
Success in advanced studies requires a strategic approach to understanding complex topics related to drug science and therapeutics. Whether you are revising key theories or applying clinical knowledge, careful preparation is crucial to mastering the material and performing well in the evaluation process.
Effective study methods and a focused mindset can make a significant difference in how well you grasp the critical concepts. To excel, it’s essential to not only memorize information but also to understand the underlying principles that connect various therapeutic practices and pharmacological agents.
By organizing your study plan, utilizing diverse resources, and practicing with sample questions, you can strengthen your knowledge and boost your confidence. With the right preparation, you will be ready to tackle even the most challenging topics and perform at your best.
Pharmacology Exam 3 Study Plan
To effectively prepare for this advanced medical assessment, it is important to establish a clear and structured study plan. A well-organized approach allows you to cover all necessary topics while ensuring you have enough time to review and practice key concepts. Prioritizing essential material and breaking down your study time into manageable sessions can greatly enhance your retention and understanding.
Begin by identifying the core areas you need to focus on, such as drug classifications, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic applications. Allocate more time to challenging topics, and integrate frequent review sessions to reinforce your memory. Utilize various resources, such as textbooks, online courses, and practice questions, to diversify your learning experience and build a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
In addition to studying theory, ensure that you practice applying your knowledge through mock tests or scenario-based questions. This helps simulate the type of thinking required during the assessment and prepares you to handle complex situations. A consistent, disciplined approach to your study schedule will provide the best chance for success.
Key Concepts to Focus On

When preparing for an advanced evaluation in drug science, it’s crucial to concentrate on the fundamental principles that underpin therapeutic practices. Understanding the relationships between drug properties, their effects on the body, and clinical applications forms the backbone of your studies. Mastery of these key concepts will allow you to approach complex scenarios with confidence.
Start by focusing on drug classifications and the different therapeutic categories, as these often form the basis for many questions. Understanding how specific substances interact with biological systems is equally important. This includes grasping concepts like absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination, which explain how drugs are processed in the body and their duration of action.
Additionally, be sure to review adverse reactions, side effects, and drug interactions, as these are critical areas of clinical practice. Recognizing how these factors can affect patient care is essential for making informed decisions. Lastly, understanding treatment protocols for various conditions and how drugs are used to manage specific diseases will ensure that you can apply your knowledge effectively under exam conditions.
Effective Time Management for Studying
Mastering time management is essential when preparing for an advanced evaluation in medical sciences. Planning your study sessions wisely ensures that you can cover all necessary material while avoiding last-minute stress. A structured approach to managing your time will allow you to retain information more effectively and build confidence in your knowledge.
Begin by breaking down your study material into smaller, manageable sections. Prioritize topics based on their difficulty and relevance, allocating more time to areas that require deeper understanding. Creating a realistic schedule that includes regular review sessions will help reinforce what you’ve learned and prevent forgetting crucial details.
Additionally, avoid cramming by spacing out your study sessions and incorporating breaks. Short breaks during study sessions can improve focus and prevent burnout. Keep track of your progress and adjust your study plan as necessary to ensure that all areas are adequately covered before the assessment date.
Understanding Drug Mechanisms
Grasping how drugs interact with the body is a cornerstone of mastering this field. Understanding the mechanisms behind how substances exert their effects helps connect theory with real-world clinical applications. This knowledge allows you to predict how various compounds will behave in different biological systems and informs therapeutic decisions.
Focus on the basic principles of drug action, such as receptor binding, signal transduction, and enzyme modulation. These concepts explain how drugs activate or block specific biological pathways, influencing physiological responses. Additionally, understanding the concept of dose-response relationships is crucial, as it defines how the amount of a drug influences its effects on the body.
Equally important is recognizing the role of pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics in shaping therapeutic outcomes. The former addresses how a drug works at the molecular level, while the latter explains how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates the drug. A solid grasp of these mechanisms enables you to better understand drug efficacy and safety, key factors in clinical practice.
Pharmacokinetics and Its Importance
Understanding how the body processes drugs is essential for predicting their effects and optimizing treatment. The study of drug movement within the body, from absorption to elimination, is key in determining how and when a drug will exert its influence. This knowledge helps ensure that medications are used effectively and safely in clinical settings.
Pharmacokinetics involves the study of how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Each of these processes plays a crucial role in determining the drug’s therapeutic potential and overall effectiveness. By understanding these mechanisms, healthcare professionals can tailor treatments to achieve optimal drug concentrations at the site of action, minimizing side effects and maximizing benefits.
Equally important is the ability to recognize factors that influence pharmacokinetic processes, such as age, liver and kidney function, and genetic variations. These factors can alter the way the body handles medications, requiring adjustments to dosing regimens. A thorough understanding of pharmacokinetics ensures that drugs are used safely, with appropriate dosing and timing to achieve the desired therapeutic outcome.
Top Resources for Exam Preparation
Having the right materials and resources is essential for efficient and effective preparation. The best tools will help reinforce key concepts, clarify difficult topics, and provide opportunities for practice. Whether you prefer books, online platforms, or interactive tools, a mix of resources can help you cover all the necessary areas and build confidence.
Here are some of the most useful resources for mastering the subject:
- Textbooks and Reference Books – Comprehensive books often provide in-depth explanations of core topics, helping to solidify your understanding of complex concepts.
- Online Learning Platforms – Websites and apps like Coursera, Khan Academy, or Medscape offer interactive lessons, video tutorials, and quizzes to reinforce your learning.
- Practice Tests and Question Banks – Access to practice questions and mock tests will allow you to assess your knowledge and familiarize yourself with the format of the questions you’ll encounter.
- Study Guides – Concise guides that summarize key concepts can be invaluable for quick reviews and reinforcing what you’ve learned.
- Peer Study Groups – Collaborating with classmates or colleagues can provide different perspectives, help with difficult topics, and offer motivation and support.
- Flashcards – Using flashcards, either physical or digital, is an effective method for memorizing important terms, drug classes, and key definitions.
By combining these resources and allocating time to each, you can develop a well-rounded understanding and ensure you are fully prepared for the upcoming assessment.
Commonly Tested Pharmacological Drugs
Familiarity with the most commonly used medications is crucial for understanding therapeutic treatments and their clinical applications. Certain drugs are frequently highlighted due to their widespread use, impact on patient care, and relevance to a variety of medical conditions. Knowing their mechanisms, indications, side effects, and contraindications will help you perform well in any assessment related to drug science.
These drugs are typically divided into classes based on their effects and mechanisms of action. Below are some key examples that are often emphasized:
- Beta-blockers – Medications like metoprolol and atenolol are frequently used for managing hypertension, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
- ACE inhibitors – Drugs such as lisinopril and enalapril are commonly prescribed for high blood pressure and chronic kidney disease.
- Antibiotics – Common antibiotics like amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin are essential in treating bacterial infections and are often included in assessments.
- Analgesics – Pain management drugs, including morphine, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen, are frequently tested for their indications and dosing regimens.
- Insulin – This medication is a cornerstone for managing diabetes and is often a focal point in understanding glucose metabolism and regulation.
- Anticoagulants – Drugs such as warfarin and heparin play vital roles in preventing blood clots and managing clotting disorders.
Focusing on these drugs, understanding their therapeutic effects, and recognizing potential side effects and interactions will ensure you are well-prepared for any clinical or theoretical questions you may face.
How to Approach Exam Questions
Successfully answering questions in a clinical assessment requires a methodical and strategic approach. Rather than rushing through the questions, it’s important to take the time to carefully analyze each one. Understanding the underlying concepts and applying your knowledge in a logical way will greatly improve your ability to choose the correct answers and perform well.
1. Read Each Question Carefully
Before jumping to conclusions, ensure you fully understand the question. Pay close attention to the wording and identify any key terms that are central to the query. Take note of words like “always,” “never,” or “most commonly” as they can alter the meaning of the question significantly. Often, a clear understanding of the question itself can point you in the right direction.
2. Eliminate Clearly Incorrect Options
For multiple-choice questions, a great strategy is to first eliminate the answers that are obviously incorrect. This narrows your options and increases your chances of selecting the correct one. If you’re left with two possible answers, carefully consider the differences between them, paying attention to fine details like drug interactions or contraindications that might distinguish the right choice.
| Common Mistakes to Avoid | How to Avoid Them |
|---|---|
| Skipping questions too quickly | Take your time and review each question fully before answering. |
| Overthinking | Stick to your first instinct unless you’re sure another answer is better. |
| Not managing time effectively | Set time limits for each section and move on if you’re stuck on a question. |
By employing these strategies, you can tackle questions with confidence and accuracy, leading to a stronger performance on your test.
Memory Techniques for Drug Names
Remembering the names of medications can be a challenging task, but employing specific memory techniques can significantly improve recall. Associating drug names with familiar concepts, patterns, or visuals helps reinforce retention and makes it easier to retrieve information during assessments. Utilizing mnemonic devices, repetition, and visualization techniques can turn memorization into a more manageable and even enjoyable process.
1. Mnemonic Devices
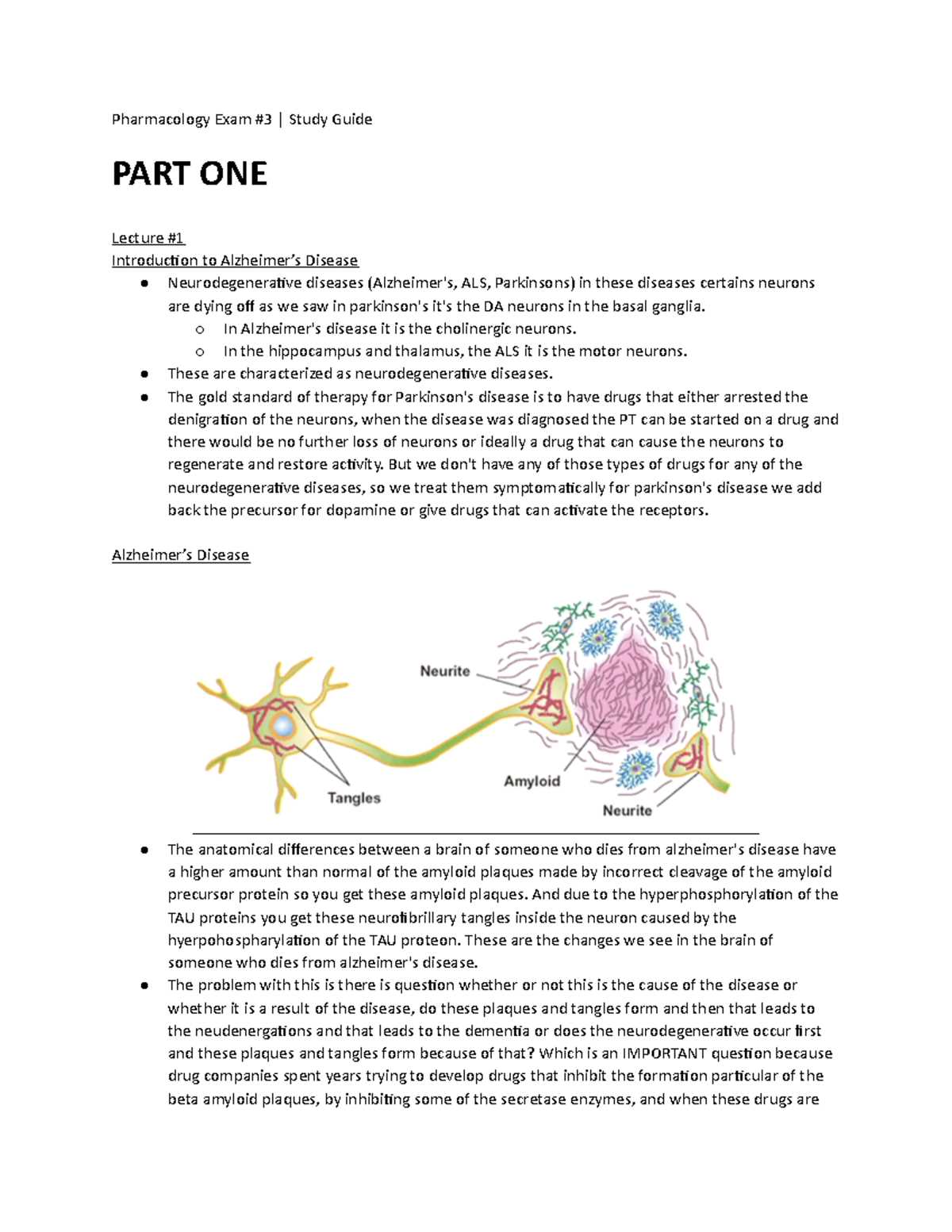
Creating mnemonics is a powerful tool for memorizing drug names. These memory aids help link a drug’s name to an easy-to-remember phrase, image, or acronym. Here are some tips for using mnemonics:
- Acronyms: Create a word or phrase where each letter stands for a part of the drug name. For example, “ACE” for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (e.g., enalapril, lisinopril).
- Rhymes or Songs: Turn complex names into short rhyming phrases or songs. This method taps into your auditory memory, which can make the names stick.
- Chunking: Break the drug names into smaller, more manageable parts. By grouping related drugs together based on their class or mechanism of action, you can recall them more easily.
2. Visualization and Association
Another effective technique is associating a drug’s name with a visual image or a real-world scenario. This mental picture helps solidify the drug’s identity and its function. Here are some examples:
- Visual Imagery: Imagine a drug’s name being represented as an object or scene that symbolizes its effect. For example, you might visualize “aspirin” as a pain-relieving pill with a bandage to emphasize its pain relief action.
- Storytelling: Create a short story where the drug’s name plays a central role in the plot. Linking the drug name to a narrative makes it more memorable.
By combining these techniques, you can improve your ability to recall drug names and their associated information quickly and accurately when needed.
Clinical Applications of Pharmacology
Understanding how medications are used in clinical practice is essential for optimizing patient care. The clinical application of drugs involves not only knowing how to prescribe them but also understanding their effects, potential side effects, and how they interact with other treatments. Proper use of these drugs can prevent, manage, and treat a wide range of conditions, making it crucial for healthcare professionals to grasp both the theoretical and practical aspects of drug use.
1. Treatment of Chronic Conditions
Medications play a pivotal role in the management of chronic conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. By understanding the appropriate classes of drugs and their mechanisms, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans that improve patient outcomes. Medications can help regulate blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of complications associated with these diseases.
2. Acute Medical Interventions
In emergency settings, quick decisions about drug administration can be life-saving. From pain management in trauma cases to the rapid administration of anticoagulants for stroke prevention, knowledge of drug actions and dosages is crucial for healthcare professionals who must act swiftly and accurately. The right medications can stabilize patients and prevent further damage in critical situations.
| Condition | Common Drugs Used | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers | Reduce blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and reducing heart rate. |
| Diabetes | Insulin, metformin | Regulate blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity or providing insulin. |
| Heart Failure | Diuretics, angiotensin receptor blockers | Improve heart function and reduce fluid retention. |
By understanding the clinical applications of various drugs, healthcare providers are better equipped to make informed decisions that directly impact patient health and recovery. Proper use ensures therapeutic success and minimizes risks associated with treatment.
Reviewing Pharmacology in Clinical Practice
In clinical practice, a solid understanding of drug mechanisms, dosages, and therapeutic effects is essential for making informed decisions that affect patient outcomes. Professionals need to continuously review and update their knowledge of how medications work in the body, as well as the potential side effects and interactions that may arise in diverse clinical scenarios. This ongoing review ensures the safe and effective use of drugs across various patient populations and medical conditions.
1. Importance of Regular Review

Regularly revisiting key drug classes, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic guidelines helps healthcare providers stay up-to-date with new developments and evidence-based practices. This review process is crucial for maintaining a high level of competency and ensuring that patient care is based on the latest clinical knowledge.
- Minimizing errors: Frequent reviews can prevent mistakes, such as incorrect drug prescriptions or overlooked side effects.
- Optimizing treatment plans: Ongoing education ensures that healthcare providers are aware of the most effective medications for various conditions.
- Managing drug interactions: Understanding the interactions between drugs helps avoid adverse effects that could compromise patient safety.
2. Methods for Reviewing Key Information
There are several strategies that healthcare professionals can use to review and reinforce their knowledge of drug therapy in clinical practice:
- Case Studies: Reviewing real-life cases and discussing treatment plans with colleagues or mentors is an effective way to integrate theoretical knowledge into clinical decision-making.
- Continuing Education: Participating in workshops, seminars, and online courses allows healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest advancements in drug therapy.
- Reference Materials: Using updated drug formularies and clinical guidelines as quick references can support informed decision-making during patient care.
By incorporating these review techniques into daily practice, healthcare professionals can ensure that their drug knowledge remains relevant, enhancing patient safety and treatment outcomes.
Strategies for Answering Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions (MCQs) are a common assessment format that requires strategic thinking and effective test-taking techniques. The goal is not only to recall facts but to apply knowledge in a way that allows for the best possible answer selection. By using specific strategies, individuals can improve their performance, reduce anxiety, and maximize their chances of selecting the correct responses.
1. Understanding the Question and Key Words
Before jumping to the answer choices, it is crucial to fully understand the question. Pay attention to key terms that may point to specific concepts or actions. Look for words like “most,” “best,” or “least,” which can alter the focus of the question. By clarifying what is being asked, you can eliminate irrelevant or incorrect options more easily.
- Look for qualifiers: Words such as “always,” “never,” “sometimes,” and “usually” can indicate the degree of certainty the question is asking about.
- Identify the core concept: Focus on what the question is really testing, whether it’s a specific process, effect, or principle.
2. Eliminate Incorrect Choices
Often, multiple choice questions include several obviously incorrect or irrelevant options. By quickly crossing out these choices, you increase your chances of selecting the correct answer. Eliminate choices that are too extreme or unrelated to the question, which may help narrow down the possibilities significantly.
- Rule out absolutes: Be cautious of answers that use extreme language (e.g., “always” or “never”) unless you’re certain it’s accurate.
- Look for patterns: In some cases, if two choices are similar or contradict each other, one is likely the correct answer.
By applying these strategies, test-takers can approach MCQs with greater confidence and accuracy, leading to better results on assessments and evaluations.
How to Organize Your Study Materials
Effective organization of study materials is crucial for successful learning and retention. When materials are systematically arranged, it becomes easier to access relevant information quickly and efficiently. This approach minimizes stress, ensures that no key concepts are overlooked, and helps create a clear path to mastering the material.
1. Categorize Your Resources
Start by grouping your materials based on the topics you need to review. This can include textbooks, notes, practice questions, and reference guides. By dividing your resources into manageable sections, you can focus on one area at a time without feeling overwhelmed.
- Group by subject: For example, organize materials related to different drug classes or treatment methods separately.
- Separate theory from practice: Keep theoretical concepts apart from application-based materials, like case studies or clinical scenarios.
2. Create a Study Schedule
Once your materials are organized, create a detailed study schedule that allocates specific time for each topic. This ensures that you cover all areas evenly and avoid cramming.
- Prioritize challenging topics: Allocate more time to areas that you find difficult, ensuring you have sufficient time to grasp those concepts.
- Set realistic goals: Break down study sessions into smaller, manageable tasks to prevent burnout.
- Review regularly: Set aside time for periodic reviews to reinforce your understanding and identify any weak spots.
3. Use Digital Tools
Digital tools, such as apps and cloud storage, can significantly streamline the organization process. Use these tools to store, access, and even share materials with peers.
- Cloud storage: Keep all your study documents in one easily accessible location.
- Note-taking apps: Use apps like Evernote or OneNote to organize your notes and keep track of important concepts.
By following these steps and keeping your study materials well-organized, you can optimize your preparation and approach your studies with confidence and clarity.
Pharmacology and Patient Safety Considerations
Ensuring patient safety is a critical aspect of medical practice, particularly when it comes to the administration of therapeutic substances. Understanding the potential risks and taking preventive measures are essential for minimizing adverse effects and ensuring the safe use of treatment options. This section highlights key safety considerations that must be kept in mind during the use of medications and their management in clinical settings.
One of the most important aspects is proper dosage. Incorrect dosing, whether under or over administration, can lead to severe complications. For this reason, it is essential for healthcare professionals to adhere to recommended guidelines and adjust treatments based on individual patient needs. Monitoring and regular assessments also play a significant role in preventing errors and ensuring safe therapeutic outcomes.
Key Considerations for Safe Medication Use
Healthcare providers must be vigilant when prescribing or administering drugs. The following points should be prioritized to minimize risks:
- Correct Identification: Always ensure that the right patient receives the prescribed treatment by confirming patient identity before any administration.
- Allergic Reactions: Consider potential allergies and monitor for any adverse reactions, particularly when introducing new medications.
- Drug Interactions: Be aware of possible interactions between prescribed medications, which can lead to increased side effects or reduced efficacy.
Patient Education and Communication

In addition to careful administration, educating patients is key to preventing medication errors. Clear communication about how and when to take their medications, as well as any potential side effects, ensures that patients are well-informed and able to follow treatment regimens accurately. It is also important to encourage patients to ask questions and report any concerns regarding their treatment.
- Clear Instructions: Provide easy-to-understand directions on the proper use of medications.
- Monitoring for Side Effects: Teach patients how to recognize and report any adverse effects they experience.
By following these safety protocols and maintaining open communication, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the risk of errors and improve patient outcomes in clinical settings.
Managing Stress Before the Exam
Managing stress before an important assessment is crucial to performing well and maintaining mental clarity. The pressure to perform can lead to anxiety, which might hinder cognitive function and focus. This section explores effective strategies to reduce stress and improve preparedness in the days leading up to the test.
One of the first steps to managing stress is recognizing its symptoms and implementing strategies that can promote relaxation and mental focus. Developing a well-organized study schedule, incorporating relaxation techniques, and ensuring adequate rest are essential components in preparing for any high-stakes test.
Effective Techniques for Stress Reduction
To manage stress effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Focused, deep breathing can help calm the nervous system and reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters, helping to alleviate stress.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can improve concentration, increase resilience to stress, and foster a sense of calm.
Building a Productive Routine
Establishing a routine is vital for minimizing last-minute stress. By creating a structured study schedule, you can avoid cramming and ensure that all topics are covered effectively. The routine should include breaks for relaxation and time for physical activity to maintain energy levels.
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Review key concepts |
| 9:00 AM – 9:15 AM | Short break and deep breathing |
| 9:15 AM – 11:00 AM | Study practice questions |
| 11:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Physical activity or walk |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch and relaxation |
| 1:00 PM – 3:00 PM | Review weak areas |
By establishing a well-balanced routine and incorporating stress-reducing techniques, you can optimize your mental state and be better prepared for the upcoming assessment. Reducing stress is not just about managing the immediate feelings of anxiety but also about setting up a sustainable approach to learning and test-taking that enhances performance.
Assessment Format Overview
Understanding the structure of an upcoming assessment is key to efficient preparation. Knowing what to expect in terms of question types, content coverage, and time constraints can help tailor your study approach and reduce anxiety. This section provides an overview of the typical format of such a test, helping you to prepare with confidence.
The assessment is typically structured into different sections, each focusing on various aspects of the material. These sections may include multiple-choice questions, short answer items, and practical case studies. Each question type assesses your ability to recall, apply, and analyze key concepts, making it essential to approach each section with the appropriate strategy.
The test format often includes a combination of factual recall and scenario-based questions. Some sections may require you to select the correct response from a list of options, while others might involve short written answers where you need to demonstrate your reasoning. Time management is crucial, as you will need to balance speed and accuracy when tackling each type of question.
Building a Study Schedule
Creating an effective study plan is crucial to achieving success when preparing for any assessment. A well-structured schedule helps you allocate time efficiently, prioritize important topics, and avoid last-minute cramming. By breaking your study sessions into manageable chunks, you can stay on track and reduce stress as the test date approaches.
Set Realistic Goals

Start by determining the number of days or weeks you have before the test and dividing that time into specific study blocks. Identify the key areas you need to focus on and set realistic goals for each session. Make sure to factor in breaks and time for revision, as consistent review is essential for long-term retention.
Stay Flexible and Consistent
While sticking to your schedule is important, it’s equally important to remain flexible. Unexpected events or challenges may arise, so it’s essential to adjust your study times as needed. Consistency is key, so try to study at the same time each day, making it a habit that fits seamlessly into your routine.
Tip: Prioritize challenging subjects or topics that require more focus, and make sure to revisit them multiple times leading up to the assessment. This way, you can ensure that you’ve fully grasped the most difficult material.
Maintaining Focus and Motivation
Staying focused and motivated during the study process can be a challenge, but it is essential for successful preparation. With the right strategies in place, you can maintain a steady level of concentration and enthusiasm throughout your preparation period. The key is to create an environment and mindset that encourages consistent progress and minimizes distractions.
Create a Positive Study Environment
A well-organized and quiet study space can significantly boost your ability to stay focused. Eliminate distractions by turning off your phone or using apps designed to block social media during study sessions. Ensure your study area is well-lit and equipped with all the materials you need, so you don’t waste time looking for resources during study time.
Set Clear Milestones and Rewards
Having clear goals can keep you motivated throughout your study period. Break your overall study plan into smaller, achievable milestones. Each time you reach a goal, reward yourself with something small, such as a short break, a snack, or a brief walk. These rewards provide positive reinforcement and help maintain your drive to keep going.
Tip: Remind yourself of the bigger picture–why you are studying and the benefits it will bring. Whether it’s achieving personal growth, advancing in your career, or reaching academic success, keeping the end goal in mind can help sustain your motivation.