In this section, we focus on essential networking knowledge that is critical for those looking to advance their skills in modern network management and configuration. The material covers a broad spectrum of topics that test your ability to understand, implement, and troubleshoot various network-related tasks.
By diving into practical configurations, troubleshooting strategies, and detailed concepts, you will gain a clear understanding of how network devices communicate, how data flows through networks, and how to optimize these processes. The exercises and questions provided aim to strengthen your grasp on both theoretical and hands-on aspects of networking.
Preparing for the challenges ahead involves mastering key principles of routing, addressing, and troubleshooting. Through targeted practice, you will build confidence in handling real-world scenarios, ensuring that you are well-equipped to manage and secure a network environment efficiently.
Networking Assessment Solutions for 2025
This section provides a comprehensive approach to the most crucial aspects of network configuration and troubleshooting. The focus is on the skills and knowledge required to effectively handle network setups, ensuring you understand the fundamental principles that govern data transfer and device interactions within a networked environment.
By thoroughly reviewing practical scenarios and theoretical concepts, you will gain a deeper insight into networking protocols, routing mechanisms, and fault isolation techniques. This preparation ensures that you are ready to address any technical challenges that may arise in real-world network management tasks.
With a focus on accuracy and efficiency, this section is designed to help you identify the right solutions for each networking task. The content aligns with the current standards and provides clear guidance on approaching common issues encountered in network troubleshooting and configuration.
Overview of Networking Concepts
This section covers key concepts that are essential for understanding how devices interact within a network, with a focus on configuration and troubleshooting. You will explore the foundational principles that guide network communication and the techniques used to optimize and maintain efficient data flow across various devices and protocols.
Core Topics in Network Management

The primary areas of focus include:
- Network addressing and routing protocols
- Configuration of devices for smooth operation
- Analyzing network performance and resolving issues
- Optimizing data transmission paths
Practical Application and Real-World Scenarios
Along with theoretical knowledge, this section emphasizes hands-on skills that are necessary for practical network management. By applying these concepts, you will learn how to:
- Configure network devices and services
- Identify common issues in real-world networks
- Utilize tools to test and verify network configurations
Key Concepts in Networking Protocols

Understanding how data moves through a network relies on knowledge of the protocols that govern communication between devices. These rules and conventions ensure seamless data exchange and are essential for efficient network operation. A strong grasp of these protocols is vital for configuring, maintaining, and troubleshooting any network environment.
Essential Networking Protocols
The most common protocols that define data flow include:
- TCP/IP – A foundational suite that allows devices to communicate over the internet
- DNS – Resolves domain names to IP addresses
- HTTP/HTTPS – Protocols for transferring web pages and encrypted communications
- FTP – Facilitates file transfers across networks
How Protocols Enable Network Communication
Each protocol is designed to handle specific aspects of network communication. For example, TCP/IP ensures data packets are transmitted reliably, while DNS ensures that devices can locate each other via human-readable names. Understanding these protocols and how they interact allows for better configuration and troubleshooting of network systems.
Understanding IP Addressing and Subnetting
IP addressing and subnetting are critical components of network design that enable devices to communicate effectively within and across networks. Properly configuring IP addresses ensures that devices can identify and connect with each other, while subnetting divides large networks into smaller, more manageable segments to optimize performance and security.
Basics of IP Addressing
An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. These addresses are divided into two main types: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses are most commonly used, consisting of four octets separated by periods. Each octet is a number between 0 and 255.
Subnetting: Breaking Down Networks
Subnetting is the process of dividing an IP address range into smaller subnets to reduce network congestion and improve security. By adjusting subnet masks, network administrators can control the number of available addresses in each subnet.
| Class | IP Range | Subnet Mask | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 | 16,777,214 |
| B | 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 | 65,534 |
| C | 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 | 254 |
Router Configuration for Network Assessments
Configuring a router properly is a fundamental skill for network management and troubleshooting. This process involves setting up routing protocols, IP addresses, and ensuring that devices on the network can communicate with one another effectively. Proper router configuration ensures data is routed efficiently, enhancing overall network performance and security.
The configuration process typically starts with basic settings such as assigning IP addresses to router interfaces, followed by enabling routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP. Additionally, security configurations such as access control lists (ACLs) and password protection play a crucial role in protecting the network from unauthorized access.
Basic Router Configuration Steps

When setting up a router, follow these key steps to ensure correct configuration:
- Assign IP addresses to router interfaces to allow communication between devices.
- Enable routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP to facilitate data packet routing across networks.
- Configure routing tables to direct traffic effectively based on the network topology.
- Set up network security through ACLs, passwords, and other methods to prevent unauthorized access.
Router Security and Best Practices
Securing the router is essential for maintaining the integrity of the network. Use strong passwords for router access, disable unused interfaces, and regularly update the router firmware to protect against vulnerabilities. Additionally, implementing ACLs to restrict traffic based on IP addresses ensures that only authorized devices can access specific parts of the network.
Network Assessment Structure
Understanding the structure of a network-related assessment is essential for efficient preparation. The format typically includes a combination of theoretical questions and practical tasks designed to test your knowledge and hands-on skills in network configuration and troubleshooting. The assessment is designed to gauge both your theoretical understanding and your ability to apply these concepts in real-world situations.
The assessment is divided into different sections, each focusing on a specific area of networking. Some sections may require you to configure devices, while others test your ability to troubleshoot network issues or understand routing protocols. It’s important to practice both the theoretical aspects, such as protocol knowledge, and practical tasks, such as configuring IP addresses and routing tables.
Assessment Components
Typically, the assessment will contain a mix of the following types of questions:
- Multiple-choice questions to test your theoretical knowledge of networking concepts and protocols.
- Drag-and-drop questions for understanding network configurations and device setups.
- Simulations that require you to configure network devices, troubleshoot issues, or analyze network behavior in real-time.
- Written responses to assess your understanding of more complex networking topics and troubleshooting strategies.
How to Approach the Assessment
To succeed, focus on understanding the key concepts in each section. Practice configuring routers, assigning IP addresses, and applying security protocols. Additionally, review troubleshooting steps for common networking issues. Developing a solid foundation in these areas will help you perform confidently during the assessment and ensure you’re able to handle both theoretical questions and practical tasks effectively.
Top Tips for Passing the Assessment
Successfully passing a networking assessment requires not only knowledge but also effective preparation and strategic thinking. To ensure you’re ready, focus on strengthening your understanding of key concepts, practicing hands-on skills, and approaching the assessment with confidence. Here are some essential tips to help you succeed.
Effective Study Strategies

To maximize your chances of passing, follow these study tips:
- Understand the Fundamentals: Make sure you have a solid grasp of networking basics such as IP addressing, routing protocols, and subnetting.
- Practice with Simulations: Hands-on practice is crucial for developing the skills needed to configure and troubleshoot networks. Use simulation tools to mimic real-world scenarios.
- Review Key Concepts: Focus on the areas most likely to appear in the assessment. Study common protocols, security configurations, and network device settings.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards to test your knowledge of networking terms, protocols, and commands. This can help reinforce your memory and quick recall.
During the Assessment
When taking the assessment, use the following strategies to stay on track:
- Manage Your Time: Pace yourself to ensure you have enough time to complete all sections. Don’t spend too long on any one question.
- Read Questions Carefully: Pay close attention to wording and instructions to avoid missing important details that could impact your answers.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If unsure about a multiple-choice question, eliminate any obviously incorrect options to increase your chances of selecting the right answer.
- Test Configurations: In practical tasks, test your configurations to ensure they work before submitting your answers. Double-check for any errors.
By following these tips and focusing on both theory and practical skills, you’ll be well-prepared to pass the assessment with confidence.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Networking Certifications
When preparing for a networking certification, many candidates fall into similar traps that can negatively affect their performance. Recognizing these common mistakes and understanding how to avoid them is essential to successfully mastering the material and passing the assessment. Below are the most frequent errors made during preparation and tips for overcoming them.
Frequent Errors in Preparation
These mistakes are often made by those studying for networking certifications:
- Skipping Hands-On Practice: Focusing only on theory can limit your ability to apply what you’ve learned. Practice using network simulators or real devices to strengthen your configuration and troubleshooting skills.
- Ignoring Basic Concepts: Neglecting to thoroughly understand basic networking principles, such as IP addressing, subnetting, and routing fundamentals, can lead to confusion when tackling more advanced topics.
- Not Mastering Key Commands: Forgetting essential commands for configuring routers, switches, and other devices can hinder your performance. It’s critical to regularly practice the commands you’ll need during the test.
- Underestimating Network Security: Overlooking network security aspects, such as firewalls, access control lists, and encryption methods, can create vulnerabilities in your knowledge. Ensure you study security concepts in depth.
- Relying Too Much on Memorization: While memorization is important, understanding the logic behind concepts is crucial. Memorizing facts without comprehending their real-world application can lead to mistakes during practical scenarios.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
To overcome these pitfalls, consider the following strategies:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice, especially in configuring devices and troubleshooting common issues, is essential for success. Hands-on experience solidifies your theoretical knowledge.
- Review Frequently: Periodically revisit concepts, particularly those you find difficult. Use practice exams and quizzes to check your progress and identify weak areas.
- Stay Organized: Keep your study materials well-organized, including command lists, key concepts, an
Study Resources for Network Configuration and Management

Successfully mastering networking concepts requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Accessing the right resources is key to building a strong understanding of network structure, protocols, and configuration methods. Whether you’re just starting or looking to deepen your skills, a variety of study materials can help reinforce important topics, such as routing, IP addressing, and network troubleshooting.
Recommended Textbooks and Guides
Books provide an in-depth look at both foundational and advanced network concepts. These texts are invaluable for understanding key principles and gaining detailed insights into network configurations:
- Networking Basics: A comprehensive guide for beginners, covering network types, device functions, and communication protocols.
- Advanced Networking Techniques: Explores complex topics such as routing algorithms, subnetting, and security protocols.
- Network Troubleshooting and Design: Focuses on practical advice for diagnosing network problems and designing efficient, scalable systems.
Online Learning Platforms
Online platforms offer flexible and interactive ways to deepen your network knowledge. These sites provide video tutorials, quizzes, and virtual labs to help you practice configuration tasks in a controlled environment:
- Udemy: Offers a wide range of courses, from network fundamentals to advanced configuration techniques, with hands-on labs to reinforce learning.
- LinkedIn Learning: Provides expert-led courses that cover everything from the basics of network setup to more advanced troubleshooting and optimization.
- Pluralsight: Offers structured learning paths and advanced-level courses for network configuration, security, and administration.
Simulation Tools for Hands-On Practice
To develop practical skills, simulation software is essential. These tools allow you to simulate real-world network environments, configure devices, and troubleshoot network issues:
- Packet Tracer: A user-friendly network simulator that allows you to create and test network designs, perfect for learning and practicing network configuration.
- GNS3: A more advanced
Preparing for Practical Networking Tasks
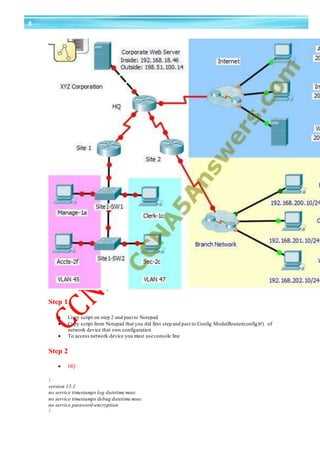
Successfully completing hands-on networking tasks requires both technical knowledge and practical experience. Whether you’re setting up a network, configuring devices, or troubleshooting issues, familiarity with common procedures and tools is essential. Preparing for these tasks involves not only learning theoretical concepts but also practicing with real devices or network simulators to develop problem-solving skills and improve efficiency. This section outlines key strategies for preparing for practical networking assignments that you’ll encounter in real-world scenarios.
To ensure you’re well-prepared, it’s crucial to engage in consistent practice and apply the knowledge you’ve gained in a controlled environment. Below are some important areas to focus on when preparing for practical networking tasks:
Task Preparation Techniques Tools & Resources Router Setup Practice configuring network interfaces, routing protocols, and access control lists. Become familiar with the command-line interface. Packet Tracer, GNS3, Physical Routers IP Address Management Practice subnetting, assigning IP addresses, and using DHCP and static IP configurations. Subnetting Calculators, Virtual Labs Network Troubleshooting Learn to identify common network issues such as connectivity problems and misconfigurations. Use diagnostic commands like ping and traceroute. Wireshark, Ping, Traceroute Security Configuration Understand how to secure networks with firewalls, VPNs, and encryption protocols. Practice securing devices and data transmission. Firewall Software, VPN Configurations, Security Simulators Regular hands-on practice, combined with theoretical knowledge, will significantly improve your ability to handle real networking tasks. By using the right tools and focusing on key areas of network configuration and troubleshooting, you’ll be well-prepared for the challenges ahead.
Exam Simulation and Practice Tests
One of the most effective ways to prepare for any certification or assessment in the field of networking is through simulated tests and practice scenarios. These exercises allow you to familiarize yourself with the format, timing, and types of questions you will face, enabling you to gauge your readiness and identify areas for improvement. By engaging in mock assessments, you can gain confidence and refine your skills in a controlled environment.
Benefits of Practice Simulations
Practice tests are designed to mirror the real assessment experience. They help in the following ways:
- Familiarization with Format: Understand the structure of questions, including multiple choice, drag-and-drop, and configuration-based queries.
- Time Management: Develop the ability to manage your time effectively, ensuring you can answer all questions within the allotted period.
- Identifying Weak Areas: Practice tests help pinpoint knowledge gaps, allowing you to focus your study efforts on areas that need improvement.
- Confidence Building: Regular practice boosts self-assurance and reduces anxiety during the actual assessment.
Recommended Resources for Practice
There are numerous tools available to help you simulate the testing environment and practice under realistic conditions:
- Simulation Software: Tools like Packet Tracer and GNS3 provide network simulation environments to practice configuring routers, switches, and network protocols.
- Online Test Platforms: Websites such as Boson, TestOut, and ExamCompass offer practice tests that closely mimic the real assessment format and difficulty level.
- Books with Practice Questions: Many study guides come with a set of practice questions and detailed explanations to reinforce key concepts.
- Flashcards: Using flashcards for rapid recall of key networking terms, protocols, and concepts can enhance retention and test readiness.
By regularly engaging with these resources and practicing under exam-like conditions, you will increase your chances of success and be well-prepared to tackle the challenges ahead.
Understanding Routing Tables and Algorithms
Routing tables and algorithms are fundamental components of network communication. These systems determine how data packets traverse a network, ensuring they reach their correct destinations. Routing tables act as databases, storing paths and routes that devices use to forward packets. Algorithms, on the other hand, define how these tables are constructed and updated based on network conditions and routing protocols.
A routing table contains a list of destination networks, the associated next hop (the next router or gateway in the path), and other attributes that help in determining the best path. These tables are updated dynamically through routing protocols, which use algorithms to evaluate various paths and make decisions based on factors like distance, cost, and network topology.
Key Components of a Routing Table
In a routing table, several critical fields provide the necessary information for efficient packet forwarding:
- Destination Network: The IP address of the network that is being routed to.
- Next Hop: The IP address of the next device (usually a router) that the packet will be forwarded to.
- Metric: A value used to determine the desirability of a route; lower values usually indicate better paths.
- Interface: The physical or virtual interface through which the packet is forwarded.
Types of Routing Algorithms
Routing algorithms are responsible for determining the best path for data to travel. The most common algorithms include:
- Distance-Vector Algorithms: These algorithms calculate the best path based on the distance to a destination. They are simple but can suffer from slower convergence times and routing loops. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a well-known example.
- Link-State Algorithms: These algorithms consider the state of the network links and provide a more accurate view of the network. They tend to converge faster and are less prone to routing loops. OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a widely used link-state protocol.
- Path-Vector Algorithms: Used in protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), these algorithms track the entire path taken by a packet, ensuring more complex routing decisions based on policies.
By understanding these components and algorithms, network professionals can better design and troubleshoot network infrastructures, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission across different devices and networks.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques
Troubleshooting is a critical skill for resolving network issues and ensuring smooth operation. By following a systematic approach, professionals can efficiently pinpoint the cause of a problem and implement a solution. Whether dealing with connectivity failures, slow performance, or configuration errors, mastering troubleshooting methods helps in identifying root causes quickly, minimizing downtime, and restoring normal network activity.
Here are some essential techniques for effective troubleshooting:
- Start with the Basics: Always verify that the basics are functioning correctly, such as power, physical connections, and device status. A simple issue, like an unplugged cable, can sometimes be the source of a problem.
- Gather Information: Collect as much data as possible from users or monitoring tools. Identify when the issue started, its symptoms, and which systems or services are affected. This can help narrow down potential causes.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Leverage built-in network diagnostic tools such as ping, traceroute, or ipconfig to check connectivity, route paths, and configuration details. These tools provide real-time feedback that can direct further actions.
- Isolate the Issue: Break down the network into smaller segments and test each one independently. This step helps to localize the problem, whether it’s isolated to a device, service, or part of the network.
- Check Configuration Settings: Ensure that all configurations, such as IP addressing, routing, and firewall settings, are correct. Misconfigured settings are a common cause of network issues and can often be resolved through detailed review and adjustments.
- Test Hypotheses: Once a potential cause is identified, test it. If a misconfiguration is suspected, make temporary adjustments and observe whether the issue is resolved. Revert changes if necessary.
- Monitor and Verify: After implementing a fix, continuously monitor the network to ensure stability. Use monitoring tools to track performance and check if the problem recurs.
- Document the Process: Kee
Reviewing Common Networking Scenarios
Understanding typical network configuration and troubleshooting scenarios is crucial for preparing for any networking assessment. These situations often require a deep understanding of network concepts, the ability to quickly identify issues, and the application of best practices for optimal configuration. Familiarity with common scenarios will enable you to effectively approach real-world problems and assessments alike, applying the right tools and methods to resolve them.
Network Configuration Issues
One of the most common situations involves configuring network devices correctly to enable smooth communication across a network. Misconfigurations can often cause issues such as incorrect routing paths, access control problems, or even complete network outages. Below are typical configuration challenges that candidates encounter:
- IP Addressing Issues: Ensuring devices are assigned the correct IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateways is vital for network communication.
- Routing Protocol Setup: Misconfiguring routing protocols can lead to traffic being sent on the wrong paths or prevent devices from communicating altogether.
- VLAN Configuration: Incorrectly setting up VLANs can lead to devices being isolated from the network or unable to communicate with other VLANs.
Troubleshooting Common Network Problems
In addition to configuration tasks, troubleshooting network connectivity problems is another essential aspect of networking assessments. Network professionals must be prepared to diagnose and solve problems related to connectivity, performance, and access control. Here are some common troubleshooting scenarios:
- Connection Drops: Intermittent connectivity loss may be caused by hardware failures, cable issues, or incorrect configurations such as mismatched duplex settings.
- Slow Network Performance: Poor performance might be the result of network congestion, improper Quality of Service (QoS) settings, or faulty routing.
- Access Control Problems: Issues like incorrect firewall rules, misconfigured access lists, or improper NAT settings can block traffic between devices or prevent remote access.
By reviewing and practicing these common network configuration and troubleshooting situations, you can develop the skills needed to tackle real-world challenges efficiently. Understanding these scenarios ensures that you’re well-prepared to deal with both theoretical and hands-on networking tasks.
Exam-Day Tips and Best Practices
The day of any assessment is crucial for ensuring success. It’s not just about what you’ve learned, but how you approach the task at hand. On the day of your test, being well-prepared mentally and physically can make all the difference in your performance. It’s important to stay calm, organized, and focused throughout the process, ensuring that you are able to recall information effectively and manage your time wisely.
Pre-Assessment Preparation
Before sitting down for the test, there are several steps you can take to maximize your performance:
- Get a Good Night’s Sleep: Rest is essential for mental clarity. Avoid cramming the night before, as lack of sleep can impair your ability to think clearly during the test.
- Eat a Balanced Meal: A nutritious breakfast or meal can provide you with the energy needed to stay focused throughout the assessment. Opt for light and balanced food to avoid feeling sluggish.
- Arrive Early: Arriving early helps you settle in and reduces any stress caused by rushing. Use the extra time to review key concepts or simply relax.
During the Assessment
Once the test begins, managing your time and approach is critical:
- Read Questions Carefully: Take your time to fully understand the question before answering. Pay attention to keywords and requirements to avoid misunderstandings.
- Time Management: Allocate a set amount of time for each section of the test, and try to stick to it. If you’re stuck on a difficult question, move on and come back to it later if you have time.
- Stay Calm and Confident: Confidence can help you think clearly. If you start feeling anxious, take a deep breath and refocus your mind on the task ahead.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you’re in the best possible position to succeed. Proper preparation, both before and during the assessment, is key to performing at your best.
How to Master Chapter 7 Content
Mastering the content of any specific section requires a structured approach to studying, consistency, and practical application. To fully understand the concepts and skills covered, it’s important to break the material into manageable parts and tackle each one systematically. With the right strategy, you can gain a deep understanding of the topics, ensuring that you’re well-prepared to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Break Down the Material
The first step in mastering the content is to divide it into smaller, more digestible topics. This way, you can focus on one concept at a time without feeling overwhelmed. Start by understanding the basics before moving on to more advanced topics. Focus on the following areas:
- Key Terminology: Familiarize yourself with important terms and definitions that are central to the material.
- Core Concepts: Understand the underlying principles and how they interconnect to form a cohesive whole.
- Practical Applications: Focus on how to implement the knowledge in real-world environments, which will help solidify your understanding.
Use Multiple Learning Resources
It’s beneficial to use a variety of study materials and resources to reinforce your learning. This can include textbooks, online tutorials, videos, practice tests, and hands-on exercises. By engaging with the material in different formats, you’ll reinforce key concepts and better retain information.
Study Resource Description Textbooks In-depth reading material with detailed explanations and examples. Online Tutorials Interactive videos and lessons that explain complex concepts in a simplified manner. Practice Tests Simulated assessments that help you test your knowledge and identify areas for improvement. Using these resources alongside practical exercises will not only improve your theoretical knowledge but also give you confidence in applying it effectively in practice.