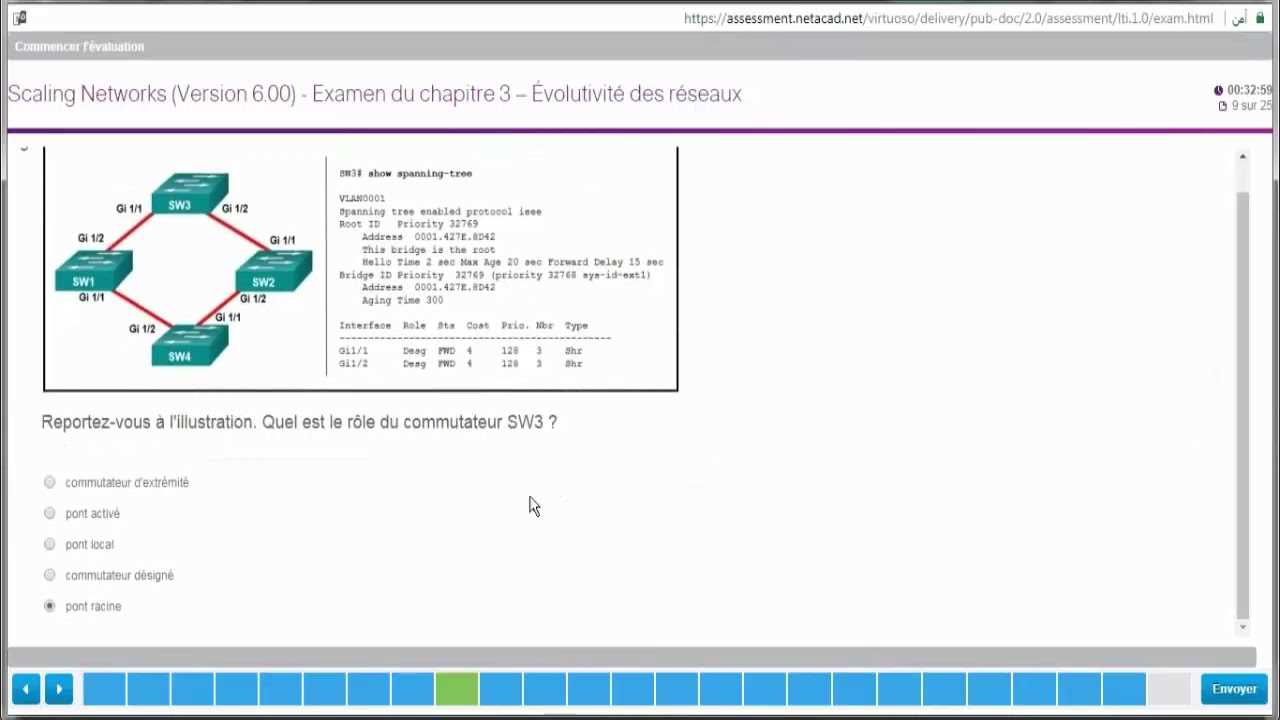
Preparing for a professional certification in networking requires a thorough understanding of both theoretical principles and practical skills. As you advance through your studies, focusing on key topics and honing your problem-solving abilities will help you achieve success. This process involves mastering a wide range of concepts that form the foundation of modern networking systems.
Effective preparation involves more than just memorizing facts; it requires applying knowledge to real-world scenarios. Whether you’re troubleshooting complex network configurations or working with routing protocols, hands-on practice is essential. Understanding the core principles will allow you to approach challenges with confidence and clarity.
In this guide, we will explore various strategies to help you build a solid grasp of networking concepts. From exploring essential protocols to mastering common commands, each step will bring you closer to mastering the material. With the right approach, you can turn your preparation into a rewarding learning experience and set yourself up for certification success.
CCNA 3 Exam Answers and Solutions
Successfully tackling the final stages of your networking certification requires more than just memorization. It demands an ability to understand core concepts, apply them practically, and troubleshoot complex scenarios. Whether you’re preparing for practice tests or real-life applications, finding the right solutions to various networking challenges is crucial. This section will guide you through some of the most common questions and solutions, ensuring you’re well-equipped for the certification process.
Effective problem-solving begins with a deep understanding of fundamental network components and their interrelationships. By approaching each challenge with a structured methodology, you can break down complex tasks into manageable steps. The key to success lies not only in knowing the right answers but also in grasping the reasoning behind each solution. This will empower you to think critically and adapt to any situation you may encounter during your certification journey.
In this section, we will explore some typical scenarios that test your ability to configure, manage, and troubleshoot network devices. Each solution will highlight best practices, providing clear explanations and actionable insights. By mastering these concepts, you’ll develop the skills needed to solve problems efficiently and confidently in both theoretical and hands-on environments.
How to Approach CCNA 3 Exam
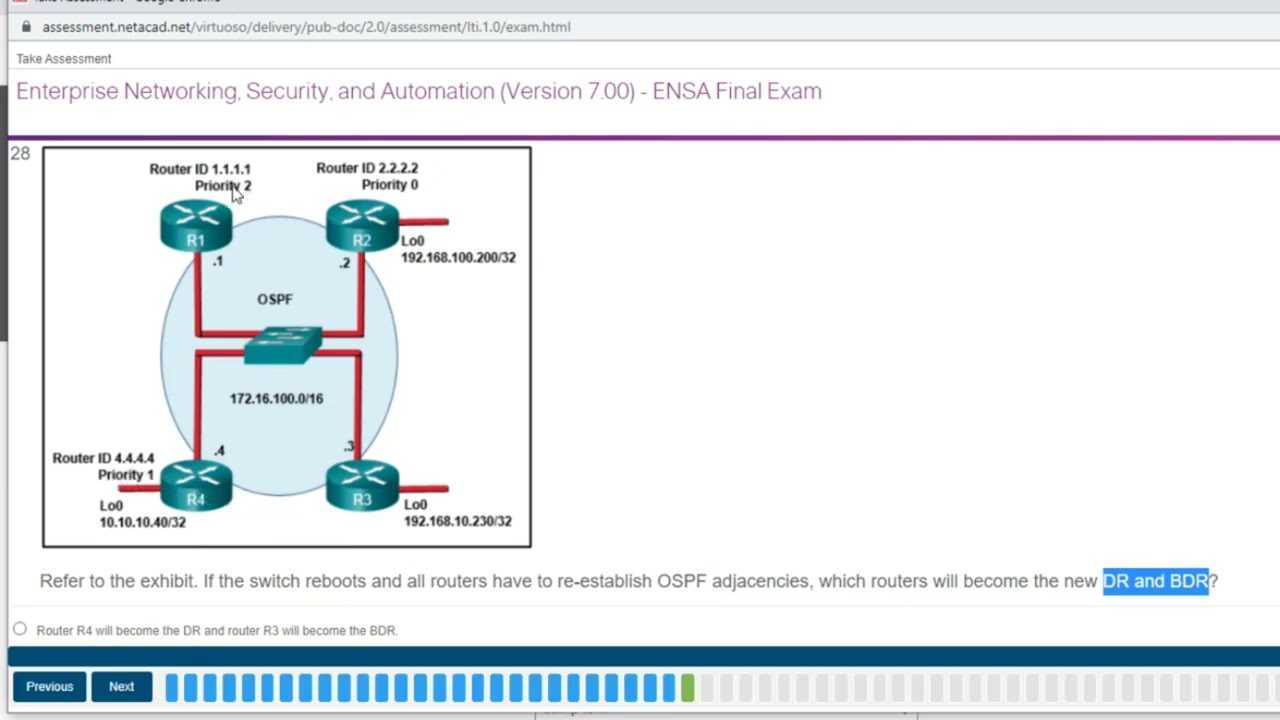
When preparing for a networking certification, it’s essential to have a clear and structured approach. The journey involves mastering various technologies, understanding complex configurations, and solving real-world problems. By organizing your study plan and focusing on practical application, you can improve both your knowledge and your ability to tackle the challenges you’ll face during the process.
Here are some strategies to guide your preparation:
- Understand the Core Concepts: Focus on key networking principles, such as routing, switching, and network security. Having a strong grasp of these topics will make it easier to solve practical problems.
- Hands-on Practice: Theoretical knowledge is crucial, but practical experience is just as important. Set up labs and simulations to apply what you’ve learned in real scenarios.
- Master Troubleshooting: A significant portion of the assessment involves troubleshooting network issues. Practice identifying problems and resolving them efficiently.
- Review and Test Your Knowledge: Regularly take practice tests and quizzes to assess your progress. This helps reinforce concepts and identify areas that need improvement.
- Time Management: Develop a strategy to manage your time effectively during the assessment. Ensure you’re familiar with the format and pacing of the tasks you’ll encounter.
By following these tips, you’ll be able to approach the challenges of certification with confidence and clarity, ensuring you’re ready to tackle both theoretical questions and hands-on tasks effectively.
Key Topics in CCNA 3 Exam
When preparing for a professional networking certification, understanding the most important concepts is critical. Several fundamental topics are essential for success, as they form the backbone of modern network infrastructures. Mastering these areas will ensure you’re well-prepared for both practical and theoretical challenges.
Networking Protocols: A deep understanding of networking protocols such as IP, TCP/IP, and OSPF is essential. These protocols are the foundation of communication between devices on a network, and knowledge of their operation will help you troubleshoot and configure networks effectively.
Routing and Switching: Routing and switching are core areas of networking. You need to understand how routers direct traffic across networks and how switches manage traffic within local networks. Concepts such as VLANs, subnetting, and routing tables should be mastered to handle configurations and optimizations efficiently.
Network Security: Securing networks from external threats is a critical skill. Topics like firewall configurations, VPNs, and intrusion detection are vital for ensuring the integrity of networked systems. Knowing how to implement security measures is a key part of network administration.
IP Addressing: Efficiently managing IP addresses and subnetting is crucial. A solid grasp of IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes, along with subnet masks, will help you configure devices and solve connectivity issues.
Network Troubleshooting: Being able to diagnose and resolve network problems is an essential skill. Understanding tools and methods for troubleshooting such as ping, tracert, and netstat will prepare you for real-world scenarios where quick problem resolution is needed.
Focusing on these key areas will provide a comprehensive understanding of networking principles and prepare you to handle the challenges of modern network administration.
Top Study Strategies for CCNA 3
Achieving success in a networking certification requires a focused and organized study plan. It’s essential to balance theoretical learning with hands-on practice to reinforce concepts and develop problem-solving skills. Adopting effective study strategies will help you stay on track and prepare thoroughly for the challenges you’ll face.
Here are some proven approaches to help you maximize your study efforts:
- Create a Structured Schedule: Set aside dedicated study time each day to ensure consistent progress. Break your study sessions into focused blocks, covering specific topics or skills. This will help you stay organized and avoid last-minute cramming.
- Practice Regularly: Hands-on experience is crucial in networking. Set up labs or simulations to practice configuring devices and solving problems. This will deepen your understanding and increase your ability to troubleshoot real-world issues.
- Use Active Recall and Spaced Repetition: Rather than passively reading through material, actively test yourself on key concepts. Revisit these concepts regularly to reinforce your memory using spaced repetition techniques. This approach improves long-term retention.
- Review Practice Questions: Regularly solve practice questions and mock tests to familiarize yourself with the format and types of problems you may encounter. This will also help identify areas that need further focus and review.
- Join a Study Group: Collaborating with peers can provide valuable insights and help clarify complex topics. Group study sessions allow you to discuss challenging concepts and share different perspectives, enhancing your understanding.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify your weaknesses early and dedicate extra time to those topics. Prioritize areas where you’re struggling to ensure you build a strong foundation in all essential networking concepts.
By implementing these strategies, you can approach your preparation with confidence and ensure you’re fully prepared to tackle both theoretical and practical challenges in networking certification.
Understanding Networking Protocols for CCNA
Networking protocols are the foundation of communication within a network. These standardized rules and conventions define how data is transmitted, routed, and processed between devices. A strong grasp of these protocols is essential for anyone aiming to manage or troubleshoot modern network infrastructures. Understanding how these protocols interact allows network professionals to optimize performance, ensure security, and resolve connectivity issues effectively.
Key Networking Protocols to Master

Among the most critical protocols are Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP), which together facilitate the majority of data transmission across networks. TCP ensures that data packets are delivered accurately and in the correct order, while IP handles the addressing and routing of packets across diverse network paths.
Another important protocol is Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), a dynamic routing protocol that enables devices to exchange routing information efficiently. Understanding how OSPF works is vital for configuring routers and ensuring data takes the optimal path across large networks.
Importance of Protocols in Network Security
Network security relies heavily on specific protocols designed to protect data. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are commonly used to encrypt communications between devices, ensuring sensitive information remains private. Similarly, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) helps network administrators monitor and control network devices, while also offering important security features when properly configured.
Having a deep understanding of these networking protocols and their functionalities enables you to design, troubleshoot, and secure complex networks. Mastery of this area will significantly contribute to success in any networking certification.
Common Mistakes in CCNA 3 Exam
When preparing for a networking certification, even experienced individuals can make certain errors that may impact their performance. These common mistakes often stem from misinterpreting questions, overlooking important details, or failing to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid them and approach your study sessions and tests with greater efficiency and confidence.
One common mistake is rushing through questions without fully analyzing the problem. This often leads to incorrect configurations or overlooking critical steps in network setups. It’s crucial to take your time, read each question carefully, and plan your approach before diving into solutions.
Another frequent issue is inadequate understanding of network topologies and device configurations. Skipping over fundamental concepts such as IP addressing, subnetting, and routing protocols can lead to confusion when facing practical tasks. Ensure you have a strong grasp of these core concepts, as they often form the basis of more complex challenges.
Failing to double-check configurations is also a common oversight. Even if you are confident in your solutions, small errors like incorrect IP addresses, improper VLAN setups, or missed routing steps can cause significant issues. Always review your configurations and ensure each step is executed correctly.
Lastly, neglecting to practice real-world scenarios is a critical mistake. Without hands-on experience, it’s difficult to truly understand how theoretical knowledge translates to practical application. Set up lab environments, run simulations, and actively troubleshoot to reinforce your learning and prepare for any challenge.
Practical Lab Exercises for CCNA
Hands-on practice is an essential part of mastering networking skills. Practical exercises allow you to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios, helping you to better understand configurations, troubleshoot issues, and optimize network performance. By simulating different network environments and problems, you develop the ability to make quick, effective decisions when managing devices and addressing network issues.
Below are some examples of lab exercises that provide valuable experience in key areas of networking:
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Addressing and Subnetting | Configure devices with appropriate IP addresses and subnet masks. Practice subnetting large networks into smaller subnets and assign IPs correctly to avoid conflicts. |
| Router Configuration | Set up routers with basic configurations, including IP routing, routing tables, and static routes. Simulate network traffic and monitor routing behavior. |
| VLAN Configuration | Create and assign VLANs to switches. Ensure proper segmentation of traffic across different network segments and troubleshoot any connectivity issues. |
| Network Troubleshooting | Simulate network failures and diagnose problems such as misconfigured IPs, broken connections, or faulty devices. Use tools like ping, tracert, and netstat to identify and resolve issues. |
| Wireless Configuration | Configure wireless access points and ensure proper security settings. Test connectivity and optimize the wireless network for performance. |
By regularly practicing these exercises, you will improve both your technical skills and problem-solving ability, ultimately preparing you to handle real-world networking tasks with confidence.
Time Management Tips for CCNA Exam
Effective time management is a crucial skill when preparing for any certification or assessment. With multiple topics to cover and limited time, organizing your study plan and learning how to allocate time during the test can significantly impact your performance. By managing your time wisely, you ensure that you can tackle all sections of the test efficiently without feeling rushed.
Here are some practical strategies to help you manage your time effectively:
- Set a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions in advance and stick to a routine. Divide your study time into manageable blocks, focusing on different topics each day. Include short breaks to avoid burnout and keep your mind fresh.
- Prioritize Key Areas: Identify the most challenging or heavily weighted topics and dedicate more time to mastering them. Ensure that you cover all necessary material but focus extra effort on areas where you feel less confident.
- Use Timed Practice Tests: Take practice tests under timed conditions. This will help you get accustomed to the pace of the assessment and improve your ability to manage time during the actual test.
- Don’t Overthink Questions: During the test, read each question carefully, but don’t dwell too long on any one item. If you’re unsure about an answer, move on and come back to it later if time allows. This prevents you from getting stuck and losing valuable time.
- Practice Time Allocation: Allocate a specific amount of time to each section of the test and stick to it. For example, if you have 100 minutes for a 50-question assessment, aim to spend about 2 minutes per question. Keep an eye on the clock and adjust if necessary.
- Review and Adjust: If time permits at the end of the test, quickly review your answers. Make sure you haven’t missed any questions, and ensure that your answers are as complete as possible. However, don’t spend too much time on reviewing–ensure that your initial responses were clear and accurate.
By adopting these time management techniques, you will approach your preparation and assessment with greater efficiency and confidence, allowing you to perform at your best.
CCNA 3 Practice Test Resources
Practicing with simulated tests is one of the best ways to prepare for any technical certification. These resources provide valuable insight into the types of questions you will encounter, as well as help you refine your ability to manage time effectively during an assessment. By regularly testing your knowledge and skills, you can identify weak areas, improve your problem-solving abilities, and gain confidence before taking the official assessment.
Top Online Platforms for Practice Tests

There are many platforms offering mock tests and interactive learning environments designed to simulate the actual assessment. Here are some reliable resources:
- Boson ExSim – Known for its high-quality practice tests, Boson provides realistic simulations that closely resemble the real assessment. The platform also includes detailed explanations of each question to help reinforce learning.
- Transcender – A popular resource among aspiring network professionals, Transcender offers challenging practice exams along with performance-tracking features to monitor your progress.
- MeasureUp – A trusted provider of practice exams that closely align with the test objectives. MeasureUp’s questions are designed to prepare you for the complexity and format of the actual assessment.
- ExamCompass – Free practice tests on various networking topics. While not as extensive as paid services, ExamCompass is a great starting point for beginners.
Additional Resources for Practice
In addition to dedicated practice test platforms, there are other resources that can supplement your preparation:
- Networking Labs: Setting up your own home lab environment to practice configurations and troubleshooting is invaluable. Use virtual machines or network simulation software like Packet Tracer to test your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Study Groups: Join online communities or study groups where you can practice test questions with peers, share knowledge, and gain different perspectives on complex topics.
- Books with Practice Questions: Many certification books come with practice questions at the end of each chapter, helping you assess your understanding as you go through the material. Books by authors like Todd Lammle and Wendell Odom are highly recommended.
By incorporating a variety of these practice resources into your study routine, you will be well-equipped to tackle the test with confidence and accuracy. These tools not only enhance your knowledge but also build the endurance required for success in the assessment environment.
Exploring Routing Concepts in CCNA 3
Routing is a core concept in networking, determining how data travels across networks. It involves directing traffic from one network to another through devices known as routers. Understanding routing protocols, how they function, and how to configure them is essential for managing and optimizing large networks. This section will dive into the different routing techniques, protocols, and configuration methods that are key to building efficient networks.
Types of Routing Protocols

There are several routing protocols used to direct traffic in a network. These protocols determine the best path for data transmission. Here’s a breakdown of the main routing protocols you’ll encounter:
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| RIP (Routing Information Protocol) | RIP is one of the oldest distance-vector routing protocols. It uses hop count as its metric to determine the best path. RIP is suitable for smaller networks but is less efficient in large-scale environments. |
| OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) | OSPF is a link-state protocol that uses the Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path. It is more efficient than RIP, especially for larger networks, and supports hierarchical routing. |
| EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) | EIGRP is a hybrid protocol that combines the best features of distance-vector and link-state protocols. It’s faster than RIP and more efficient than OSPF in certain scenarios. |
| BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) | BGP is used to route data between different networks, commonly known as inter-domain routing. It’s highly scalable and is typically used by Internet service providers and large organizations. |
Configuring Routing on Routers
Configuring routing involves setting up the router with the correct protocol and ensuring that it can properly direct traffic. Here are the key steps involved:
- Enable Routing Protocol: The first step is to enable the appropriate routing protocol on the router (e.g., RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP).
- Define Networks: Specify the networks that the router will manage and communicate with other routers.
- Configure Interfaces: Each router interface must be configured with an IP address and subnet mask. This is essential for routing traffic to the correct destinations.
- Verify Routing Tables: After configuring the routing protocol, verify that the routing table contains the correct routes for network traffic.
By understanding and mastering these routing concepts and configurations, you can efficiently manage network traffic, reduce bottlenecks, and ensure seamless communication between different parts of the network.
Essential Command Syntax for CCNA 3
In network administration, understanding the correct syntax for commands is crucial for configuring and troubleshooting devices such as routers and switches. Command-line interfaces (CLI) are typically used to interact with these devices, and knowing the proper structure and format of each command is vital for successful network management. This section covers the essential command syntax you will need to effectively work with network devices and configure key settings.
Basic Command Structure
Every command issued in a router or switch CLI has a specific structure. The general syntax consists of several key elements:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Command | The main action or instruction, such as “show”, “configure”, or “enable”. |
| Parameters | Additional information that specifies the action, such as interface names, IP addresses, or specific settings. |
| Arguments | Values that define the parameters in more detail, such as “0/0”, “GigabitEthernet1”, or “192.168.1.1”. |
| Options | Optional elements that modify the behavior of the command, such as “verbose” for more detailed output. |
Commonly Used Commands
Below are some essential commands that network administrators commonly use when configuring and troubleshooting networking devices:
- show running-config – Displays the current configuration of the device.
- show ip interface brief – Provides a quick overview of the router or switch interfaces and their statuses.
- enable – Switches to privileged EXEC mode, allowing access to more advanced commands.
- configure terminal – Enters global configuration mode, where the device settings can be modified.
- interface [interface name] – Used to configure a specific interface on a device (e.g., “interface GigabitEthernet0/1”).
- ping [IP address] – Sends a test packet to a remote host to check network connectivity.
- copy running-config startup-config – Saves the current configuration to the device’s startup configuration file.
- exit – Exits from the current mode or interface configuration.
By mastering these fundamental commands and understanding their syntax, you will be able to configure, manage, and troubleshoot networking devices with ease. These commands form the foundation of network operations and are essential for maintaining a functional and efficient network.
Real-World Applications of CCNA 3 Knowledge
The knowledge gained through networking courses plays a crucial role in the practical world of network administration. As technologies evolve, understanding how networks operate and how to manage them efficiently becomes essential for ensuring reliable and secure communication systems. This section explores how the concepts learned in network configuration and management can be applied in real-world scenarios, making a tangible impact on business operations and technology infrastructure.
Optimizing Network Performance
One of the primary real-world applications is optimizing network performance. Professionals who understand network routing, switching, and troubleshooting can implement strategies to ensure fast, reliable data transmission across different network environments. Whether it’s configuring routing protocols like OSPF or implementing VLANs, these tasks are critical for improving network efficiency and reducing downtime.
Enhancing Network Security
Another essential application is the implementation of network security measures. Knowledge of firewalls, access control lists (ACLs), and encryption techniques allows network administrators to safeguard sensitive data. By configuring security features on routers and switches, professionals can protect their organizations from external threats, ensuring that only authorized users have access to specific resources.
Building Scalable Network Infrastructures
As companies grow, so do their networking needs. The skills learned in network design and planning enable professionals to build scalable infrastructures that can expand as the company’s requirements increase. This involves designing networks that can handle increased traffic, adding redundant connections for reliability, and ensuring that all components work together seamlessly.
In practice, network administrators use their understanding of subnetting, IP addressing, and routing protocols to design and maintain systems that can support thousands of devices, from workstations to servers and mobile devices. These skills are in high demand in industries ranging from telecommunications to financial services, where network uptime and data integrity are paramount.
By applying the concepts learned in real-world settings, professionals help organizations stay connected, secure, and efficient, contributing directly to the success of modern enterprises.
Preparing for Troubleshooting Questions
Troubleshooting is a vital skill for anyone working in network administration. The ability to identify, diagnose, and resolve issues quickly and efficiently is essential to maintaining network uptime and performance. In this section, we will focus on how to prepare for common troubleshooting scenarios that you might encounter during assessments or in a professional setting. Proper preparation involves understanding the tools, methodologies, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Key Troubleshooting Methodologies
When faced with a network issue, having a systematic approach is crucial. Below are some essential troubleshooting steps that will guide you through solving problems effectively:
- Identify the Problem: Gather as much information as possible about the issue. This includes understanding the symptoms, error messages, and affected devices.
- Establish a Theory of Probable Cause: Based on the information collected, make an educated guess about what might be causing the issue. This theory will direct the next steps in troubleshooting.
- Test the Theory: Verify your theory by testing possible causes. This might involve checking configurations, verifying cables, or running diagnostic commands.
- Establish a Plan of Action: Once the cause is identified, plan the steps to fix the problem. Consider the resources required, downtime, and the steps involved.
- Verify the Solution: After applying the fix, test the network to ensure that the issue is resolved. Monitor the system for any new issues that may arise.
- Document the Process: Keeping detailed records of the problem and the solution helps prevent future issues and provides valuable insights for future troubleshooting.
Common Troubleshooting Tools and Techniques
In addition to following a structured methodology, it’s essential to be familiar with the tools and techniques used in network troubleshooting. Here are some of the most common tools and their uses:
- Ping: A simple tool used to test network connectivity between devices. It can help identify basic issues like network downtime or misconfigured interfaces.
- Traceroute: This tool helps trace the path data takes to reach its destination. It can be useful for diagnosing routing issues or determining where packets are being delayed.
- Telnet/SSH: These command-line tools allow administrators to access and configure remote devices securely. They are often used for troubleshooting connectivity or configuration issues on network devices.
- Show Commands: These commands are used on routers and switches to display the status of various system components, such as interfaces, routing tables, and logs. They are essential for diagnosing issues related to device configuration.
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer used to capture and analyze traffic. It’s useful for troubleshooting network communication issues and identifying potential bottlenecks or security vulnerabilities.
Mastering these tools and techniques will help you approach troubleshooting questions with confidence, whether you’re working on real-world network issues or preparing for an assessment. Remember, consistent practice and a methodical approach are key to becoming proficient in troubleshooting network problems.
How to Master IPv4 and IPv6
Understanding and mastering both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing is crucial for anyone involved in networking. These protocols are the backbone of modern internet communication, and knowing how to configure, troubleshoot, and optimize them is essential for network administrators. This section will provide practical strategies to help you become proficient in both IPv4 and IPv6.
Key Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
Before diving into the details of configuration and management, it’s important to understand the primary differences between IPv4 and IPv6. Here are the main distinctions:
- Address Length: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, whereas IPv6 utilizes 128-bit addresses, providing a much larger address space.
- Address Notation: IPv4 addresses are written in decimal (e.g., 192.168.1.1), while IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
- Address Configuration: IPv4 relies on manual configuration or DHCP, whereas IPv6 can auto-configure addresses using Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC).
- Routing: IPv6 simplifies routing and reduces the need for network address translation (NAT), which is often necessary with IPv4.
Mastering IPv4
IPv4 remains the most widely used protocol for internet communication. To become proficient in IPv4, consider the following steps:
- Understand the Addressing Structure: Get familiar with IPv4 address classes (A, B, C, D, E) and subnetting. Subnetting is particularly important for dividing a network into smaller, more manageable segments.
- Practice Subnetting: Subnetting is a critical skill for IPv4 configuration. Practice calculating network addresses, subnet masks, and determining valid host ranges.
- Know Reserved Addresses: Be aware of special IPv4 address ranges such as private addresses (e.g., 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.0.0/16) and multicast addresses.
- Familiarize Yourself with Routing: Understand the different routing protocols used in IPv4 networks, such as RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP.
Mastering IPv6
Although IPv6 is becoming more widely adopted, many professionals still find it challenging. To master IPv6, follow these strategies:
- Learn the Address Format: Get comfortable with the hexadecimal notation and understand how to represent IPv6 addresses in shorthand form (e.g., collapsing consecutive zeros).
- Understand IPv6 Prefixes: Study the different IPv6 address prefixes, such as the Global Unicast Address (GUA) and Link-Local Address (LLA), and learn how they are used in networks.
- Configure IPv6 Addresses: Practice configuring IPv6 addresses manually or through auto-configuration methods like SLAAC. Learn how to assign and verify IPv6 addresses on routers and hosts.
- Work with IPv6 Routing: Understand how routing works in IPv6, including how routing protocols like OSPFv3 and EIGRP for IPv6 operate. Pay attention to how
Network Design Questions in CCNA 3
Designing a network involves considering a variety of factors to ensure that the infrastructure is reliable, scalable, and efficient. The process requires a solid understanding of how different components interact and how to align them with business or technical requirements. This section covers the key concepts and strategies necessary to approach network design tasks effectively.
When tasked with creating a network design, there are several critical elements to focus on, including topology selection, addressing schemes, and performance optimization. Each decision made during the design process can have a significant impact on the network’s overall performance and security. Therefore, it’s important to address both theoretical knowledge and practical skills to succeed in network design challenges.
Here are some common aspects to consider when designing a network:
- Topology Selection: Choose the right topology based on the organization’s needs. Common topologies include bus, star, ring, and mesh, each offering different advantages in terms of reliability and scalability.
- Addressing and Subnetting: Properly segmenting the network using subnetting ensures efficient use of IP address space and minimizes network congestion. It’s essential to understand how to allocate addresses to different segments based on network requirements.
- Routing and Switching: Deciding between routing protocols (such as RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP) and switching techniques (Layer 2 vs Layer 3) is key to ensuring smooth communication between devices and optimal traffic management.
- Redundancy and Failover: Incorporating redundancy at various levels of the network ensures high availability. This includes using techniques like spanning tree protocol (STP) and link aggregation to prevent single points of failure.
- Security Considerations: Securing the network from unauthorized access and potential threats is crucial. Using firewalls, encryption, and proper access control mechanisms is essential to protect sensitive data.
Understanding the requirements and constraints of the network design is vital for making informed decisions. Whether it’s designing for a small office or a large enterprise, the goal is to create a system that meets performance, scalability, and security standards while remaining cost-effective.
Using Study Guides Effectively
Study guides are essential tools for mastering complex concepts and preparing for assessments in the field of networking. By providing structured content and focused exercises, these resources help reinforce key topics and build a deeper understanding of networking principles. However, using them effectively requires more than just reading through the material–it involves a strategic approach to maximize retention and comprehension.
To make the most out of study guides, it is important to approach them systematically. This involves reviewing the material in a manner that strengthens both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Here are some strategies to ensure that study guides serve their purpose efficiently:
Prioritize Core Concepts
When using study guides, focus on mastering the core concepts before diving into advanced topics. Start with the foundational areas, such as networking protocols, routing and switching principles, and addressing schemes. Ensure that you have a solid understanding of these key areas before tackling more complex material. This foundational knowledge will make it easier to understand advanced topics later on.
Active Learning and Practice
It is essential to apply what you’ve learned through hands-on practice. Many study guides provide practice questions, lab exercises, and simulation tasks that allow you to work with real-world scenarios. By actively engaging with the material and solving practical problems, you can strengthen your understanding and improve your troubleshooting skills.
- Practice with labs: Recreate network setups using simulation software or physical hardware to deepen your practical knowledge.
- Review practice questions: Regularly attempt mock tests and quizzes to assess your knowledge and identify weak areas that need further attention.
- Utilize summaries and key points: At the end of each section, pay attention to the key takeaways and summaries, as these often highlight the most important concepts.
By following these techniques and utilizing the study guide effectively, learners can develop a strong foundation, improve problem-solving abilities, and be better prepared for any challenges they may encounter in their network studies.