
The rise of technology in modern defense systems has brought new challenges to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining operational integrity. As military personnel increasingly rely on digital tools and networks, the need to understand and mitigate online threats has never been more critical. Proper education on these topics ensures that soldiers are equipped to handle potential risks and prevent security breaches.
Effective protection in a military setting requires a comprehensive approach to digital safety, where every individual is informed of common risks and equipped with the skills to counteract them. This proactive stance minimizes the chances of exploitation by malicious actors and reinforces a culture of security throughout the organization.
With sophisticated online attacks becoming more frequent, it is essential that service members understand how to identify potential dangers, from simple scams to complex cyber intrusions. By addressing these issues head-on, armed forces can maintain the confidentiality and efficiency of their operations, ensuring mission success in an increasingly connected world.
Cyber Awareness Training Army Answers
Effective defense in the digital realm starts with informed individuals who understand the risks associated with technology and online platforms. For personnel working in high-stakes environments, the ability to identify potential threats and respond accordingly is essential. The knowledge gained through structured programs helps reduce the risk of breaches and empowers service members to maintain the security of sensitive data and communication channels.
While many aspects of digital defense can be learned through general education, specific guidance tailored to the needs of military personnel ensures the highest level of preparedness. Below are some common topics and solutions covered in programs designed to enhance security knowledge and skills:
| Topic | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing and Social Engineering | Understanding deceptive practices used to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information. | Recognizing signs of phishing attempts and employing cautious practices when handling unsolicited emails or messages. |
| Safe Use of Devices | Guidelines for maintaining the security of mobile devices, laptops, and other tech tools used for military tasks. | Implementing strong passwords, encryption, and regular software updates to ensure device protection. |
| Data Protection | Methods for safeguarding confidential information both in transit and at rest. | Using encryption techniques, secure file-sharing methods, and ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized personnel. |
| Incident Response | Steps to take when a security breach is suspected or detected. | Establishing protocols for reporting incidents, containing threats, and mitigating potential damage quickly and efficiently. |
| Safe Communication | Ensuring that all forms of communication, especially digital, remain secure from unauthorized access. | Using encrypted messaging systems and verified channels for official communications to prevent interception. |
By mastering these core concepts, personnel can play an active role in the overall security infrastructure, ensuring that operational integrity remains intact. The ability to recognize and respond to potential threats strengthens the collective defense and minimizes risks to national security.
Importance of Cyber Security in the Army
As modern military operations increasingly depend on digital technologies, the need to protect sensitive data and communication networks has grown exponentially. Ensuring robust defense against malicious threats is vital not only for safeguarding classified information but also for maintaining operational efficiency and national security. Without effective digital defense strategies, even small vulnerabilities can compromise larger missions and undermine strategic goals.
Risks to Military Operations
Threats targeting military infrastructure can range from espionage to sabotage, and their consequences can be catastrophic. Some of the key risks include:
- Unauthorized access to classified files and documents
- Interception of communication and intelligence transmissions
- Destruction or manipulation of critical data systems
- Disruption of operational systems and weaponry
Essential Strategies for Protection
Implementing comprehensive protection measures involves a multi-layered approach, ensuring every individual and system is adequately secured. The following strategies are fundamental to mitigating risks:
- Continuous monitoring of network traffic and system vulnerabilities
- Regular software and security protocol updates
- Strict access control and authentication procedures
- Training personnel to recognize potential threats
By prioritizing these measures, military forces can create a secure environment, enabling efficient operations while defending against both internal and external threats. A well-prepared force is essential for countering evolving risks in an increasingly interconnected world.
Common Cyber Threats Facing Military Personnel
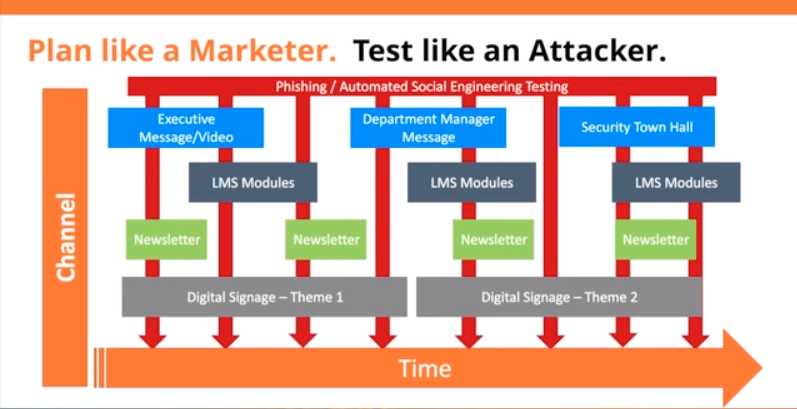
As military personnel rely more on digital platforms for communication, intelligence, and operations, they face an increasing number of threats from malicious actors seeking to compromise critical systems. Understanding the variety of risks involved is essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring the success of military missions. These threats are constantly evolving, making it crucial for service members to stay vigilant and prepared.
Types of Digital Threats
Several types of digital threats are commonly directed at military personnel. These include:
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive attempts to steal sensitive information by masquerading as trustworthy sources, often through emails or fake websites.
- Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to systems, including viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Social Engineering: Manipulation techniques used to deceive individuals into divulging confidential information, often by exploiting human psychology.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Attempts to overwhelm and disrupt military networks, making them inaccessible by flooding them with unnecessary data or requests.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
With technological advancements, new risks continue to emerge. Among the growing concerns are:
- Insider Threats: Personnel or contractors with access to sensitive systems who intentionally or unintentionally expose information or compromise security.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated, long-term attacks by well-funded groups aiming to infiltrate networks and steal critical data over extended periods.
- Mobile Device Vulnerabilities: As more military personnel use personal and government-issued devices for communication and operations, these devices become prime targets for cyberattacks.
Recognizing these threats is only the first step. Implementing effective countermeasures is essential for maintaining operational security and minimizing risks to personnel and national security.
Basic Principles of Cyber Hygiene
Maintaining a high level of digital cleanliness is crucial for protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure operations. Just as personal hygiene prevents physical illness, good digital habits help safeguard against online threats and minimize vulnerabilities in military and defense environments. Adopting strong security practices in everyday activities is the foundation for a resilient defense posture.
Key Habits for Strong Digital Security
There are several key practices that personnel should follow to maintain strong security hygiene:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Create complex passwords that are difficult to guess, and ensure they are different for each account or system.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Use additional verification methods, such as text messages or authentication apps, to enhance account security.
- Update Software Regularly: Ensure that all systems and devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates to fix vulnerabilities.
- Be Cautious with Links and Attachments: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources to prevent malware infections.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use encryption to protect important information both while it is stored and while being transmitted.
Building a Culture of Digital Security
Adopting these practices on an individual level is essential, but fostering a broader culture of vigilance within a team or organization can greatly enhance overall defense. This can be achieved through:
- Frequent Security Audits: Regular checks and assessments help identify potential weaknesses in the system.
- Clear Reporting Channels: Encourage quick reporting of any suspicious activity or security breaches.
- Regular Security Drills: Conducting mock scenarios where personnel can practice responding to digital threats builds readiness and strengthens response capabilities.
By adopting these essential principles, military personnel can significantly reduce their exposure to digital threats and contribute to a safer, more secure operational environment.
How to Recognize Phishing Attempts
One of the most common tactics used by malicious actors to steal sensitive information is through deceptive messages designed to appear legitimate. Recognizing these attempts is crucial for protecting both personal and organizational data. These fraudulent schemes often manipulate human psychology, tricking individuals into revealing passwords, financial information, or even access to secure systems. Awareness and caution are the first lines of defense against these threats.
Signs of Phishing Attempts
Phishing messages can be tricky to spot, but there are several red flags to watch for:
- Unusual Sender Information: Check the email address or phone number closely. Fraudulent messages often come from addresses that look similar to legitimate ones but with slight alterations (e.g., missing letters or extra characters).
- Urgent Requests: Scammers often create a sense of urgency, pressuring you to act quickly by claiming an account will be locked, or a security breach has occurred.
- Suspicious Links: Hover over any links in the message to check the URL. Fraudulent links often lead to fake websites designed to steal information.
- Grammatical Errors: Poor grammar, spelling mistakes, or awkward phrasing are common in phishing attempts, as scammers may not be native speakers or may not pay attention to detail.
- Requests for Sensitive Information: Legitimate organizations will never ask you to provide personal or confidential details through unsecured channels such as email or text.
How to Protect Yourself
Knowing how to identify phishing attempts is one part of the solution; the next is ensuring that you follow safe practices when handling suspicious communications:
- Verify the Source: If you receive a suspicious message, contact the organization directly through an official number or website to confirm whether the request is legitimate.
- Don’t Click on Links: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or untrusted sources. Type the website address directly into the browser instead.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication on important accounts to add an extra layer of security in case your credentials are compromised.
- Report Suspicious Messages: Report any potential phishing attempts to your IT department or the appropriate security team to prevent further incidents.
By staying vigilant and following these guidelines, you can greatly reduce the chances of falling victim to phishing attacks and protect yourself from online fraud.
Protecting Sensitive Information Online
In today’s digital world, safeguarding confidential data is more critical than ever. With the growing reliance on online platforms for communication, financial transactions, and personal information sharing, it is essential to adopt strategies that minimize the risk of exposure. Whether dealing with government, business, or personal data, keeping this information secure is fundamental to preventing unauthorized access and potential misuse.
There are several methods available to help protect sensitive data from being compromised. Below are key practices that ensure better protection for online information:
| Method | Description | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Converting sensitive information into an unreadable format to prevent unauthorized access during transmission. | Use strong encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256) and ensure encrypted communication when sending or storing sensitive data. |
| Password Management | Using complex and unique passwords to protect digital accounts from unauthorized access. | Create long, random passwords and use password managers to store them securely. Enable multi-factor authentication where possible. |
| Secure Communication Channels | Utilizing encrypted channels to protect the integrity and confidentiality of messages and data. | Use encrypted messaging apps or email services that offer end-to-end encryption for sensitive communications. |
| Data Masking | Hiding specific data within a dataset to prevent unauthorized users from viewing sensitive information. | Apply data masking techniques in databases and systems, ensuring only authorized personnel can access specific data fields. |
| Regular Software Updates | Keeping all software up to date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities. | Ensure automatic updates are enabled, and manually check for updates if needed, especially for operating systems and security tools. |
Adopting these practices is essential to securing personal and professional data from digital threats. By incorporating a combination of encryption, secure channels, and diligent password management, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of exposing sensitive information online. These steps, though simple, go a long way in protecting the integrity of digital operations and maintaining privacy in an increasingly connected world.
Cybersecurity Protocols for Military Networks
In the context of defense operations, safeguarding the integrity of communication systems and digital infrastructures is paramount. Military networks are particularly vulnerable to a range of malicious threats due to the sensitivity of the information they handle. To protect against these risks, robust protocols must be established, ensuring that all data transmitted, stored, or processed within these networks remains secure. These security measures must be comprehensive, adaptable, and capable of defending against a variety of evolving threats.
Key Security Measures for Military Networks
Military networks require specialized protocols to ensure the safety of sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Below are some of the most important protocols used in securing these systems:
- Encryption Standards: Strong encryption algorithms are applied to both data at rest and data in transit to ensure unauthorized parties cannot access or decipher the information.
- Access Control: Restricting network access to authorized personnel only through secure authentication methods, such as smart cards or biometric identification.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Advanced firewalls are used to monitor and block unauthorized traffic, while intrusion detection systems (IDS) identify and respond to any potential breaches.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create secure, encrypted connections for remote access to military networks, ensuring that data remains protected during transmission over unsecured channels.
- Regular System Audits: Periodic security audits and vulnerability assessments are conducted to identify weaknesses and ensure compliance with military security protocols.
Best Practices for Network Security
To maintain a high level of security, it is essential for military personnel to follow best practices when interacting with military networks:
- Implementing Zero Trust Architecture: Adopting a zero trust model, where every access request is verified, regardless of the origin, helps minimize internal threats and ensures continuous security.
- Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring of network activity allows for the early detection of unusual behavior, and detailed logging helps to trace any security incidents that occur.
- Software Updates: Regularly updating operating systems, software, and applications ensures known vulnerabilities are patched and the network remains secure.
- Employee Education: Personnel must be trained on the latest security protocols and the risks of common threats such as phishing, malware, and social engineering attacks.
By adhering to these protocols and best practices, military networks can remain secure and resilient against a wide range of cyber threats, ensuring that sensitive information and critical operations remain protected at all times.
Role of Password Management in Cyber Defense
Effective password management is a cornerstone of any comprehensive security strategy. As digital threats become more sophisticated, the importance of safeguarding access credentials cannot be overstated. Strong, unique passwords serve as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. Without proper password control, even the most advanced security measures can be compromised.
In defense environments, where the protection of classified information and critical infrastructure is paramount, ensuring that passwords are properly managed is essential. A single weak or reused password can be the key to breaching an entire network, making it crucial to adopt best practices that limit exposure to such risks.
Key Practices for Effective Password Management
Adopting a structured approach to password management significantly enhances overall security. The following practices are essential for maintaining robust defense:
- Use Complex and Unique Passwords: Passwords should be long, unpredictable, and contain a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Reusing passwords across multiple accounts increases the risk of a security breach.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding a second layer of protection through MFA ensures that even if a password is compromised, unauthorized users cannot access the system without additional verification.
- Implement Password Expiration Policies: Regularly updating passwords reduces the likelihood of a successful attack. Passwords should be changed periodically, especially for sensitive accounts or systems.
- Utilize Password Managers: These tools help generate and store complex passwords securely, preventing users from relying on weak or easily guessable credentials.
- Monitor and Audit Password Usage: Regular audits ensure compliance with password policies and help identify any unusual access patterns that may indicate a security breach.
The Impact of Poor Password Management
Neglecting password security can have devastating consequences, especially in high-stakes environments. Poor password management can lead to:
- Unauthorized Access: Weak or reused passwords are easy targets for attackers using brute-force or credential-stuffing techniques.
- Data Breaches: If attackers gain access to critical systems, they can steal, modify, or destroy valuable information, causing significant harm to both operations and national security.
- Compromised Trust: Failure to protect login credentials erodes trust in digital systems, damaging an organization’s reputation and its ability to operate securely.
By establishing a strong password management system, personnel can greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and enhance the overall security posture of their networks and systems. A disciplined approach to password protection is a fundamental aspect of any effective defense strategy.
Understanding Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks rely on manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. These attacks exploit human behavior and psychological vulnerabilities, rather than relying solely on technological flaws. By targeting the way people think and act, attackers can bypass even the most advanced security measures. Understanding how these attacks work is crucial for preventing them and protecting sensitive data.
Common Types of Social Engineering Attacks
There are several common tactics used by attackers in social engineering schemes. The most frequent types include:
- Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages designed to trick individuals into revealing personal information, such as passwords or account details. These often appear to come from trusted sources, like banks or government agencies.
- Spear Phishing: A more targeted form of phishing, where attackers tailor their messages to specific individuals or organizations, making them seem even more legitimate.
- Pretexting: Attackers create a fabricated scenario or pretext to convince individuals to release sensitive information. This could involve impersonating a colleague, contractor, or even a trusted authority figure.
- Baiting: This involves enticing victims with promises of rewards, such as free software or media, in exchange for downloading malicious files or revealing sensitive data.
- Tailgating: In this type of attack, an unauthorized person gains physical access to a secure area by following someone with authorized access, often under the guise of needing assistance or being in a hurry.
How to Defend Against Social Engineering Attacks
While these attacks are based on manipulating human behavior, there are steps individuals can take to protect themselves:
- Be Skeptical: Always question unsolicited requests for sensitive information, especially if they come through email, phone, or social media. If in doubt, verify the request through official channels.
- Verify Identity: If someone asks for information, ensure you verify their identity through an independent means, rather than relying solely on the information they provide.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security, such as a code sent to your phone, helps protect accounts even if login credentials are compromised.
- Educate and Train: Regular education on recognizing suspicious activity and the risks of social engineering can help individuals become more cautious and aware of potential threats.
- Limit Personal Information Online: The less personal information you share publicly, the less likely you are to become a target for attackers who rely on social media or public records to craft convincing scams.
By understanding how social engineering attacks work and implementing preventive measures, individuals and organizations can reduce their vulnerability and strengthen their overall security posture.
Responding to a Security Breach
When a security breach occurs, swift and effective action is crucial to minimize damage and protect sensitive data. The response to a breach must be coordinated, methodical, and focused on containing the threat while assessing its impact. The quicker the response, the better the chances of limiting the breach’s scope and mitigating potential harm. Understanding the proper steps to take during and after a security incident can significantly reduce risks and help prevent further vulnerabilities from being exploited.
There are several key actions that should be taken when a breach is detected. These steps not only help contain the threat but also assist in identifying the source and preventing future incidents:
Immediate Steps to Take
- Isolate Affected Systems: Quickly disconnect compromised devices or systems from the network to stop the spread of the attack and prevent further damage.
- Assess the Breach: Identify the extent of the breach. Determine which systems were affected, what data may have been compromised, and the nature of the threat (e.g., malware, unauthorized access).
- Notify Key Stakeholders: Alert relevant personnel, including IT teams, management, and possibly external vendors or authorities, depending on the severity of the incident.
- Preserve Evidence: Avoid altering or deleting any data related to the breach. Preserving logs, files, and system images will help in the investigation and provide important evidence for forensic analysis.
Post-Incident Actions

After containing the breach and ensuring no further damage occurs, the focus shifts to recovery and long-term prevention:
- Conduct a Thorough Investigation: Work with internal and external experts to investigate the breach’s origin, how it was executed, and any vulnerabilities that were exploited. This step is essential for understanding how the breach occurred and for strengthening future defenses.
- Communicate with Affected Parties: Notify anyone impacted by the breach, including customers, employees, or partners. Transparent communication is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance with legal or regulatory requirements.
- Patch Vulnerabilities: Once the breach source is identified, quickly address any security gaps by applying necessary patches or system updates. Strengthen weak areas in the network to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Monitor Systems Post-Breach: After restoring systems, continuously monitor network activity to detect any signs of lingering threats or attempted follow-up attacks. Ensure that all systems are functioning as expected without any residual issues.
Finally, the breach response process should be used as a learning opportunity. Regularly reviewing incident responses and incorporating improvements will help build a more resilient security posture for the future.
The Impact of Malware on Military Operations
Malware can severely disrupt the smooth functioning of any organization, especially in critical sectors such as defense. In military environments, where security and efficiency are of utmost importance, the presence of malicious software can have devastating effects. These threats can compromise sensitive information, impair communications, and even disable key operational systems, putting missions at risk and potentially endangering personnel and national security.
As military networks and devices become more connected and integrated, the risk of malware attacks increases. Understanding the potential consequences of these attacks is crucial for mitigating their impact and implementing effective countermeasures to protect essential operations.
Key Risks Posed by Malware
Malware can take various forms and have a wide range of impacts, including but not limited to the following:
- Data Theft: Malware can steal confidential military data, such as strategic plans, personnel records, or weapon systems information, which can then be used by adversaries to gain an advantage.
- Disruption of Communications: Some types of malware can disable communication systems, causing delays or complete outages in vital coordination efforts, which can be disastrous in the midst of critical missions.
- Loss of Operational Control: Certain malware, such as ransomware, can lock or encrypt critical operational systems, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid, effectively halting military functions.
- Espionage: Malware can be used for espionage purposes, allowing hostile actors to monitor military activities, track personnel, and gain access to classified intelligence.
- Infiltration of Supply Chains: Malware attacks can infiltrate supply chains, disrupting logistics, manufacturing processes, or the delivery of crucial resources to troops, weakening operational readiness.
Strategies to Counter Malware Threats
While the risks associated with malware are significant, there are strategies that can help minimize the impact and protect military operations:
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping systems, software, and devices up-to-date with the latest security patches helps close vulnerabilities that malware could exploit.
- Network Segmentation: By segmenting networks into smaller, isolated sections, any malware that infiltrates one part of the system can be contained and prevented from spreading to other critical areas.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implementing robust monitoring tools allows military IT personnel to detect suspicious activities quickly and respond to potential threats before they cause significant damage.
- Employee Training: Educating personnel on recognizing phishing attempts, suspicious links, and unsafe behaviors can reduce the likelihood of malware being introduced into military systems by human error.
- Backup Systems: Regularly backing up critical data ensures that, in the event of a malware attack, vital information can be restored without paying a ransom or losing valuable resources.
Given the profound potential consequences, it is essential for military organizations to take proactive steps to defend against malware attacks and prepare for quick responses to mitigate damage if an attack occurs. Effective cybersecurity measures, including vigilant monitoring and a well-trained workforce, are essential for safeguarding military operations and maintaining national security.
Training Military Personnel on Digital Security Best Practices
Ensuring the safety of digital systems and sensitive data in defense environments requires that all personnel understand and follow established best practices. Educating individuals on how to recognize potential threats, safely handle information, and securely interact with technology is critical in preventing breaches and maintaining operational integrity. Effective training programs equip military personnel with the knowledge and skills needed to protect against various digital risks, from phishing scams to unauthorized access.
The need for comprehensive digital security education is especially important in military settings, where the potential consequences of a breach can have far-reaching implications. By promoting strong security habits and reinforcing proper protocols, personnel can contribute to a more secure and resilient operational environment.
Key Topics for Digital Security Training
When training personnel, several key areas must be covered to ensure a well-rounded understanding of digital security practices:
- Strong Password Management: Personnel must be taught to use complex, unique passwords for different accounts and systems, as well as the importance of regularly updating them and using multi-factor authentication.
- Phishing Recognition: Training should include lessons on identifying fraudulent emails, messages, and phone calls designed to steal personal information or introduce malicious software.
- Secure Communication Practices: Personnel should learn how to securely send and receive sensitive information, including using encryption and other secure channels to protect data in transit.
- Device Security: It’s crucial for individuals to understand how to secure their devices, including laptops, smartphones, and USB drives, against theft or unauthorized access through strong passwords and encryption.
- Incident Response Protocols: Personnel must be trained on the proper steps to take if a security breach occurs, including how to report the incident and respond in a timely and efficient manner.
Training Formats and Approaches
Effective training is not just about conveying theoretical knowledge but also providing hands-on experience to ensure personnel can apply security principles in real-world situations. Below are some methods for delivering engaging and practical training:
| Training Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Interactive Simulations | Engage personnel in real-world scenarios, such as simulated phishing attempts or mock cyberattacks, to practice identifying and responding to threats. |
| Workshops and Seminars | Offer in-person or virtual workshops that cover essential topics, providing personnel with opportunities to ask questions and discuss best practices with experts. |
| Regular Refresher Courses | Offer ongoing, periodic training sessions to keep personnel updated on the latest security trends, techniques, and emerging threats. |
| Online Learning Platforms | Provide access to digital training modules and resources that personnel can complete at their own pace, ensuring flexibility and accessibility. |
Ultimately, ensuring that personnel are well-prepared to handle digital security challenges requires a combination of education, practical experience, and continuous reinforcement of best practices. By instilling a culture of security-minded behavior, military organizations can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and enhance their overall operational effectiveness.
Effective Use of Encryption in Military Settings
In military operations, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access is essential to maintaining strategic advantage and operational security. Encryption plays a pivotal role in ensuring that data, both in transit and at rest, remains secure from interception and unauthorized decryption. By converting readable data into a coded format that can only be accessed with the correct decryption key, encryption safeguards communications, intelligence, and critical infrastructure from potential threats.
The application of encryption techniques is vital in military settings, where the integrity and confidentiality of data can have significant consequences. Understanding how and when to implement encryption is crucial for preserving mission success and preventing adversaries from gaining access to sensitive materials.
Key Applications of Encryption in Military Operations
Encryption is applied in various contexts within military environments to ensure that sensitive information is protected across different systems and networks. Some of the most common uses include:
- Secure Communications: Encryption is used to protect messages exchanged between units, command centers, and other military personnel, ensuring that only authorized individuals can decrypt and read the information.
- Data Protection: Files containing sensitive operational plans, personnel records, and intelligence reports are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access, even if physical devices are stolen or lost.
- Authentication and Identity Protection: Encryption helps verify the identity of individuals accessing military systems or networks, ensuring that only authorized users are granted access to classified data and resources.
- Secure Tactical Networks: Encryption is used to protect tactical communications and network infrastructures that military units rely on during operations, safeguarding against potential cyberattacks or eavesdropping.
Best Practices for Implementing Encryption
While encryption is a powerful tool, its effectiveness depends on how well it is implemented. Below are some best practices for using encryption in military settings:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Strong Encryption Algorithms | Ensure that encryption algorithms are robust and up-to-date. Commonly used standards like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) offer strong protection against modern decryption attempts. |
| Regularly Update Encryption Keys | Encryption keys should be updated regularly to minimize the risk of key compromise. Using rotating or dynamic keys enhances security by preventing attackers from gaining long-term access. |
| End-to-End Encryption | Where possible, use end-to-end encryption for all communications, ensuring that data is encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted by the intended recipient. |
| Multi-Layered Security | Encryption should be part of a broader security strategy that includes other protective measures, such as firewalls, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, to provide comprehensive defense against threats. |
| Train Personnel | Ensure that all personnel understand the importance of encryption and how to use encryption tools effectively. Proper training minimizes the risk of human error and ensures the proper handling of sensitive information. |
By following these best practices, military organizations can better protect their sensitive data, maintain the integrity of their operations, and prevent adversaries from gaining unauthorized access. Encryption, when implemented effectively, is an indispensable part of the broader security framework that underpins military success and operational resilience.
Ensuring Safe Use of Military Devices

In any defense organization, the safe handling and use of electronic devices is critical to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining operational efficiency. Devices such as laptops, smartphones, and communication tools are integral to daily operations, but they also pose significant security risks if not properly secured. Protecting these devices from unauthorized access, malware, and theft requires a combination of strict protocols, regular monitoring, and user awareness.
Effective management of military devices ensures that personnel can access necessary resources without compromising security. Implementing the right protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents, which could otherwise jeopardize missions or put valuable assets at risk.
Key Guidelines for Safe Device Usage

To ensure military devices are used securely, personnel should follow the following essential guidelines:
- Use Strong Authentication: Ensure all devices require strong passwords and, when possible, multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Install Security Updates: Regularly update the software and operating systems on all devices to patch known vulnerabilities and defend against emerging threats.
- Enable Full Disk Encryption: All sensitive data stored on devices should be encrypted, making it unreadable to unauthorized users even if the device is lost or stolen.
- Use Secure Networks: Always connect to secure, encrypted networks and avoid using public Wi-Fi for accessing sensitive information or performing critical tasks.
- Implement Device Lock Features: Enable automatic lock settings on devices after a short period of inactivity to prevent unauthorized access when left unattended.
- Regularly Back Up Data: Maintain up-to-date backups of all important information to ensure it can be restored in case of device failure or compromise.
Preventing Unauthorized Access and Theft
Preventing unauthorized access to military devices is crucial to maintaining the integrity of both sensitive data and overall operational security. Below are additional steps to protect devices from theft or unauthorized use:
- Physical Security: Always store devices in secure locations, and ensure that portable devices are never left unattended in public or unsecured areas.
- Remote Wipe Capability: Enable remote wipe features on devices to erase all data if a device is lost or stolen, minimizing the risk of data exposure.
- Monitor Device Usage: Implement monitoring tools to track the usage of devices and detect any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
- Educate Personnel: Regularly remind personnel of the importance of physical security and the potential risks associated with device misuse or careless handling.
By adhering to these practices, military personnel can reduce the likelihood of device-related security breaches and ensure that critical operations and sensitive information remain secure. Ensuring the safe use of devices is a vital part of a broader security strategy that protects national interests and maintains operational effectiveness.
Security Regulations for Military Personnel
Maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information is a fundamental requirement for all military personnel. In an increasingly digital world, ensuring that data, communication, and operational systems remain secure is crucial to national defense and operational success. Various rules and guidelines govern the handling of electronic systems and information within the military to minimize risks and prevent breaches that could compromise missions or personnel safety.
Adhering to these security regulations is essential to protect against malicious threats, unauthorized access, and potential data leaks. Military personnel must be thoroughly familiar with and comply with these directives to help maintain the highest levels of operational security at all times.
Core Security Regulations for Personnel
Military personnel are required to follow a set of comprehensive regulations to ensure the safe handling of digital and physical assets. Some key regulations include:
- Access Control: Personnel must be granted access only to information that is necessary for their role. Permissions should be regularly reviewed and adjusted to ensure compliance with the principle of least privilege.
- Data Protection: Sensitive information must be securely stored and transmitted. Encryption techniques are required for all classified or high-value data, both at rest and during transit, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Device Management: All military-issued devices must be regularly updated with the latest security patches, configured to meet strict security standards, and used in accordance with established security protocols.
- Incident Reporting: Any security incidents, including potential breaches or suspicious activities, must be reported immediately to the appropriate authorities for prompt investigation and response.
- Secure Communication: Communication channels used for transmitting sensitive information must be encrypted and protected from interception or unauthorized access. This includes both internal and external communication methods.
- Authentication Standards: Strong, multi-factor authentication methods must be implemented across all systems to ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical systems and networks.
Compliance and Penalties
Failure to comply with these regulations can have severe consequences. Military personnel are held accountable for their actions when it comes to data security and device management. Penalties for non-compliance may include disciplinary action, loss of access to sensitive information, or even criminal charges in cases of deliberate negligence or malicious intent.
Regular audits and assessments help ensure that all personnel are adhering to the required security measures. It is essential that each individual within the organization is aware of their responsibilities and the importance of safeguarding sensitive materials and systems.
By following these established regulations, military personnel can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches, protect vital resources, and contribute to the overall mission of safeguarding national security.