
As you prepare for your upcoming assessment, it’s important to understand the key concepts that cover the body’s structure and its intricate functions. Focusing on the main systems will help you grasp how various organs and tissues work together to maintain balance and support overall well-being.
The process of studying these complex systems requires attention to detail and an understanding of both microscopic structures and their larger roles in the body. Whether it’s the way muscles contract or how the heart circulates blood, each topic provides insight into how the body operates efficiently.
By diving into the material systematically, you can improve retention and ensure you are well-equipped to answer questions accurately. Organizing your studies around the functions and relationships of these systems will enhance your grasp of the material, making the preparation process more manageable and effective.
Body Systems Review and Preparation

This section is designed to guide you through the essential topics that will help you perform well in your upcoming test. Understanding how the various systems in the body interact and support one another is crucial for mastering the material. A deep dive into the key concepts will ensure you’re well-prepared to handle complex questions on the test.
Important Topics to Focus On
- Muscle structure and contraction mechanisms
- Circulatory system functions and blood flow
- Respiratory pathways and gas exchange
- Nervous system regulation and neural pathways
- Endocrine signaling and hormone production
- Digestive processes and nutrient absorption
- Bone structure and skeletal functions
Effective Study Strategies
- Review diagrams and models to visualize structures
- Create flashcards for key terms and definitions
- Practice answering sample questions under timed conditions
- Group study sessions to discuss complex concepts
- Use mnemonic devices for memorizing critical pathways and processes
By covering these areas thoroughly, you can approach the test with confidence. Consistent review and active engagement with the material will make a significant difference in your performance.
Key Topics for Body Systems Review

Understanding the core areas of study is essential for success in the upcoming assessment. These topics cover the fundamental systems of the body, exploring how each system functions individually and in concert with others. By focusing on these key areas, you can build a strong foundation of knowledge necessary for accurate responses during the test.
Some of the primary subjects include muscle function, nervous system pathways, cardiovascular health, respiratory processes, and endocrine regulation. Mastering these concepts will help you connect theoretical knowledge with practical applications, making complex questions easier to tackle.
Understanding the Nervous System Basics
The nervous system plays a vital role in coordinating all bodily functions, from sensory perception to motor responses. Understanding its structure and function is essential for grasping how the body communicates and reacts to internal and external stimuli. This section will help you familiarize yourself with the key components of the nervous system and their specific roles in maintaining overall function.
Key Components of the Nervous System
- Brain – Central control center for processing information
- Spinal Cord – Pathway for signals between the brain and body
- Nerves – Communication channels that transmit signals to and from the brain
- Neurons – Specialized cells responsible for transmitting electrical impulses
- Synapses – Junctions between neurons that allow signal transmission
Functions of the Nervous System
- Sensory Input – Collecting information from internal and external environments
- Integration – Processing sensory information and determining appropriate responses
- Motor Output – Sending signals to muscles and glands to trigger responses
- Homeostasis Regulation – Maintaining internal balance through feedback mechanisms
Focusing on these components will provide a strong understanding of how signals are transmitted and processed, helping you retain essential concepts for the test. Being able to visualize how each part interacts will allow you to better comprehend the material as a whole.
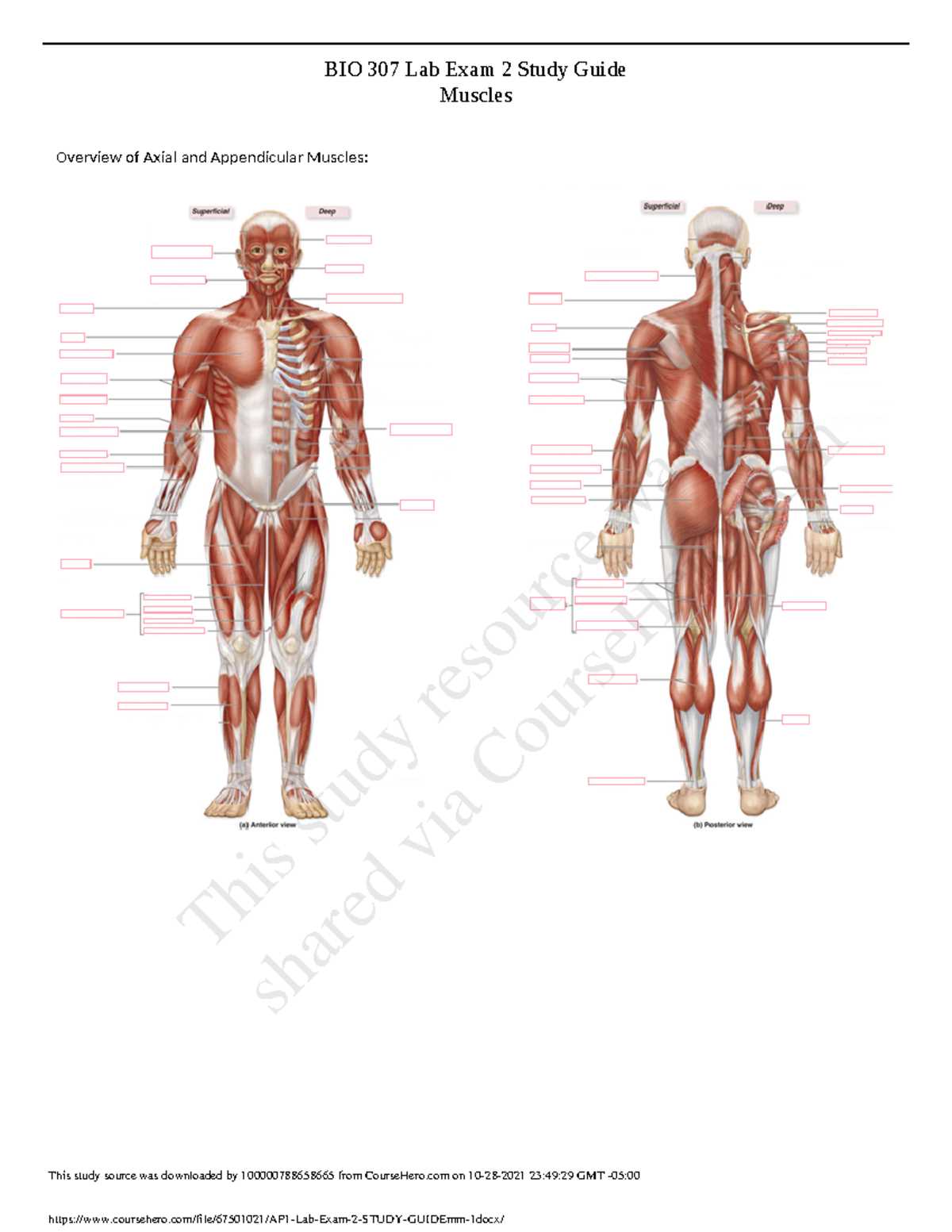
Muscle Function and Structure Explained
Muscles are essential for enabling movement and supporting various bodily functions. Their structure allows them to generate force, control movement, and provide stability to the body. Understanding how muscles work at both the microscopic and macroscopic levels will help you grasp their important roles in overall health and function.
Types of Muscles
- Skeleton Muscles – Voluntary muscles responsible for body movement
- Smooth Muscles – Involuntary muscles found in organs and blood vessels
- Cardiac Muscles – Specialized muscles that make up the heart
How Muscles Work
- Contraction – The process where muscles shorten to produce movement
- Relaxation – The return of muscles to their original length after contraction
- Energy Use – Muscles rely on ATP for energy to perform work
- Coordination – Muscles work together to produce smooth and controlled movements
By exploring the different types of muscles and understanding how they function, you will gain a deeper understanding of how movement is achieved and maintained within the body. This knowledge will be key when answering related questions in the test.
Digestive System Essentials for Study
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Understanding how this process works is essential for mastering related concepts. From the mouth to the intestines, each part of the system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and energy balance.
Focusing on the structure and function of key organs, as well as the stages of digestion, will provide a clear understanding of how food is processed. Additionally, recognizing common disorders can help deepen your comprehension of how the system may fail or become disrupted.
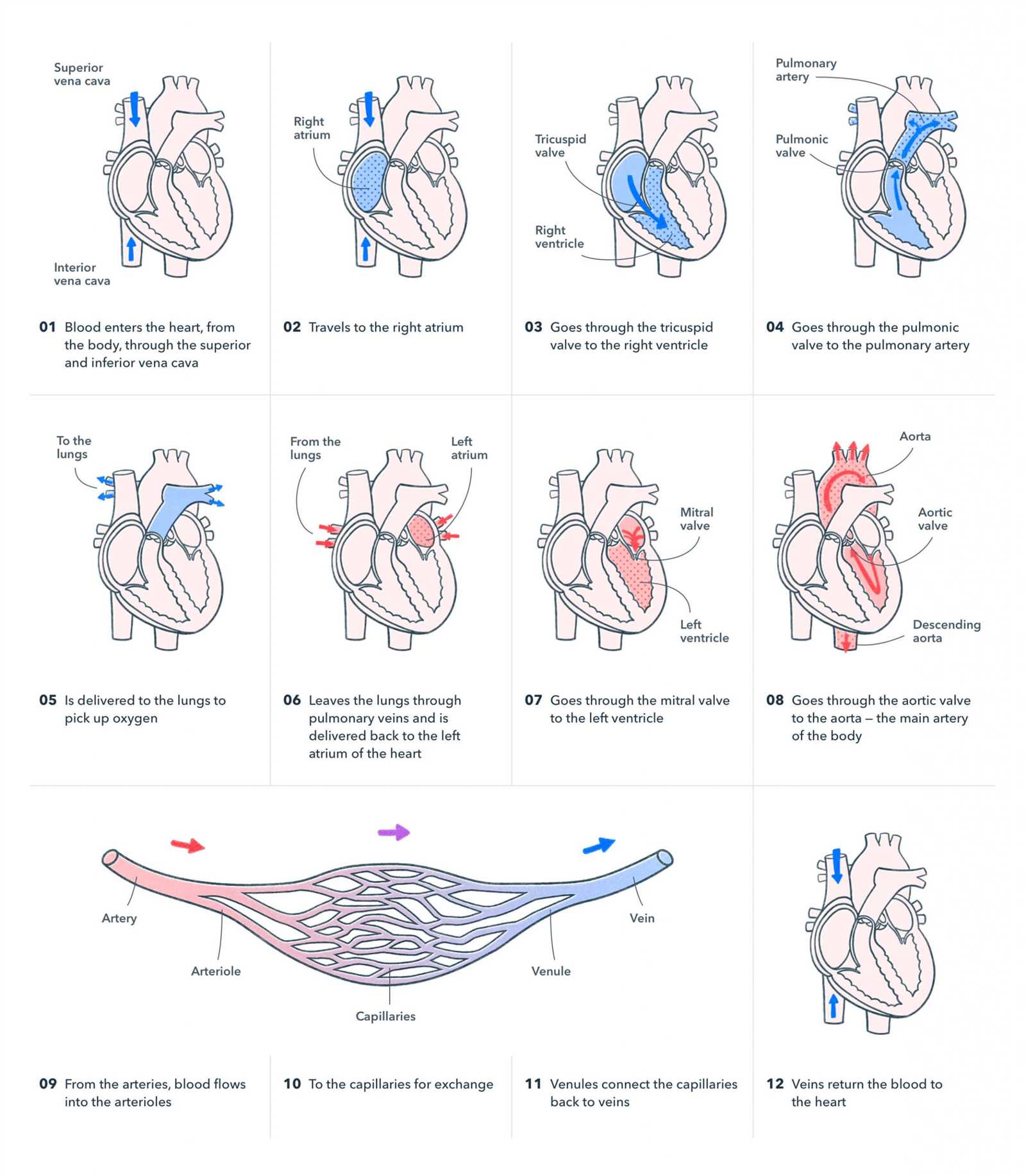
Circulatory System and Its Components
The circulatory system is essential for transporting blood, nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the body. This intricate network ensures that every cell receives the necessary substances for energy production and maintains a healthy environment. Understanding its key components and how they interact is fundamental to grasping how the body functions as a whole.
Main Components of the Circulatory System
- Heart – The central organ that pumps blood throughout the body
- Blood Vessels – Arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry blood to and from various tissues
- Blood – A fluid containing red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma
How the Circulatory System Works
- Oxygen and Nutrient Transport – Blood carries essential elements to cells, enabling proper functioning
- Waste Removal – Blood removes waste products like carbon dioxide from tissues
- Thermoregulation – Blood helps regulate body temperature by distributing heat
- Immune Defense – White blood cells protect the body from pathogens
Understanding the structure and function of these components provides insight into how the body maintains balance and supports life. Recognizing the pathways and functions will be helpful for efficiently navigating related questions in your studies.
Respiratory System Key Points to Know
The respiratory system is responsible for providing oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. Understanding its structure, function, and processes is essential for mastering how the body takes in vital gases and maintains homeostasis. This section highlights the key points that will aid in understanding how breathing supports overall health.
Primary Components of the Respiratory System

- Nasal Passages – Air enters the body, where it is filtered, warmed, and moistened.
- Lungs – The main organs where gas exchange occurs between blood and air.
- Trachea – A tube that connects the mouth and lungs, allowing air to pass freely.
- Alveoli – Tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen is transferred into the blood.
Respiratory Processes
- Inhalation – The process of drawing air into the lungs, bringing oxygen for the body.
- Exhalation – The release of carbon dioxide from the body as a waste product.
- Gas Exchange – Oxygen moves from the alveoli into the blood, while carbon dioxide is expelled.
- Regulation – The respiratory rate is controlled based on blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Familiarity with these essential concepts will help you understand the vital role the respiratory system plays in maintaining proper function and overall well-being. Mastery of these topics is crucial for addressing related questions during your review.
How the Endocrine System Works

The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through the release of hormones. These chemical messengers are secreted by specialized glands and travel through the bloodstream to target organs, influencing processes such as metabolism, growth, mood, and reproductive functions. Understanding how these hormones are produced and their effects on the body is essential for grasping the overall functioning of the system.
Major Glands in the Endocrine System
| Gland | Hormones Produced | Primary Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Hypothalamus | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) | Regulates hormone release from the pituitary gland |
| Pituitary Gland | Growth hormone (GH), Prolactin, Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Controls other endocrine glands and regulates growth |
| Thyroid Gland | Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) | Regulates metabolism and energy production |
| Adrenal Glands | Cortisol, Adrenaline, Aldosterone | Regulates stress response, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon | Regulates blood sugar levels |
Hormonal Regulation and Feedback Mechanisms
The release of hormones is tightly regulated by feedback mechanisms. These systems maintain balance within the body by adjusting hormone production based on the body’s needs. For example, when blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin to lower them. When levels drop too low, glucagon is released to raise them back up. This process ensures that the body maintains stable internal conditions, which is essential for proper health.
Important Cardiovascular Terms and Concepts
The cardiovascular system is essential for maintaining proper circulation, ensuring that oxygen, nutrients, and waste products are transported throughout the body. Understanding the key terms and concepts associated with this system is vital for grasping how the heart and blood vessels work together to support overall health. This section covers some of the most important concepts you should know when studying this system.
Key Terms in Cardiovascular Function
- Cardiac Output – The amount of blood the heart pumps per minute, an important indicator of heart function.
- Blood Pressure – The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, crucial for determining circulation efficiency.
- Heart Rate – The number of heartbeats per minute, influencing how quickly blood circulates through the body.
- Stroke Volume – The volume of blood pumped by the heart with each beat, an important measure of heart efficiency.
Circulatory Pathways

- Systemic Circulation – The path that oxygen-rich blood follows from the heart to the body and back.
- Pulmonary Circulation – The circuit that transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation and returns oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
Understanding these terms will help you grasp how the cardiovascular system maintains proper blood flow and regulates critical bodily functions. A strong foundation in these concepts is essential for comprehending more complex cardiovascular processes.
Study Tips for Nervous System Questions
Preparing for questions related to the nervous system requires a solid understanding of how the body’s communication network functions. By breaking down complex concepts into manageable parts and using effective study techniques, you can master this topic with confidence. This section provides strategies and tips to help you retain critical information and perform well when reviewing the system’s key components and processes.
Focus on Key Structures and Functions
- Neurons – Understand the role of these specialized cells in transmitting electrical signals across the body.
- Synapses – Learn how information is passed between neurons through chemical signals, crucial for communication in the brain and spinal cord.
- CNS vs. PNS – Make sure to differentiate between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord).
Use Visual Aids to Reinforce Concepts

Visual tools, such as diagrams of the brain, spinal cord, and neural pathways, can be incredibly helpful when studying this topic. Drawing or reviewing charts can help reinforce the structural relationships within the system. Associating visuals with terms and functions allows you to grasp the material more effectively and recall it easily when needed.
By staying organized and focusing on the core functions, you will be better equipped to answer questions related to the nervous system with ease. Regular review and using active recall techniques will ensure long-term retention of critical details.
Common Mistakes in Anatomy Exams
When studying for assessments on the body’s structure and functions, many students tend to make recurring mistakes that can hinder their performance. Understanding the most common errors can help you avoid them and improve your results. This section explores typical pitfalls and offers guidance on how to avoid these mistakes during preparation and on test day.
Lack of Focus on Terminology
Misunderstanding key terms is a frequent issue. Terms related to body structures, processes, and their relationships can be complex. Failing to fully grasp their meanings or confusing similar terms can lead to incorrect answers. For example, distinguishing between terms like “ventral” and “dorsal,” or “medial” and “lateral,” is critical in answering spatial and directional questions.
Skipping Practice with Diagrams

Neglecting to study visuals is another common mistake. Many students underestimate the importance of visual aids such as diagrams or charts. These tools are essential for understanding the relationships between different structures and for memorizing their locations. Practice identifying structures on diagrams can significantly improve recall during assessments.
Overlooking Functional Aspects
Focusing only on structure while ignoring the functional aspects of body systems is another key mistake. It is important to understand not just where something is located, but also how it works. For instance, knowing how the heart pumps blood or how nerve impulses are transmitted will help you answer questions that go beyond memorization of locations and structures.
Avoiding these common mistakes requires careful study, attention to detail, and regular practice. By focusing on terminology, using visual aids, and understanding the functionality of body systems, you can improve your performance and boost your confidence for upcoming assessments.
Tips for Memorizing Physiology Terms
Memorizing complex terms related to body functions can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it becomes much easier. Understanding the meanings of specific words and concepts is essential for mastering the material. This section offers useful tips to help you effectively memorize critical terms related to bodily processes and functions.
Use Mnemonics

Mnemonics are powerful memory tools that can make complex terms easier to recall. Try creating acronyms or memorable phrases that relate to the terms you’re studying. For example:
- “BRAIN” for the major functions of the brain: Balance, Respiration, Autonomic functions, Integration, and Neurons.
- “SALTS” for electrolytes: Sodium, Acid, Lithium, Potassium, and Sulfur.
These mnemonics will allow you to link multiple concepts together and make the terms more memorable.
Break Down Complex Words
Many terms can be broken down into smaller parts, such as prefixes, roots, and suffixes. Understanding the meaning of these smaller components can help you decode unfamiliar words. For example:
- “Cardiovascular”: “Cardio” (heart) + “vascular” (blood vessels).
- “Hematopoiesis”: “Hemo” (blood) + “poiesis” (formation).
By breaking words into their components, you can gain a better understanding of their meanings and make them easier to remember.
Use Flashcards
Flashcards are an excellent tool for active recall and repetition. Create a set of flashcards with the term on one side and its definition or function on the other. Regularly reviewing these cards will reinforce your memory and make it easier to retain important terms.
Practice in Context
Simply memorizing terms is not enough; understanding how they fit into the bigger picture is crucial. Try using the terms in sentences or explaining them to others. This helps reinforce the connection between the terms and their real-world applications, making them easier to recall during assessments.
By using mnemonics, breaking down complex words, using flashcards, and practicing terms in context, you can enhance your ability to memorize essential physiology terms effectively.
Digestive System Disorders Overview
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste, but various disorders can disrupt these essential functions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of common digestive conditions is crucial for maintaining overall health. This section offers an overview of several key digestive disorders and their impact on the body.
Common Digestive Disorders
There are several disorders that can affect the digestive system, each with its own set of symptoms and treatments. Some of the most common conditions include:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. Symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional disorder of the intestines characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine, causing malabsorption of nutrients and a range of gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Lactose Intolerance: The inability to properly digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products, leading to symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
Managing Digestive Disorders
Proper management of digestive disorders typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical interventions. Key strategies include:
- Dietary Changes: Reducing the intake of certain foods, such as spicy dishes, dairy, or gluten, can significantly improve symptoms for many individuals.
- Medications: Antacids, probiotics, and medications to reduce inflammation or regulate bowel movements may be prescribed depending on the condition.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor symptoms and prevent complications.
By understanding the most common digestive system disorders, their causes, and effective management strategies, individuals can better navigate the challenges these conditions present and improve their overall digestive health.
Understanding Bone Structure and Function
The skeletal system plays a fundamental role in providing structural support, protecting vital organs, and enabling movement. Bones are not only the framework of the body but also complex structures with various functions essential for maintaining health. Understanding the organization and roles of bones helps in grasping how the body maintains its shape, protects itself, and allows mobility.
Bone Structure
Bones are composed of several layers and tissues that work together to provide strength, flexibility, and functionality. The key components include:
- Cortex: The outer layer of bone, made up of compact bone tissue, is dense and provides strength to resist bending and fracturing.
- Spongy Bone: Located at the ends of bones, this porous tissue contains marrow and reduces the weight of bones while maintaining structural integrity.
- Bone Marrow: Found within the spongy bone, this soft tissue produces red and white blood cells, playing a critical role in the body’s blood supply.
- Periosteum: A thin membrane covering the outer surface of bones, it is rich in blood vessels and nerves and plays a role in bone repair and growth.
Bone Function
Bones serve multiple functions that are crucial for the body’s overall well-being. These include:
- Support: The skeletal system provides a rigid structure that supports the body’s muscles and organs, allowing the body to maintain its shape.
- Movement: Bones serve as levers for muscles, enabling movement and flexibility. Joints, where bones meet, allow for various types of motion.
- Protection: Bones protect vital organs, such as the skull safeguarding the brain and the rib cage encasing the heart and lungs.
- Mineral Storage: Bones store essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which can be released into the bloodstream when needed for various metabolic processes.
By understanding the structure and function of bones, we gain insight into how the body maintains its physical integrity, responds to stress, and adapts to its environment over time.
Reproductive System Key Facts
The reproductive system is responsible for the continuation of species through the processes of reproduction. It includes organs that facilitate the creation of offspring and play a crucial role in the development of secondary characteristics that define each gender. Understanding this system is essential for grasping how life perpetuates itself biologically.
Key Components of the Reproductive System
The primary components of the reproductive system are designed to carry out reproduction, hormone regulation, and sexual differentiation. These include:
- Gonads: The ovaries in females and testes in males are the central organs, responsible for producing gametes (eggs and sperm) and reproductive hormones.
- Reproductive Tracts: The male tract includes the vas deferens and urethra, while the female tract involves the fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
- External Genitalia: In males, the penis and scrotum; in females, the vulva, which includes the labia and clitoris.
- Hormonal Regulation: Hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone regulate the functions of the reproductive organs and influence sexual development and fertility.
Function and Processes
The main processes governed by the reproductive system include:
- Fertilization: The process by which sperm and egg combine to form a zygote, initiating pregnancy.
- Gestation: In females, the fertilized egg implants in the uterus, where it develops into a fetus over the course of pregnancy.
- Sexual Differentiation: The development of physical characteristics that distinguish males from females, driven by genetic and hormonal factors.
- Puberty: The period of sexual maturation, during which the body develops the capacity for reproduction and the physical traits associated with adulthood emerge.
By understanding the basic structures and functions of the reproductive system, we can appreciate how this system supports life, regulates fertility, and impacts overall health and development.
Reviewing Hormonal Regulation in Physiology

Hormonal regulation is a vital process for maintaining balance within the body. It involves the secretion of chemical messengers that regulate various physiological functions, such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood. These hormones are produced by specialized glands and travel through the bloodstream to target organs, where they influence specific actions and processes.
The endocrine system is the main player in this regulatory process, coordinating the actions of different hormones and ensuring that the body responds appropriately to internal and external changes. Understanding how these hormones interact with cells and tissues is essential for grasping how the body maintains homeostasis.
Key Glands and Their Functions
Various glands in the body play a crucial role in hormone production. Below is an overview of the main glands involved in hormonal regulation:
| Gland | Primary Hormones | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary Gland | Growth hormone (GH), Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Controls growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions. |
| Thyroid Gland | Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) | Regulates metabolism, energy production, and overall growth. |
| Adrenal Glands | Adrenaline, Cortisol | Manage the body’s response to stress and regulate metabolism. |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon | Regulate blood sugar levels and energy production. |
| Ovaries/Testes | Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone | Control reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics. |
Regulation and Feedback Mechanisms
The release of hormones is controlled by complex feedback mechanisms that ensure the proper levels of each hormone are maintained. These feedback loops can be positive or negative, depending on the body’s needs.
- Negative Feedback: This is the most common regulatory mechanism, where the body reduces hormone production when levels reach a desired threshold. For example, when thyroid hormone levels are high, the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is inhibited.
- Positive Feedback: Less common but important, this occurs when the secretion of a hormone is enhanced as a result of a stimulus. An example is the release of oxytocin during childbirth, which intensifies contractions and accelerates labor.
By regulating hormone levels effectively, the body maintains optimal function and adjusts to varying conditions, ensuring health and well-being. Understanding how these hormones work in tandem with each other is key to mastering the complexity of bodily functions.