
As you approach the final stage of your networking certification journey, understanding the essential concepts and protocols is crucial. With a clear focus on critical areas of networking, you can better navigate the challenges of the test and increase your chances of success.
Familiarizing yourself with key networking topics, such as IP addressing, routing, and security, will give you a comprehensive foundation for the assessment. Practical experience combined with theoretical knowledge is the best approach to mastering the material and feeling confident on test day.
In this guide, we will explore the most important subjects to review, along with tips and strategies to ensure you’re fully prepared to tackle the challenges ahead. Preparation is the key to unlocking your potential and achieving certification success.
CCNA2 v6 Final Exam Overview

Preparing for the certification assessment in networking requires a thorough understanding of key concepts that encompass a range of essential technologies. The evaluation is designed to test your knowledge of networking fundamentals, protocols, and troubleshooting skills that are vital for real-world network environments.
Core Areas of Focus
The test covers a variety of networking topics, each contributing to your ability to design, configure, and manage networks effectively. Key areas to focus on include:
- Routing protocols and their configurations
- Switching concepts and VLANs
- Network security fundamentals and configurations
- Addressing schemes and subnetting
- Network troubleshooting methods and best practices
Exam Structure and Format
Understanding the structure of the test is crucial for successful preparation. The assessment typically consists of multiple types of questions designed to evaluate your practical and theoretical knowledge. These may include:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Drag-and-drop exercises
- Simulation-based tasks
Familiarizing yourself with these question formats will help improve your response time and accuracy on test day.
Key Topics to Study for Success
To ensure you are well-prepared for the networking certification, focusing on the most important concepts will help you build a solid foundation. Mastering these topics will not only improve your performance on the assessment but also strengthen your skills for practical network management tasks.
Essential Areas of Focus

Concentrate on these core subjects to ensure you cover all necessary material:
- IP Addressing and Subnetting – Understanding how IP addresses work and how to efficiently divide networks is crucial for configuring devices and managing network traffic.
- Routing Protocols – Familiarize yourself with the configurations and behaviors of dynamic routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, and RIP.
- Network Security – Learn about access control, firewall settings, VPNs, and common security threats to safeguard network infrastructure.
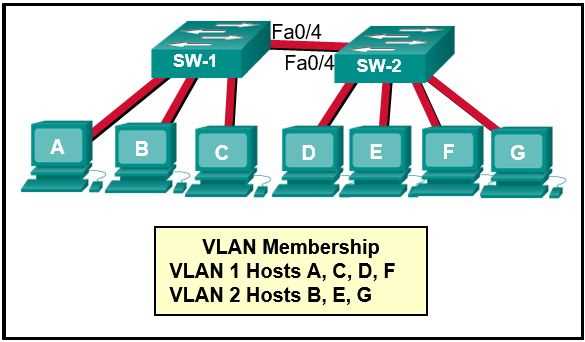
- VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing – Understand how VLANs operate and how to configure inter-VLAN routing for seamless communication across networks.
- Switching Concepts – Grasp the basics of switch operation, port security, and troubleshooting techniques to resolve common issues.
Practical Application and Labs
In addition to theoretical knowledge, hands-on practice is vital. Use lab environments to practice configuring devices, testing connectivity, and troubleshooting common network problems. This will give you real-world experience and prepare you for simulation questions on the test.
Understanding Routing and Switching Protocols
Routing and switching protocols are fundamental to the operation of any network. These protocols ensure that data flows efficiently across devices and networks, enabling communication between different systems. By understanding how these protocols work and how they are configured, you gain the ability to design, manage, and troubleshoot network infrastructures effectively.
Routing protocols are responsible for determining the best path for data to travel between different networks. They make decisions based on factors such as network topology, link speed, and congestion. Common routing protocols include OSPF, EIGRP, and RIP, each with its own strengths and application areas.
Switching protocols, on the other hand, operate within a single network and focus on moving data between devices on the same network segment. The primary goal is to ensure that devices within a network can communicate without unnecessary delays. VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) are often used in conjunction with switching protocols to segment traffic and improve network efficiency.
Mastering the configuration and troubleshooting of both routing and switching protocols is critical for building robust and scalable network infrastructures. Hands-on practice with real-world scenarios can help solidify your understanding of these concepts and improve your network management skills.
TCP/IP Model and OSI Layers
Understanding the layered architecture of networking protocols is essential for troubleshooting, configuring, and optimizing communication between devices. Both the TCP/IP model and the OSI model provide frameworks that help break down complex networking functions into manageable layers, each responsible for specific tasks in the communication process.
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model consists of seven layers, with each layer serving a distinct role in the transmission of data. Understanding the functions of each layer helps you identify where problems may occur in the network and how to resolve them efficiently.
- Layer 7 – Application: Provides network services directly to end-users and applications.
- Layer 6 – Presentation: Responsible for data translation, encryption, and compression.
- Layer 5 – Session: Manages sessions and controls the dialog between devices.
- Layer 4 – Transport: Ensures reliable data transfer and error correction.
- Layer 3 – Network: Handles routing and addressing to ensure data reaches its destination.
- Layer 2 – Data Link: Manages node-to-node communication and error detection.
- Layer 1 – Physical: Deals with the actual hardware transmission of data over the network medium.
In contrast, the TCP/IP model condenses these seven layers into four main layers, offering a more simplified approach to networking. The layers of the TCP/IP model include:
- Application: Combines OSI’s Application, Presentation, and Session layers.
- Transport: Manages end-to-end communication and data reliability.
- Internet: Focuses on routing, addressing, and packet forwarding (equivalent to OSI’s Network layer).
- Link: Handles data link and physical transmission processes.
Familiarity with both models helps you understand how data travels across networks, and enables you to design and troubleshoot network communication more effectively.
Subnetting Made Simple
Subnetting is a crucial skill for anyone working with networks. It involves dividing an IP address range into smaller, more manageable segments, allowing for better organization, improved security, and efficient use of available addresses. Understanding subnetting is essential for configuring networks and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
The process of subnetting can seem complex at first, but breaking it down into simple steps makes it more manageable. By learning how to calculate subnet masks and understanding the relationship between network addresses and host addresses, you can easily apply this knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Key Concepts of Subnetting
- IP Addressing: An IP address is divided into two parts: the network portion and the host portion. Subnetting allows you to adjust the size of each portion to fit the network’s needs.
- Subnet Mask: The subnet mask is used to define which part of the IP address refers to the network and which part refers to the host.
- Network and Broadcast Addresses: Each subnet has a network address (used to identify the subnet) and a broadcast address (used for sending messages to all devices within the subnet).
Steps to Subnetting
Here’s a simple approach to subnetting:
- Determine the number of required subnets: Start by figuring out how many subnets are needed for your network.
- Find the appropriate subnet mask: Calculate the subnet mask based on the required number of subnets.
- Divide the IP address range: Use the subnet mask to break the IP address range into smaller subnets, ensuring that each subnet has enough IP addresses for its devices.
- Assign IP addresses: Finally, assign IP addresses to the devices in each subnet, keeping track of the network and broadcast addresses.
Once you get the hang of these steps, subnetting becomes a straightforward process. Practicing with different scenarios will further solidify your understanding and improve your confidence when applying subnetting in real-world networks.
VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) allow network administrators to segment a physical network into multiple logical networks, improving organization, security, and traffic management. By dividing a network into VLANs, devices within a VLAN can communicate freely, while traffic between different VLANs requires additional configuration to route the traffic effectively.
Inter-VLAN routing enables communication between devices in different VLANs. Without proper routing, devices in separate VLANs cannot exchange information. This is where routers or layer 3 switches come into play, facilitating the communication between VLANs through routing protocols or manual configuration.
VLAN Configuration Basics

Setting up VLANs typically involves configuring switches to assign ports to specific VLANs. Each VLAN is identified by a unique VLAN ID, and traffic is tagged with this ID as it moves through the network.
Inter-VLAN Routing Configuration
Once VLANs are set up, inter-VLAN routing is required to allow communication between them. There are two main methods to achieve this:
- Router-on-a-Stick: A single physical router interface is used, and subinterfaces are created for each VLAN.
- Layer 3 Switch: A Layer 3 switch is configured to perform routing directly between VLANs without the need for a separate router.
Example of Inter-VLAN Routing Configuration
Below is a simple table showing how to configure inter-VLAN routing using the “Router-on-a-Stick” method:
| Device | Interface | VLAN | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Router | GigabitEthernet0/1.10 | VLAN 10 | 192.168.10.1 |
| Router | GigabitEthernet0/1.20 | VLAN 20 | 192.168.20.1 |
| Switch | GigabitEthernet0/1 | VLAN 10 | — |
| Switch | GigabitEthernet0/2 | VLAN 20 | — |
In this example, the router uses subinterfaces to route between VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, with each VLAN having its own unique IP address. The switch ports are assigned to the respective VLANs, ensuring proper segmentation and communication.
With proper configuration of VLANs and inter-VLAN routing, network performance and security can be greatly enhanced, enabling better traffic management and reducing unnecessary broadcasts across the network.
Understanding Network Security Fundamentals
Network security is a critical component in protecting data, devices, and systems from unauthorized access, attacks, and other threats. It involves a combination of tools, policies, and procedures designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information as it is transmitted across the network. In today’s interconnected world, robust security measures are essential for maintaining a safe and reliable network environment.
Effective network security requires a layered approach, incorporating multiple defenses to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. This approach often involves firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and access control mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users can access network resources.
Core Principles of Network Security
The core principles of network security include:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Integrity: Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and not tampered with during transmission.
- Availability: Ensuring that network resources are accessible and functional when needed by authorized users.
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users, devices, or applications before granting access to network resources.
Common Security Threats
Networks are vulnerable to various types of security threats that can disrupt operations or compromise sensitive data. Some common threats include:
| Threat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to systems or networks. |
| Phishing | Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by impersonating legitimate entities. |
| DDoS Attacks | Distributed denial-of-service attacks aim to overwhelm and disrupt network services. |
| Man-in-the-Middle Attacks | Interception and alteration of communication between two parties without their knowledge. |
By understanding these fundamental principles and recognizing common threats, network administrators can take proactive steps to safeguard their network and ensure a secure computing environment for all users. Implementing proper security measures helps to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and ensures business continuity.
Access Control Lists and NAT Concepts
Network security and address management are essential aspects of modern networking. Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Network Address Translation (NAT) are two fundamental concepts used to control and manage network traffic effectively. ACLs help filter traffic based on predefined rules, while NAT modifies the IP address information in packet headers to facilitate communication between different networks.
ACLs play a crucial role in enhancing security by controlling what traffic can pass through a router or switch. By defining rules based on source/destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports, ACLs help block or allow specific traffic based on these criteria. NAT, on the other hand, is widely used for address conservation and security, as it enables multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address when accessing external networks like the internet.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs are used to filter network traffic by defining permit or deny rules based on specific criteria. They are typically applied at the router or firewall level to control access to resources and services.
- Standard ACLs: These filters only check the source IP address of packets and allow or deny traffic based on that alone.
- Extended ACLs: These provide more detailed filtering by evaluating multiple packet attributes, such as source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports.
- Named ACLs: These allow users to assign a descriptive name to the ACL for easier management and organization.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT allows multiple devices in a private network to communicate with external networks using a single public IP address. It helps conserve IP address space and provides an additional layer of security by hiding internal network addresses.
- Static NAT: Maps a private IP address to a specific public IP address on a one-to-one basis. This is useful for services that need to be accessible from outside the network.
- Dynamic NAT: Uses a pool of public IP addresses and dynamically assigns one of these addresses to a device when it needs to communicate externally.
- Port Address Translation (PAT): Often called “NAT overload,” this method allows many internal devices to share a single public IP address by using different port numbers.
By combining ACLs and NAT, network administrators can enhance both security and address management, ensuring that only authorized traffic can pass through a network while efficiently handling IP address allocation for internal devices.
OSPF and EIGRP Protocols Explained
Routing protocols are essential for ensuring that data can efficiently travel across networks, dynamically determining the best paths to reach destination devices. Two widely used interior gateway protocols (IGPs) are OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol). Both are used for routing decisions within an autonomous system but operate based on different principles and mechanisms. Understanding these protocols helps network administrators optimize routing strategies and improve network efficiency.
OSPF and EIGRP are both designed to handle large-scale networks, but they differ in their approach to route calculation, convergence times, and scalability. OSPF is a link-state protocol, whereas EIGRP is a hybrid protocol that combines characteristics of both distance-vector and link-state protocols. These differences influence their performance and suitability in various network environments.
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)

OSPF is a link-state protocol that calculates the shortest path first (SPF) using the Dijkstra algorithm. It is commonly used in large enterprise networks and supports a hierarchical design using areas to optimize routing performance.
- Link-State Advertisements (LSAs): OSPF routers share information about their interfaces and neighbors via LSAs, which helps build a complete network map.
- Area Design: OSPF allows for network segmentation into areas, reducing routing table size and enhancing scalability.
- Fast Convergence: OSPF responds quickly to network changes by recalculating the SPF tree and propagating updates throughout the network.
- Open Standard: OSPF is an open standard, making it compatible across different vendors’ equipment.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary hybrid protocol that combines the best aspects of link-state and distance-vector protocols. It is known for its fast convergence and efficient use of network resources.
- Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL): EIGRP uses DUAL to calculate the best paths and provide loop-free routing. It ensures fast convergence and reliable network routing.
- Support for Multiple Protocols: EIGRP supports multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IP, IPX, and AppleTalk, making it versatile in diverse network environments.
- Partial Updates: Unlike distance-vector protocols, EIGRP only sends updates when there is a change in the network, reducing bandwidth usage.
- Fast Convergence: EIGRP offers rapid convergence due to its ability to maintain backup routes and quickly switch to an alternative route if the primary one fails.
While both OSPF and EIGRP have their strengths, the choice between them often depends on the network’s size, the desired scalability, and vendor requirements. OSPF is suitable for large-scale networks that require a robust, vendor-neutral solution, while EIGRP is preferred in Cisco-dominant environments due to its performance and scalability advantages.
Basic Troubleshooting Techniques
When network issues arise, it’s essential to have a systematic approach to identify and resolve the problem efficiently. Troubleshooting involves analyzing network behavior, isolating issues, and applying corrective actions based on the symptoms observed. The goal is to restore normal network functionality as quickly as possible while minimizing downtime and disruption.
Effective troubleshooting relies on a combination of understanding network design, using diagnostic tools, and following a step-by-step process to narrow down potential causes. Whether dealing with connectivity problems, slow performance, or device failures, a structured approach ensures that you address the root cause rather than just temporary symptoms.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
The troubleshooting process can be broken down into a few key steps to simplify the approach and ensure all possible causes are considered:
- Identify the Problem: Gather as much information as possible about the issue. Determine when the problem began, which devices are affected, and whether the issue is isolated or widespread.
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure all cables are securely connected and that no hardware malfunctions are present. Check for issues such as loose cables or unplugged devices.
- Ping and Traceroute: Use tools like ping and traceroute to test connectivity and determine where the traffic is getting blocked or delayed along the network path.
- Check Configuration Settings: Review device configurations for potential misconfigurations, such as incorrect IP addresses, subnet masks, or routing entries that could cause disruptions.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Leverage network monitoring tools, such as Wireshark or NetFlow, to gather deeper insights into network traffic and identify anomalies.
- Isolate the Cause: Once the symptoms are observed and initial checks are made, isolate the affected component (e.g., router, switch, server, or cable) and test it in isolation to determine the cause.
- Resolve and Verify: Implement the corrective action, whether it’s reconfiguring a device, replacing faulty hardware, or adjusting routing protocols. After resolution, verify that the issue is resolved by testing network functionality again.
By following these fundamental troubleshooting steps, network administrators can diagnose and resolve issues effectively. It’s important to remain methodical and patient, as solving network problems often requires a process of elimination and careful analysis of all variables involved.
Lab Preparation and Hands-On Practice
Practical experience is a vital part of mastering networking concepts and gaining the confidence needed to troubleshoot and configure devices in real-world scenarios. Lab preparation allows you to simulate network configurations, test different protocols, and gain hands-on experience with tools and devices. The combination of theoretical knowledge and practical application is essential for solidifying your understanding and improving your problem-solving skills.
Engaging in lab exercises helps reinforce key concepts such as IP addressing, routing, VLANs, and network security. Hands-on practice provides an opportunity to experiment with network configurations, test different setups, and witness how changes affect network behavior. This experience not only prepares you for technical challenges but also boosts your ability to think critically under pressure.
Setting Up Your Lab Environment
Before diving into hands-on practice, setting up a proper lab environment is essential. Whether you’re using physical hardware or virtualized environments, having the right tools in place will allow you to simulate real-world network conditions and troubleshoot effectively.
- Choose the Right Equipment: Ensure you have the necessary routers, switches, and end devices (e.g., computers, servers) to build various network scenarios.
- Use Virtual Labs: Software platforms like Cisco Packet Tracer, GNS3, or VIRL offer virtualized environments that allow you to practice without needing physical equipment.
- Network Design: Plan your network topology in advance. Start with a simple design and expand it as you learn more about complex configurations.
- Testing Tools: Utilize tools such as ping, traceroute, and Wireshark to diagnose issues and observe network traffic.
Effective Practice Techniques
When it comes to hands-on practice, the goal is not just to complete exercises but to truly understand the reasoning behind each configuration and action. Here are some effective strategies for maximizing the benefit of lab work:
- Start with Basics: Begin by practicing fundamental tasks like configuring IP addresses, testing connectivity, and troubleshooting common issues like network loops and routing errors.
- Simulate Real-World Scenarios: Set up various network topologies and configure them as you would in a real business environment. Test everything from simple LANs to complex enterprise networks.
- Document Your Work: Keep track of configurations and changes made during lab sessions. Documentation will help you troubleshoot more efficiently and track your progress.
- Experiment with Failures: Introduce intentional faults or misconfigurations into your network and practice diagnosing and fixing them. This will prepare you for real-life troubleshooting situations.
By dedicating time to proper lab preparation and hands-on practice, you will significantly enhance your skills and deepen your understanding of networking principles. This practical experience is key to excelling in real-world network environments and mastering network management tasks.
Reviewing Common Exam Questions
One of the most effective ways to prepare for any certification assessment is to review and practice with common questions. These questions not only help familiarize you with the format of the assessment but also highlight recurring topics and concepts that are frequently tested. By practicing with these types of questions, you can sharpen your understanding of core networking principles and identify areas where further study is needed.
Reviewing common questions gives you insight into the types of scenarios and problems you may face during the actual test. It allows you to apply your theoretical knowledge in a practical context, ensuring you are ready to tackle various challenges on the assessment. Understanding the structure of these questions and practicing problem-solving techniques will help you approach the test with greater confidence and efficiency.
Types of Commonly Asked Questions
The questions on the assessment often cover a range of topics that test your comprehension of networking concepts, configurations, and troubleshooting. Here are some common question types you may encounter:
- Multiple Choice: These questions require you to choose the correct answer from a list of options. They typically focus on theoretical knowledge, protocols, and best practices.
- Configuration Tasks: These questions present a network scenario where you need to apply your knowledge to configure devices, IP addresses, routing protocols, or VLANs.
- Scenario-Based Questions: These questions simulate real-world situations and require you to identify and solve problems using your technical understanding. They often involve troubleshooting or network optimization tasks.
- Drag-and-Drop: In these questions, you are asked to match the correct items, such as network devices, protocols, or commands, based on the scenario presented.
Strategies for Reviewing Common Questions
To effectively review common questions, you need to employ a strategy that allows you to assess your strengths and weaknesses, while reinforcing key concepts. Here are some tips:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice with sample questions helps you become familiar with the content and test format. This also improves your time management during the assessment.
- Understand the Reasoning: Don’t just memorize answers–focus on understanding why a particular answer is correct. This deepens your comprehension and helps in troubleshooting real-world scenarios.
- Review Correct and Incorrect Answers: After answering practice questions, review both correct and incorrect responses. Identify why a certain answer was right or wrong to ensure you grasp the underlying concepts.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Practice under timed conditions to simulate the pressure of the actual assessment. This will help you manage your time effectively and reduce stress on the day of the test.
By reviewing common questions and practicing regularly, you can improve both your theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring you are well-prepared for the assessment. This focused approach will help you approach the test with confidence and achieve a successful outcome.
Time Management During the Exam
Efficient time management is one of the most critical skills during any assessment. Knowing how to allocate time appropriately across different sections of the test can significantly impact your performance. Proper time management ensures that you have enough time to thoroughly read and answer each question, while also leaving room for review and troubleshooting in case of difficulties. Without it, you may find yourself rushing through questions or leaving some unanswered, which can lower your score.
It is essential to develop a strategy for approaching the assessment that allows for maximum efficiency. Understanding the structure and time requirements of each section can help you plan your pace effectively. In this section, we will discuss practical time management strategies to help you stay on track and complete the assessment confidently.
Key Strategies for Effective Time Management
- Understand the Test Structure: Before starting the assessment, familiarize yourself with the number of questions, types of questions (multiple choice, scenario-based, etc.), and the time allocated for each section. This will allow you to allocate your time accordingly.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Begin with the questions you find easiest. This boosts your confidence and ensures you don’t waste time on questions you already know the answers to.
- Time per Question: Set a reasonable time limit for each question based on its difficulty. For instance, spend more time on scenario-based or configuration questions, while answering multiple choice questions more quickly.
- Avoid Overthinking: If you’re stuck on a question, make your best guess and move on. Spending too much time on one question can cause you to run out of time for others. You can always return to tough questions later.
- Use the “Mark for Review” Feature: Many assessments provide a feature to mark questions for later review. If you’re unsure of an answer, mark it and move on. Come back to it once you’ve completed the rest of the test.
Creating a Time Management Plan

Having a clear plan of action for the time you spend on each section of the test is crucial for staying on track. Below is a sample time management plan you can follow during your assessment:
| Section | Time Allocation |
|---|---|
| Introduction/Instructions | 5 minutes |
| Multiple Choice Questions | 1 minute per question |
| Configuration/Scenario-Based Questions | 3-5 minutes per question |
| Review and Recheck | 10-15 minutes |
This time plan serves as a guideline and can be adjusted based on the complexity of the questions. The important thing is to keep a steady pace, avoid rushing, and leave time to review your answers.
By managing your time effectively during the assessment, you can ensure that you have enough time to showcase your knowledge, solve problems efficiently, and check your work for any potential errors. This strategy is key to achieving success in any technical assessment.
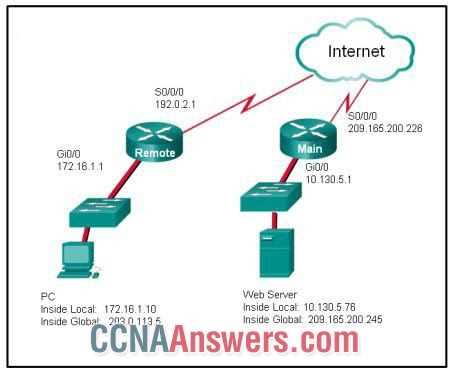
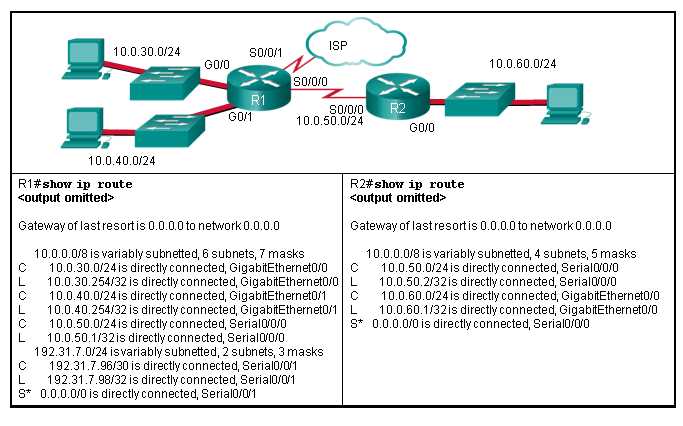
Understanding Routing Tables and Addressing
Routing tables and addressing are fundamental concepts in network communication. A routing table is a key component in determining how data packets travel across a network, helping devices understand where to send information based on destination addresses. Each router within a network uses these tables to make decisions about forwarding data to the correct next hop or endpoint. In this section, we will explore how routing tables function, the role of addressing in these processes, and how they work together to ensure efficient data transfer across networks.
Effective addressing is essential for ensuring that data packets are directed to the correct destination. Without a properly configured routing table and accurate addressing, network communication could become inefficient or even fail altogether. Routing tables contain information about network paths, and these tables are built and updated dynamically as devices exchange data. Understanding the basics of routing tables and addressing is crucial for network design, management, and troubleshooting.
To understand how routing tables work, it’s important to recognize the role of network addressing, which typically involves the use of IP addresses. These unique identifiers are essential for differentiating devices on the network, enabling routers to make accurate forwarding decisions. Let’s break down the key components and how they contribute to the overall routing process.
Study Materials and Resources
When preparing for any technical certification, it is important to have the right materials and resources at your disposal. These resources help you understand the underlying concepts, reinforce your learning, and provide practice opportunities to test your knowledge. In this section, we will explore various tools and study aids available to help you succeed, including textbooks, online courses, practice exams, and hands-on labs.
Choosing the best study materials can make a significant difference in how efficiently you can prepare. Comprehensive study guides, detailed video tutorials, and practical labs are all valuable resources that allow you to deepen your understanding of key topics. Whether you prefer structured learning paths or self-paced practice, it’s important to use a combination of resources to cover all aspects of the subject matter.
Recommended Study Resources
| Resource Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Books | Comprehensive guides that cover the theory and concepts in detail. | “Networking Essentials”, “Routing and Switching Study Guide” |
| Online Courses | Interactive courses that provide video lessons and exercises. | Udemy, LinkedIn Learning |
| Practice Tests | Simulated exams that mimic the real test environment. | Exam-labs, Boson |
| Labs | Hands-on practice environments to reinforce your skills. | Packet Tracer, GNS3 |
Where to Find Reliable Study Materials
Many online platforms offer high-quality resources, including official training providers and peer-reviewed websites. Additionally, engaging with community forums and discussion groups can provide insights and tips from others who have already completed the certification. Combining these materials will give you a well-rounded understanding and better preparation for success.
Best Practices for Exam Day
On the day of the test, your preparation and mindset are just as important as your study materials. Following a set of best practices can help you approach the challenge with confidence and increase your chances of success. Proper planning, time management, and focus will enable you to navigate through the test effectively and perform at your best.
To maximize your chances of success, it’s crucial to stay calm, manage your time wisely, and approach each question methodically. Ensure that you get enough rest the night before and have everything you need for the test day, such as identification, materials, and a well-prepared mindset. Below are some tips to help you prepare for the test day and achieve the best results.
Before the Test
- Get Plenty of Rest: A good night’s sleep ensures you’re mentally sharp and focused for the test.
- Review Key Concepts: Focus on the core topics and areas that you may find challenging.
- Plan Your Time: Arrive early, ensuring you have plenty of time to settle in and avoid any last-minute stress.
- Prepare Your Materials: Double-check that you have all the necessary materials, such as identification, pens, and any required accessories.
During the Test
- Read Questions Carefully: Pay close attention to the wording of each question to avoid misunderstandings.
- Time Management: Allocate time to each section based on its difficulty and mark allocation. Don’t spend too long on any one question.
- Stay Calm: If you encounter a difficult question, stay calm and move on. You can always return to it later.
- Answer All Questions: Don’t leave any questions unanswered. If unsure, make an educated guess.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When preparing for a certification or assessment, it’s essential to be aware of the common pitfalls that many candidates face. These mistakes can not only impact your performance but also lead to unnecessary stress or confusion during the process. By recognizing these common errors ahead of time, you can take proactive steps to avoid them and ensure a smoother experience.
One of the key areas where candidates often falter is in their time management, which can lead to rushing through questions or leaving some unanswered. Another common issue is not thoroughly understanding the core concepts, which may result in misinterpretation of questions. Below are several typical mistakes that you should avoid to help improve your chances of success.
- Rushing Through Questions: Trying to answer too quickly can lead to careless mistakes. Take your time and read each question thoroughly before responding.
- Skipping Over Hard Questions: It’s tempting to skip difficult questions, but this can waste time. If you encounter a challenging question, try to eliminate obviously incorrect answers and make your best guess, then come back to it later.
- Ignoring Key Study Topics: Failing to cover all necessary topics during preparation can leave you unprepared for certain areas of the assessment. Make sure to review all major concepts.
- Overlooking Instructions: Not carefully reading instructions or question requirements can lead to misunderstanding what is being asked. Always pay attention to the specific wording of instructions.
- Overconfidence: It’s important to approach the assessment with confidence, but overconfidence can cause mistakes. Always review your answers and stay mindful of any potential errors.
- Not Practicing Hands-On Skills: Theoretical knowledge is important, but practical skills are equally crucial. Ensure you practice with real-world scenarios to reinforce what you’ve learned.
Post-Assessment Steps and Certification
After completing an assessment, it’s crucial to understand the steps that follow in order to properly evaluate your performance and proceed toward certification. The period following the assessment is just as important as the preparation phase, as it helps you understand where you stand and what additional actions are needed to attain your certification. Whether you pass or need to retake the assessment, the process remains essential for professional growth and recognition.
Once you receive your results, take the time to analyze your performance. If successful, the next step involves preparing for certification issuance. If you didn’t achieve the desired result, don’t be discouraged–this is an opportunity to pinpoint areas for improvement and retake the test when ready. Below are some key steps to follow after completing the assessment:
Review Your Results
- Understand Your Strengths and Weaknesses: Review the areas where you performed well and those that need more focus. This will help guide your future learning.
- Seek Feedback: Some assessments provide feedback on specific answers. Use this to improve your knowledge and performance.
- Stay Positive: If you didn’t pass, view it as a learning experience. Take the time to revisit any challenging topics and enhance your understanding before retaking the assessment.
Certification Issuance
- Receive Your Certification: Upon passing, you’ll receive your official certification. This may be provided digitally or in a physical format, depending on the assessment provider.
- Celebrate Your Achievement: Earning a certification is a significant accomplishment. Take pride in your hard work and dedication.
- Update Your Resume and LinkedIn: Add your new certification to your professional profiles. This can improve your career prospects and showcase your skills to potential employers.
Remember, the journey doesn’t end with the certification. Continue to stay updated with the latest industry trends and keep enhancing your knowledge to stay competitive in the field.