.
Understanding the Structure
- Read Through Thoroughly: Ensure you fully understand the context before diving into detailed analysis. Take the time to read the entire sheet and identify the key objectives.
- Highlight Important Points: As you go through the material, underline or highlight significant data points, key events, or crucial instructions that will guide the next steps.
- Organize Information: Break down the information into manageable sections or categories. This can include dates, individuals involved, or events, which will make it easier to analyze connections later.
Cross-Referencing and Fact-Checking
- Verify Consistency: Ensure that the data within the activity sheets is consistent with other related documents or previous findings. Discrepancies may highlight areas that require further investigation.
- Fact-Check Key Details: Confirm the accuracy of names, locations, times, and any other details that could be pivotal to the overall understanding of the situation.
- Compare with Known Information: Cross-reference with other case materials or databases to ensure the activity sheet aligns with established facts.
Drawing Conclusions
- Identify Patterns: Look for recurring themes or trends that may emerge. Patterns in the data can often lead to valuable insights or hypotheses.
- Assess Relevance: Not all information in the sheets may be immediately relevant. Evaluate which facts or events are essential to solving the case and focus on them.
- Document Your Findings: Keep detailed notes on your analysis, including any assumptions, connections, or conclusions drawn from the sheet. This can be crucial for later stages of the process.
By following these tips, you can ensure a more organized and efficient approach to analyzing investigation activity sheets, ultimately aiding in clearer insights and stronger case resolutions.
Improving Knowledge with Practice Questions

Engaging with practice questions is one of the most effective ways to deepen understanding and sharpen skills in any field. By testing knowledge through simulated scenarios, individuals can identify areas of strength and those that need further attention. This method allows for a more interactive approach to learning, making it easier to retain complex concepts and apply them in real-world situations.
| Topic | Example Question | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Evidence Handling | What steps should be taken to properly collect and preserve a piece of evidence from a crime scene? | To test knowledge on proper procedures and protocol for maintaining evidence integrity. |
| Interview Techniques | What are the best practices for conducting an effective witness interview? | To assess understanding of communication strategies and techniques for obtaining accurate information. |
| Data Analysis | How would you analyze data collected from digital sources to identify patterns? | To evaluate the ability to interpret complex data and draw logical conclusions. |
By practicing with a variety of questions, learners can improve critical thinking, enhance their problem-solving skills, and develop a more comprehensive understanding of key concepts. Moreover, this approach prepares individuals for real-life challenges, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle diverse situations effectively.