
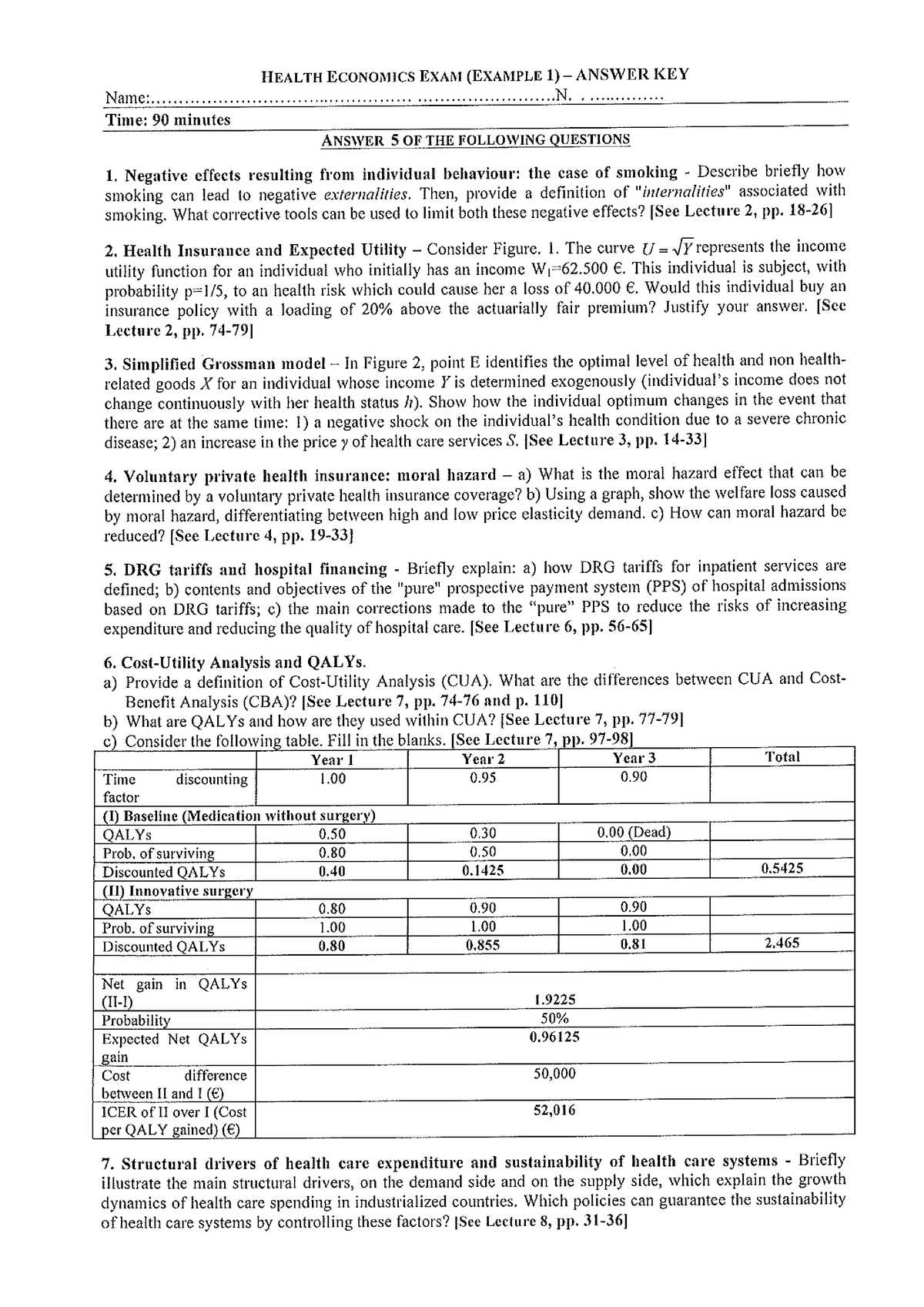
In order to succeed in advanced assessments related to the economic aspects of healthcare, it’s crucial to develop a deep understanding of key principles that govern the system. A strong grasp of how resources are allocated and the influence of policy decisions can significantly impact performance. Whether you’re tackling theoretical frameworks or practical case studies, this knowledge is essential to mastering the subject.
Comprehending market behaviors, resource distribution, and government roles will provide a solid foundation for answering questions effectively. To excel, one must be able to integrate these concepts into real-world scenarios, demonstrating both analytical skills and critical thinking. Anticipating the types of questions and preparing solutions in advance will not only boost confidence but also improve accuracy during assessments.
Throughout this guide, you’ll encounter strategies designed to help refine your approach. Developing effective strategies for approaching complex problems and learning how to communicate your understanding clearly can make a significant difference in your results. With the right preparation, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging topics in this field.
Preparation for Advanced Assessments in Healthcare Studies
Successfully tackling assessments in the field of healthcare resource management requires a strategic approach to understanding core principles. Mastering concepts such as the distribution of resources, the role of policies, and the factors influencing demand and supply is essential. A well-rounded understanding allows for effective application of theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios.
To prepare effectively, it is important to break down complex concepts into manageable parts. Focus on key topics, such as pricing strategies, efficiency measures, and market dynamics. Practice solving problems by applying these ideas to various situations, ensuring you can address both theoretical and practical questions with confidence.
Organizing study sessions around these core areas and using past materials to guide your preparation will help strengthen your grasp on the subject. Reviewing case studies, analyzing research papers, and exploring real-life examples will also deepen your comprehension. By focusing on these strategies, you can improve both your understanding and ability to apply key ideas when faced with difficult problems.
Key Concepts to Master
Mastering the fundamental principles that govern the allocation of resources in the healthcare sector is crucial for success. Understanding the driving forces behind market decisions, the impact of policies, and the role of various stakeholders will provide the foundation needed to tackle complex scenarios. A solid grasp of these ideas enables better application of theory to practice and prepares you for challenging questions.
Resource Allocation and Market Dynamics
The ability to analyze how resources are distributed across different sectors and the influence of market forces is essential. Key elements include understanding supply and demand, pricing mechanisms, and the role of government intervention. Each concept is interlinked and helps build a comprehensive picture of how decisions affect outcomes within healthcare systems.
Cost-Benefit and Efficiency Analysis
Evaluating the effectiveness of policies and programs requires a solid understanding of cost-benefit analysis and efficiency metrics. These tools help measure the impact of different strategies, weighing costs against expected benefits. Mastering these analyses will enable you to assess healthcare initiatives and identify the most efficient use of resources.
| Concept | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Supply and Demand | Understanding how the availability of services interacts with consumer needs. | Determines pricing and access to healthcare services. |
| Market Failure | Occurs when markets do not efficiently allocate resources. | Justifies the need for government intervention or regulation. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Assessing the relative cost of interventions compared to their outcomes. | Used to prioritize healthcare spending based on outcomes. |
Understanding Health Care Market Structures

To navigate the complexities of the healthcare system, it is essential to comprehend how different market structures operate and influence decision-making processes. These structures define the interaction between service providers, consumers, and regulators, shaping the availability and accessibility of services. Each type of market structure has unique characteristics that affect pricing, competition, and the overall efficiency of service delivery.
Types of Market Structures

The healthcare sector operates under various market structures, each having a distinct influence on how services are delivered and accessed. Understanding these structures allows for better decision-making and evaluation of policies. Here are some key types:
- Perfect Competition: This rare structure is characterized by many service providers and equal access to information for consumers.
- Monopoly: A market structure where one provider dominates, often leading to higher prices and reduced competition.
- Oligopoly: A few large providers control the market, influencing prices and service quality.
- Monopolistic Competition: Multiple providers offer differentiated services, creating competition based on factors other than price.
Impact of Market Structures on Service Delivery
Each market structure has a direct impact on how healthcare services are delivered, priced, and regulated. Providers and policymakers must understand these influences to create effective strategies and maintain quality care. Key points include:
- Pricing: Different market structures can result in varied pricing strategies, which can either benefit or disadvantage consumers.
- Accessibility: Market concentration can limit or enhance access to necessary services depending on the level of competition.
- Quality of Care: The level of competition can incentivize providers to improve service quality, although this may not always be the case in monopolistic or oligopolistic markets.
Important Theories in Healthcare Resource Management
Understanding key theoretical frameworks is essential for analyzing how resources are allocated, distributed, and managed within healthcare systems. These theories provide valuable insights into decision-making processes, the behavior of different market participants, and the effectiveness of various policies. By applying these concepts, professionals can better assess challenges and opportunities in the sector.
Supply and Demand Theory
One of the most fundamental concepts in resource management is the principle of supply and demand. This theory explains how the quantity of services offered by providers and the demand from consumers influence the price and availability of healthcare services. The balance between supply and demand determines the accessibility of care and can be impacted by various factors such as government regulations or changes in population health.
Adverse Selection and Moral Hazard
Two closely related concepts, adverse selection and moral hazard, play a significant role in shaping the behavior of both consumers and providers. Adverse selection occurs when there is an imbalance in information between parties, often leading to a disproportionate number of high-risk individuals seeking services. Moral hazard refers to the behavior of individuals or providers when they are shielded from the consequences of their actions, leading to inefficiencies or overuse of resources. Both of these concepts are critical to understanding issues such as insurance markets and healthcare access.
Pricing Strategies in Health Care

Effective pricing strategies are crucial for ensuring that healthcare services are accessible while maintaining financial sustainability for providers. Pricing decisions can significantly impact patient access to care, the quality of services, and the overall efficiency of the system. Various approaches are used to determine the cost of services, each with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Common Pricing Approaches

Healthcare providers employ a range of pricing strategies, depending on market conditions, competition, and regulatory guidelines. Some of the most commonly used pricing models include:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: A fixed markup is added to the cost of providing a service to determine the final price. This model is straightforward but can lead to inefficiencies if costs are not carefully managed.
- Value-Based Pricing: Prices are set based on the perceived value of services to the patient. This approach aims to align the cost of care with outcomes and patient satisfaction, but it can be challenging to measure value accurately.
- Tiered Pricing: Different levels of service are offered at varying price points, allowing patients to select the level of care they need based on their budget. This strategy is often used in elective or non-urgent services.
- Negotiated Pricing: Insurers and providers negotiate prices for services, often resulting in discounts or bundled packages. This model is common in private insurance systems and may benefit both parties through reduced costs.
Impact of Pricing on Access and Quality

The way services are priced can influence both the accessibility and quality of care. Key considerations include:
- Affordability: Higher prices can restrict access to care for low-income individuals, leading to disparities in health outcomes.
- Incentives for Providers: Pricing strategies can incentivize providers to offer more services or prioritize certain types of care, potentially affecting patient outcomes.
- Regulatory Influence: Government regulations often play a role in setting limits or guidelines on pricing, especially in public health systems.
Government’s Role in Health Care Resource Management
The government plays a critical role in shaping the structure and functioning of healthcare systems. Through policies, regulations, and funding mechanisms, governments influence how services are provided, who has access to care, and the overall cost of services. The presence of public intervention ensures that the system operates efficiently, addresses market failures, and provides equitable access to necessary care.
Government involvement includes regulating pricing, ensuring quality standards, and providing funding through public programs. Additionally, it helps in promoting public health initiatives, managing healthcare infrastructure, and implementing policies that guide the actions of private providers. This central role allows governments to address challenges such as healthcare affordability, accessibility, and inequality.
In many cases, the government also acts as a payer for healthcare services, either directly through nationalized systems or by subsidizing insurance for individuals. This role helps to mitigate the financial burden on individuals, ensuring that essential services are available to a broader population, regardless of their financial status. Through these various channels, the government seeks to improve the overall functioning of the system and protect the well-being of the public.
Health Insurance Models Explained
Various models of insurance are used to manage the costs of healthcare and provide coverage for individuals. These models define how services are paid for, who bears the financial responsibility, and how risk is shared across a population. Understanding the different models helps to evaluate their effectiveness in delivering affordable and accessible care while maintaining quality standards.
Types of Insurance Models
Insurance models can vary widely, from government-funded systems to private market solutions. Each model has its own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the specific needs of the population it serves. Some common models include:
- Single-Payer System: In this model, the government is the sole provider of insurance, financing services through taxes. It guarantees universal coverage but may face challenges related to cost control and service wait times.
- Private Insurance: Insurance is provided by private companies, either through employers or directly purchased by individuals. This model offers more choice but can result in higher premiums and unequal access to care.
- Employer-Sponsored Insurance: Employers provide insurance coverage to their employees, often subsidizing the cost. This model is common in many countries but can leave individuals without employment without coverage.
- Community Rating: Insurance premiums are set based on the average cost of care for a community, not individual health status. This helps to reduce discrimination based on pre-existing conditions but may result in higher premiums for healthier individuals.
Challenges in Implementing Insurance Models
Each model comes with its own set of challenges. The balance between affordability, access, and quality is a delicate one, and no system is perfect. Key issues to consider include:
- Cost Control: Keeping the cost of insurance premiums and healthcare services manageable can be difficult, especially in systems where there is significant government funding or reliance on private insurers.
- Access to Care: In some models, such as private insurance, individuals may face barriers to access due to high premiums or limited provider networks.
- Equity: Ensuring that all individuals, regardless of income or employment status, have equal access to necessary services is a common concern, especially in mixed models.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis in Health

Cost-effectiveness analysis is a method used to evaluate the relative costs and outcomes of different interventions. By comparing the costs of various treatments or strategies with their health outcomes, decision-makers can determine which options provide the best value for the resources spent. This approach is particularly useful in resource-limited settings, where allocating funds efficiently is crucial to maximizing public benefit.
Key Components of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
The analysis involves several key components that help in determining the most efficient use of resources. These include:
- Costs: The financial investment required to implement an intervention, including direct and indirect costs such as treatment expenses, personnel, and operational resources.
- Effectiveness: The health outcomes achieved from an intervention, typically measured in terms of improved quality of life, disease prevention, or extended life expectancy.
- Outcome Measurement: A common metric for effectiveness is the quality-adjusted life year (QALY), which combines both the quantity and quality of life gained through an intervention.
Applications and Limitations
Cost-effectiveness analysis is widely used to inform policy decisions, prioritize funding, and guide clinical choices. It helps healthcare providers and governments decide which treatments, programs, or technologies should be implemented based on their overall benefit to society. However, the method is not without its limitations:
- Data Quality: The accuracy of the analysis depends heavily on the quality and availability of data on both costs and outcomes.
- Generalizability: Results from one context or population may not always apply to others, limiting the applicability of findings.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of QALYs or other outcome measures may not capture all the complexities of health or individual preferences, potentially leading to ethical dilemmas in decision-making.
Impact of Policy on Health Systems

Public policy plays a significant role in shaping the structure, performance, and sustainability of healthcare systems. Government decisions regarding funding, regulation, and accessibility directly influence the delivery of care, the allocation of resources, and the overall effectiveness of healthcare services. These policies can lead to improvements in population health, better access to services, or, in some cases, unintended consequences that require further adjustments.
Key Areas Affected by Policy
Policies influence a variety of critical areas within the healthcare system. Some of the most important areas include:
- Access to Care: Policy decisions regarding insurance coverage, subsidies, and the expansion of services can either improve or limit access to essential care for different segments of the population.
- Cost Control: Regulatory policies can determine the pricing of services, the reimbursement rates for providers, and the overall financial sustainability of the system.
- Quality of Services: Regulations that set standards for care and the implementation of quality control measures can lead to improvements in patient outcomes and service delivery.
- Workforce Management: Policies that impact training, compensation, and working conditions of healthcare professionals can affect the quality and availability of care.
Unintended Consequences of Policy
While policies are designed to improve the system, they can sometimes have negative or unforeseen effects. These consequences can include:
- Access Inequality: Well-meaning policies may unintentionally widen the gap between different socioeconomic groups, particularly if certain services are underfunded or unavailable in underserved areas.
- Increased Burden on Providers: Policies aimed at reducing costs may place additional pressure on healthcare providers, leading to burnout or compromised patient care.
- Regulatory Overload: Excessive regulation may result in administrative complexity, which can detract from the focus on patient care and service efficiency.
Behavioral Economics in Health Care
Behavioral insights have increasingly been applied to the realm of healthcare to understand and influence the decision-making of both patients and providers. By analyzing how people make choices in situations involving uncertainty, risk, and long-term consequences, this field helps in designing better policies and interventions that encourage healthier behaviors, optimize resource use, and improve overall outcomes. This approach goes beyond traditional models by recognizing that human decisions are often driven by biases and irrationalities.
Key Concepts in Behavioral Health Decisions
Behavioral models highlight various psychological factors that impact healthcare-related decisions. Some of these factors include:
- Present Bias: People tend to favor immediate rewards over future benefits, which can affect decisions related to prevention, treatment adherence, and lifestyle choices.
- Loss Aversion: The tendency to fear losses more than valuing gains can discourage individuals from making necessary changes or investing in preventive measures.
- Framing Effects: The way information is presented can significantly impact choices, such as the wording of health recommendations or treatment options.
Applications of Behavioral Insights

By applying behavioral economics principles, healthcare systems can develop strategies that guide individuals towards better health outcomes. These strategies can include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Options | Automatically enrolling patients in preventive programs or offering healthier choices as the default can nudge individuals to make better decisions without forcing them. |
| Incentives | Offering small rewards or discounts for achieving health-related goals can motivate individuals to make healthier choices. |
| Social Norms | Highlighting that others in a community are engaging in beneficial health behaviors can influence individuals to adopt similar behaviors. |
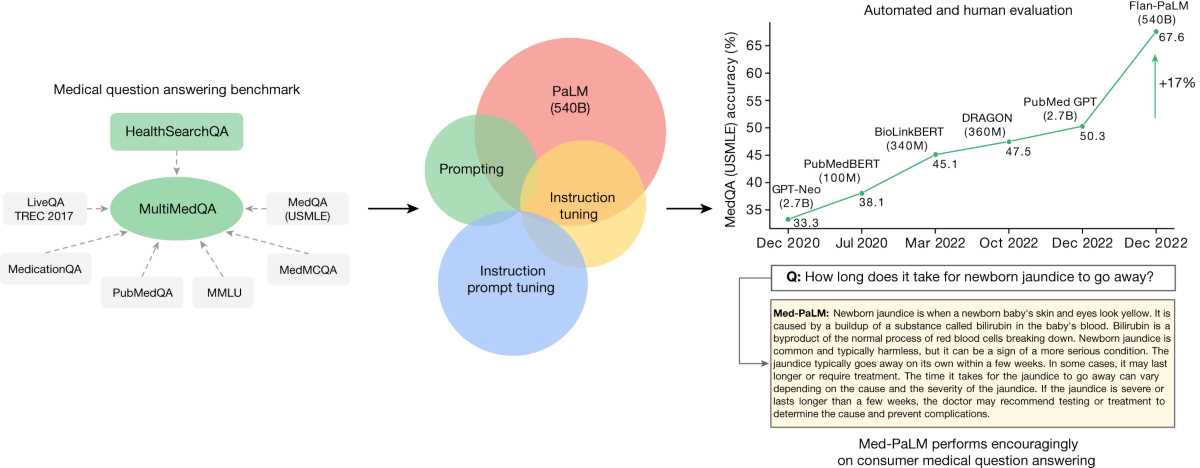
Health Economics and Public Health
The intersection of policy, resource allocation, and community well-being plays a critical role in shaping the effectiveness of public welfare systems. Decision-makers need to understand how resources can be used efficiently to maximize societal well-being while addressing the health needs of various populations. This field explores the balance between the costs of interventions and their outcomes, seeking strategies that improve overall societal welfare.
Public health programs are designed to improve the health of populations through disease prevention, education, and accessibility to services. However, the implementation of these programs often requires careful consideration of their financial implications, sustainability, and broader social impacts. Analyzing these factors helps in making informed decisions that improve the quality of life for entire communities.
Policy-makers must consider a variety of factors, such as:
- Resource Allocation: How to distribute limited resources effectively across different programs to achieve the greatest benefit for society.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Identifying the most cost-efficient ways to deliver services and prevent disease within a given budget.
- Impact Evaluation: Assessing the long-term benefits and outcomes of public health initiatives, both economically and socially.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a system where investments in public well-being not only reduce overall healthcare costs but also lead to a healthier, more productive society. By incorporating economic analysis into public health decision-making, the overall effectiveness and efficiency of these programs can be greatly enhanced.
Analyzing Health Care Demand and Supply
Understanding the dynamics between the need for medical services and their availability is essential for designing efficient and effective healthcare systems. The demand for care often depends on various factors, including population health, income levels, and insurance coverage, while the supply is influenced by the number of providers, technology, and resources available. Analyzing these factors helps policymakers balance access to services and control costs.
Factors Influencing Demand
The demand for medical services is not only driven by illness but also by broader socioeconomic factors. Some key elements that affect demand include:
- Income Levels: Higher income typically increases the ability to pay for care, leading to greater demand for services.
- Insurance Coverage: Access to insurance coverage often increases demand as individuals are more willing to seek care when they face lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Demographic Trends: Aging populations or those with higher rates of chronic conditions will generally experience greater demand for healthcare services.
Factors Influencing Supply
The availability of healthcare services depends on several factors that determine the capacity to provide care. Key elements include:
- Provider Availability: The number of healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and specialists, directly affects the supply of services.
- Technological Advances: New treatments, diagnostic tools, and medical technologies can increase the efficiency and availability of care.
- Government Policies: Regulations and incentives that affect healthcare providers can impact the number of services available and their distribution.
By analyzing both demand and supply, policymakers can identify gaps in service delivery and allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that care is accessible to those who need it most while maintaining financial sustainability.
Market Failures and Health Economics

In certain cases, markets fail to allocate resources efficiently, leading to suboptimal outcomes for individuals and society. These failures often occur in sectors where goods and services are essential but may not be provided in the most efficient or equitable manner. The healthcare sector is a prime example of such a market failure, where the complexities of demand, supply, and externalities can result in inefficient resource distribution.
Market failures can take various forms, each contributing to inefficiencies or inequalities in access to necessary services. These failures can be attributed to issues like asymmetry of information, monopolistic behavior, and external costs that aren’t reflected in market prices. Understanding these failures is essential for designing policies and interventions that aim to correct imbalances and improve the functioning of the sector.
Common types of market failures in this context include:
| Type of Market Failure | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Asymmetric Information | When one party in a transaction has more or better information than the other, leading to poor decision-making and inefficiencies. |
| Monopoly Power | When a single provider dominates the market, reducing competition and often leading to higher prices and reduced service quality. |
| Externalities | Unintended consequences of market transactions that affect third parties, such as the spread of infectious diseases or environmental impacts. |
| Public Goods | Services that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, like public health programs, which may be underprovided in a free market system. |
Addressing market failures requires targeted interventions, such as government regulations, subsidies, or public health programs, to ensure that resources are allocated in ways that maximize societal welfare. By correcting these inefficiencies, policymakers can help improve access to essential services and reduce inequalities in care.
Assessing Health Care Efficiency
Evaluating the effectiveness of a service system is crucial to understanding how well it utilizes available resources to achieve desired outcomes. In the context of providing medical care, efficiency refers to the ability to deliver services that maximize health outcomes while minimizing costs. Achieving high efficiency requires balancing multiple factors, such as quality of care, patient satisfaction, and the costs of delivering care. By assessing these elements, stakeholders can identify areas of improvement and better allocate resources to meet the needs of the population.
One of the core aspects of assessing efficiency is the measurement of inputs versus outputs. Inputs in this context refer to the resources used in the delivery of services, such as labor, equipment, and facilities, while outputs are the health outcomes that result from these resources. Measuring how effectively these inputs translate into desirable outputs allows for comparisons across different systems and helps inform policy decisions.
Several methods and frameworks are commonly used to assess efficiency in care systems:
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis: This approach compares the cost of different interventions relative to their effectiveness in achieving health outcomes. It helps determine the best use of limited resources.
- Productivity Measures: These assess the output (e.g., number of treatments or patient recoveries) relative to the input, providing insight into the operational efficiency of care delivery.
- Benchmarking: This method involves comparing the performance of a healthcare system to others that are considered best-in-class, providing a standard for assessing efficiency and identifying best practices.
Efficiency is not solely about reducing costs, but about ensuring that resources are used in the most impactful ways possible. While some systems may focus on cost reduction, others may prioritize quality or accessibility. A holistic approach to efficiency assessment requires considering a wide range of factors, including equitable access to care, long-term outcomes, and the well-being of patients.
By applying these assessment techniques, healthcare systems can uncover inefficiencies, improve resource allocation, and ultimately provide better care to individuals at a more sustainable cost.
Examining Research Methods in Health Systems

Understanding the frameworks and methodologies used to investigate various aspects of healthcare is essential for analyzing the effectiveness of policies, programs, and services. The tools employed in research help uncover insights about the allocation of resources, decision-making processes, and the outcomes of different interventions. These methods are crucial for providing evidence that can guide policy development and optimize the delivery of care.
In this field, researchers often employ both qualitative and quantitative techniques to gather data, evaluate outcomes, and analyze trends. By combining different methods, they are able to draw more comprehensive conclusions about how to best organize and allocate resources in health services. Below are several commonly used approaches in this research:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This method compares the costs of interventions to the benefits they bring, allowing decision-makers to assess whether a particular intervention is worth the investment.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs): RCTs are used to measure the effectiveness of healthcare interventions by randomly assigning participants to treatment or control groups, helping to isolate the impact of the intervention.
- Survey Methods: Surveys are frequently used to gather data from patients, healthcare professionals, and the general public about their experiences, satisfaction, and the outcomes of treatments.
These research techniques can be combined and adapted to suit different types of studies, from assessing the effectiveness of new treatments to evaluating healthcare policies on a broader scale. Whether it’s through observing trends in data or conducting in-depth interviews, the goal is to provide meaningful insights that can improve the functioning of healthcare systems.
By applying these research methods, scholars and practitioners can contribute to the continuous improvement of services, ensuring that interventions are evidence-based and that resources are utilized in the most effective manner possible.
Common Mistakes in Assessments of Health Systems
When preparing for assessments related to the functioning and analysis of healthcare systems, students often face challenges that can hinder their ability to perform well. These challenges stem from a variety of factors, including misinterpretation of key concepts, lack of understanding of the practical application of theories, and insufficient attention to detail during the problem-solving process. Recognizing and avoiding these common pitfalls can greatly improve the chances of success.
Here are some of the most frequent mistakes that occur during assessments on the topic:
1. Misunderstanding Key Concepts
Many students fail to grasp essential concepts, leading to confusion when it comes time to apply them in practical scenarios. For example, mixing up the differences between fixed and variable costs, or misunderstanding the role of incentives in decision-making, can result in incorrect answers and misinterpretations.
2. Lack of Application to Real-World Situations
Another common error is the inability to relate theoretical knowledge to actual healthcare settings. While it is important to understand core theories and principles, students often struggle when it comes to applying them to case studies or practical examples. This is particularly true when analyzing healthcare policies or assessing the effectiveness of interventions.
| Error Type | Impact on Assessment | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Misunderstanding key concepts | Leads to incorrect interpretations and answers | Review key terms and definitions regularly |
| Failure to apply theory | Misses practical applications and analysis | Practice case studies and real-world scenarios |
| Rushed calculations or reasoning | Results in mistakes in complex problem-solving | Take time to double-check work and break down complex problems |
Addressing these issues through focused study and practice can help mitigate common mistakes. By ensuring a clear understanding of fundamental concepts and refining the ability to apply knowledge to realistic scenarios, students can improve their performance and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
How to Approach Assessment Questions
When tackling questions in assessments, a clear and methodical approach is essential for success. Whether you’re analyzing a theoretical concept or applying a practical framework, understanding how to break down the question and structure your response can make a significant difference. By focusing on key areas and organizing your thoughts effectively, you can maximize your chances of providing thorough and accurate answers.
Here are some steps to help guide you through the process:
1. Read the Question Carefully
- Take time to read each question thoroughly. Identify key terms and instructions to ensure you fully understand what is being asked.
- Highlight or underline any important details to help you focus on the most relevant aspects of the question.
2. Break Down Complex Questions
- For multi-part or complex questions, divide them into smaller sections and address each part individually.
- Start with the most straightforward parts and work your way to the more challenging aspects.
3. Plan Your Answer
- Before writing your response, take a few minutes to organize your thoughts.
- Create an outline or structure to ensure that your answer flows logically and covers all the necessary points.
4. Focus on Key Points

- Make sure to address the most important concepts and support your answers with relevant examples or evidence when possible.
- Avoid going off-topic or adding unnecessary details that may detract from the clarity of your response.
5. Review Your Work
- Once you’ve completed your answer, take time to review it for accuracy and coherence.
- Check that you’ve answered all parts of the question and correct any grammatical or spelling mistakes.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to approach assessment questions in a structured and efficient manner. Remember, clarity and precision are key to demonstrating your understanding and ability to apply concepts effectively.
Tips for Exam Success
Achieving success in any assessment requires more than just memorizing facts. It demands a strategic approach to studying, problem-solving, and time management. By understanding the key principles and applying the right techniques, you can effectively demonstrate your knowledge and skills, ensuring that your performance reflects your preparation.
1. Master Core Concepts
Before diving into practice questions, make sure you fully understand the fundamental principles that form the basis of the subject. This includes grasping key theories, models, and frameworks. The better you understand these concepts, the easier it will be to apply them to a variety of questions.
- Review lecture notes and textbooks to reinforce your understanding of essential topics.
- Identify key themes that are likely to appear in the assessment and focus your study on these areas.
2. Practice Problem-Solving
It’s essential to practice applying your knowledge to solve problems. This helps you become familiar with how to approach questions and organize your answers logically. Regular practice also improves your speed and confidence during the test.
- Work through past questions to identify the types of problems you may encounter and develop strategies for tackling them.
- Time yourself while practicing to simulate the conditions of the actual assessment.
By focusing on mastering the foundational principles and practicing problem-solving regularly, you can increase your confidence and readiness for any assessment. Remember, thorough preparation is the key to success, and with the right approach, you can achieve your best results.