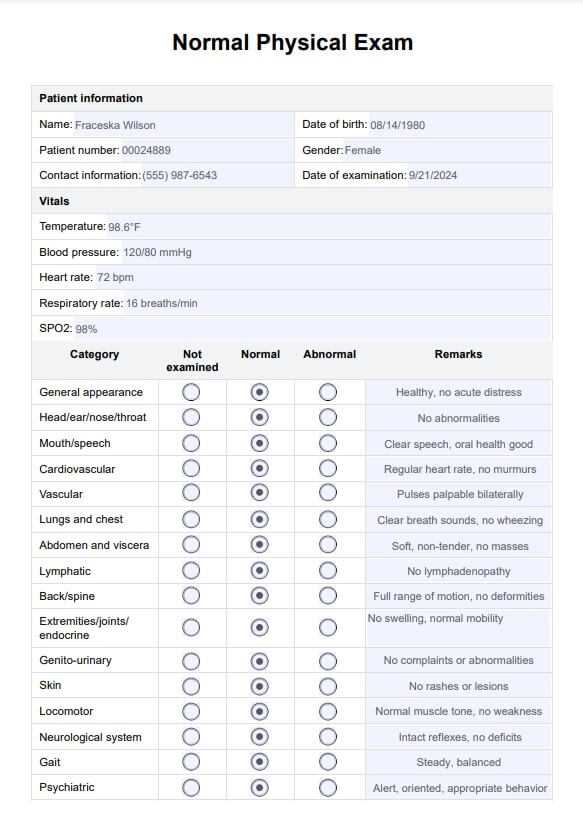
In the medical field, conducting a thorough evaluation of a patient’s overall well-being is crucial. A well-structured approach ensures that all necessary factors are considered, from the initial consultation to the detailed inspection of various body systems. This process plays a significant role in diagnosing conditions and providing optimal care.
Professionals rely on organized checklists to guide them through every aspect of a patient’s evaluation. These tools help streamline the assessment, enabling healthcare providers to remain focused and efficient while documenting key findings. With the right structure, each part of the body can be reviewed systematically, reducing the chance of oversight.
Effective documentation is an essential part of this process, not only for medical records but also to improve communication between healthcare teams. With an accurate record of the evaluation, future care decisions can be made with a clear understanding of the patient’s health status.
Complete Health Evaluation Overview
In healthcare, a well-organized approach to assessing a patient’s condition ensures that all key aspects of their well-being are addressed. This structured method allows for a systematic review, focusing on essential areas such as vital signs, organ function, and overall physical state. A thorough evaluation is crucial for identifying underlying issues and making informed decisions about treatment plans.
By using a consistent framework, healthcare providers can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of their assessments. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also supports clear and concise documentation. A detailed record helps to track changes in a patient’s health over time, facilitating better continuity of care.
Key Components of a Health Assessment
To ensure a thorough evaluation of a patient’s health, certain fundamental elements must be addressed. Each of these components plays a crucial role in identifying potential concerns and providing a complete understanding of the individual’s condition. A careful review of each area contributes to a comprehensive assessment process.
The first step typically involves gathering the patient’s medical history, which provides vital context for the evaluation. This includes previous conditions, lifestyle factors, and any relevant family history. Following this, a detailed inspection of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature, is essential to understanding the current state of health.
Next, the healthcare provider systematically examines various body systems, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems. Palpation, auscultation, and percussion techniques are often employed to assess organ function and detect abnormalities. These methods allow for a hands-on understanding of potential health issues that might not be immediately apparent through visual inspection alone.
How to Structure Your Evaluation Framework

Establishing a clear and organized approach to a health assessment is crucial for ensuring that all necessary information is collected systematically. By structuring the process effectively, healthcare providers can ensure consistency, minimize the risk of oversight, and improve the quality of care. This methodical approach helps both in the immediate review and for long-term patient monitoring.
When creating such a framework, it is important to divide the process into logical sections, each focusing on different aspects of the patient’s health. This enables healthcare professionals to remain focused on each area while maintaining a smooth flow. Below is an example of how the assessment can be structured for maximum efficiency:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient History | Collect essential information on the patient’s medical background, family health, and lifestyle factors. |
| Vital Signs | Record measurements such as blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and respiratory rate to establish a baseline. |
| General Appearance | Observe the patient’s overall condition, including posture, alertness, and any visible signs of illness or discomfort. |
| Cardiovascular Function | Assess the heart and circulatory system for any irregularities such as abnormal rhythms or changes in pulse. |
| Respiratory Function | Evaluate lung health by observing the patient’s breathing and listening for any abnormal sounds or patterns. |
| Musculoskeletal System | Inspect the joints, muscles, and bones for any signs of pain, stiffness, or limitations in movement. |
By breaking the process down into clear sections, the evaluation becomes more efficient, thorough, and easy to document. This structured framework not only improves the quality of the assessment but also supports better decision-making and continuity of care.
Importance of Patient History Collection

Gathering a patient’s history is one of the most essential steps in any healthcare assessment. This process allows healthcare providers to understand the context of a patient’s health, uncover potential risk factors, and identify early signs of chronic conditions. By collecting relevant details about past medical issues, family history, and lifestyle habits, professionals can make more informed decisions and provide tailored care.
Identifying Risk Factors
Patient history serves as a vital tool in identifying any hereditary or environmental risk factors that might contribute to health conditions. Understanding whether a patient has a family history of certain diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, or cancer, can help predict their likelihood of developing similar issues. Moreover, habits like smoking or a sedentary lifestyle can play a significant role in the onset of certain conditions. By recognizing these risk factors early, medical professionals can offer preventive advice and closely monitor the patient’s health.
Personalizing Care and Treatment
A well-documented history allows healthcare providers to personalize care, ensuring that treatments and interventions are specifically suited to the patient’s needs. For example, knowing a patient’s previous treatments, allergies, or reactions to medications can help in selecting the most appropriate therapy. By understanding their past experiences, practitioners can also avoid potential complications and improve overall treatment outcomes.
Systematic Approach to Physical Assessment

A structured and methodical approach to evaluating a patient’s health is crucial for obtaining accurate and comprehensive information. By following a consistent framework, healthcare providers can ensure they don’t overlook important details, while also improving the reliability and efficiency of the assessment process. This approach helps organize the steps and allows the practitioner to focus on each area of the body systematically, ensuring that all aspects of the patient’s condition are evaluated thoroughly.
The assessment should typically begin with an overview of the patient’s general condition, such as their appearance, mental state, and vital signs. After that, a systematic review of each bodily system follows, ranging from cardiovascular to musculoskeletal functions. By working through the body’s systems in an organized sequence, clinicians can more easily identify abnormalities and document any findings with precision. This process not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also supports the development of a clear and actionable care plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
Documentation Guidelines for Health Providers
Accurate and thorough documentation is essential for healthcare providers to ensure continuity of care, legal protection, and clear communication within the healthcare team. Proper record-keeping helps track a patient’s progress, identifies any changes in their condition, and ensures that all interventions are documented for future reference. By following established guidelines, healthcare professionals can maintain high standards of care and avoid critical errors.
Key Principles for Effective Documentation
When documenting patient information, clarity and precision are paramount. All relevant details should be recorded in a consistent and organized manner to ensure that anyone reviewing the records can easily understand the patient’s condition, history, and treatment plan. Key principles include the use of objective language, avoiding ambiguity, and ensuring that all notes are legible and timely. Additionally, it is essential to document all interactions with the patient, including assessments, treatments, and follow-up plans.
Essential Elements of Medical Documentation

Effective medical documentation includes several key elements to ensure completeness and accuracy. This typically involves documenting the patient’s health history, presenting symptoms, physical observations, diagnostic findings, and any treatments or procedures performed. Additionally, healthcare providers should include their clinical judgments, follow-up plans, and any patient instructions given. The following table outlines these essential components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient History | Includes information about past medical conditions, family history, and lifestyle factors that may influence the patient’s health. |
| Presenting Symptoms | Details the patient’s current symptoms, including duration, severity, and any changes since onset. |
| Physical Observations | Describes findings from the clinical examination, including vital signs, general appearance, and specific system assessments. |
| Diagnostic Findings | Records any results from laboratory tests, imaging studies, or other diagnostic procedures that support the clinical assessment. |
| Treatments and Procedures | Includes details of any treatments or procedures performed during the consultation or hospital visit. |
| Follow-Up Plans | Outlines the next steps, including further tests, referrals, or instructions given to the patient for their care. |
By adhering to these documentation guidelines, healthcare providers ensure the integrity of patient records, contribute to efficient care coordination, and provide a clear and accurate account of medical interactions. This practice also plays a critical role in meeting legal and regulatory standards within the healthcare industry.
Assessing Vital Signs Accurately
Accurate measurement of a patient’s vital statistics is essential for evaluating their overall health and identifying potential underlying conditions. These key indicators provide critical insight into the functioning of the body’s essential systems and can highlight deviations that may require immediate attention. By ensuring that these measurements are taken precisely and consistently, healthcare professionals can make well-informed decisions about patient care and treatment plans.
Vital signs typically include parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature. Each of these must be measured with the correct technique, as errors or inconsistencies can lead to misinterpretations of a patient’s condition. It is important for healthcare providers to be familiar with the normal ranges for these measurements, understand factors that may influence them, and use appropriate tools and techniques for obtaining reliable data.
For instance, heart rate should be measured for a full minute to accurately assess rhythm and strength, while blood pressure readings should follow specific protocols to avoid false readings, such as ensuring the cuff is at the correct size and the patient is positioned properly. Similarly, temperature should be recorded using reliable thermometers suited to the clinical setting, and respiratory rate should be counted unobtrusively to avoid altering the patient’s natural breathing pattern.
Head and Neck Evaluation Methods
Assessing the head and neck region is a fundamental aspect of any medical evaluation. This process involves examining various structures to identify abnormalities, pain, or signs of underlying medical conditions. A thorough assessment requires a combination of observation, palpation, and specific testing to ensure that no critical details are overlooked. Key areas of focus include the scalp, face, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, throat, and lymph nodes.
During the assessment, a healthcare professional may use the following methods:
- Inspection: A visual examination of the head and neck to identify asymmetry, swelling, discoloration, or other visible changes.
- Palpation: Gently feeling for abnormalities such as lumps, tenderness, or enlarged structures, particularly in the lymph nodes, thyroid, and salivary glands.
- Auscultation: Listening to the sounds produced by the neck and upper chest area, such as the carotid arteries, for any abnormal murmurs or bruits.
- Range of Motion Testing: Checking the flexibility and movement of the neck to identify restrictions or discomfort.
- Neurological Assessment: Evaluating the function of cranial nerves, including vision, facial sensation, and motor functions.
These methods allow the healthcare provider to gather essential information for diagnosis and treatment. In some cases, further diagnostic tests or imaging studies may be required to confirm the presence of any conditions or abnormalities.
Examining the Cardiovascular System
Assessing the cardiovascular system is a crucial part of any medical evaluation. This process focuses on evaluating the heart and blood vessels to identify potential signs of heart disease, poor circulation, or other related health issues. By observing and palpating different areas of the chest and neck, along with listening to heart sounds, clinicians can gain valuable insights into the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Key components of the assessment include:
- Inspection: Visual examination of the chest for abnormalities such as asymmetry, visible pulsations, or swelling. Also, look for signs of peripheral edema in the lower extremities.
- Palpation: Gently feeling for the apex beat, checking for any abnormal pulsations or thrills. This step also includes assessing the carotid pulse and peripheral pulses.
- Auscultation: Listening to heart sounds using a stethoscope. Focus on the rhythm, rate, and any abnormal sounds such as murmurs, gallops, or clicks.
- Blood Pressure Measurement: Accurate assessment of blood pressure to detect signs of hypertension or hypotension.
- Peripheral Circulation Check: Examining the arms and legs for signs of poor circulation, such as changes in skin color, temperature, and the presence of edema.
A thorough cardiovascular examination allows healthcare providers to detect early signs of heart conditions and vascular problems, aiding in early diagnosis and timely intervention.
Approaching Respiratory System Assessments
Evaluating the respiratory system is a vital component of any health evaluation, as it provides essential information about a patient’s lung and airway function. By carefully observing breathing patterns, palpating the chest, and auscultating lung sounds, healthcare providers can identify signs of respiratory distress, infections, or other lung-related issues. A thorough respiratory assessment helps in diagnosing conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Key Observations in Respiratory Assessments
The first step in assessing respiratory health involves visual inspection. Clinicians will look for signs such as labored breathing, chest wall movement, and whether the patient is using accessory muscles to breathe. Abnormalities like wheezing, coughing, or changes in skin color should be noted, as they may indicate respiratory distress or insufficient oxygenation.
Auscultation and Palpation Techniques
Next, palpation and auscultation are performed. Palpating the chest can help detect abnormal vibrations or tenderness, which might signal an underlying issue. Using a stethoscope, the provider listens to lung sounds to identify any wheezing, crackles, or abnormal breath sounds, which can indicate conditions like fluid in the lungs or bronchial obstruction. These findings, combined with a detailed patient history, lead to a clearer understanding of the patient’s respiratory status.
Abdominal Examination Techniques
The assessment of the abdominal area is a critical part of evaluating overall health, as it provides important insights into the function of various internal organs. By using a systematic approach, healthcare providers can identify signs of gastrointestinal, hepatic, or renal issues, such as inflammation, fluid buildup, or tenderness. A thorough examination involves inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation to detect abnormalities that could point to underlying conditions.
Inspection and Palpation
Inspection is the first step in an abdominal examination. The clinician looks for visible signs such as asymmetry, distention, or skin changes. Patients may display symptoms like bruising, scars, or bulging, which can indicate a problem with internal structures. Following inspection, the abdomen is palpated gently to assess for tenderness, firmness, or any abnormal masses. Palpation can help detect issues like enlarged organs or abnormal growths that may not be visible but can be felt through the skin.
Auscultation and Percussion
After the initial hands-on examination, auscultation is performed using a stethoscope to listen for bowel sounds and the presence of any abnormal gurgling or silence that could suggest an obstruction. Percussion involves tapping the abdomen to evaluate the size and consistency of organs, such as the liver or spleen, and to check for fluid accumulation or air pockets. These techniques, combined with patient history and symptoms, provide a comprehensive picture of abdominal health.
Neurological and Musculoskeletal Assessments
Evaluating the function of both the nervous and musculoskeletal systems is essential to understanding a patient’s overall well-being. The nervous system controls body functions, while the musculoskeletal system provides structure and movement. Analyzing both systems together allows clinicians to identify any impairments that may affect coordination, strength, and reflexes, as well as identify signs of neurological or muscular disorders.
Neurological Evaluation

A neurological assessment involves examining cognitive function, sensory responses, and motor abilities. Key areas of focus include:
- Reflexes: Testing deep tendon reflexes (such as the knee-jerk) helps evaluate spinal cord and nerve function.
- Sensory Perception: The ability to detect sensations, such as light touch, pain, and temperature, is checked on different body parts.
- Cranial Nerve Function: Evaluating the 12 cranial nerves ensures that all sensory and motor pathways in the head and neck are intact.
- Motor Skills: Assessment of muscle strength, coordination, and balance helps detect abnormalities in movement or signs of paralysis.
Musculoskeletal Evaluation
The musculoskeletal system examination focuses on assessing muscle strength, joint flexibility, and posture. The clinician looks for any signs of weakness, pain, or deformities that could suggest underlying conditions such as arthritis or muscle atrophy. Key aspects include:
- Range of Motion (ROM): Checking the full movement capacity of joints such as the shoulders, knees, and hips to detect stiffness or restricted movement.
- Muscle Strength: Testing for muscle strength in different areas of the body to identify any weakness or loss of function.
- Posture and Gait: Observing the way the patient stands, walks, or moves to detect signs of discomfort, abnormal gait, or balance issues.
These assessments, when done together, provide valuable information about the interaction between the nervous and musculoskeletal systems, allowing for early detection and management of disorders that could impair daily activities or quality of life.
Special Considerations for Pediatric Patients
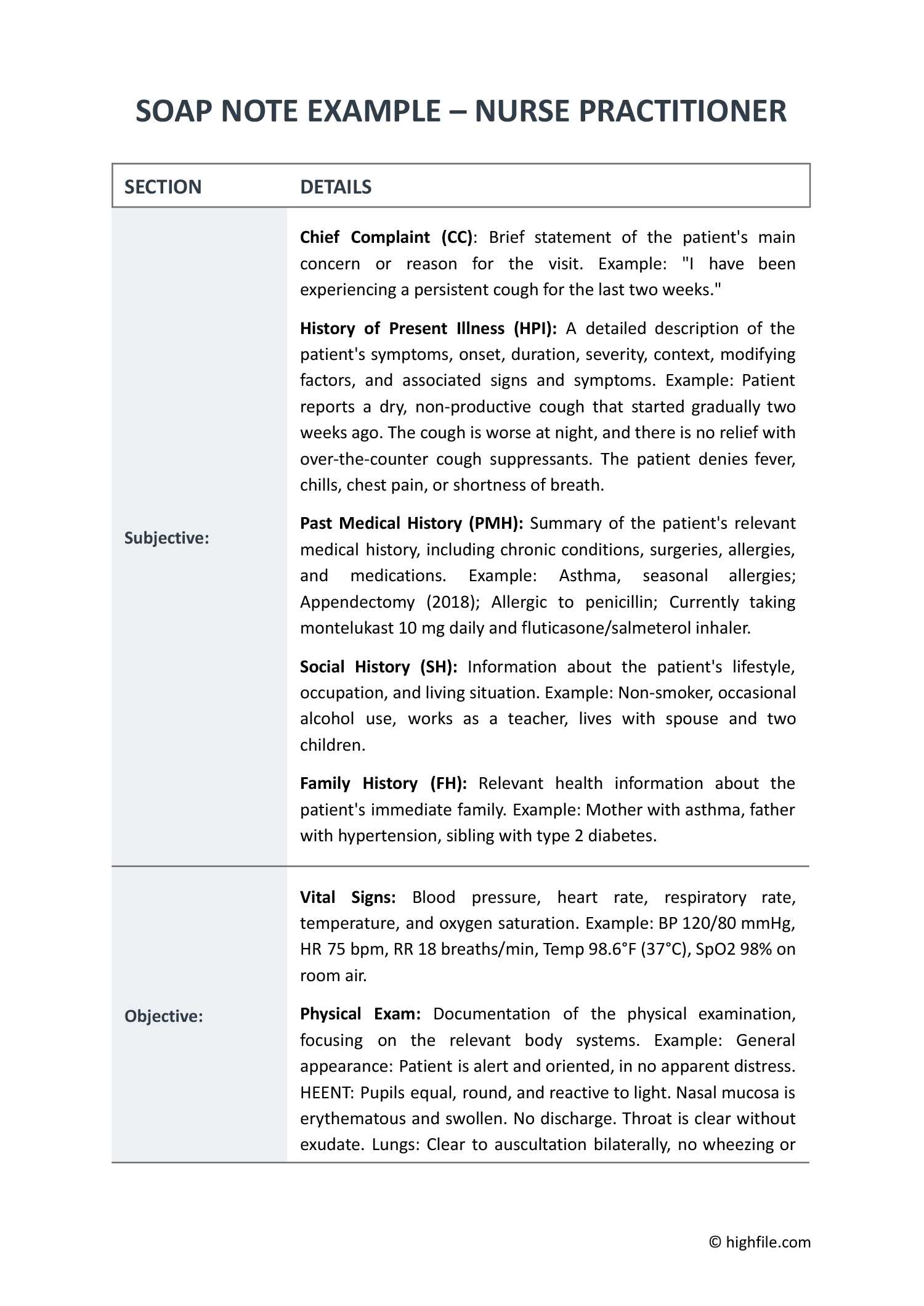
When assessing younger patients, there are unique factors to consider in order to ensure an accurate evaluation while minimizing discomfort. Children may not always have the ability to communicate their symptoms clearly, making it crucial for healthcare providers to adapt their approach. Establishing trust and creating a child-friendly environment can significantly impact the quality of the assessment process.
Communication with Caregivers: Parents or guardians are an essential part of the assessment process. They can provide important information about the child’s medical history, growth patterns, and any behavioral changes. Understanding family dynamics and environmental factors is equally crucial for an effective assessment.
Age-Appropriate Techniques: The methods used to assess a pediatric patient should be tailored to their developmental stage. For infants, observation and gentle palpation are key, whereas toddlers and older children can be engaged with more interactive methods, such as demonstrating the procedures on toys or using simple language. Keeping the assessment brief and incorporating play elements can reduce anxiety and ensure cooperation.
Growth and Developmental Milestones: Monitoring physical growth and developmental milestones is a fundamental aspect of pediatric care. Regular check-ups often focus on tracking weight, height, head circumference, and motor skills to ensure that the child is meeting expected developmental stages. Delays or deviations may indicate underlying health concerns.
Emotional and Psychological Needs: Children are particularly sensitive to stress and fear, so a calm, gentle approach is important. Using a reassuring tone, explaining procedures in a non-threatening way, and involving the child in the process can help reduce anxiety. In some cases, distraction techniques, such as offering a toy or watching a video, can keep the child engaged and relaxed during the assessment.
By considering these factors, healthcare providers can ensure a comprehensive evaluation while fostering a positive and supportive experience for pediatric patients and their families.
Adjusting for Elderly Patients’ Needs
When working with older adults, healthcare professionals must consider specific factors that affect both the assessment process and the quality of care. Aging often brings changes in physical, cognitive, and emotional health, all of which can influence how a person responds to care. Therefore, adapting methods and approaches to meet the unique needs of elderly patients is essential for accurate evaluations and effective treatment.
Physical Limitations and Sensory Changes
Mobility issues, such as difficulty walking or standing for long periods, are common in older patients. It is important to accommodate these challenges by offering assistance, using appropriate support devices, and providing seating during lengthy assessments. Additionally, sensory impairments, such as hearing loss or diminished vision, may require modifications, such as speaking clearly, using hearing aids, or ensuring the environment is well-lit. Tailoring the environment to these needs ensures a smoother and more comfortable experience for the patient.
Cognitive and Emotional Considerations
Cognitive decline can affect an elderly patient’s ability to follow instructions or recall information accurately. In these cases, healthcare providers should offer clear and simple explanations and consider involving family members or caregivers in the process. Taking extra time to allow the patient to express themselves without rushing can help avoid frustration and ensure that all concerns are addressed. Additionally, emotional well-being plays a significant role in older adults’ health. Many elderly patients experience feelings of isolation, anxiety, or depression, which can impact their willingness to participate in assessments. Providing reassurance, establishing trust, and creating a positive atmosphere are key to successful interactions.
By adjusting to these needs, healthcare providers can ensure that elderly patients receive the appropriate care while maintaining their dignity and comfort throughout the process.
Addressing Mental Health in Physical Exams
When conducting a complete health evaluation, it is essential to recognize the connection between mental well-being and overall physical health. Mental health can significantly influence how patients perceive their symptoms, engage with healthcare providers, and manage chronic conditions. Incorporating mental health considerations into the assessment process can help identify underlying issues and contribute to more effective and holistic care.
Identifying Emotional and Psychological Concerns
Patients may not always openly discuss emotional struggles or mental health issues during assessments, either due to stigma or a lack of awareness of their own condition. It is important to create an open and non-judgmental environment, where patients feel comfortable sharing their concerns. Healthcare professionals should actively listen for signs of anxiety, depression, or stress that might manifest in physical complaints or altered behavior. Asking open-ended questions about mood, sleep patterns, and social support can help reveal underlying issues that affect both mental and physical health.
Integrating Mental Health Support into the Care Plan
Collaborating with mental health professionals is crucial when addressing psychological issues that arise during health assessments. In some cases, it may be necessary to refer patients to a therapist or counselor for further evaluation and support. Additionally, addressing mental well-being in the treatment plan–whether through medication, lifestyle modifications, or counseling–can improve patient outcomes and enhance overall care. Patients with mental health challenges often experience better results when their psychological needs are incorporated into their healthcare strategy.
Recognizing the role of mental health in a patient’s overall well-being not only improves diagnosis accuracy but also enhances the quality of care provided, ensuring a more comprehensive approach to health management.
Using Technology for Exam Documentation
Incorporating digital tools into the documentation process has transformed the way healthcare professionals record patient information. With advancements in technology, manual note-taking and paper records are gradually being replaced by electronic systems that streamline the documentation process, reduce errors, and improve accessibility. Utilizing technology for recording patient details not only enhances efficiency but also ensures better data management and analysis.
Benefits of Digital Documentation
- Increased Accuracy: Electronic records help reduce human errors that can occur in handwritten notes, ensuring more accurate information is captured.
- Time Efficiency: Digital tools allow for faster data entry, as healthcare providers can use voice recognition or customizable templates to input key information quickly.
- Improved Accessibility: With digital systems, patient records are easily accessible by authorized professionals, promoting better collaboration and coordination of care.
- Enhanced Security: Electronic documentation is often more secure than paper records, with built-in features like encryption and password protection to ensure patient confidentiality.
Types of Technology in Documentation
There are various digital tools available for healthcare providers to use when documenting patient assessments and histories:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): These systems store patient information, including medical history, medications, and previous visits, all in one place for easy retrieval.
- Voice Recognition Software: This allows healthcare providers to dictate notes verbally, speeding up the documentation process while maintaining accuracy.
- Mobile Health Applications: Many apps now allow providers to capture and store patient information from mobile devices, making it easier to document in real-time during patient interactions.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These tools offer guidance on clinical decisions based on patient data, enhancing decision-making and the overall quality of care.
By embracing technology, healthcare providers can improve their documentation practices, resulting in more accurate, efficient, and secure patient records that ultimately contribute to better patient care.
Best Practices for Comprehensive Evaluation
Conducting a thorough assessment requires a systematic approach to ensure all relevant factors are considered. This process should involve gathering detailed patient information, performing careful observations, and documenting findings accurately. Adhering to best practices ensures a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition and promotes effective decision-making and treatment planning.
Key Strategies for Effective Evaluation
- Start with a Clear Patient History: Begin by collecting detailed information about the patient’s medical history, symptoms, lifestyle, and family background. This foundation helps identify potential risk factors and underlying conditions.
- Prioritize Systematic Observation: Use a structured approach to observe the patient, assessing all relevant body systems in a logical sequence. This helps avoid overlooking any important aspect of their health.
- Engage in Active Listening: Pay close attention to the patient’s concerns, allowing them to explain their symptoms and experiences fully. This builds trust and ensures no critical details are missed.
- Utilize Evidence-Based Tools: Incorporate validated tools, scales, and guidelines during the evaluation. These resources enhance the accuracy and consistency of assessments.
- Document Findings Clearly: Record all relevant observations, tests, and patient responses in a clear, organized manner. Accurate documentation ensures continuity of care and facilitates future reference.
Ensuring Comprehensive Coverage
- Holistic Approach: Consider both physical and psychological factors in the evaluation. Mental health, lifestyle habits, and environmental influences all contribute to the patient’s overall well-being.
- Adapt to Patient Needs: Tailor the approach to the specific needs of the patient. This may involve adjusting for age, communication challenges, or specific health conditions that require special attention.
- Collaborative Care: Engage with other healthcare providers as necessary. A team-based approach helps to address complex cases more effectively and provides a broader perspective on the patient’s condition.
- Follow Up: Ensure that any findings are followed up with additional tests, referrals, or monitoring as needed. A comprehensive evaluation doesn’t end with the first assessment.
By following these best practices, healthcare professionals can ensure that their evaluations are thorough, accurate, and patient-centered, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.