
Studying the vast and intricate world of the oceans requires a deep understanding of various interconnected systems. Whether it’s the physical processes governing water movement or the diverse life forms that thrive beneath the surface, mastering these topics is essential for excelling in assessments. With so many concepts to grasp, knowing where to focus your efforts can make all the difference.
Preparation is key when tackling questions on this subject. It’s not just about memorizing facts but understanding the core principles that drive ocean dynamics, marine life, and environmental impacts. Identifying recurring themes and key topics can help you structure your study sessions effectively.
By honing in on critical areas and reviewing essential topics, you can approach any assessment with confidence. This guide will offer valuable insights and practical tips to help you navigate through the complexities and perform your best when testing your knowledge of the ocean world.
Mastering Marine Science Assessments
To succeed in your upcoming evaluation of ocean science, it’s crucial to be well-prepared in key subject areas. Understanding the fundamental processes that shape the seas and their ecosystems will provide a strong foundation. Review topics that cover the physical, chemical, and biological aspects of the oceans, as well as the impact of human activities on marine environments.
Essential Concepts to Study
Focus on core themes such as the movement of ocean waters, climate patterns, and the role of marine organisms in various ecosystems. Make sure to cover tidal forces, ocean currents, and the importance of marine biodiversity. Grasping the interactions between the ocean’s layers and the atmosphere is vital for understanding global climate systems and environmental shifts.
Preparation Tips for Success
Effective study strategies include breaking down complex topics into manageable sections and prioritizing areas with the greatest weight in assessments. Regular review of practice questions, along with understanding the reasoning behind each answer, can improve both speed and accuracy. Utilize visual aids such as diagrams and charts to reinforce your understanding of physical processes and biological cycles.
Key Concepts to Focus On

To excel in assessments related to marine science, it’s important to prioritize the most significant topics. Focusing on foundational principles will help you better understand the interconnected systems that govern the ocean. Mastering these core concepts ensures a comprehensive grasp of the subject, allowing for more effective application in various testing scenarios.
Key areas to study include the physical properties of seawater, such as temperature, salinity, and density, as well as their influence on currents and water circulation. A deep understanding of marine ecosystems, including food chains, habitats, and biodiversity, is also essential. Additionally, consider the role of human activity on ocean health, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change impacts.
Common Marine Science Question Types
When preparing for assessments in marine science, it’s helpful to familiarize yourself with the types of questions that are commonly asked. These questions are designed to test your understanding of key principles and your ability to apply them to real-world scenarios. Knowing what to expect can help you focus your studies more effectively.
Questions typically fall into several categories:
- Multiple Choice: These questions often test your knowledge of definitions, key facts, and basic concepts. They require you to identify the correct answer from a list of options.
- Short Answer: These questions focus on your ability to recall specific information and explain concepts in a concise manner.
- Diagram-Based Questions: Often accompanied by a diagram or chart, these questions ask you to interpret or label parts of marine systems, such as currents or ecosystems.
- Essay Questions: These are designed to evaluate your understanding of broader concepts and your ability to explain complex processes in detail.
- Problem-Solving: These questions present a scenario and require you to apply your knowledge to solve a specific issue, such as predicting the effects of climate change on marine life.
By practicing these types of questions, you’ll improve both your understanding and your ability to respond quickly and accurately during the actual test.
Understanding Ocean Currents for Exams
Ocean currents are fundamental to understanding how water moves across the globe, influencing weather patterns, marine life, and even human activity. Grasping the basic principles behind these currents is essential for any assessment on marine science. By focusing on how currents form, their effects, and the factors that drive them, you can build a solid foundation for answering related questions.
Currents are primarily driven by wind, temperature differences, and the Earth’s rotation. It’s also important to understand how they interact with landmasses and oceanic features like the continental shelf. To help visualize these interactions, consider the following table which highlights some of the key currents and their characteristics:
| Current | Location | Driving Force | Effect on Climate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gulf Stream | North Atlantic | Wind, Earth’s rotation | Warms Europe, impacts weather |
| California Current | North Pacific | Temperature, Earth’s rotation | Cooler coastal temperatures |
| Equatorial Current | Equator | Trade winds | Regulates tropical climates |
| Antarctic Circumpolar Current | Southern Ocean | Earth’s rotation, wind | Regulates Southern Hemisphere weather |
Understanding these key currents will allow you to recognize their global importance, particularly in the context of climate regulation and marine ecosystems. Make sure to review diagrams and practice interpreting current patterns for a more comprehensive understanding.
Marine Biology Topics to Review
Marine biology is a critical area of study, focusing on the various life forms that inhabit our oceans. A strong understanding of this subject is vital for assessments, as it covers the diversity of species, ecosystems, and the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments. Review of the following essential topics will help you prepare effectively for any related questions.
Marine Ecosystems and Habitats
Understanding the different types of marine ecosystems is essential. These include coral reefs, kelp forests, deep-sea environments, and open ocean ecosystems. Each of these habitats supports unique organisms and has distinct physical and biological characteristics. Be sure to review the types of species that thrive in these environments, as well as the ecological roles they play.
Adaptations of Marine Organisms

Marine organisms have evolved various adaptations to survive in the ocean’s harsh conditions. Review the physiological and behavioral traits that allow species to thrive in diverse environments. These adaptations include thermoregulation, buoyancy control, and specialized feeding mechanisms. Understanding how these adaptations support survival in different marine zones will be key for answering related questions.
Important Ocean Zones to Study
The vastness of the oceans is divided into various regions that support distinct environments and life forms. Understanding these ocean zones is essential for grasping how marine systems function and how different species interact with their surroundings. Each zone has unique characteristics, and knowing these differences will help you navigate related topics effectively.
Here are some of the most important ocean zones to focus on:
- Epipelagic Zone (Sunlight Zone): This zone extends from the surface to about 200 meters deep, where most ocean life is found. It is characterized by abundant light, making it the primary area for photosynthesis.
- Mesopelagic Zone (Twilight Zone): Located between 200 to 1,000 meters deep, this zone has minimal light, leading to unique adaptations in marine species. Many creatures here use bioluminescence for survival.
- Bathypelagic Zone (Midnight Zone): This deep zone, ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 meters, is completely dark. Organisms here have adapted to extreme pressure and cold temperatures.
- Abyssopelagic Zone (Abyss): Extending from 4,000 meters to the ocean floor, this zone is one of the least explored. It is characterized by freezing temperatures, high pressure, and total darkness.
- Hadalpelagic Zone (Trench Zone): Found in the deepest parts of ocean trenches, this zone is home to some of the most extreme environments on Earth, where life forms have evolved to withstand crushing pressures and lack of light.
By understanding the defining features of each of these zones, you’ll have a clearer picture of how life is adapted to the various conditions of the ocean. Be sure to study the organisms that inhabit each zone and how they contribute to the overall health of marine ecosystems.
Role of Plate Tectonics in Oceans
Plate tectonics plays a fundamental role in shaping the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s oceans. The movement of tectonic plates affects the formation of ocean basins, the creation of underwater mountain ranges, and the occurrence of seismic activity. Understanding these geological processes is crucial for comprehending oceanic features and their influence on global ecosystems and climate.
How Plate Movements Shape Ocean Features
The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into large, rigid plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them. As these plates move, they interact at boundaries–divergent, convergent, and transform–leading to various geological phenomena. The most prominent ocean features formed by plate tectonics include mid-ocean ridges, oceanic trenches, and subduction zones.
Types of Plate Boundaries and Their Effects
The interactions between tectonic plates give rise to various oceanic structures. Here’s a breakdown of how these boundaries influence ocean formation:
| Plate Boundary Type | Location | Ocean Features Created |
|---|---|---|
| Divergent | Mid-Ocean Ridges | New oceanic crust, underwater mountain ranges |
| Convergent | Subduction Zones | Deep ocean trenches, volcanic islands |
| Transform | Fault Zones | Earthquakes, shifting of ocean floors |
These interactions not only affect the physical landscape of the ocean but also have profound implications for marine life, ocean currents, and the overall health of marine ecosystems.
How to Prepare for Marine Science Labs
Preparing for hands-on sessions in marine science requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. To succeed, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the tools, techniques, and concepts that will be applied during the lab exercises. Preparation not only ensures you understand the objectives of each experiment but also enhances your ability to analyze data effectively and collaborate with peers.
Here are a few key steps to help you get ready:
- Review Key Concepts: Brush up on the theories and principles that will be explored in the lab. Understand the underlying science behind the experiments to grasp how different variables affect the results.
- Understand the Lab Procedures: Read through the lab manual or instructions beforehand to familiarize yourself with the methods you’ll be using. Knowing the steps in advance will help you work efficiently and avoid confusion during the session.
- Prepare Necessary Equipment: Ensure you know how to use the equipment required for the lab. Whether it’s microscopes, water sampling tools, or other instruments, understanding their function will streamline your work.
- Ask Questions: If any part of the procedure or concept is unclear, don’t hesitate to ask your instructor or peers for clarification. Having a clear understanding before starting will prevent mistakes and enhance the learning experience.
- Take Notes: During the lab, keep detailed notes of your observations, measurements, and results. Accurate documentation is essential for analyzing data and drawing conclusions later.
By preparing in advance, you will be able to approach each lab session with confidence, improving both your practical and analytical skills in marine science.
Ocean Chemistry and its Impact

The chemical composition of the world’s oceans plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, supporting marine ecosystems, and shaping the Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. The interaction of various elements, compounds, and gases in the ocean influences everything from water quality to the health of marine organisms. Understanding these processes is vital for addressing environmental challenges and predicting the future of oceanic systems.
Key Chemical Components of Seawater
Seawater is primarily composed of water (H2O) along with dissolved salts, gases, and organic compounds. The most abundant component is sodium chloride (NaCl), but there are also significant amounts of magnesium, calcium, sulfate, and potassium. These dissolved substances influence the physical properties of seawater, such as its density, temperature, and salinity. The balance of these chemicals is essential for the survival of marine organisms and the stability of the ocean environment.
Impact of Ocean Chemistry on Marine Life
The chemistry of the ocean directly affects the health and behavior of marine species. Changes in factors like pH levels (acidification), nutrient concentrations, and oxygen availability can have profound impacts on marine ecosystems. Acidification, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, weakens the shells of marine organisms such as corals, mollusks, and plankton, threatening the entire food chain. Additionally, fluctuations in nutrient levels can lead to harmful algal blooms, disrupting marine food webs.
Understanding these chemical dynamics is essential for managing ocean resources and mitigating the effects of human activities on the marine environment.
Climate Change and Ocean Systems
The relationship between climate change and the world’s oceans is complex and interconnected. As global temperatures rise, various oceanic processes are significantly impacted, affecting both marine ecosystems and human societies. These changes include alterations in sea level, ocean temperature, circulation patterns, and the health of marine life. Understanding how shifting climate conditions interact with ocean systems is crucial for predicting future environmental outcomes and formulating effective solutions.
Rising temperatures are one of the most noticeable consequences of climate change. As the atmosphere warms, it increases the heat absorbed by the oceans, causing water temperatures to rise. This not only disrupts the habitats of marine species but also affects ocean currents, which regulate global climate patterns. Changes in circulation can have far-reaching effects, influencing weather systems, coastal regions, and marine biodiversity.
Moreover, ocean acidification, a result of higher CO2 levels, is another pressing concern. The ocean absorbs about a quarter of human-generated CO2, leading to a decrease in pH levels. This acidification can harm calcifying organisms such as corals and shellfish, which rely on calcium carbonate to form their shells and skeletons. The ripple effect of this damage extends to entire marine ecosystems, affecting species diversity and the stability of food chains.
Understanding these critical connections between climate change and ocean systems is essential for addressing the challenges posed by a warming planet and for developing strategies to mitigate adverse impacts on marine life and coastal communities.
Marine Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Marine ecosystems are some of the most diverse and complex environments on Earth. They support a wide array of life forms, from the smallest plankton to the largest whales, all interacting within intricate food webs. These ecosystems play a vital role in maintaining the health of the planet by regulating climate, providing oxygen, and sustaining biodiversity. However, human activities and environmental changes pose significant threats to these delicate systems, impacting both species diversity and ecosystem stability.
Types of Marine Ecosystems
Marine ecosystems vary greatly, with each supporting unique communities of organisms. Some of the most important types include:
- Coral Reefs: Often called the “rainforests of the sea,” coral reefs are home to a vast number of species. They are critical for marine biodiversity, offering shelter and feeding grounds for many organisms.
- Estuaries: These coastal areas where freshwater meets saltwater serve as nurseries for many marine species, providing a rich mix of nutrients and diverse habitats.
- Open Ocean: The vast expanse of the open ocean is home to a wide variety of species that are adapted to its challenging conditions, including deep-sea organisms that thrive in the darkness of the ocean’s depths.
- Mangroves: Coastal areas with salt-tolerant trees, mangrove forests are crucial for coastal protection, carbon sequestration, and as breeding grounds for many marine species.
Importance of Biodiversity in Marine Environments
The diversity of life within marine ecosystems provides numerous benefits, not only to the organisms that inhabit these areas but also to human societies. Healthy marine biodiversity helps maintain ecosystem functions such as nutrient cycling, oxygen production, and climate regulation. Furthermore, the rich variety of species in marine environments contributes to the development of new medicines, food sources, and sustainable resources.
Preserving marine biodiversity is essential for maintaining the balance of ocean systems. As human impacts increase, including pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction, efforts to protect these ecosystems are crucial for ensuring the survival of countless species, some of which are yet to be discovered.
Top Resources for Preparation
Effective preparation for any assessment requires the right tools and resources. By utilizing a range of study aids, students can better understand complex topics and reinforce their knowledge. Whether through textbooks, online platforms, or practice materials, selecting the most reliable and comprehensive resources is essential for success. Below are some of the top resources that can help streamline the study process and increase confidence before a challenging evaluation.
Recommended Study Guides and Textbooks
Textbooks and study guides are foundational tools in understanding core concepts. Popular academic textbooks provide in-depth explanations, diagrams, and exercises that make learning easier. These books break down complicated ideas into manageable sections, often supplemented by review questions to test comprehension. Some of the top recommended resources include:
- Comprehensive Textbooks: Choose textbooks that cover the full scope of your subject, including both theoretical and practical applications. These books often offer chapter summaries and review questions at the end of each section.
- Subject-Specific Study Guides: These guides are typically designed for self-study, providing concise overviews, key concepts, and sample questions to aid in understanding major themes.
Online Platforms and Tools
Online platforms have revolutionized study techniques, offering interactive learning and access to a wealth of information at your fingertips. These resources allow students to engage with material in a more dynamic way, often through videos, quizzes, and discussions. Some of the most effective online tools include:
- Khan Academy: This free online resource offers clear, concise video tutorials on a wide variety of subjects, breaking down complex ideas into digestible lessons.
- Quizlet: A popular tool for creating digital flashcards and quizzes, Quizlet helps reinforce key terms and concepts, allowing for easy self-testing.
- Coursera: Offering courses from universities and institutions worldwide, Coursera provides in-depth learning materials, videos, and assessments on various topics.
By leveraging these resources, students can tailor their study approach to fit their learning preferences, ensuring they are well-prepared for any upcoming assessment.
Time Management Tips for Assessments

Efficiently managing your time during an assessment is crucial to performing well. Proper time allocation ensures that you can thoroughly answer all questions, avoid rushing, and stay calm under pressure. Effective time management involves organizing your approach before and during the test, prioritizing tasks, and staying focused throughout. Here are some key strategies to help optimize your time and improve your performance during any assessment.
Planning Before the Assessment

Preparation is half the battle when it comes to managing time during any assessment. The more organized you are beforehand, the smoother the process will be. Some helpful steps to take before the test include:
- Understand the Format: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the test, including the types of questions (e.g., multiple-choice, essays, short answers), so you can allocate time accordingly.
- Review Key Topics: Make a list of the most important concepts and areas likely to be tested. This focused review will help you feel more confident and efficient when answering questions.
- Practice with Timed Quizzes: Take practice tests under timed conditions to get used to managing your time effectively and identifying areas where you may need to improve.
Effective Time Allocation During the Assessment
During the assessment itself, it’s essential to allocate time strategically for each section. Here are some tips on how to distribute your time:
| Task | Time Allocation |
|---|---|
| Review Instructions | 5 minutes |
| Multiple-Choice Questions | 1 minute per question |
| Short Answer Questions | 2-3 minutes per question |
| Essay Questions | 15-20 minutes per question |
| Final Review | 5-10 minutes |
By assigning approximate time limits for each section, you can ensure that you don’t spend too much time on any one question, leaving enough time to address all parts of the assessment thoroughly.
Staying aware of the clock throughout the assessment, but not obsessing over it, helps maintain a steady pace and reduces stress. Be flexible with your time, but keep track to avoid rushing through the final stages of the test.
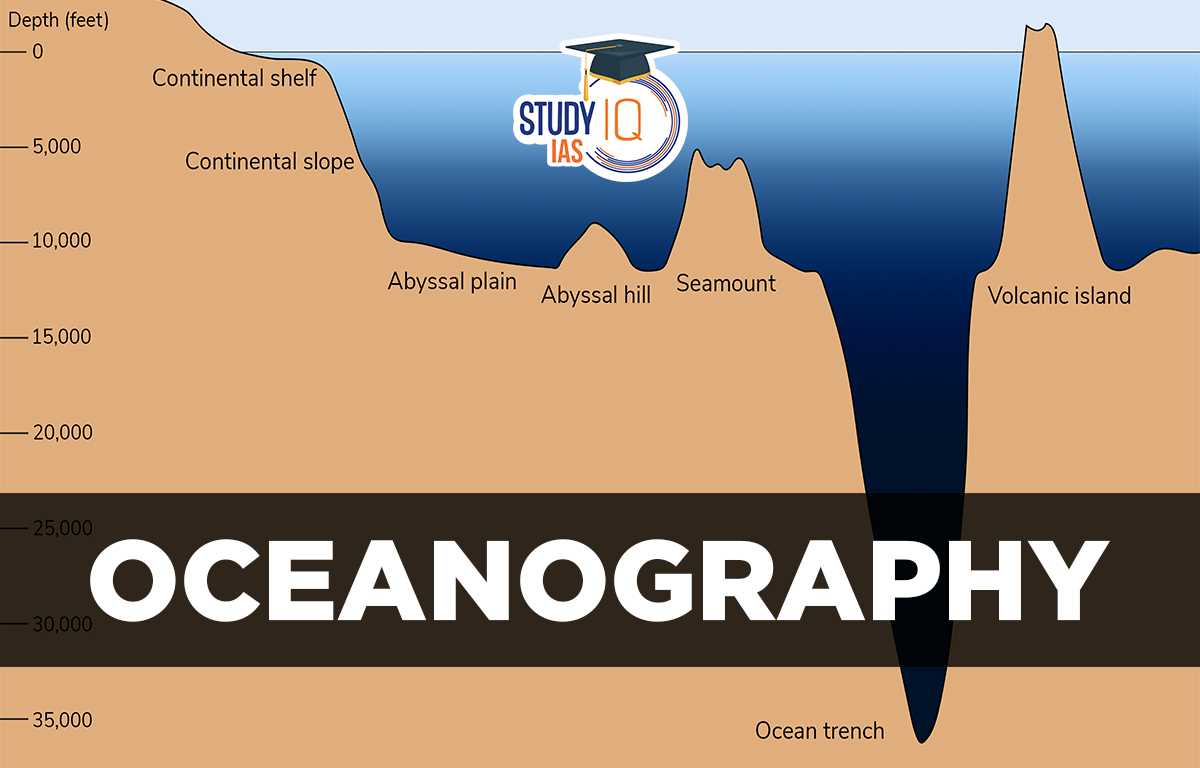
Reviewing Geological Oceanography Topics
When preparing for assessments related to the Earth’s underwater features and processes, it’s important to focus on the key geological aspects that shape the ocean’s structure. This includes understanding the formation, movement, and interaction of tectonic plates beneath the ocean floor, as well as how these forces influence ocean basins, coastlines, and underwater features. A solid grasp of these topics provides the foundation for interpreting various geological phenomena in marine environments.
Key concepts to review include the processes that drive the movement of the Earth’s crust, the formation of oceanic features such as ridges, trenches, and seamounts, and the role of plate tectonics in shaping the seafloor. Additionally, understanding the composition of ocean sediments and the impact of geological processes on marine ecosystems is essential for a comprehensive understanding of Earth’s oceans.
Plate Tectonics and Ocean Floor Structure

Plate tectonics play a significant role in shaping the oceanic landscape. The movement of tectonic plates results in the formation of key oceanic structures, such as mid-ocean ridges, deep ocean trenches, and volcanic islands. These features contribute to the overall dynamics of the ocean floor and influence ocean circulation and biodiversity. Key topics to study include:
- Mid-Ocean Ridges: Areas where tectonic plates are diverging, leading to the formation of new oceanic crust.
- Subduction Zones: Locations where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, often creating deep ocean trenches and volcanic activity.
- Seafloor Spreading: The process by which new oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges and moves outward.
Marine Sediments and Their Formation
The study of ocean sediments reveals much about the Earth’s history, climate, and tectonic activity. These sediments are classified based on their origin, such as lithogenous, biogenous, and hydrogenous. Understanding sediment types, deposition processes, and their role in the oceanic environment is crucial for geological studies. Important areas to review include:
- Sediment Transport: The movement of sediments by ocean currents and their deposition in different regions of the seafloor.
- Biogenous Sediments: Sediments derived from the remains of marine organisms, including shells and plankton.
- Hydrogenous Sediments: Sediments that form directly from chemical reactions in seawater.
Reviewing these key geological topics helps build a deeper understanding of how Earth’s physical processes shape the oceans and their ecosystems.
Understanding Ocean Waves and Tides
Grasping the dynamics of the movement of water in oceans is fundamental to understanding coastal and marine environments. Waves and tides, driven by various forces, play a crucial role in shaping the ocean’s behavior and influencing weather patterns, coastal geography, and marine ecosystems. By exploring their formation, characteristics, and effects, one gains insights into their impact on marine life and human activities.
Waves are primarily caused by wind blowing across the ocean surface, transferring energy to the water. Tides, on the other hand, are long-period fluctuations caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. Both waves and tides are essential components of the marine system, with waves affecting the shoreline and tides influencing ocean currents and coastal ecosystems.
Types of Ocean Waves
Waves vary in size, shape, and frequency depending on the forces that generate them. Understanding the different types of waves and their characteristics is essential for analyzing their behavior in various marine contexts. Key types of waves include:
- Wind-Driven Waves: These waves are created by the friction between the wind and the water’s surface, typically varying in size from small ripples to massive storm waves.
- Seismic Waves: Caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic activity, these waves can travel great distances and are capable of generating tsunamis.
- Capillary Waves: Small ripples formed by the wind’s surface tension, these waves are generally short in length and low in height.
The Impact of Tides on Oceans
Tides, influenced by the moon’s gravitational pull and the Earth’s rotation, create regular fluctuations in ocean water levels. Tidal movements have far-reaching effects, from driving coastal currents to affecting marine organisms’ behaviors. Key tidal concepts to review include:
- Spring Tides: These occur when the sun, moon, and Earth are aligned, resulting in the highest and lowest tides of the month.
- Neap Tides: These occur when the sun and moon are at right angles to each other, producing smaller tidal ranges.
- Diurnal Tides: Characterized by one high tide and one low tide per day, typically observed in some parts of the world.
Understanding the forces behind both waves and tides allows for a deeper appreciation of their roles in shaping the ocean environment and influencing coastal activities.
Practical Tips for Oceanography Exams

Preparing for assessments in marine sciences requires a strategic approach that focuses on understanding the core concepts and applying them to real-world scenarios. Whether the test is written or practical, a well-rounded preparation plan can make a significant difference in performance. By focusing on key topics, practicing problem-solving techniques, and reviewing past materials, students can boost their confidence and improve their results.
Effective preparation not only involves reviewing course materials but also adopting practical strategies that make the studying process more efficient. Time management, practice with mock questions, and collaboration with peers are essential tools for success. The following tips can help streamline your approach to studying for assessments in the marine sciences field.
Focus on Core Concepts
Understanding fundamental principles is crucial when preparing for any scientific assessment. Key areas to focus on include:
- Water Composition and Chemistry: Review the chemical properties of seawater, including salinity, pH levels, and temperature variations.
- Marine Ecosystems: Study the interdependence of organisms in different habitats, such as coral reefs, deep ocean ecosystems, and estuaries.
- Ocean Currents and Circulation: Be sure to understand how currents are formed and their impact on climate, weather, and marine life.
Practice with Past Papers
One of the best ways to prepare for assessments is to practice with past questions. This helps in several ways:
- Familiarity with Question Formats: By reviewing previous assessments, you’ll become accustomed to the types of questions you may encounter, whether multiple-choice, short answer, or essay-type.
- Time Management: Practicing under timed conditions helps you manage the time effectively during the actual assessment.
- Identifying Weak Areas: Regularly testing yourself can reveal areas where further revision is needed.
By incorporating these practical strategies into your study routine, you can improve your ability to tackle challenges with confidence and perform effectively during assessments in the field of marine sciences.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Exams
When preparing for and taking assessments, many students fall into common traps that can affect their performance. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for improving results and avoiding unnecessary mistakes. A careful approach to studying, time management, and attention to detail during the test can make a significant difference in achieving the desired outcome.
In this section, we will discuss some of the most frequent errors that students make during assessments and provide tips on how to avoid them. By recognizing these issues beforehand, you can better navigate the assessment process and increase your chances of success.
Preparation Mistakes
Many issues can arise during preparation that may impact performance during the assessment. To avoid these common errors, consider the following:
- Procrastination: Delaying study sessions until the last minute leads to inadequate preparation. Starting early ensures that you have time to thoroughly understand key concepts.
- Relying Only on Memorization: Focusing solely on rote learning can hinder your ability to apply knowledge. Instead, focus on understanding the underlying principles and how they connect.
- Neglecting Practical Skills: It’s important to practice problem-solving and applying theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. Skipping practical exercises may lead to gaps in your understanding.
Test-Taking Mistakes
Even with solid preparation, certain behaviors during the test can lead to mistakes that affect the outcome. Here are some common test-taking pitfalls to avoid:
- Not Managing Time Properly: Many students spend too much time on difficult questions and run out of time for easier ones. Allocate your time wisely across all sections of the assessment.
- Skipping Instructions: Ignoring the instructions or misinterpreting them can lead to incorrect answers. Always read the instructions carefully before starting each section.
- Overthinking or Second-Guessing: While it’s important to review your answers, overanalyzing can lead to unnecessary changes or confusion. Trust your first instinct when answering most questions.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can enhance your performance and approach assessments with greater confidence and clarity. Focus on building effective study habits, managing your time wisely, and staying calm during the test to ensure that you achieve the best results possible.
Last-Minute Review Strategies for Success
As the assessment day approaches, it’s natural to feel the pressure of reviewing vast amounts of material in a limited amount of time. However, with the right approach, you can make the most of these final hours and ensure that you’re well-prepared. Focusing on key concepts, reinforcing your strengths, and managing stress effectively will help you maximize your chances of success in the short time you have left.
This section provides practical strategies for a productive last-minute review. These techniques are designed to help you concentrate on the most critical topics while staying calm and focused, even when time is tight.
Effective Last-Minute Study Techniques
In the final hours before the assessment, efficient use of your time is essential. Here are some strategies to help you stay on track:
- Prioritize Key Topics: Focus on the areas that are most likely to appear on the assessment or the ones you feel less confident about. Skim through your notes and highlight the most critical concepts and definitions.
- Use Active Recall: Test yourself on the material you’ve studied. Instead of passively reviewing your notes, ask yourself questions and try to answer them from memory. This will reinforce your understanding and help with retention.
- Review Past Assignments and Quizzes: Go through previous assessments, assignments, and practice questions to identify any recurring themes or topics that may be important for the test.
- Use Flashcards: If you’ve prepared flashcards, now is the time to review them. These can help reinforce important terms and concepts quickly.
Managing Stress and Time
As you approach the final moments of preparation, managing your time and stress levels becomes just as important as reviewing content. Here are some tips to help you stay calm and organized:
- Take Short Breaks: Studying for long hours without rest can lead to burnout. Take short breaks every 25-30 minutes to refresh your mind and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Well: Ensure you are physically ready by staying hydrated and eating nutritious snacks. Your brain performs better when it’s properly fueled.
- Sleep Well: Even in the last hours, don’t sacrifice sleep. A good night’s rest will help improve focus and retention, ensuring that you perform at your best.
- Stay Positive: Keep a positive mindset. Confidence can make a significant difference in how well you perform. Trust in your preparation and stay calm during the test.
By using these strategies, you’ll be able to make the most of your last-minute review and approach the assessment with confidence. Stay focused, manage your time wisely, and take care of yourself, and you’ll be ready for success.