
Effective preparation for any competitive assessment requires not only understanding the concepts but also practicing through various exercises. By tackling a wide range of practice material, you can identify strengths, address weaknesses, and build the necessary confidence to excel. This section provides key resources and insights to enhance your preparation.
Practicing regularly with exercises designed to reflect the actual challenge will improve your ability to think critically and solve problems efficiently under time pressure. Developing a strategic approach to each task ensures you’re well-equipped for every section.
Additionally, analyzing your performance and reviewing detailed explanations of each solution will help deepen your understanding. Embracing this process of active learning is essential for mastering the skills required to succeed.
GMAT Exam Sample Questions and Answers
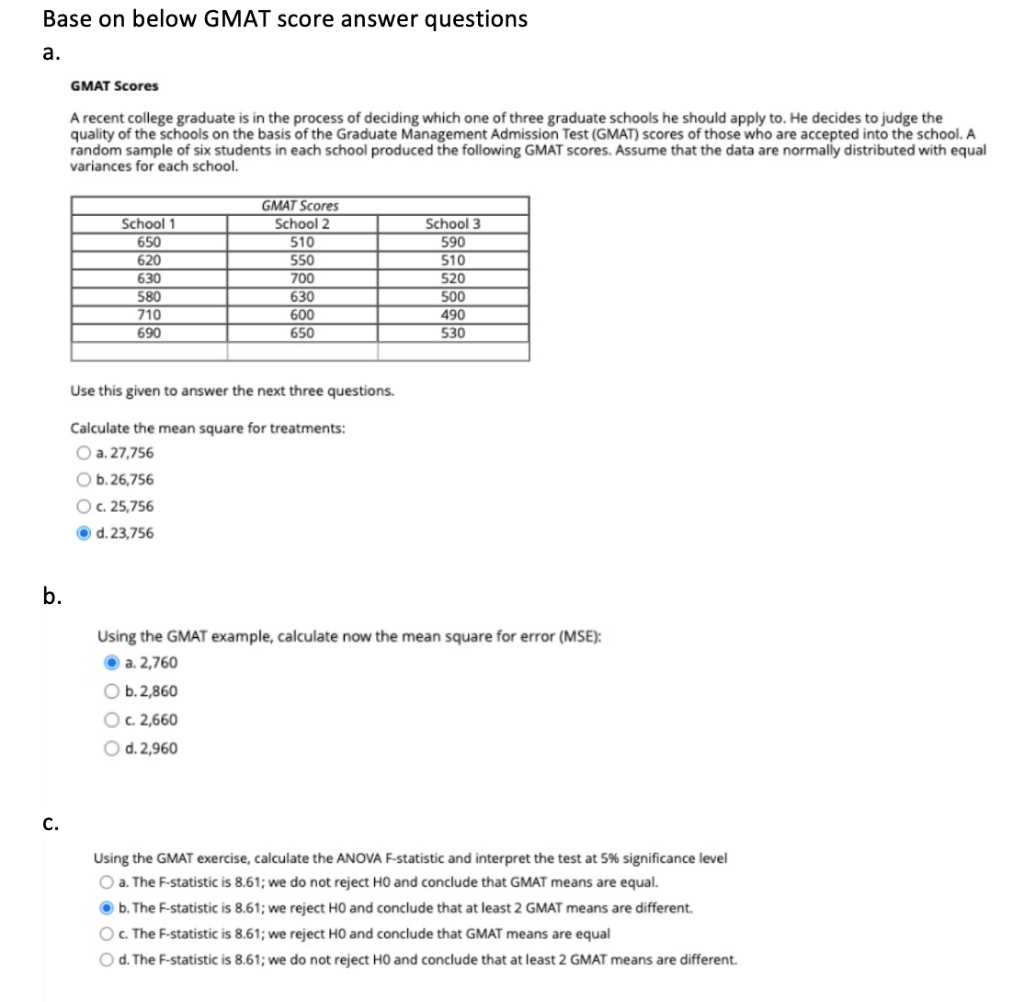
In order to prepare effectively for any competitive test, it’s important to engage with realistic practice exercises that mirror the structure and difficulty of the actual assessment. Working through different problem types helps familiarize you with the format, making it easier to identify patterns and increase accuracy when time is limited.
Practice Exercises for Quantitative Section

The quantitative section challenges your ability to solve math problems quickly and accurately. Below are some common types of problems you may encounter:
- Arithmetic and number properties
- Algebra and equations
- Data interpretation and analysis
- Word problems involving ratios, percentages, and proportions
Focus on improving speed without sacrificing accuracy. Try to solve each problem within a set time limit to simulate the real test environment.
Practice Exercises for Verbal Section
The verbal section tests your reading comprehension, sentence correction, and critical reasoning skills. The following exercises are typically included:
- Identifying errors in sentence structure and grammar
- Understanding and interpreting written passages
- Logical reasoning and argument evaluation
It’s essential to practice these exercises regularly, as they help refine your ability to read quickly, understand complex information, and make well-reasoned decisions.
Understanding GMAT Question Formats
Familiarizing yourself with the structure of various tasks is essential for successful preparation. Each section of the test presents a unique set of challenges, and understanding the format will help you navigate them efficiently. Knowing what to expect allows you to strategize your approach and manage your time effectively during the assessment.
The problems are designed to test your ability to think critically, solve complex problems, and reason logically under time constraints. There are different types of tasks, each with its own set of rules and methods for tackling. Some require numerical calculations, while others assess your understanding of language, logic, and data analysis.
How to Approach GMAT Quantitative Questions
The quantitative section evaluates your ability to solve mathematical problems efficiently and accurately. To excel in this part, it’s important to develop a systematic approach that helps you quickly identify key information and apply the right strategies to find solutions.
Key Strategies for Solving Mathematical Problems
Effective problem-solving in the quantitative section requires practice and familiarity with different types of problems. Here are some tips to improve your performance:
- Understand the problem before attempting a solution–read carefully to identify the given data and what is being asked.
- Break down complex problems into simpler steps, focusing on one element at a time.
- Use estimation techniques to quickly eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
- Master basic mathematical concepts, such as algebra, geometry, and arithmetic, as these frequently appear in problems.
Common Types of Quantitative Tasks
Understanding the types of mathematical tasks you’ll encounter is crucial for preparing effectively. Here are some common categories:
- Arithmetic and number properties, such as fractions, percentages, and ratios
- Algebraic expressions, equations, and inequalities
- Data interpretation, where you analyze tables, graphs, and charts
- Word problems that require translating text into mathematical equations
By mastering these techniques and practicing regularly, you’ll increase both your speed and accuracy in solving mathematical tasks. Remember, each problem requires a unique approach, but with consistent effort, you can improve your performance significantly.
Tips for GMAT Verbal Section Success
The verbal section of any competitive assessment challenges your ability to comprehend written material, identify language errors, and evaluate arguments logically. To perform well, it is essential to develop skills in reading comprehension, sentence correction, and critical reasoning. By applying the right techniques, you can enhance your accuracy and efficiency in answering verbal tasks.
Strategies for Improving Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension tasks test your ability to understand and analyze written passages. Here are some strategies to excel in this section:
- Focus on identifying the main ideas and themes of each passage.
- Pay attention to the tone and purpose of the author’s arguments.
- Practice reading complex texts to improve speed without sacrificing understanding.
Effective Sentence Correction Techniques
Sentence correction problems assess your ability to identify grammatical errors and improve sentence structure. To succeed in this area, consider the following tips:
- Understand common grammar rules, such as subject-verb agreement and parallel structure.
- Look for clarity, conciseness, and consistency when evaluating sentence choices.
- Eliminate answers that introduce unnecessary changes or errors in meaning.
Critical Reasoning and Argument Evaluation
Critical reasoning tasks measure your ability to evaluate arguments and assess conclusions based on provided evidence. Use these guidelines:
- Carefully analyze the argument’s structure, identifying assumptions and conclusions.
- Focus on the strength of the evidence supporting the argument.
- Practice identifying flaws in reasoning and logical gaps.
Verbal Section Time Management
Managing your time efficiently is key to success in the verbal section. Here’s a helpful time management guide:
| Task | Suggested Time Limit |
|---|---|
| Reading Comprehension | 3-4 minutes per passage |
| Sentence Correction | 1-2 minutes per question |
| Critical Reasoning | 2-3 minutes per question |
By following these strategies and practicing regularly, you will improve your verbal skills, increase your confidence, and enhance your performance on the test.
Mastering Analytical Writing Assessment
The analytical writing assessment measures your ability to think critically and express ideas clearly in writing. Success in this section relies on your capacity to analyze an argument, identify key elements, and present a structured critique. A well-organized and logical response will not only demonstrate your understanding but also your ability to communicate effectively under time constraints.
Understanding the Task
The main objective of this section is to evaluate your critical thinking skills and your ability to communicate your analysis. You’ll be presented with an argument, and your task is to examine the reasoning behind it, pointing out flaws and weaknesses in a coherent manner. Focus on the structure of the argument, considering factors such as:
- Assumptions made by the author
- The strength of the evidence presented
- The overall logical flow of the argument
Effective responses do not require you to agree or disagree with the argument but to assess the reasoning behind it. Presenting a well-reasoned critique with clear, organized ideas is key to success.
Structure Your Response Effectively
Organizing your response clearly and logically is crucial for conveying your analysis. A typical structure includes:
- Introduction: Briefly introduce the argument and state your intention to critique its reasoning.
- Body Paragraphs: In each paragraph, focus on a specific flaw or weakness in the argument. Support your critique with logical explanations and examples.
- Conclusion: Summarize the points you’ve made and reiterate your overall analysis of the argument.
Practice writing responses within the time limit to ensure you can organize your thoughts quickly and effectively. By focusing on clear, logical structure and strong reasoning, you will be well-prepared to excel in this section.
Effective Time Management for GMAT
Mastering time management is one of the most important aspects of preparing for any competitive assessment. With a limited amount of time to answer a wide variety of tasks, being able to allocate time effectively is crucial for maximizing your score. The key is to maintain a steady pace while ensuring you don’t rush through problems, which could lead to unnecessary mistakes.
Strategic planning before and during the test allows you to approach each section with confidence. By practicing time-bound exercises, you can determine how much time to dedicate to each task. This will help you avoid spending too much time on challenging questions while ensuring you have enough time for the easier ones.
Time Allocation for Each Section
Each part of the test requires a different level of attention, and knowing how to allocate time properly is vital:
- Quantitative Section: Aim to spend no more than 2-3 minutes per problem. If you’re stuck on a difficult problem, move on and return to it if time permits.
- Verbal Section: Focus on reading comprehension and sentence correction within 1-2 minutes per question. Practice reading quickly and comprehending key points.
- Writing Assessment: Dedicate around 30 minutes to structure and write your response. Plan for 5 minutes of brainstorming, 20 minutes of writing, and 5 minutes for review.
Tips for Staying on Track
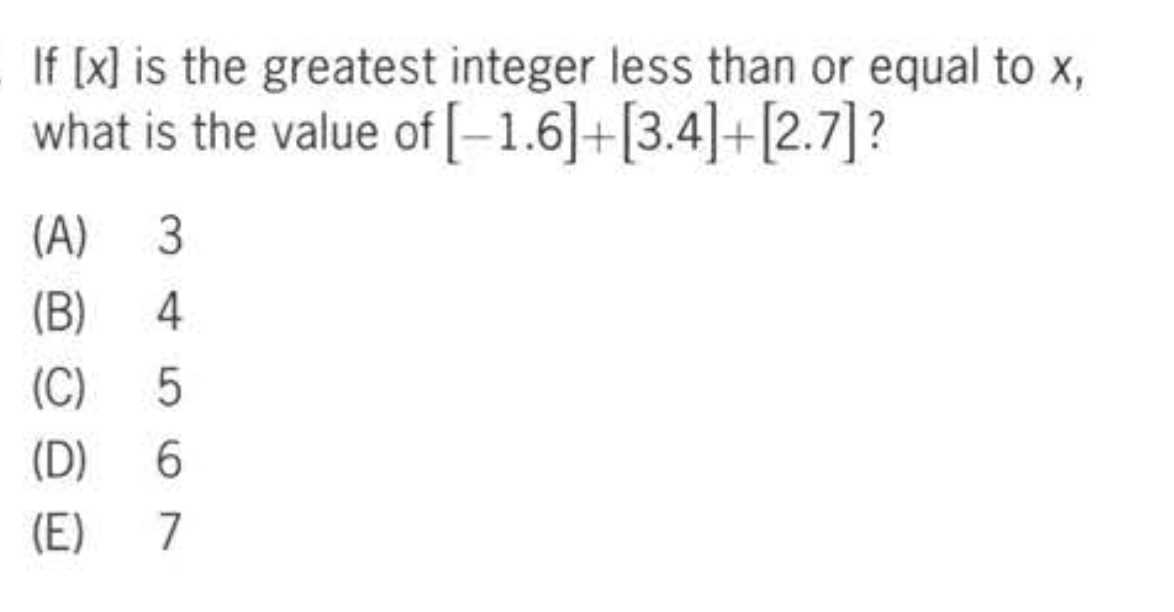
To ensure you stay on time, consider these strategies:
- Prioritize: Tackle easier questions first to build momentum and save time for more difficult tasks.
- Practice: Consistently practice under timed conditions to get used to the pressure and improve your speed.
- Stay calm: Keep a positive mindset. If you start to feel rushed, take a few seconds to refocus and regain your composure.
By managing your time wisely and practicing regularly, you can optimize your performance and ensure you have enough time to address all sections thoroughly.
Common Mistakes in GMAT Exams
Many individuals make avoidable errors during assessments, often due to misreading instructions, mismanaging time, or overlooking key details. These mistakes can significantly impact performance and result in a lower score. By identifying and understanding common pitfalls, you can avoid them and improve your overall performance on test day.
Misreading the Instructions
One of the most frequent mistakes is misinterpreting the instructions for a particular task. This can lead to incorrect approaches or missed opportunities to answer the question correctly. To prevent this, take a moment to carefully read each instruction and ensure you understand what is being asked before proceeding.
- Review key phrases that indicate the type of answer required (e.g., “choose the best answer” or “select all that apply”).
- Double-check the task’s format to avoid confusion between different types of problems.
Time Mismanagement
Time management is another critical factor. Many candidates either rush through the easier questions and spend too much time on complex ones or neglect to pace themselves, leaving too little time for the final questions. This can lead to incomplete sections and missed points.
- Practice pacing yourself during mock sessions to develop a natural rhythm.
- Identify questions that can be answered quickly and move on to maximize efficiency.
By being mindful of these common errors, you can focus your energy on answering questions accurately and efficiently, helping to achieve a stronger performance.
GMAT Critical Thinking Practice Questions
Critical thinking is an essential skill for success in any competitive assessment. This section challenges your ability to evaluate arguments, identify logical flaws, and think analytically. The goal is to develop a deeper understanding of how reasoning works and to practice applying it effectively in different scenarios.
Example Problem 1: Logical Inference
Consider the following argument:
“All successful companies invest heavily in marketing strategies. Company X has invested in marketing strategies. Therefore, Company X is successful.”
Evaluate the reasoning in the statement above. Which of the following best describes the flaw in the argument?
- It assumes that marketing investment alone determines a company’s success.
- It overlooks the importance of other business factors beyond marketing.
- It fails to consider the possibility that Company X’s marketing strategies are ineffective.
Example Problem 2: Identifying Assumptions
Read the following statement:
“Since many people enjoy listening to classical music, it should be played more often on public radio stations.”
What assumption does the speaker make in this argument?
- That classical music is universally appreciated.
- That the popularity of classical music automatically justifies its frequency on radio.
- That public radio stations have the resources to play more classical music.
By practicing with these types of problems, you can enhance your ability to critically assess arguments and strengthen your analytical reasoning skills.
Sentence Correction Sample Exercises
In this section, you’ll practice identifying and correcting errors in sentence structure, grammar, and clarity. Sentence correction tasks assess your ability to identify mistakes in various aspects of language use, such as verb tense, subject-verb agreement, word choice, and sentence construction. These exercises will help you sharpen your grammatical skills and improve the clarity and flow of your writing.
Exercise 1: Correct the Sentence
Read the sentence below and identify the error:
Despite the difficulties, the team managed to complete their project ahead of schedule, and they were extremely proud of the results achieved.
| Option | Correction |
|---|---|
| A | Despite the difficulties, the team managed to complete their project ahead of schedule and were extremely proud of the results achieved. |
| B | Despite the difficulties, the team managed to complete their project ahead of schedule, and they were extremely proud of the results being achieved. |
| C | Despite the difficulties, the team managed to complete its project ahead of schedule, and they were extremely proud of the results achieved. |
| D | Despite the difficulties, the team managed to complete their project ahead of schedule, and the results were achieved with pride. |
The correct sentence is found in Option A, as it removes redundancy and uses the correct pronoun agreement (“team” is singular, so “it” should be used instead of “they”).
Exercise 2: Choose the Best Option
Select the best alternative that improves the clarity and correctness of the following sentence:
The committee debated extensively on the new policy and they ultimately decided that a final vote will be held next week.
| Option | Correction |
|---|---|
| A | The committee debated extensively on the new policy and ultimately decided that a final vote will be held next week. |
| B | The committee extensively debated on the new policy, and it was ultimately decided that a final vote will be held next week. |
| C | The committee debated extensively on the new policy, and they ultimately decided that a final vote would be held next week. |
| D | The committee debated extensively about the new policy, and they ultimately decided that the final vote will be held next week. |
The correct answer is Option A. It improves the sentence by removing unnecessary words (“on the new policy”) and simplifying the phrasing to enhance clarity.
By regularly practicing these types of exercises, you can improve your ability to identify errors and correct them swiftly, improving both your writing and analytical abilities.
Problem Solving Question Examples
In this section, you’ll find exercises designed to enhance your problem-solving abilities. These types of questions assess your capacity to apply mathematical concepts and logical reasoning to identify solutions. They can cover a range of topics including arithmetic, algebra, and data interpretation. The goal is to improve both your technical skills and your ability to reason through complex scenarios efficiently.
Example 1: Basic Arithmetic Problem
A factory produces 500 units of product each day. If the production rate increases by 10% every month, how many units will be produced after 3 months?
- A. 500
- B. 550
- C. 600
- D. 665
Solution: The initial production is 500 units. After 1 month, the production increases by 10%, so the new rate is 500 × 1.10 = 550 units. After the second month, the production is 550 × 1.10 = 605 units. After the third month, it increases again: 605 × 1.10 = 665 units. Thus, the correct answer is D. 665 units.
Example 2: Algebraic Problem
If 3x – 5 = 16, what is the value of x?
- A. 5
- B. 7
- C. 6
- D. 4
Solution: To solve for x, first add 5 to both sides of the equation: 3x = 21. Then divide both sides by 3 to get x = 7. Therefore, the correct answer is B. 7.
These exercises are designed to improve your ability to solve problems quickly and accurately under timed conditions. Practice similar problems to develop your skills further and boost your confidence.
How to Tackle Data Sufficiency
Data sufficiency questions test your ability to assess whether the information provided is enough to solve a problem. These types of problems challenge you to determine whether you have sufficient data to answer a question without necessarily solving it fully. Instead of focusing on solving the problem step-by-step, your task is to evaluate the provided statements and decide if they allow you to reach a definitive conclusion.
The key to mastering data sufficiency is understanding the structure of the problem and quickly evaluating the provided information. You should be comfortable with various types of questions involving algebra, geometry, arithmetic, and word problems. The goal is to use logic and reasoning to determine whether the available data is adequate for answering the question, and if not, why not.
Steps to Approach Data Sufficiency Questions
Follow these steps to enhance your ability to solve data sufficiency problems efficiently:
- Step 1: Read the question carefully and understand what is being asked. Focus on what the question requires rather than the details of the problem.
- Step 2: Identify the two statements given. Evaluate each one individually and then together, considering whether the information is sufficient to answer the question.
- Step 3: Eliminate irrelevant details. Often, extraneous information is included to confuse you. Focus on what directly contributes to answering the question.
- Step 4: Apply the answer choices logically. The possible answers typically indicate whether each piece of information alone is sufficient, both together are sufficient, or neither provides enough data to solve the problem.
Example Problem
Is x > 3?
- Statement 1: x + 2 > 5
- Statement 2: x – 1 > 2
Solution: Statement 1: x + 2 > 5 implies x > 3. So, this statement alone is sufficient to answer the question.Statement 2: x – 1 > 2 implies x > 3. This statement also provides sufficient information on its own.
Since both statements individually provide enough information to answer the question, the correct answer is Answer: D, which indicates both statements together are sufficient.
By practicing these types of questions, you’ll develop the ability to evaluate data quickly and accurately, ensuring that you’re ready to handle these challenging problems effectively in your preparation.
Reading Comprehension Practice Tests
Reading comprehension exercises are designed to evaluate your ability to understand and analyze written material. These types of tasks test how well you can grasp the main ideas, identify key details, and make inferences from passages. To succeed, it’s important to not only focus on the text itself but also practice strategies for answering related questions efficiently.
Effective practice involves engaging with a variety of passage types, ranging from narrative and descriptive to argumentative and technical. Each passage will come with a set of questions that assess your ability to understand the content deeply, identify the author’s tone, and apply critical thinking to extract meaning beyond the surface level.
Tips for Tackling Reading Comprehension Tasks
- Read Actively: Focus on the key points in each paragraph. Highlight or note down main ideas as you read to help retain important information.
- Understand the Structure: Pay attention to how the passage is organized. Recognize how the author introduces ideas, provides supporting details, and concludes the argument.
- Answer Strategically: When answering questions, avoid re-reading the entire passage. Instead, refer to specific sections that address the question directly.
- Manage Your Time: Practice answering questions within a set time limit. This will help you balance speed and accuracy under test conditions.
Example Passage and Questions
Passage:
“Artificial intelligence has revolutionized many industries, from healthcare to transportation. The ability to analyze large datasets and automate tasks has not only made businesses more efficient but also opened new opportunities for innovation. However, with these advancements come concerns about privacy, job displacement, and ethical implications. It is essential to strike a balance between progress and responsibility to ensure the benefits of AI outweigh its potential risks.”
- Question 1: What is the primary concern mentioned about artificial intelligence?
- A. Efficiency
- B. Job displacement
- C. Innovation
- D. Cost
- Question 2: How does the author suggest addressing the challenges posed by artificial intelligence?
- A. By limiting technological advancements
- B. By balancing progress with responsibility
- C. By focusing only on efficiency
- D. By eliminating concerns about privacy
Solution:
– The correct answer to Question 1 is B. Job displacement, as it is specifically mentioned in the passage.
– The correct answer to Question 2 is B. Balancing progress with responsibility, as indicated in the last sentence of the passage.
By practicing with a variety of reading comprehension exercises, you’ll develop the skills needed to efficiently analyze passages and answer questions correctly under time pressure. Regular practice will also help you refine your ability to identify key ideas, making the process of understanding and responding to complex texts much easier.
Improving Your Score with Practice

Consistent practice is essential for enhancing your performance on any assessment. By engaging regularly with practice material, you can identify areas of weakness, sharpen your skills, and build the confidence needed to tackle complex problems. It’s not just about repetition; it’s about actively learning from mistakes and refining your approach.
One of the key benefits of regular practice is its ability to familiarize you with the test structure, the types of tasks you will encounter, and the strategies that work best for solving different problem types. The more you practice, the more efficient and effective your approach will become, especially under timed conditions.
Effective Strategies for Maximizing Practice
- Set a Consistent Schedule: Allocate specific times each day or week for practice sessions. Consistency helps improve focus and retention.
- Review Mistakes Thoroughly: After each practice session, take the time to understand where you went wrong and why. This reflection is key to avoiding repeated errors.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Practice under realistic time constraints to get accustomed to managing your time effectively during the actual assessment.
- Mix Practice Types: Work on a variety of question types, such as critical reasoning, quantitative problems, and reading comprehension, to ensure balanced preparation.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a record of your practice test results to identify trends and improvements, helping you adjust your strategy over time.
How to Stay Motivated During Practice
- Set Achievable Goals: Break down your preparation into smaller, manageable targets to maintain motivation throughout your study journey.
- Reward Yourself: Celebrate small victories and progress. Rewarding yourself can make the practice process more enjoyable and sustainable.
- Stay Positive: Keep a growth mindset. Even if you encounter setbacks, remember that progress is a result of continued effort and learning.
By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you will gradually build the skills and confidence necessary to excel. Regular practice, combined with thoughtful review and goal setting, can significantly improve your score and better prepare you for the challenges ahead.
Integrated Reasoning Practice Questions

The ability to analyze and interpret complex data is crucial in many assessments, and honing this skill is essential for performing well. This section focuses on exercises designed to challenge your ability to synthesize information from different sources and make decisions based on multiple types of data. These tasks require you to evaluate visual information, text, and numbers, all while developing your logical reasoning skills.
By engaging with practice tasks that test your integrated reasoning abilities, you can become more comfortable with the various question formats and strategies. Regular exposure to these types of exercises will sharpen your analytical mindset and improve your capacity to make quick, accurate judgments under pressure.
Types of Integrated Reasoning Tasks
These tasks typically involve the integration of data from tables, graphs, and written passages. Here are some common formats:
- Multi-Source Reasoning: You will be provided with multiple data sources, and the challenge is to extract relevant information to answer questions.
- Graphics Interpretation: Questions based on graphs, charts, and visual data to test how well you interpret and draw conclusions from visual stimuli.
- Two-Part Analysis: Each question requires you to solve two linked problems, testing your ability to evaluate and solve complex, multi-faceted issues.
- Table Analysis: You’ll analyze tables of data, sorting and interpreting it to answer questions based on what you deduce from the information.
Example Practice Tasks
Below are a couple of sample tasks designed to help you understand how to approach integrated reasoning questions:
| Task Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Multi-Source Reasoning | Given data from a financial report and a company’s annual review, determine which investment opportunity offers the highest return. |
| Graphics Interpretation | Examine a bar chart showing market trends over 10 years and predict the potential for future growth based on the current pattern. |
| Two-Part Analysis | Determine the cost-benefit ratio of two projects, considering both initial investment and long-term returns. |
| Table Analysis | Analyze a table displaying sales figures for different regions and determine which region’s sales grew the most last quarter. |
Regularly practicing these types of tasks can help you develop the skills necessary to efficiently interpret data and solve problems under time constraints. Understanding the different formats and mastering each one will significantly improve your overall performance in reasoning tasks.
Test Strategy for Maximum Efficiency
Efficiently navigating a challenging assessment requires a well-thought-out approach that balances speed and accuracy. Developing a strategy is key to managing time effectively while ensuring the quality of your responses. A focused approach helps you avoid unnecessary stress, enabling you to perform at your best under pressure.
The key to success lies in preparation, time management, and knowing when to move on from a question. By mastering these elements, you can maximize your score without wasting valuable time on particularly difficult sections. In this section, we will cover several strategies to help you streamline your approach and increase your chances of success.
Time Management Techniques
Properly managing time is one of the most important aspects of any test. Here are some techniques to help you manage your time more effectively:
- Set a Time Limit for Each Question: Allocate a specific amount of time for each question based on its difficulty. If you find yourself spending too much time on one question, move on to the next.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Start with the questions you feel most confident about. This helps build momentum and ensures that you secure easy points early on.
- Don’t Get Stuck: If you find a question particularly challenging, don’t spend too much time trying to solve it. Skip it and come back later if time permits.
- Review Your Answers: If you finish early, use the remaining time to review your answers. Double-check for simple mistakes or misinterpretations of questions.
Focus on Strategy, Not Just Content
While mastering the content is crucial, developing a solid strategy for approaching different types of tasks can be just as important. Here are a few tips to help you maximize your strategy:
- Understand the Format: Familiarize yourself with the structure and format of the test. Knowing what to expect will help you mentally prepare for the types of questions you’ll encounter.
- Use Process of Elimination: If you’re unsure about an answer, eliminate the most obviously incorrect options first. This increases your chances of selecting the right answer even when you’re not entirely sure.
- Practice Under Timed Conditions: Simulate test conditions by practicing with time constraints. This will help you get used to the pressure and learn how to pace yourself more effectively.
By combining effective time management with a focused, strategic approach, you can significantly improve your performance and achieve the best possible result in the assessment.
Understanding Scoring and Percentiles
When preparing for a challenging assessment, it’s important to understand how scores are calculated and what they truly represent. The scoring system can often be complex, but understanding it helps you set realistic goals and better interpret your performance. This section will explain the key aspects of scoring and percentiles, helping you gain clarity on how your efforts translate into results.
In most standardized assessments, your final score is not just a raw number but also reflects how you perform relative to others. Understanding the scale and the percentile system can give you a clearer picture of where you stand and how to target your preparation effectively.
Scoring Breakdown
Your overall score is typically composed of multiple sections, each contributing to your final result. Here’s an overview of how the scoring usually works:
- Overall Score: The final score is usually calculated from the combined performance in several sections of the test. Each section may have its own scoring range, and the cumulative score provides an overall assessment of your abilities.
- Section Scores: Each part of the test contributes a certain number of points to your total score. You may see separate scores for various areas such as quantitative reasoning, verbal reasoning, and analytical writing, depending on the format.
- Scaled Scores: The raw score from each section is converted into a scaled score. This scaling adjusts for any differences in test difficulty, ensuring fairness and consistency across different test versions.
Understanding Percentiles
Percentiles represent your performance compared to other test takers. They are often used to provide context for your score. Here’s how percentiles are typically interpreted:
- Top Percentiles: A higher percentile indicates that you performed better than a significant portion of your peers. For example, being in the 90th percentile means you performed better than 90% of other participants.
- Below Average Percentiles: A lower percentile shows that your performance was below the average. However, it’s important to remember that percentiles vary depending on the group of test takers and the specific assessment.
- Context Matters: Percentiles are relative. A score in the 80th percentile may be impressive in one context but may not be sufficient in a more competitive pool. Always consider the context in which your score will be viewed.
By understanding how scores and percentiles are calculated, you can better interpret your results and make more informed decisions about your preparation and next steps.
How to Interpret Answer Explanations
Understanding the reasoning behind your responses is a critical part of preparing for any standardized assessment. It’s not just about knowing what the correct answer is, but also understanding why it is correct and how the other options fall short. In this section, we’ll discuss how to approach answer explanations, helping you gain a deeper insight into the reasoning process and improve your performance on future challenges.
Answer explanations are designed to break down the thought process behind each correct solution, as well as to clarify why other options may not be the best choice. By carefully reviewing these explanations, you can identify common pitfalls, recognize patterns in your mistakes, and refine your problem-solving techniques. Here’s how you can make the most of these insights:
Focus on the Key Concepts
Each explanation typically highlights the fundamental concepts required to solve the problem. Pay close attention to the following:
- Core principles: Look for any underlying concepts, such as mathematical formulas, logical reasoning principles, or language structures, that were crucial for arriving at the correct answer.
- Methodology: Identify the specific approach or method that led to the solution. Understanding the steps involved will help you apply similar techniques to other problems in the future.
- Common mistakes: Explanations often point out common errors that people make. Take note of these to avoid repeating them in subsequent exercises.
Analyze Each Option
When reviewing an explanation, don’t just focus on the correct answer–examine why the other options were incorrect. This will help you understand why certain strategies work better than others:
- Eliminating wrong answers: Answer explanations often include a discussion of why other options are flawed. Understanding these reasons will sharpen your ability to quickly eliminate incorrect choices in the future.
- Comparing approaches: Sometimes, more than one approach can solve a problem. The explanation may present an alternative method for arriving at the correct solution, which you can use to expand your problem-solving toolbox.
- Clarifying misconceptions: Some incorrect options may stem from common misconceptions or misinterpretations of the problem. Recognizing these patterns helps you avoid making similar mistakes in the future.
By focusing on the key concepts, analyzing the incorrect options, and understanding the reasoning behind the correct answer, you can use answer explanations as a powerful tool to enhance your learning process and improve your problem-solving skills over time.