In any professional field, understanding the fundamentals is essential for success. When preparing for an evaluation, grasping core principles, legal standards, and practical applications can make a significant difference in performance. This section is designed to help you navigate the most important topics that are frequently tested in the field of protective services.
By focusing on critical procedures, regulations, and best practices, you can better anticipate the challenges that may arise during your assessment. Whether it’s identifying potential risks or knowing the protocols for various scenarios, this guide will help you strengthen your knowledge and approach each task with confidence.
Effective preparation goes beyond memorizing facts; it’s about developing a deep understanding of how to apply your knowledge in real-world situations. We’ll explore key themes that are central to your upcoming evaluation, offering insights and strategies for mastering the material efficiently.
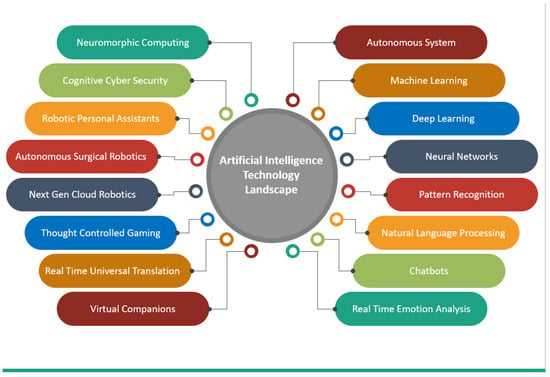
Understanding Key Concepts in Security
In any protective services role, a solid understanding of fundamental principles is essential for ensuring safety and effective risk management. Key concepts shape how professionals respond to challenges, enforce protocols, and maintain order in various environments. Mastering these concepts forms the backbone of any effective approach to safety management.
Familiarity with core ideas, such as risk assessment, threat identification, and emergency response, is crucial. These principles guide decision-making processes and determine how effectively professionals can handle unforeseen situations. Recognizing potential hazards and knowing the appropriate steps to mitigate them are essential skills in this field.
Additionally, understanding the legal framework within which protective services operate is fundamental. Laws and regulations influence the approach to monitoring, reporting, and intervention, helping professionals navigate complex scenarios while ensuring compliance with applicable standards.
Common Topics on the Security Exam
In the process of preparing for a professional evaluation, certain topics are more likely to appear than others. Understanding these key areas ensures better focus and readiness. These subjects not only represent essential knowledge but also cover a wide range of scenarios that are vital to the responsibilities in protective services.
Risk Identification and Management
One of the most critical areas involves understanding how to identify and assess potential risks. Knowing how to evaluate situations, detect threats, and implement preventive measures is fundamental. Professionals need to be able to quickly recognize hazards and determine the best course of action to minimize harm.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities
Another core area revolves around the legal obligations and ethical standards that govern the profession. This includes understanding relevant laws, rules, and regulations, as well as the ethical decision-making required to handle situations in a lawful and responsible manner. Professionals are expected to be well-versed in their rights, duties, and limits of authority within the framework of the law.
Essential Security Procedures You Must Know
In any environment where sensitive information and assets are involved, certain procedures are critical for ensuring the protection of people, resources, and data. Adhering to these practices minimizes risks and fosters a secure atmosphere, whether in physical spaces or virtual networks. Below are fundamental practices that everyone should be familiar with to maintain safety and prevent unauthorized access.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
The first line of defense is preventing individuals from gaining access to areas or systems without proper authorization. This can involve various measures, from identity verification to the use of restricted zones. Key practices include:
- Implementing multi-factor verification processes
- Using security badges or biometrics for physical spaces
- Configuring strong password policies and regular updates
- Monitoring access logs for unusual activity
Incident Response and Management
When an unauthorized attempt or breach occurs, having a clear procedure in place is essential. This ensures quick and efficient handling of the situation, minimizing potential damage. Important components of an incident response plan include:
- Establishing a chain of command for reporting breaches
- Containing and isolating the affected systems immediately
- Conducting thorough investigations to determine the root cause
- Implementing corrective actions to prevent future incidents
By mastering these practices, individuals and organizations can better safeguard their operations and respond swiftly to threats, reducing overall vulnerability.
Strategies for Effective Exam Preparation
Preparing for any assessment requires more than just reviewing notes. It involves careful organization, efficient time management, and actively engaging with the material to ensure full comprehension. By establishing a clear plan, staying consistent, and using targeted study techniques, you can increase your chances of success and reduce stress. Below are key strategies to help optimize your preparation process.
Effective Time Management
Time management is essential for staying on track and avoiding the pressure of last-minute studying. Breaking down your study time into manageable blocks and ensuring each topic gets adequate attention will make the process less overwhelming. Here is a sample schedule that can help you organize your week effectively:
| Day | Focus Area | Study Time | Break Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Core Topics Overview | 2 hours | 15 minutes |
| Tuesday | Advanced Concepts | 2 hours | 15 minutes |
| Wednesday | Hands-on Practice | 2 hours | 15 minutes |
| Thursday | Topic Reviews and Recap | 1.5 hours | 10 minutes |
| Friday | Mock Questions and Final Review | 2 hours | 15 minutes |
Active Learning Techniques
Passive reading can only take you so far. Engaging with the material through active learning techniques enhances understanding and retention. Some strategies to consider include:
- Creating flashcards to reinforce key concepts
- Writing summaries or paraphrasing information in your own words
- Completing practice problems or past questions
- Drawing diagrams or mind maps to visualize complex ideas
These techniques help to deepen your understanding and prepare you to recall and apply knowledge under pressure.
Understanding Legal Terms and Definitions
In any field involving regulations, clear understanding of key terminology is crucial for interpreting guidelines, obligations, and rights effectively. Grasping the precise meaning of legal terms ensures that all parties involved are on the same page and helps avoid misunderstandings. This section focuses on explaining common legal terms that play a significant role in agreements, frameworks, and rules.
Common Legal Terms
Legal language can often seem complex, but breaking it down into simpler definitions can make it more accessible. Below are some essential terms frequently encountered in legal contexts:
- Obligation – A duty or responsibility that a party must fulfill under the terms of an agreement or law.
- Liability – The state of being responsible for something, especially legally, such as the obligation to compensate for damage or loss.
- Jurisdiction – The official power to make legal decisions and judgments, often defined by geographic area or subject matter.
- Clause – A specific provision or section within a legal document that details a particular aspect of the agreement.
Interpreting Legal Terms
Understanding these terms in context is essential for proper application. Legal definitions may vary depending on the jurisdiction or the document in question, which is why it’s important to always verify the meaning within the applicable framework. Additionally, some terms may require further clarification through case law or legal precedents to ensure they are applied correctly in practice.
Key Security Policies for Final Exam
When preparing for important assessments, it is crucial to be aware of the guidelines and protocols in place to ensure a fair and safe environment. These rules are designed to protect both the integrity of the process and the individuals involved. Understanding these policies can help reduce any risks and ensure that the evaluation is conducted smoothly. Below are some key policies that students and invigilators must follow.
| Policy Area | Details | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Identification Verification | Ensure all participants present proper identification to verify their eligibility. | Prevents impersonation and ensures only authorized individuals are taking the assessment. |
| Prohibited Items | Clear instructions on items that cannot be brought into the testing space (e.g., electronic devices). | Maintains fairness by preventing cheating or the use of unauthorized resources. |
| Behavioral Expectations | Guidelines regarding behavior, including no talking, no disruptions, and adherence to instructions. | Ensures a focused and distraction-free environment for all participants. |
| Time Management | Clear rules on the allotted time for the assessment and the process for requesting additional time if necessary. | Promotes fairness and equality by ensuring everyone has the same amount of time to complete the task. |
Risk Management and Security Solutions
Identifying and addressing potential threats is essential in maintaining a stable and efficient environment. By understanding the risks involved, individuals and organizations can implement effective measures to mitigate those threats. This section outlines key strategies for managing risks and adopting practical solutions to safeguard operations and assets.
Identifying Potential Risks
The first step in managing risks is to recognize the factors that could cause harm or disruption. These risks can range from technological vulnerabilities to human errors or natural disasters. Understanding the nature and likelihood of these risks helps in prioritizing response strategies. Common risk categories include:
- Technological Risks: Threats arising from system malfunctions, cyberattacks, or data breaches.
- Operational Risks: Issues stemming from process failures, staff errors, or inefficiencies.
- Compliance Risks: Violations of laws or regulations that could lead to legal penalties.
- Environmental Risks: Dangers related to natural disasters or environmental hazards that could disrupt operations.
Implementing Mitigation Strategies
Once risks are identified, effective solutions must be put in place to reduce their impact. Strategies may vary depending on the nature of the threat but often involve a combination of preventive measures, contingency plans, and recovery protocols. Some proven mitigation approaches include:
- Regular Training and Awareness: Ensuring that staff are aware of risks and know how to act in critical situations.
- Technology Integration: Using advanced tools and software to detect and prevent potential threats in real time.
- Redundancy Systems: Implementing backup systems to ensure continuity in case of a failure.
- Insurance and Risk Transfer: Reducing financial exposure by transferring risks to external parties through insurance or contracts.
By combining these strategies, organizations can minimize the impact of unforeseen events and maintain a secure, stable environment.
Security Protocols and Compliance Standards
In any environment that involves sensitive information or regulated activities, adherence to specific guidelines and frameworks is crucial. These established protocols ensure the protection of data and maintain the trust of all involved parties. Compliance with industry standards not only reduces risks but also fosters a structured approach to mitigating potential threats. This section outlines the importance of such protocols and how they contribute to maintaining high operational integrity.
Compliance standards often include a set of rules or criteria that organizations must meet to operate legally and safely. They are designed to ensure consistency in practices and safeguard information from unauthorized access or misuse. Some of the key protocols include:
- Data Encryption: Protecting sensitive data by converting it into a secure format that can only be accessed or decrypted by authorized individuals.
- Access Control: Implementing restrictions on who can view or modify certain information, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to critical resources.
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic reviews and assessments to ensure ongoing compliance with internal and external regulations.
- Incident Response Plans: Developing clear protocols for identifying, addressing, and recovering from security breaches or other emergencies.
In addition to the technical measures, maintaining adherence to recognized industry standards is essential for demonstrating commitment to ethical and legal responsibilities. For example, standards such as ISO 27001 for information security management or PCI DSS for payment card industry protection provide comprehensive frameworks to ensure proper handling of sensitive data. Complying with these standards not only strengthens an organization’s operations but also builds confidence with stakeholders.
Top Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
When preparing for a major assessment, it’s crucial to be aware of common pitfalls that can hinder performance. Avoiding these mistakes will help ensure that you are fully prepared and can approach the challenge with confidence. This section outlines some of the most frequent errors and provides advice on how to sidestep them.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Procrastination: Delaying study sessions can lead to rushed preparation and increased stress. Start early to ensure adequate time to review all material thoroughly.
- Ignoring Instructions: Failing to read instructions carefully can result in misunderstanding the requirements. Always take the time to review guidelines before starting.
- Overlooking Key Concepts: Focusing too much on minor details while neglecting major topics can affect overall performance. Ensure you have a well-rounded understanding of all subjects.
- Skipping Practice Questions: Practice questions help familiarize you with the format and highlight areas needing further study. Don’t skip this essential step in your preparation.
Strategies for Success
- Time Management: Plan your study schedule carefully to avoid cramming. Break down study sessions into manageable chunks with specific goals for each.
- Stay Calm: Exam anxiety can lead to mistakes. Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, to stay focused and composed.
- Review Your Work: Always leave time at the end to review your answers. Look for any missed questions or errors that could be corrected.
- Seek Clarification: If something is unclear, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification before moving forward. This can prevent misunderstandings that affect your performance.
Exam Techniques for Time Management
Effective time management is one of the most important skills when facing any high-pressure evaluation. The ability to allocate time wisely ensures that all questions are answered thoughtfully and thoroughly, while also avoiding unnecessary stress. In this section, we explore proven techniques to help you manage your time effectively during an assessment.
Time Management Strategies
- Read All Instructions First: Before starting any task, read through all instructions and questions carefully. This will help you understand what’s required and avoid wasting time later on.
- Prioritize Questions: Start with the questions you find easiest. This boosts confidence and leaves more time for challenging ones.
- Set Time Limits: Assign a specific amount of time to each question or section and stick to it. This will prevent you from spending too much time on one item.
- Leave Time to Review: Reserve the last few minutes for reviewing your work. This allows you to correct any mistakes or answer any questions you may have skipped.
Time Allocation Example
| Task | Time Allotted |
|---|---|
| Read all instructions and questions | 5 minutes |
| Answer easy questions | 30 minutes |
| Answer challenging questions | 40 minutes |
| Review answers | 10 minutes |
By managing your time efficiently, you will be able to approach the task with a clear mind and ensure you complete all sections with ample time for review. This structured approach minimizes the risk of errors caused by rushing and maximizes your performance.
How to Answer Scenario-Based Questions
Scenario-based questions are designed to test your ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations. These questions present a hypothetical situation, requiring you to analyze the details, identify key issues, and provide a solution. Answering them effectively demands both critical thinking and a clear, structured approach.
Steps to Approach Scenario-Based Questions

- Read the Scenario Carefully: Ensure you understand every detail. Take note of the context, the challenges presented, and any instructions or specific requirements mentioned.
- Identify Key Points: Focus on the most relevant facts in the scenario. These will often involve problems that need resolution, key stakeholders, or constraints to consider.
- Analyze the Situation: Consider the possible outcomes of different actions. Weigh the pros and cons of various approaches, and think about any risks or benefits that could arise.
- Formulate Your Answer: Provide a clear, concise solution. Explain why this approach is the best option based on the scenario’s context and your analysis.
Example Breakdown
Consider the following scenario:
A company is facing an unexpected data breach. Employees are concerned about privacy and sensitive information. How should the company address the situation to ensure both security and compliance?
In this case, you would:
- Identify the key issues: data breach, employee concerns, privacy, and compliance.
- Analyze the situation: What are the immediate steps to mitigate damage? What are the legal and ethical obligations?
- Provide a solution: The company should act swiftly by informing affected individuals, securing the system, and notifying the relevant authorities as per privacy laws.
By structuring your answer this way, you demonstrate not only your understanding of the material but also your ability to apply it in practical, high-pressure situations.
Best Study Resources for Security Exams
When preparing for assessments in fields related to protective measures and risk management, using the right study materials is crucial for success. Quality resources can help you grasp complex concepts, stay updated on the latest trends, and apply your knowledge effectively in various situations. Below are some of the best study tools that can enhance your preparation and boost your confidence.
Top Recommended Books and Texts
- Comprehensive Guides: Books that provide in-depth coverage of fundamental principles, best practices, and real-world applications.
- Reference Manuals: Manuals designed to explain technical terms and provide step-by-step instructions for troubleshooting and problem-solving in specific areas.
- Case Study Compilations: Books filled with real-world case studies that showcase how theoretical knowledge is applied in practical scenarios.
Online Learning Platforms
- Interactive Courses: Platforms offering video lessons, quizzes, and assignments that help reinforce theoretical understanding while giving a hands-on approach.
- Webinars and Tutorials: Live sessions where experts discuss key topics, followed by Q&A sessions to clarify doubts and deepen understanding.
- Study Groups and Forums: Online communities where individuals share study tips, resources, and personal experiences, helping each other prepare more efficiently.
In addition to books and online courses, practice tests and mock scenarios are also invaluable tools to check your understanding and readiness. Combining these resources will provide a comprehensive approach to mastering the material.
Security Officer Roles and Responsibilities
The role of a security officer is crucial in maintaining the safety and well-being of individuals and properties. These professionals are responsible for monitoring activities, preventing incidents, and ensuring a secure environment. While the specifics of their duties may vary based on the setting, their core responsibilities remain consistent in safeguarding assets and responding to potential risks.
Key Responsibilities
- Patrolling: Regularly walking or driving around the premises to detect any unusual behavior or potential threats.
- Surveillance: Monitoring video feeds, alarms, and other security systems to ensure the safety of people and assets.
- Access Control: Managing entry points, verifying credentials, and ensuring unauthorized individuals do not enter restricted areas.
- Incident Response: Responding to emergencies such as break-ins, medical situations, or safety hazards and taking appropriate action to mitigate damage.
- Reporting: Documenting incidents, hazards, or suspicious activities, and preparing detailed reports for management or law enforcement when needed.
Skills and Qualities
- Attention to Detail: Observing surroundings carefully to spot potential threats before they escalate.
- Communication: Effectively interacting with colleagues, clients, and authorities to report incidents or request assistance.
- Problem-Solving: Quickly assessing situations and determining the best course of action to ensure safety.
- Physical Stamina: Being able to respond promptly to situations that may require physical activity, such as evacuations or arrests.
By upholding these responsibilities, security officers play a critical role in maintaining order and ensuring that environments are safe for everyone involved.
Preparing for Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions often assess a broad range of knowledge and can appear to be straightforward, but they require careful preparation and strategic thinking. Understanding how to approach these types of questions can make a significant difference in performance. Rather than just memorizing facts, it is important to develop an ability to think critically and eliminate incorrect options efficiently.
Effective Strategies
- Understand Key Concepts: Focus on understanding core principles and themes instead of memorizing isolated facts. This will allow you to better evaluate the options presented in the questions.
- Read Carefully: Pay attention to every word in the question, especially qualifiers such as “always,” “never,” “most likely,” or “least likely,” as they can significantly change the meaning of the question.
- Process of Elimination: Eliminate the obviously wrong answers first. Often, there are one or two options that are clearly incorrect, which increases your chances of selecting the right answer.
- Look for Clues: Sometimes, one part of the question or answer choices will provide clues that can help guide you to the correct response.
- Manage Your Time: If you’re stuck on a question, move on and return to it later. Spending too much time on one question can hurt your overall performance.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overthinking: While it’s important to think critically, avoid getting caught up in complex reasoning for questions with clear and simple answers.
- Changing Answers: Trust your initial judgment. Studies show that changing answers often leads to mistakes, so only change your answer if you are sure it is incorrect.
- Skipping Questions: If time allows, answer all questions. Even if you’re unsure about some, try to make an educated guess rather than leaving them blank.
By applying these strategies and avoiding common mistakes, you can improve your ability to tackle multiple choice questions effectively and increase your chances of success.