For aspiring legal professionals, obtaining a license to practice law involves a rigorous and structured process designed to test knowledge, skills, and ethical judgment. The journey is critical for ensuring that candidates are fully prepared for the responsibilities that come with representing clients in a courtroom and beyond.
In this guide, we will explore the steps involved in becoming licensed to practice law in the state, focusing on the requirements, preparation strategies, and the key components of the assessment. This process is a milestone that requires dedication, careful planning, and a clear understanding of what lies ahead.
Whether you’re in the early stages of your legal education or preparing for the final hurdles, this information will equip you with the essential tools and insights to navigate the licensing system with confidence. Understanding the structure, requirements, and strategies for success will be crucial as you move toward achieving your professional goals.
Illinois Licensing Assessment Overview
The licensing assessment for legal professionals in the state is a comprehensive process that evaluates the candidate’s proficiency in various areas of law. It serves as the final step before individuals are granted permission to practice law and represent clients in legal matters. The evaluation is structured to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that candidates are well-prepared for their legal careers.
While the structure may vary slightly across different regions, the core principles and subjects covered remain consistent. Candidates are expected to demonstrate competence in a range of legal topics, from contracts and civil procedure to ethics and professional responsibility. Success in this assessment is crucial for any aspiring attorney seeking to establish their practice in the state.
Understanding the format, subjects, and preparation strategies for this important milestone can significantly enhance one’s chances of success. It is essential for candidates to familiarize themselves with the requirements and structure of the assessment to approach it with confidence and clarity.
What is the Legal Licensing Assessment
This assessment is designed to evaluate the knowledge and competency of aspiring legal professionals before they are granted permission to practice law. It is a standardized test that ensures all candidates meet the necessary qualifications to represent clients, engage in legal procedures, and uphold the ethical standards of the profession.
Key Components of the Assessment
The evaluation consists of multiple sections that assess various aspects of legal knowledge. These sections focus on topics such as constitutional law, civil procedure, contracts, and legal ethics. Candidates must demonstrate both theoretical understanding and the ability to apply legal principles in practical scenarios.
| Section | Subjects Covered | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple-Choice | Constitutional Law, Torts, Contracts | 200 Questions |
| Essays | Legal Writing, Ethics, Civil Procedure | 3 Essay Questions |
| Practical Tasks | Professional Responsibility, Legal Analysis | Practical Scenarios |
Purpose and Importance
The primary objective of this assessment is to ensure that legal professionals possess the necessary skills to practice law effectively and ethically. It serves as the final step before entering the legal profession, ensuring that all attorneys have met the state’s standards for legal competence.
Eligibility Requirements for the Licensing Assessment
Before candidates can participate in the legal licensing process, they must meet specific qualifications set forth by the state. These criteria ensure that only individuals who have completed the necessary academic and professional steps are eligible to take the test. Meeting these requirements is essential for anyone wishing to pursue a legal career in the region.
Applicants must have completed their legal education from an accredited institution, typically holding a law degree or its equivalent. In addition, they must demonstrate that they meet certain character and fitness standards, ensuring that they possess the moral integrity required for the profession.
Academic and Educational Prerequisites
To be eligible for the licensing process, candidates must have earned a law degree from a program recognized by the relevant accrediting bodies. This ensures that all candidates have undergone rigorous training in the core aspects of law. Some jurisdictions may also accept foreign degrees if they meet specific equivalency standards.
Character and Fitness Requirements
In addition to academic credentials, applicants must submit to a background check to assess their moral fitness to practice law. This includes an evaluation of any criminal history, financial responsibility, and other factors that might affect an individual’s suitability for legal practice.
Assessment Structure and Content Areas
The legal licensing assessment is structured to thoroughly evaluate a candidate’s proficiency across a wide range of legal topics. The test is designed to ensure that individuals have a deep understanding of both theoretical and practical legal principles. It combines multiple question formats, including multiple-choice, essay writing, and practical exercises, to assess different facets of legal expertise.
The content of the assessment covers a broad spectrum of legal subjects, with each section focusing on specific areas that are essential for practicing law. Candidates are expected to demonstrate their knowledge of key concepts, the ability to apply legal reasoning, and their competence in solving legal issues under real-world conditions.
Core Areas of Focus
The primary content areas tested in the assessment include foundational topics such as constitutional law, contracts, torts, civil procedure, and criminal law. Each area is crucial for ensuring that candidates can navigate the complexities of legal cases, whether they involve litigation or client consultation.
Assessment Components
| Component | Subjects Included | Test Type |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple-Choice | Constitutional Law, Civil Procedure, Torts | 200 Questions |
| Essays | Contracts, Ethics, Legal Writing | 3 Written Essays |
| Practical Scenarios | Legal Analysis, Professional Responsibility | Scenario-Based Questions |
In addition to these core topics, candidates must also demonstrate their understanding of professional ethics and legal conduct. The ability to make sound legal decisions and advise clients appropriately is a critical aspect of the licensing process, ensuring that future attorneys are equipped to handle the responsibilities of the profession.
Preparing for the Legal Licensing Assessment
Preparing for the legal qualification process requires thorough planning, dedication, and a strategic approach. The process can be demanding, but with the right resources and techniques, candidates can increase their chances of success. Proper preparation not only helps in mastering the required content but also builds the confidence needed to perform well under pressure.
Steps to Prepare Effectively
A solid preparation plan involves several key steps that allow candidates to organize their study schedule and focus on the most critical areas. Below are some essential actions to take when getting ready for the qualification process:
- Review the full structure of the test and understand the types of questions that will be asked.
- Identify the core legal subjects and prioritize studying them based on their weight in the assessment.
- Practice answering past questions to familiarize yourself with the format and timing of the test.
- Consider joining a study group or taking review courses to gain insights from peers and experts.
Study Resources and Materials
Having the right materials is crucial to ensuring a comprehensive preparation. Here are some resources commonly used by candidates:
- Study Guides: Detailed books that break down key topics and provide practice questions.
- Online Courses: Structured lessons offered by experienced instructors, often including practice exams.
- Past Papers: Reviewing past assessments can help candidates understand the question format and focus areas.
- Flashcards: Useful for memorizing important rules and legal principles.
By following a well-structured plan and using the right resources, candidates can approach the qualification process with confidence and significantly improve their chances of success. Regular practice, time management, and a focus on understanding key legal concepts are vital to mastering the test.
Study Materials and Resources
To succeed in the legal qualification process, it’s essential to have access to the right study materials and resources. These tools help break down complex legal topics and provide candidates with the practice they need to master key concepts. Whether using books, online courses, or practical exercises, effective study resources are crucial for building a strong foundation of legal knowledge and skills.
Recommended Study Materials
Various types of study materials are available, each catering to different learning styles and preferences. Some materials focus on comprehensive reviews of legal principles, while others provide focused practice in specific areas of law. Below are a few of the most popular types of resources:
- Comprehensive Textbooks: These books cover a wide range of legal topics, offering explanations, case studies, and practice questions.
- Outline Guides: These resources condense the most important topics into concise outlines, making it easier to review large amounts of material quickly.
- Study Flashcards: Flashcards are ideal for memorizing key terms, legal definitions, and important rules that candidates need to recall quickly during the assessment.
Online Platforms and Courses
In addition to traditional study materials, many candidates benefit from online platforms and interactive courses that provide structured lessons and personalized study plans. These resources can simulate the actual testing environment, allowing candidates to practice under timed conditions and receive immediate feedback.
- Online Review Courses: Many organizations offer courses specifically designed to prepare candidates for the legal qualification process, providing in-depth lessons on essential topics.
- Practice Tests: Online platforms often offer practice tests that mimic the structure and content of the actual assessment, giving candidates the opportunity to assess their readiness.
- Video Lectures: Visual learners can benefit from video lectures, which explain legal concepts in a dynamic and engaging format.
Using a combination of these study materials and resources will ensure candidates are well-prepared for the legal qualification process, helping them to approach the assessment with confidence and thorough understanding.
Understanding the Multistate Legal Assessment
The multistate portion of the legal licensing process is a standardized test designed to assess a candidate’s understanding of fundamental legal principles that apply across various jurisdictions. It is a key component of the overall qualification process, focusing on testing knowledge in critical areas such as constitutional law, contracts, and torts. This section ensures that candidates have a broad and consistent understanding of essential legal concepts applicable in any state.
The multistate component is typically made up of multiple-choice questions that cover a wide range of legal topics. This format allows candidates to demonstrate their ability to apply legal principles to hypothetical scenarios and test their knowledge of widely accepted laws and standards.
Key Features of the Multistate Test
- Wide Scope: The questions span a variety of topics, including constitutional law, civil procedure, contracts, torts, and criminal law.
- Multiple-Choice Format: Candidates must answer a set of multiple-choice questions, designed to test their knowledge and critical thinking abilities under time constraints.
- Objective Measurement: This portion of the qualification process offers an objective means of assessing how well candidates understand essential legal principles.
Core Subjects Covered
- Constitutional Law: Examines the fundamental principles and legal concepts outlined in the nation’s Constitution.
- Torts: Focuses on civil wrongs that cause harm to individuals or property, including negligence, defamation, and product liability.
- Contracts: Tests knowledge of the creation, interpretation, and enforcement of legally binding agreements.
- Civil Procedure: Focuses on the rules and processes governing the resolution of disputes in civil courts.
- Criminal Law: Assesses understanding of criminal offenses, defenses, and the general principles governing criminal liability.
By mastering the multistate section, candidates demonstrate their proficiency in the foundational aspects of law, ensuring that they are well-prepared for the demands of the legal profession. Preparing thoroughly for this section is essential for achieving a strong overall score in the legal licensing process.
Practical Tips for Success
Achieving success in the legal qualification process requires more than just mastering the material; it also involves strategies for effective studying, managing time, and staying mentally and physically prepared. Proper planning and focused effort can help ensure that candidates approach the test with confidence and perform at their best. Here are some actionable tips to help candidates succeed during their preparation and on test day.
Effective Study Strategies
Creating a structured and disciplined study plan is one of the most important steps toward success. It is crucial to allocate time for each topic, review regularly, and balance study sessions with adequate rest. Below are some key strategies to enhance your study routine:
- Set Clear Goals: Break down the study material into manageable sections, and set specific, measurable goals for each study session.
- Use Active Recall: Instead of passively reading, test your knowledge by actively recalling information and explaining concepts in your own words.
- Practice Under Real Conditions: Simulate the test environment by practicing with timed mock exams and sample questions.
- Review and Reinforce: Regularly review previously studied topics to reinforce your memory and understanding.
Maintaining Mental and Physical Wellness
While rigorous preparation is necessary, it is equally important to maintain a healthy balance. Physical and mental well-being play a crucial role in how well you perform on the actual test day. Here are some tips to keep you in top shape:
- Take Breaks: Study in focused intervals, taking short breaks in between to avoid burnout and maintain productivity.
- Get Enough Sleep: Ensure you get enough rest in the weeks leading up to the test to optimize brain function and concentration.
- Eat Well and Stay Hydrated: Eating nutritious meals and staying hydrated will help you stay alert and energized.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to reduce stress and stay calm.
By implementing these practical tips into your routine, you will be better prepared to face the challenges of the legal qualification process. Consistent effort, effective study habits, and maintaining your health can significantly improve your chances of success.
How to Register for the Test
Registering for the legal qualification process involves several important steps to ensure that you are eligible to take the test. The registration process typically requires submitting various documents, paying a fee, and meeting specific eligibility criteria. Below is an outline of the necessary steps you need to follow in order to complete the registration and secure your spot for the assessment.
Step-by-Step Registration Process
Follow the steps below to properly register for the legal qualification process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Review Eligibility | Ensure you meet all the eligibility requirements, including education, character, and moral fitness. |
| 2. Submit Application | Complete the official application form provided by the relevant regulatory body. This form will ask for personal information, educational history, and other required details. |
| 3. Pay Registration Fee | Pay the required registration fee. The amount varies depending on the jurisdiction, and fees are typically non-refundable. |
| 4. Submit Required Documents | Submit any necessary supporting documents, such as transcripts, proof of legal education, and identification. |
| 5. Wait for Confirmation | Once your application is reviewed, you will receive confirmation of your registration and information regarding the test schedule. |
By following these steps carefully and submitting all required documentation, you will successfully register for the legal qualification process and be prepared for the next steps in your career.
Test Day Tips and Procedures
When the day of the legal qualification assessment arrives, it’s crucial to approach it with a clear strategy and a calm mindset. The procedures on the test day are designed to ensure that everything runs smoothly, so being prepared and knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety. Below are some essential tips and guidelines to follow to ensure you are fully ready for the day.
What to Expect on Test Day
On the day of the assessment, you will need to follow a series of procedures to check in and begin the test. Being prepared for these steps will help you feel more confident and focused.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Arrival Time | Arrive at the testing center early, at least 30 minutes before the scheduled start time, to allow for check-in and any security procedures. |
| 2. Check-In Process | You will need to present a valid photo ID, confirmation of registration, and any other required documents to verify your identity and eligibility. |
| 3. Test Materials | Make sure you bring all necessary materials, such as pencils, erasers, and any permitted reference materials. Check the instructions to confirm what is allowed. |
| 4. Follow Instructions | Listen carefully to the test administrator’s instructions before starting. Make sure you understand the rules, timing, and any specific procedures for the test. |
| 5. Breaks | There will be scheduled breaks during the test. Use these breaks to stretch, hydrate, and refocus. Avoid getting too distracted or stressed during these intervals. |
Key Tips for Success
- Stay Calm: Remember to take deep breaths if you start to feel anxious. Keep a positive mindset and trust your preparation.
- Time Management: Watch the clock closely and pace yourself throughout the test. Don’t spend too much time on any one question.
- Read Carefully: Make sure to read each question thoroughly before answering. Understand the problem and the answer choices before making your selection.
- Stay Organized: Keep your workspace neat and organized to avoid confusion during the test.
By following these tips and understanding the procedures, you will be able to approach the test day with confidence and clarity. Preparation is key to ensuring that everything runs smoothly and that you are able to perform at your best.
Scoring and Results Process
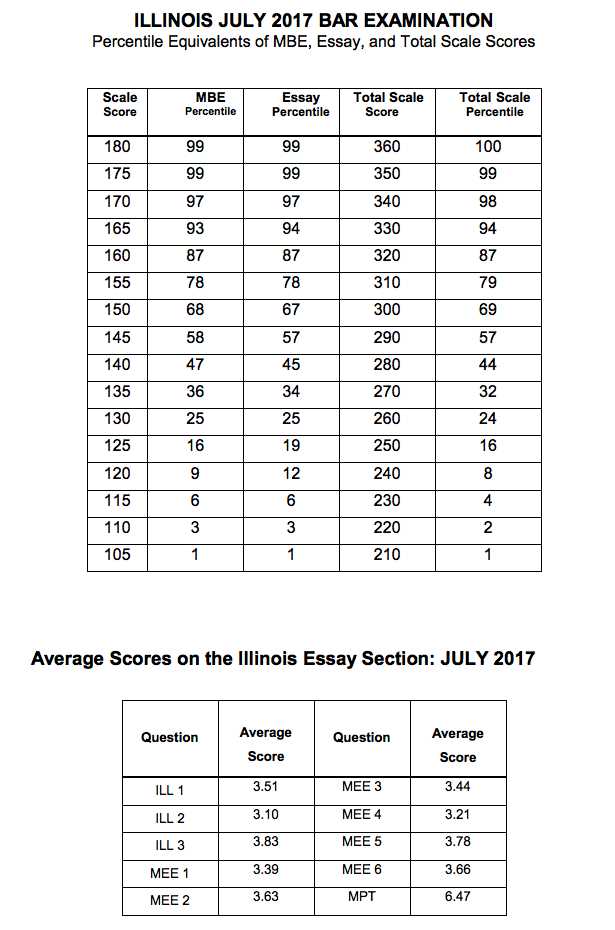
After completing the legal qualification process, the next step is understanding how the results are calculated and what the process of receiving them entails. The scoring process ensures that candidates are evaluated fairly based on their performance across multiple areas of law. It’s important to know the key aspects of how scores are determined and how results are communicated to candidates.
How the Scoring Works
In this process, scores are based on your performance in various sections of the assessment, each with a different weight. These sections are carefully graded, and the final score represents your overall proficiency in legal knowledge and reasoning.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: A significant portion of the test is based on multiple-choice questions that assess your knowledge of essential legal principles. These questions are automatically graded, ensuring accuracy and fairness.
- Essay Responses: Some sections of the test require you to write essays demonstrating your understanding of complex legal issues. These are scored manually by trained evaluators.
- Practical Scenarios: You may also encounter practical scenarios, where your ability to apply legal principles in real-world situations is assessed. These are scored based on the clarity and logical reasoning of your responses.
Receiving Your Results
Once the scoring is completed, results are typically made available within a few weeks. The results will provide you with detailed feedback on your performance, including scores for individual sections and an overall score. In some jurisdictions, you may also receive information about your ranking compared to other candidates.
- Online Access: Results are often posted online through a secure portal. You will receive instructions on how to access your score once it is available.
- Official Notification: In addition to online access, some candidates receive official notification via email or mail with detailed results and next steps.
- Re-Evaluation: If you are dissatisfied with your score, some jurisdictions allow for a re-evaluation process. Be sure to check the specific rules and timelines for requesting this service.
Understanding the scoring and results process is essential for managing expectations and planning your next steps after completing the assessment. Being informed can help alleviate stress and ensure that you are prepared for what comes next in your legal journey.
Understanding State Legal Admission Rules
When aspiring to become a licensed legal professional, understanding the admission rules set by the jurisdiction where you intend to practice is essential. These guidelines outline the steps candidates must follow to gain eligibility for legal practice, ensuring they meet the required standards and qualifications. The admission process typically involves several stages, including education, testing, and professional conduct assessments.
Education and Qualifications
To be eligible for legal practice, candidates must meet certain educational requirements. Most jurisdictions require the completion of a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree from an accredited law school. In addition, candidates must demonstrate that they have received proper legal training in areas relevant to their practice.
- Law School Graduation: Candidates must graduate from a law school that is accredited by the appropriate educational authorities.
- Course Requirements: Certain courses or subjects may be mandatory for admission. These could include ethics, constitutional law, and legal writing.
- Bar Preparation: Many candidates enroll in preparatory programs designed to help them pass the qualification assessments.
Character and Fitness Evaluation
Aside from academic qualifications, most jurisdictions require candidates to undergo a character and fitness evaluation. This process assesses whether the applicant has the moral and ethical standards necessary for legal practice. It typically involves disclosing any past criminal history, financial issues, or disciplinary actions from previous professional roles.
- Disclosure Requirements: Candidates must submit detailed information about their background, including any legal, financial, or disciplinary issues.
- Background Check: A thorough background check is conducted to ensure that applicants meet the professional and ethical standards for legal practice.
- Integrity Assessment: The review process may include interviews or additional documentation to assess the applicant’s integrity and fitness to practice law.
Familiarizing yourself with the specific admission rules of your jurisdiction will help you navigate the process smoothly and ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria to practice law.
What Happens After Passing the Exam
Successfully completing the qualification process is a major achievement, but it marks only the beginning of your legal career. After passing the assessment, there are several important steps to take before you can officially begin practicing law. These steps ensure that you meet all the requirements necessary to obtain your professional license and start working in your chosen field.
Receiving Your License
Once you pass the qualification test and meet all other requirements, you will receive your legal license, allowing you to practice law. This process typically includes the following:
- Official Notification: You will be formally notified of your success through an official letter or online portal, confirming that you have met all requirements.
- Oath of Office: Most jurisdictions require you to take an oath of office, swearing to uphold the law and act ethically in your professional conduct.
- License Issuance: After taking the oath, you will receive your license, which serves as your official certification to practice law in the jurisdiction.
Post-License Responsibilities
Even after receiving your license, there are additional responsibilities and ongoing requirements to maintain your right to practice law. These often include continuing legal education and adhering to the ethical standards set by your profession.
- Continuing Legal Education (CLE): Many jurisdictions require legal professionals to complete a certain number of CLE hours to stay updated on legal developments and maintain their license.
- Professional Conduct Rules: As a licensed legal practitioner, you must continue to abide by the ethical guidelines and rules of professional conduct set by your local bar association or legal governing body.
- Renewal and Fees: Legal licenses typically require renewal every few years, often accompanied by fees or additional requirements for continuing education.
After passing the assessment and receiving your license, you will officially be able to practice law, but your professional development does not stop there. Staying informed about legal updates and maintaining ethical practices are key components of a successful legal career.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
As you prepare for the qualification process, it’s essential to be aware of common missteps that can hinder your success. Avoiding these mistakes can help ensure that you stay on track and are fully prepared when it’s time to face the assessment. From poor planning to lack of focus, understanding the typical pitfalls can give you a significant advantage.
Neglecting Thorough Preparation
One of the biggest mistakes candidates make is underestimating the amount of preparation required. Skipping study sessions or not dedicating enough time to review key materials can lead to unnecessary stress and poor performance. Effective preparation includes:
- Consistent Study Schedule: Develop and stick to a regular study routine to cover all necessary topics.
- Comprehensive Review: Ensure you understand each subject area and don’t skip over difficult concepts.
- Practice Tests: Take practice tests to become familiar with the test format and to gauge your readiness.
Overlooking Time Management
Time management is critical, especially during the test. Many candidates struggle to complete all the questions within the time limit because they fail to pace themselves properly. To manage your time effectively:
- Set Time Limits: Allocate specific time blocks for each section and stick to them.
- Avoid Spending Too Much Time on One Question: If you’re stuck, move on and return to difficult questions later.
- Practice Under Time Pressure: Simulate the actual testing environment by practicing with time constraints.
Failing to Focus on the Right Areas

It’s easy to get lost in the details and focus too much on areas that are less important. Be sure to prioritize the most heavily tested topics and areas where you feel the least confident. Prioritization involves:
- Reviewing Test Content Outlines: Understand which areas are most likely to appear on the test and allocate more time to those subjects.
- Identifying Weak Points: Spend more time reinforcing areas where you lack knowledge or struggle to understand the concepts.
Avoiding these common mistakes can set you up for success, helping you approach the qualification process with confidence and preparedness. Effective planning, time management, and focus are key to achieving the results you’re striving for.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Exam
When preparing for the qualification process, many candidates have common questions regarding the structure, requirements, and expectations. Below are some frequently asked questions that can help clarify the most important aspects of the assessment.
What are the eligibility requirements for this qualification?
To be eligible for the qualification process, candidates generally need to have completed a recognized law degree and meet specific residency or educational requirements. Detailed eligibility criteria can be found on the official governing body’s website.
How is the assessment structured?
The process consists of multiple sections, including multiple-choice questions, written responses, and practical skills evaluations. The questions typically cover a wide range of legal principles and are designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
When is the qualification held?
It is usually conducted on a scheduled basis throughout the year, with specific dates provided in advance. Candidates must register before a deadline to secure their spot for a particular session.
How long does the qualification process take?
The assessment itself generally takes a few days to complete, with different sections held on separate days. Results are typically available within a few weeks after the conclusion of the process.
What happens if I fail?
If a candidate does not pass the assessment, they are usually permitted to retake it. However, certain conditions, such as waiting a specified period or completing additional coursework, may apply before re-registration is allowed.
Can I use study aids during the process?

Study aids, including legal texts and notes, are generally not permitted during the assessment. However, there may be specific allowances for certain tools, such as a limited set of materials or software, depending on the format of the process.
How are results calculated?
Scores are usually based on the candidate’s performance across all sections, with a minimum passing score required. The weighting of each section may vary, and candidates are often given detailed score reports after the process.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Eligibility requirements | Completion of a recognized law degree and meeting residency or educational requirements. |
| Assessment structure | Multiple-choice questions, written responses, and practical skills evaluations. |
| Frequency of assessment | Scheduled throughout the year with specific registration deadlines. |
| Time required | Typically a few days with results available in a few weeks. |
| Retake policy | Candidates can usually retake the process with certain conditions. |
| Use of study aids | Generally not permitted, but some tools may be allowed depending on format. |
| Score calculation | Based on performance across sections, with a minimum passing score. |
These answers should help guide candidates in their preparations, providing clarity on the expectations and procedures involved in the process.
Legal Career Opportunities After the Bar
Successfully completing the qualification process opens up numerous professional pathways within the legal field. After certification, individuals are qualified to pursue a variety of roles that can range from practicing as an attorney in different legal specialties to positions in government, corporate law, or academia.
Traditional Legal Careers
For those looking to practice law in a traditional sense, there are several potential career paths:
- Private Practice Attorney: Many individuals choose to work for law firms, representing clients in a variety of legal matters such as civil litigation, family law, criminal defense, and business law.
- Public Defender: Those passionate about criminal law may choose to work as public defenders, representing individuals who cannot afford private legal counsel.
- Prosecutor: Lawyers may choose to work for the government in criminal prosecution, handling cases against individuals or entities accused of breaking the law.
- Corporate Counsel: In-house legal advisors work for businesses, providing counsel on a range of legal issues related to contracts, mergers, intellectual property, and regulatory compliance.
Alternative Legal Careers
In addition to traditional roles, there are other legal career options available:
- Legal Educator: Some graduates may opt to teach law at a university or law school, sharing their knowledge and expertise with the next generation of legal professionals.
- Compliance Officer: Many industries require legal professionals to ensure that companies comply with laws and regulations. Compliance officers are responsible for reviewing and managing legal risks within companies.
- Legal Consultant: Lawyers may choose to work as independent consultants, providing expert advice to businesses, non-profits, or governments on legal matters, without representing clients in court.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Legal professionals can work for organizations that focus on social justice, advocacy, or human rights, using their skills to promote public interest causes.
Emerging Fields and Specializations
As the legal profession evolves, new fields and specializations are emerging, providing additional opportunities:
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: With the rise of digital technology, legal professionals specializing in data privacy laws and cybersecurity are increasingly in demand.
- Environmental Law: As environmental issues become more pressing, lawyers specializing in environmental policy, regulation, and advocacy play an important role in protecting natural resources.
- Intellectual Property Law: Specializing in patents, trademarks, and copyrights, intellectual property attorneys help protect creators’ rights and ensure innovation.
Ultimately, the legal profession offers a wide variety of career paths for qualified individuals. Whether working in a courtroom, advising businesses, or working for social change, legal professionals have numerous opportunities to make a significant impact in their chosen field.
Top Resources for Bar Examinees
Preparing for a professional qualification test can be a daunting task, but with the right resources, candidates can significantly enhance their chances of success. Several tools and platforms are available to help examinees with everything from practice questions to study guides and expert advice.
Study Guides and Practice Materials
Comprehensive study materials are essential for any candidate looking to succeed. These resources typically cover all necessary content areas and provide practice questions that mirror the actual test format:
- Bar Review Courses: Many candidates opt for structured courses provided by major bar review companies. These programs offer in-depth lessons, practice exams, and personalized feedback to guide students throughout their preparation.
- Practice Question Banks: Access to extensive practice questions helps candidates become familiar with the format of the test. Many platforms provide question banks that allow users to track their progress over time.
- Study Guides: Well-organized study guides break down the material into manageable sections, highlighting key concepts and strategies to enhance retention and understanding.
Online Resources and Tools
In addition to physical study materials, online tools offer interactive and flexible options to support preparation:
- Flashcards: Digital flashcard apps like Quizlet allow examinees to create custom flashcards or use pre-made sets to memorize important legal concepts, statutes, and case law.
- Webinars and Online Workshops: Many organizations offer live webinars, workshops, and on-demand video lessons that allow students to learn from experts and ask questions in real-time.
- Study Groups and Forums: Online forums, such as Reddit and dedicated legal communities, provide candidates with a space to share study tips, ask for advice, and support each other throughout the preparation process.
Additional Helpful Tools
There are also other tools that can help candidates streamline their study process and track progress:
- Time Management Apps: Efficient time management is key to successful studying. Apps like Trello or Notion help examinees stay organized by setting deadlines and creating study schedules.
- Practice Simulations: Some platforms offer full-length practice simulations that mirror the actual testing experience. These tools can help candidates get comfortable with timing and the structure of the test.
- Legal Research Tools: Access to legal databases like Westlaw or LexisNexis is essential for reviewing case law, statutes, and legal principles, especially for writing and multiple-choice sections.
By utilizing a combination of these resources, candidates can create a comprehensive study plan, enhance their knowledge, and approach the qualification process with confidence.