
In this section, we will delve into the core principles of the United States health reform initiative, focusing on the laws designed to enhance access to medical services and improve the overall system. These policies aim to increase affordability, provide essential services, and ensure wider coverage for citizens across the country.
Grasping the fundamental components of these regulations is essential for anyone studying or working in the healthcare sector. Understanding how these policies function, who benefits, and how they impact various groups can significantly influence your preparedness for assessments related to this field. A solid grasp of the subject matter will ensure a well-rounded comprehension of the legislative framework and its real-world applications.
Health Reform Policy Fundamentals

This section covers key topics related to the landmark reforms aimed at reshaping the healthcare landscape in the United States. The primary focus is on understanding the core elements that define the law, its goals, and how it aims to improve accessibility and affordability for individuals and families. Familiarity with these concepts is essential for anyone seeking to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
From eligibility requirements to the various subsidies available, the material explores how the new regulations influence both private and public health insurance options. It also addresses the critical areas of coverage, including the protection of individuals with pre-existing conditions, the expansion of low-income assistance, and the rules governing health exchanges. A solid grasp of these details is vital for mastering the content and answering related questions accurately.
Examining the implications of these reforms will also help to clarify how different groups are affected, whether it’s through access to services or financial support. Mastering the principles outlined in this section will ensure preparedness for a variety of assessments within this area of study.
Overview of the Healthcare Reform Law
The health reform legislation introduced sweeping changes to the U.S. healthcare system, aiming to expand coverage, improve care, and reduce costs for millions of Americans. By targeting inefficiencies, it set out to create a more accessible system for individuals and families, regardless of income or pre-existing conditions. This initiative shifted the way both private and public health insurance markets operate, providing new opportunities for coverage and support.
The law includes several key provisions designed to protect consumers, reduce healthcare spending, and increase the overall quality of care. Below is an outline of some of the most critical elements of the reform:
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Expanded Coverage | Increased the number of individuals eligible for coverage through public programs and private plans. |
| Pre-Existing Conditions | Prohibited insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing health issues. |
| Health Insurance Marketplaces | Established state-level exchanges where individuals can shop for insurance plans. |
| Medicaid Expansion | Extended eligibility for Medicaid to more low-income individuals in participating states. |
| Cost Assistance | Offered subsidies and tax credits to help lower-income people afford health coverage. |
These elements represent just a portion of the law’s impact. Understanding how each of these provisions works is key to grasping the overall structure and objectives of the legislation.
Key Principles of the Health Law
This section focuses on the fundamental principles that underpin the health reform initiative. At its core, the law aims to ensure broader access to medical services, enhance the quality of care, and reduce financial burdens on individuals. The legislation works by addressing various aspects of healthcare, such as affordability, coverage, and consumer protection, making it a crucial part of the healthcare landscape in the U.S.
The law emphasizes key concepts such as expanding coverage for the uninsured, preventing discrimination based on health status, and supporting preventive care. It also introduces measures to make health insurance more transparent and accessible for individuals and families. These principles create a more equitable system, particularly for vulnerable groups who may have previously struggled to obtain necessary healthcare.
By focusing on inclusivity and protection, the law seeks to create a system that benefits both individuals and the broader healthcare system, aiming to reduce overall costs while improving service quality and access.
Eligibility for Health Coverage Under ACA
Understanding who qualifies for health coverage under the reformed health system is essential to navigating the available options. The law establishes specific criteria for individuals and families, determining eligibility for various types of insurance plans, subsidies, and government programs. These guidelines ensure that more people have access to affordable coverage, regardless of their previous health conditions or financial situation.
Eligibility is primarily determined by factors such as income, age, employment status, and residence. Below are the key categories of individuals who are eligible for coverage:
- Low-Income Individuals: People who fall within certain income thresholds may qualify for subsidies or Medicaid expansion, depending on their state of residence.
- Families: Families with dependents may also be eligible for coverage through marketplace plans or government programs if they meet the financial criteria.
- People with Pre-existing Conditions: Insurers cannot deny coverage to individuals based on pre-existing health conditions.
- Young Adults: Young individuals up to age 26 can remain on their parent’s insurance plan, regardless of their status as a dependent.
- Self-Employed and Uninsured Workers: Individuals who are not covered through an employer can apply for health plans through the marketplace, with subsidies available for those who meet the income criteria.
These categories represent the broad scope of individuals eligible for coverage under the reformed healthcare system. It is important to understand how these qualifications apply in specific situations, as they can significantly affect the options and costs associated with obtaining health insurance.
Health Insurance Marketplaces Explained
Health insurance exchanges provide a platform for individuals and families to compare, shop for, and purchase coverage that meets their needs and fits their budget. These marketplaces were created to simplify the process of obtaining insurance by offering a centralized location where multiple plans can be reviewed, ensuring consumers make informed decisions. The exchanges are designed to promote competition and transparency among insurers, while also offering financial assistance to those who qualify.
The marketplaces operate at both the federal and state levels, with some states managing their own platforms while others rely on the federal government. These exchanges provide a variety of health plans with varying coverage levels, allowing consumers to choose based on their health needs and financial situation. Key features of the marketplaces include:
- Plan Comparison: Consumers can easily compare different insurance plans based on premiums, coverage, and out-of-pocket costs.
- Financial Assistance: Subsidies and tax credits are available to lower-income individuals to help reduce the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Open Enrollment Periods: The exchanges operate within set enrollment windows, during which individuals can sign up or make changes to their coverage.
- Subsidized Coverage for Low-Income Individuals: Depending on income, some people may qualify for Medicaid or subsidized plans to make insurance more affordable.
These platforms play a crucial role in expanding access to healthcare by providing more affordable and accessible insurance options for those who may have struggled to find coverage otherwise. Understanding how these marketplaces function is key to navigating the available plans and maximizing the benefits of these options.
Subsidies and Cost Assistance Options

Financial support plays a vital role in making health insurance affordable for individuals and families. To help lower-income people afford coverage, various subsidies and assistance programs are available through government-backed initiatives. These options aim to reduce premiums, lower out-of-pocket costs, and ensure that more people have access to necessary health services.
Types of Financial Assistance
There are several ways people can receive financial help when purchasing insurance through the marketplace. The most common forms of assistance include premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, which are designed to decrease the overall financial burden on those who qualify.
- Premium Tax Credits: These subsidies are provided to reduce the monthly cost of health insurance premiums for eligible individuals and families based on their income and household size.
- Cost-Sharing Reductions: These assist with reducing out-of-pocket expenses such as copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance for individuals with lower incomes.
Eligibility for Financial Assistance
To qualify for these subsidies, individuals and families must meet certain income criteria. Generally, assistance is available to those whose income falls between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level. Additionally, eligibility is also influenced by the state in which a person resides, as some states have expanded Medicaid programs that provide additional assistance.
By providing these financial options, the government helps ensure that even those with limited resources can access quality health coverage, thus reducing the risk of medical debt and improving overall public health. Understanding these cost assistance programs is crucial for anyone navigating the insurance marketplace.
Understanding Medicaid Expansion Benefits
Medicaid expansion represents a significant shift in the accessibility of health coverage for low-income individuals and families. By broadening the eligibility criteria, it aims to provide healthcare to a larger segment of the population, particularly those who previously did not meet the requirements for government assistance. This expansion offers more comprehensive coverage options and financial support to those in need.
Key Advantages of Medicaid Expansion
The expansion of Medicaid brings several key benefits that improve access to healthcare, reduce financial burdens, and increase overall health outcomes. Some of the primary advantages include:
- Increased Eligibility: More individuals and families now qualify for Medicaid, particularly those with incomes just above the federal poverty line.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Expanded Medicaid includes a wide range of health services, including preventive care, mental health services, and prescription medications.
- Financial Protection: With Medicaid, beneficiaries are shielded from high out-of-pocket costs, ensuring that healthcare remains affordable even for those with limited financial resources.
Who Benefits from Medicaid Expansion?
Eligibility for Medicaid expansion varies by state, but it generally includes individuals under 65 with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. Additionally, other factors like residency and citizenship status may affect eligibility. The expansion also aims to help vulnerable groups, including:
- Low-Income Adults: Adults without dependent children who previously did not qualify for Medicaid.
- Parents: Parents with incomes too high to qualify for the traditional Medicaid program but too low to afford private insurance.
- Childless Adults: Individuals who do not have children and were previously excluded from many government programs.
Overall, the expansion offers a powerful tool for improving access to essential healthcare services and reducing disparities in health outcomes. It ensures that more people can receive necessary care without the risk of financial hardship, thus strengthening public health as a whole.
Individual Mandate and Tax Penalties
The individual mandate was a key provision designed to encourage broad participation in the healthcare system. It required individuals to maintain a minimum level of health coverage or face a penalty when filing their taxes. The goal was to ensure that more people had insurance, which would in turn help lower overall healthcare costs by spreading risks across a larger pool of insured individuals.
While the penalty structure served as a significant incentive to purchase coverage, changes over time have altered its impact. The tax penalties tied to not having insurance were meant to balance the costs of providing care to everyone, including those with pre-existing conditions or who may require expensive treatment.
Understanding the Penalty Structure
For most years, individuals who did not have qualifying coverage faced a penalty, which was calculated in one of two ways, whichever was higher:
- Flat Penalty: A set amount per person or per family, usually determined annually and adjusted for inflation.
- Percentage of Income: A percentage of household income that exceeded a certain threshold, with caps applied to prevent excessive penalties.
Changes to the Individual Mandate
The penalty for not maintaining coverage was reduced to $0 starting in 2019 for most states. However, some states have implemented their own individual mandate penalties, ensuring that the incentive to have insurance remains in place at the state level. In these states, individuals who do not maintain health coverage are still subject to penalties when filing their state taxes.
Although the federal penalty no longer applies, the individual mandate remains a crucial component of the broader healthcare system for certain areas. Understanding how these penalties work, and how they may vary by state, is key to making informed decisions about health coverage options and ensuring compliance with the law.
Employer Responsibilities for Coverage
Employers play a significant role in ensuring their employees have access to affordable health coverage. Depending on the size of the company and other factors, businesses are required to offer insurance options or face penalties. The goal of these requirements is to reduce the burden of healthcare costs on individuals while ensuring that employees can maintain their well-being and productivity.
Employers are responsible for providing coverage to their employees and, in some cases, to their dependents. To comply with the law, employers must offer plans that meet certain minimum standards, including coverage for essential health benefits. Failure to do so can result in financial penalties for the business.
For larger employers, the law stipulates that health insurance must be offered to full-time employees and their families, ensuring that the coverage is both affordable and comprehensive. Businesses with fewer employees may not be required to provide insurance, but they may still offer it as a benefit.
Essential Health Benefits Under ACA
Health insurance plans are required to cover a set of core services to ensure that individuals receive comprehensive care. These services are designed to address a wide range of medical needs, from preventive care to emergency treatment. By guaranteeing that certain essential services are covered, the healthcare system ensures that people have access to necessary care without facing excessive costs.
The law outlines a list of essential health benefits that must be included in most health insurance plans. These benefits are designed to cover a broad spectrum of health needs, including both physical and mental health services. By establishing these minimum standards, the goal is to promote overall well-being while protecting individuals from high medical expenses.
List of Essential Health Benefits

- Ambulatory patient services: Outpatient care that does not require an overnight stay in a hospital.
- Emergency services: Coverage for urgent and emergency medical conditions, including ambulance services.
- Hospitalization: Inpatient care in a hospital, including surgeries and overnight stays.
- Maternity and newborn care: Health services related to pregnancy, childbirth, and care for newborns.
- Mental health and substance use disorder services: Coverage for mental health treatment and substance abuse rehabilitation.
- Prescription drugs: Coverage for medications that are necessary to treat various health conditions.
- Rehabilitative services and devices: Services to help people recover from injuries or manage chronic conditions, including physical therapy and medical equipment.
- Laboratory services: Diagnostic tests and procedures, including blood tests and imaging studies.
- Preventive and wellness services: Services that help maintain health and prevent illness, such as vaccinations and screenings.
- Pediatric services: Healthcare for children, including oral and vision care.
By requiring these benefits, the healthcare system ensures that individuals receive necessary care across a variety of health needs. This standardization helps prevent gaps in coverage, ultimately providing better protection for people’s health and financial stability.
Impact of ACA on Pre-Existing Conditions

One of the most significant changes brought about by healthcare reform was the protection of individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Before these reforms, people with chronic illnesses or prior health issues often faced discrimination by insurers, resulting in either higher premiums or denial of coverage. The new rules eliminated these practices, ensuring that people could not be excluded or charged exorbitantly based on their health history.
The shift in policy means that individuals no longer have to worry about losing coverage or facing financial barriers due to previous diagnoses. Health insurance companies are now required to provide coverage to all applicants, regardless of their medical history, and cannot impose waiting periods for treatment related to pre-existing conditions.
Expanded Access to Coverage
With these protections in place, individuals with pre-existing conditions can now access insurance plans without fear of being rejected. This expansion of coverage has had a profound impact on many who were previously uninsured due to their health status. It has allowed those with chronic diseases, disabilities, and other ongoing health issues to obtain necessary treatments, medications, and preventive care.
Elimination of Exclusions and Waiting Periods
Another important aspect of the reforms was the elimination of exclusion periods and waiting times for people with pre-existing conditions. Previously, some insurers imposed waiting periods before providing coverage for certain conditions, leaving individuals vulnerable to financial hardships if they required immediate care. With the new regulations, individuals are guaranteed access to the full spectrum of services from the moment their coverage begins, regardless of their prior medical history.
Overall, these changes have contributed significantly to reducing the inequality in healthcare access and have provided a much-needed safety net for millions of Americans, ensuring they are not excluded from necessary care due to their health status.
Preventive Services and ACA Guidelines
Preventive healthcare is a key component in maintaining long-term well-being and reducing the overall cost of medical treatment. By addressing health issues before they become serious, individuals can avoid expensive treatments and improve their quality of life. To support this, health insurance plans are now required to provide a range of preventive services at no additional cost to the policyholder, promoting early detection and prevention of various conditions.
The guidelines set forth by the healthcare reforms ensure that specific preventive services are covered by most insurance policies. These services include screenings, vaccinations, and counseling that aim to reduce the risk of serious health problems, offering a proactive approach to healthcare management. By removing financial barriers to these essential services, individuals are encouraged to take advantage of early interventions that can detect conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease in their early stages.
Key Preventive Services Covered
- Screenings for chronic conditions: Regular tests for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Vaccinations: Immunizations for children and adults to prevent infectious diseases such as flu, pneumonia, and hepatitis.
- Cancer screenings: Tests for breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancers to detect early signs and improve treatment outcomes.
- Contraceptive methods: Coverage for birth control and family planning services to support reproductive health.
- Mental health screenings: Assessments for depression and other mental health conditions to support overall emotional well-being.
- Preventive counseling: Services related to weight management, smoking cessation, and diet to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Impact on Public Health and Costs
By incorporating these preventive services into health insurance plans, the aim is to catch health problems early, when they are more treatable and less costly. This approach not only enhances the well-being of individuals but also reduces the strain on the healthcare system by preventing costly interventions later on. Additionally, individuals who engage in preventive care are more likely to lead healthier lives, contributing to a decrease in the prevalence of serious health conditions.
Navigating Health Plan Types and Options
Choosing the right healthcare coverage can be a complex decision, as there are various types of plans available to meet different needs. Each option offers different levels of coverage, costs, and benefits, making it essential for individuals to understand the key features and limitations of each plan. The variety of available plans allows people to select the one that best fits their healthcare needs, budget, and preferences.
When exploring available health coverage, it is important to consider factors such as monthly premiums, out-of-pocket costs, network coverage, and the specific services provided. By understanding these aspects, individuals can make an informed choice that aligns with their personal and family health requirements. Navigating through different options can seem overwhelming, but understanding the basics of plan types and how they work can simplify the process.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
HMO plans often have lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other plans, but they also come with more restrictions. With an HMO, individuals are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all their care. Referrals from the PCP are necessary to see specialists, and coverage typically only extends to services provided within the network. This plan type can be ideal for those who prefer a straightforward, managed approach to healthcare.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans

PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, allowing individuals to see specialists or out-of-network providers without a referral. While PPOs tend to have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs than HMO plans, they provide a broader range of healthcare options. This flexibility makes PPOs appealing for those who value choice and convenience, particularly if they need specialized care or prefer to see providers outside the network.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans
EPO plans are similar to PPO plans in terms of flexibility, but they typically do not cover any out-of-network care, except in emergencies. While EPOs may have lower premiums than PPOs, they offer fewer options for out-of-network providers. Individuals who are comfortable staying within a specific network may find EPOs a cost-effective choice.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)

HDHPs are characterized by higher deductibles and lower premiums. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) that allow individuals to save money tax-free for medical expenses. HDHPs may be suitable for individuals who are relatively healthy, have few medical expenses, and want to save on monthly premiums while benefiting from the ability to contribute to an HSA.
By carefully reviewing the details of each plan type, individuals can make a more informed decision about which coverage best meets their healthcare needs. Understanding the options and weighing the pros and cons of each can help ensure that the chosen plan provides the necessary coverage without overextending one’s budget.
ACA and the Prevention of Discrimination
One of the key aspects of recent healthcare reforms is the commitment to eliminating discrimination within the healthcare system. The goal is to ensure that all individuals have equal access to services regardless of their background, identity, or health status. The law prohibits certain types of discriminatory practices by healthcare providers, insurers, and employers, creating a more inclusive environment for patients seeking medical coverage and treatment.
These protections aim to address disparities that historically existed within the system, where specific groups, such as those with pre-existing conditions, women, and minority populations, often faced higher costs or were excluded from coverage. By setting clear guidelines against discrimination, this law seeks to create a more equitable healthcare landscape for everyone, especially vulnerable populations.
Prohibition of Discriminatory Practices by Insurers
Insurance providers are now prohibited from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions or charging higher premiums for individuals due to their medical history. This means that individuals who previously struggled to access coverage due to health factors are now protected. Insurers must also offer coverage for essential health services, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their health status, have access to the care they need without facing financial barriers or discrimination based on gender, race, or other factors.
Equal Treatment for All Patients
In addition to insurers, healthcare providers must also comply with non-discrimination rules, offering the same quality of care to all patients regardless of their background. This includes prohibiting discrimination on the basis of gender identity, sexual orientation, and disability. The law mandates that healthcare services are accessible and non-discriminatory, ensuring that every individual receives fair treatment and is not denied services due to factors unrelated to their medical needs.
These regulations have helped to level the playing field, promoting fairness and increasing trust in the healthcare system. As a result, patients can seek the medical care they need with the confidence that they will not face bias or unequal treatment because of their personal characteristics or health history. The emphasis on anti-discrimination measures continues to be an essential component in improving the overall quality and accessibility of healthcare for all individuals.
Enrollment Periods and Deadlines
Understanding the timelines and deadlines for signing up for health coverage is crucial for individuals seeking to secure appropriate insurance. These enrollment windows are set annually and determine when individuals can apply for or change their health plans. Missing these deadlines could lead to penalties or a gap in coverage, so it’s essential to be aware of the specific periods when enrollment is open.
The enrollment process is typically divided into different periods, such as open enrollment, special enrollment, and annual renewal. Each period has specific eligibility criteria and timeframes during which individuals can make changes to their health coverage or enroll for the first time. Knowing the difference between these periods can help prevent unnecessary complications when seeking coverage.
Key Enrollment Periods
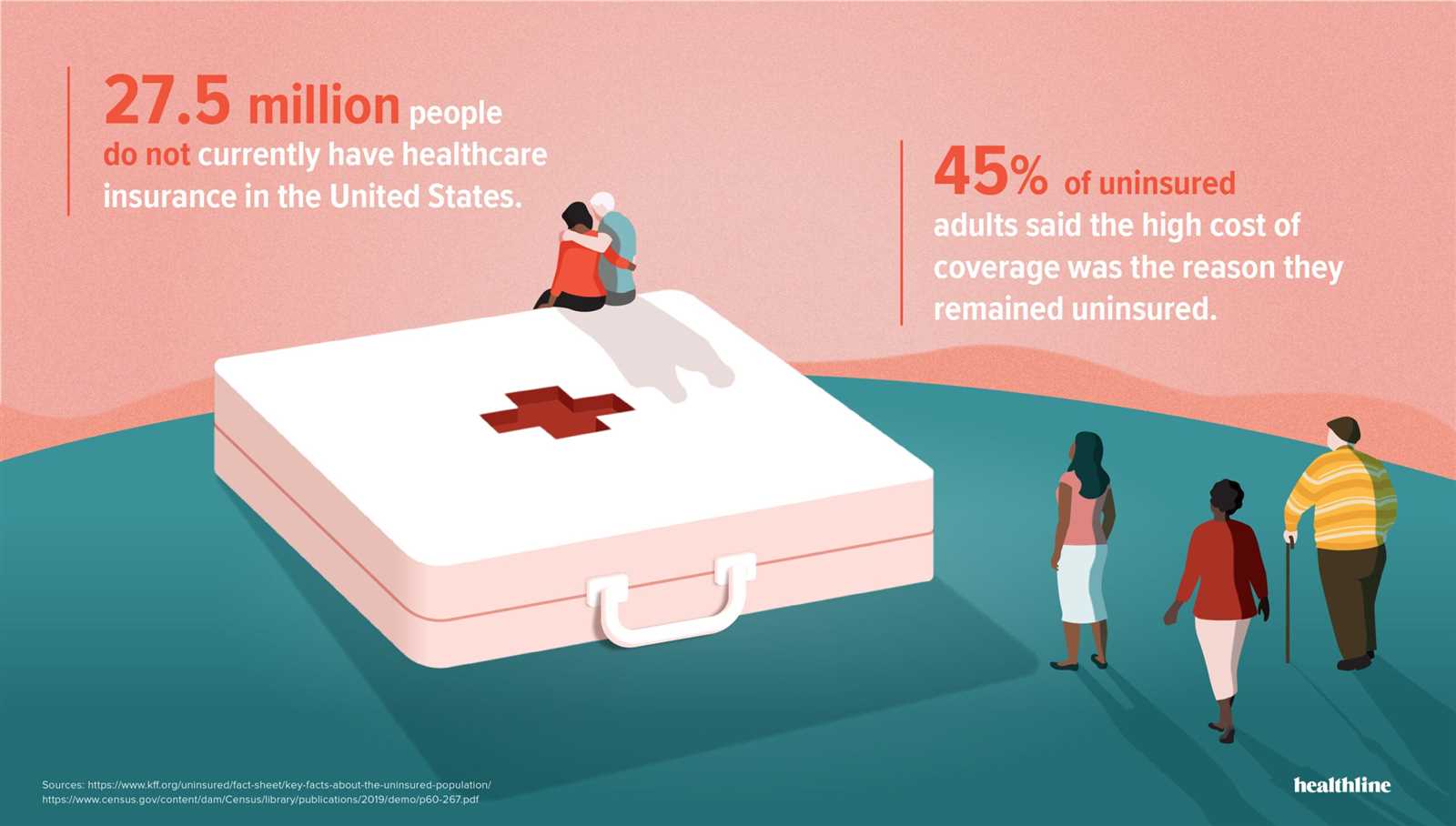
There are several important enrollment periods that individuals should be aware of:
| Enrollment Period | Timeframe | Eligibility |
|---|---|---|
| Open Enrollment | Typically occurs once a year for a few months | Available to everyone who wants to sign up for health insurance or switch plans |
| Special Enrollment | Triggered by life events (e.g., marriage, moving, job loss) | For those who experience qualifying life events |
| Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment | Year-round | Available to those who qualify based on income and other factors |
Consequences of Missing Deadlines

If individuals miss the open enrollment period, they may have to wait until the next enrollment window unless they qualify for special circumstances. Missing out on timely enrollment could mean not being able to enroll or adjust coverage until the next designated time, which could leave individuals without necessary healthcare protection.
To avoid such issues, it is crucial to stay informed about the key dates and monitor any updates provided by health insurance programs. Setting reminders or consulting with an insurance advisor can help ensure that enrollment is completed on time, allowing individuals to secure the healthcare they need without unnecessary delays.
Changes in ACA After 2020
Over the years, several adjustments have been made to the healthcare reform laws, and changes introduced after 2020 have had a significant impact on individuals’ access to insurance and the cost of coverage. These modifications reflect shifts in policy priorities, economic conditions, and political decisions that have influenced the structure and reach of the health coverage system.
While some changes aim to improve accessibility, others focus on reducing the financial burden on individuals and expanding eligibility. These revisions are important for those who rely on government-sponsored health plans, as they can affect both the types of plans available and the subsidies offered to lower-income individuals.
Key Modifications After 2020
Several notable changes occurred post-2020, many of which were designed to increase affordability and expand coverage. Some of the key changes include:
| Change | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| End of the Individual Mandate Penalty | The penalty for not having health insurance was reduced to $0 for most states. | This change allows individuals to forgo health coverage without financial consequences, although some states still impose penalties. |
| Enhanced Premium Tax Credits | Increased subsidies for middle-income individuals, making coverage more affordable. | This adjustment has helped reduce out-of-pocket costs for a wider range of people, especially those ineligible for Medicaid. |
| Expansion of Medicaid in Certain States | Several states expanded Medicaid eligibility, providing coverage for more low-income individuals. | This change has increased access to health insurance for many previously ineligible residents in expansion states. |
| Special Enrollment Periods | Introduced additional open enrollment windows due to the COVID-19 pandemic. | Allowed people to enroll in or switch plans during periods outside the regular open enrollment season, improving coverage access during the health crisis. |
These updates reflect the ongoing evolution of healthcare policies in the United States. As political landscapes and economic conditions shift, additional changes may be made in the future, further reshaping the options available to individuals seeking affordable and comprehensive coverage.
Common ACA Question Topics
When studying for assessments related to health coverage reforms, it is crucial to understand the main areas of focus that commonly appear in evaluations. These topics often include the key features of the legislation, the structure of health plans, eligibility requirements, and the rules surrounding enrollment. Additionally, financial assistance options and the impact on specific populations are also commonly tested subjects. Below are several critical topics that candidates should be familiar with to perform well on these assessments.
Key Areas to Study
- Health Coverage Eligibility – Understanding who qualifies for various insurance programs, including Medicaid expansion and marketplace coverage, is essential. This includes the income limits and other criteria determining eligibility.
- Marketplace Functioning – Knowledge about how individuals access health plans through federal or state-run exchanges, and how the plans differ in terms of coverage and cost, is important for assessments.
- Subsidies and Financial Assistance – Familiarity with the types of financial support available to help individuals pay for insurance, such as tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, is often tested.
- Plan Benefits and Coverage – It is essential to understand what types of services are covered under different plans and what benefits are considered essential, as this is a central topic in many evaluations.
Additional Topics of Focus
- Preventive Health Services – Understanding the guidelines for covered preventive services and how they contribute to overall health management is often featured in question sets.
- Tax Penalties and Individual Mandates – The rules regarding penalties for not maintaining coverage and the changes to such mandates after 2020 are important subjects in most assessments.
- Employer Responsibilities – Knowledge of the requirements placed on employers to provide insurance coverage or face penalties is critical.
- Changes Post-2020 – Familiarity with significant updates to the system, including the elimination of the individual mandate penalty and other reforms, is also commonly tested.
By focusing on these core topics, individuals preparing for assessments can build a strong foundation of knowledge that will help them navigate the various aspects of health coverage legislation. These subjects not only form the backbone of most evaluations but are also essential to understanding how the system operates in practice.
Studying Tips for ACA Exams
Preparing for assessments related to health coverage reforms requires a strategic approach to ensure comprehensive understanding and retention of key concepts. A successful study plan involves breaking down complex topics, focusing on high-yield areas, and practicing problem-solving. Below are some helpful strategies that can make your preparation more effective and efficient.
Effective Study Strategies
- Break Down Complex Topics – Health coverage systems can seem overwhelming, so it’s important to break topics into smaller, manageable sections. For instance, divide your study into eligibility requirements, health plan options, financial assistance, and penalties.
- Create a Study Schedule – Plan your study sessions in advance. Allocate time to review each topic, giving yourself ample time to master challenging areas before moving on to others.
- Use Practice Questions – Regularly test your knowledge with practice questions or quizzes. This helps you assess your understanding of key concepts and identify areas where you need more review.
- Focus on High-Yield Topics – Some topics, such as eligibility criteria, subsidies, and preventive health services, are more likely to appear in assessments. Make sure to allocate extra time to master these high-yield areas.
- Take Breaks – Avoid long, unproductive study sessions. Regular breaks allow your brain to rest and improve focus during study sessions.
Study Tools and Resources
| Resource | Usefulness |
|---|---|
| Online Practice Tests | Helpful for simulating test conditions and reinforcing knowledge through repetitive questioning. |
| Study Guides | Structured guides with summaries, outlines, and key terms can help you organize and simplify information. |
| Flashcards | Flashcards are great for memorizing key terms, definitions, and concepts. They are portable and effective for on-the-go review. |
| Group Study | Collaborating with peers can provide different perspectives and fill gaps in your knowledge. |
By using these strategies and resources, you can enhance your comprehension and retention of the material, making your study process more productive. Staying organized, practicing regularly, and focusing on important concepts will ensure that you’re well-prepared for any assessment.