
Understanding how the human body responds to physical activity is a critical component in various fields related to movement and health. Gaining insight into these processes allows individuals to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios effectively.
From analyzing energy systems to comprehending how muscles adapt, this subject requires a blend of scientific understanding and practical application. By preparing thoroughly, you can enhance your ability to interpret data, solve problems, and connect theory with practice.
This guide will help you review core topics, highlight areas of importance, and provide strategies for retention. With the right approach, you can confidently tackle challenges and deepen your comprehension of human performance dynamics.
Understanding the Basics of Exercise Physiology
Physical activity plays a significant role in maintaining overall health and improving various bodily functions. To understand the impact of movement on the body, it’s essential to explore how different systems respond and adapt to physical challenges. This section delves into the fundamental concepts that explain how the body works during physical exertion and how it adjusts over time to enhance performance and endurance.
Key Concepts of Human Movement
The human body consists of several systems that work together to enable and optimize movement. Here are some of the core areas involved:
- Muscle function: The role of muscles in generating force and enabling movement.
- Cardiovascular response: How the heart and blood vessels adapt to support increased demands during physical activity.
- Respiratory function: The way the lungs and airways facilitate oxygen exchange to sustain prolonged effort.
- Energy systems: Different pathways the body uses to produce the energy needed for physical exertion.
Adaptive Mechanisms to Physical Stress
The body does not simply react to physical demands; it adapts to improve efficiency and performance over time. The key adaptive processes include:
- Muscle adaptation: Increased muscle strength and endurance from repeated stress, leading to greater efficiency.
- Cardiovascular adaptation: Improved heart function and blood circulation, supporting better oxygen delivery.
- Respiratory adaptation: Enhanced lung capacity and breathing efficiency to meet the needs of the body during intense activity.
By understanding how the body reacts to and adapts from various forms of movement, individuals can better approach training, recovery, and long-term physical goals.
Key Concepts for Exam Preparation
To perform well in any evaluation of human performance and physical adaptation, it’s essential to focus on several core principles that underlie the subject. Mastery of these concepts will help build a strong foundation and improve your ability to recall critical information during assessments. This section highlights key areas that require attention and understanding for successful outcomes.
Foundational Knowledge

There are several fundamental topics that are crucial to grasp for any assessment in this field:
- Muscle mechanics: Understanding how muscles generate force, contract, and contribute to movement.
- Energy production: The processes that the body uses to produce energy for sustained activity, including aerobic and anaerobic pathways.
- Cardiovascular function: The heart’s role in circulating oxygen-rich blood and removing waste products.
- Respiratory system: The mechanisms behind gas exchange, breathing rates, and how the body utilizes oxygen during strenuous efforts.
Adapting to Physical Stress
It is equally important to understand how the body adapts to regular physical challenges. Key areas of adaptation include:
- Muscle adaptation: How muscles strengthen and improve endurance through regular, progressive overload.
- Cardiovascular adaptation: The heart’s increased capacity to pump blood more efficiently as a result of consistent effort.
- Energy system adaptation: How energy pathways evolve to become more efficient and better suited for varying levels of intensity.
Focusing on these concepts will ensure a comprehensive understanding and better retention of critical information necessary for success in evaluations.
Common Misconceptions to Avoid
When preparing for an assessment on the body’s response to physical activity, it’s important to be aware of common misunderstandings that can hinder understanding. By recognizing and correcting these misconceptions, you can deepen your knowledge and enhance your ability to apply key concepts accurately. Below are some frequent errors to avoid as you study the subject.
Misunderstanding Key Processes
Many individuals mistakenly simplify complex biological mechanisms. Here are some common errors:
| Misconception | Correct Understanding |
|---|---|
| Muscle fatigue is only caused by lactic acid buildup. | Fatigue is a result of multiple factors, including energy depletion, neurological factors, and metabolic changes. |
| Cardiovascular efficiency only improves with intense exercise. | Cardiovascular benefits occur with regular, moderate activity, not just high-intensity effort. |
| Strength gains are the result of muscle size increase alone. | Strength gains also involve neural adaptations, improving coordination and motor unit recruitment. |
Overlooking Long-Term Adaptations
Another area of confusion involves the way the body adapts over time. Key points to remember include:
- Adaptation is gradual: The body does not adjust instantly to physical demands, and improvements require consistent effort over time.
- Rest is critical: Adequate recovery is necessary for proper adaptation and to avoid overtraining.
- Different intensities lead to different adaptations: Low-intensity and high-intensity activities stimulate different physiological responses.
By addressing these misconceptions, you can ensure a more accurate understanding of how the body responds and adapts to various physical activities.
How to Analyze Movement Patterns

Understanding how the body moves during various physical activities is crucial for evaluating performance and preventing injury. To accurately assess movement, one must focus on specific techniques and principles that highlight the interaction between muscles, joints, and overall posture. This section explores the steps to break down and analyze patterns of motion effectively.
First, it is essential to observe the sequence of movements, identifying the primary actions involved. Pay attention to how different body parts work together to produce a fluid and coordinated motion. Key elements to analyze include:
- Joint angles: Observe the position and range of motion of joints during different phases of the movement.
- Posture alignment: Check if the body maintains an optimal alignment throughout the action to prevent undue strain.
- Muscle engagement: Identify which muscles are actively involved in the movement and how they contribute to the overall action.
Another critical aspect is to assess the timing and rhythm of the movement. A well-coordinated pattern involves synchronized actions, where muscle groups work together seamlessly. Evaluating the flow of motion can help determine if the movement is efficient or if adjustments are needed to improve performance.
By breaking down each movement into these components, you can identify areas of improvement, enhance technique, and reduce the risk of injury.
The Role of Nutrition in Performance
Nutrition plays a crucial role in optimizing bodily functions and enhancing overall physical performance. The body requires a balanced intake of nutrients to fuel activity, support recovery, and maintain energy levels throughout the day. A well-planned diet can directly influence strength, endurance, and overall athletic capability.
Key nutrients essential for performance include:
- Carbohydrates: The primary source of energy during moderate to high-intensity activities, carbohydrates help maintain blood sugar levels and replenish glycogen stores.
- Proteins: Crucial for muscle repair and growth, proteins help the body recover after intense physical effort.
- Fats: Provide long-lasting energy and are important for endurance activities, especially during prolonged efforts.
- Vitamins and minerals: Support various bodily functions, including immune response and muscle function, and aid in energy production.
Timing and balance of these nutrients also play a significant role in maximizing performance. Proper intake before, during, and after physical activity can help optimize energy availability, enhance recovery, and improve overall results. Consideration of hydration is equally important, as staying properly hydrated supports bodily functions and prevents fatigue.
By understanding the relationship between nutrition and performance, individuals can tailor their diets to meet the specific demands of their activities and achieve their desired outcomes more effectively.
Tips for Memorizing Scientific Terms
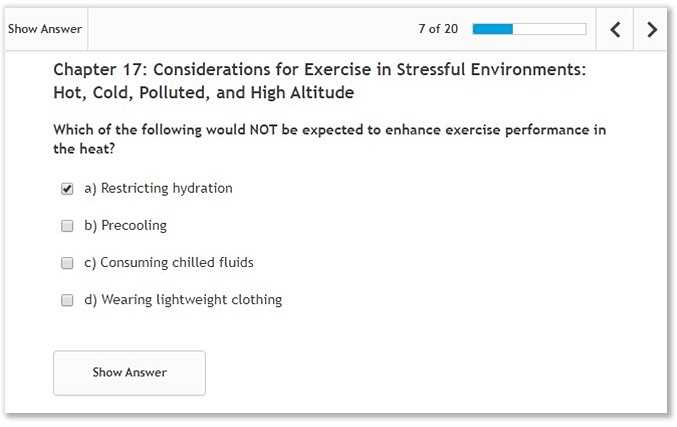
Mastering complex terminology is often a significant challenge when studying subjects related to human movement and bodily functions. However, with the right techniques, it becomes easier to retain and recall key concepts. This section provides useful strategies to enhance memory and improve retention of scientific vocabulary.
Effective Techniques for Retention

Several methods can help make the learning process more efficient:
- Break down terms: Divide complex terms into smaller, more manageable parts. For example, understanding prefixes and suffixes can help decipher the meaning of unfamiliar words.
- Use visualization: Associating a term with an image or concept can enhance recall. Create mental pictures of the term’s function or relation to the body.
- Create flashcards: Write the term on one side and its definition or an example on the other. Regularly review them to reinforce memory.
- Mnemonics: Develop acronyms or phrases that help you remember the term’s meaning. For example, using a memorable sentence to link various concepts together.
Reinforcing Through Repetition
Consistent repetition is key to long-term retention. Review terms regularly and test yourself on both the definitions and how they apply to real-world scenarios. Additionally, teaching others or discussing these terms in study groups can reinforce understanding and strengthen memory.
By integrating these methods into your study routine, you can more effectively memorize scientific terms and enhance your ability to recall them when needed.
Practice Strategies for Complex Calculations
Complex calculations are often required when analyzing human performance and interpreting data related to bodily functions. Mastering these calculations can be a challenge, but with the right strategies, you can improve your ability to solve problems accurately and efficiently. This section outlines effective methods for approaching and practicing these types of problems.
Step-by-Step Approach
Breaking down each calculation into smaller, more manageable steps is a key strategy for success. Follow these guidelines to ensure accuracy:
- Understand the formula: Before starting, ensure you have a clear understanding of the equation you are working with. Know what each variable represents and how to interpret the units involved.
- Identify the known values: Carefully extract all the information provided in the problem. List the known quantities and make sure you understand what is being asked.
- Substitute values and simplify: Plug the known values into the formula. Simplify the equation step by step, taking care to handle operations correctly.
- Check units: Pay close attention to units throughout the calculation. Ensure that units cancel appropriately and that the final result has the correct units.
Consistent Practice and Application
Regular practice is essential to becoming proficient with complex calculations. Work through different types of problems, starting with simpler ones and gradually progressing to more challenging examples. This approach will build your confidence and speed. Additionally, applying calculations to real-world scenarios can help reinforce understanding and make the process more meaningful.
By consistently practicing these strategies and approaching each problem methodically, you can significantly improve your ability to handle complex calculations with precision and ease.
Importance of Cardiovascular System Knowledge
A thorough understanding of the cardiovascular system is essential for evaluating how the body responds to various physical activities. This system plays a pivotal role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products. By gaining insights into how the heart, blood vessels, and blood function together, one can better understand the body’s capabilities and limitations during different types of physical exertion.
Key Functions of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is integral to maintaining homeostasis and supporting optimal performance. Some of its most critical functions include:
- Oxygen transport: The system is responsible for circulating oxygen-rich blood to muscles and organs, facilitating energy production during activity.
- Nutrient delivery: Blood carries essential nutrients to cells, enabling sustained effort and recovery after physical strain.
- Waste removal: The heart and blood vessels work together to remove metabolic byproducts, such as carbon dioxide, preventing the buildup of harmful substances.
- Temperature regulation: The circulatory system helps regulate body temperature by distributing heat and facilitating cooling mechanisms during intense activity.
Impact on Performance and Recovery

Knowledge of how the cardiovascular system adapts to regular physical demands is critical for optimizing performance and recovery. Understanding how heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output change during different intensities of activity allows for better training programs and performance goals. Additionally, a well-functioning cardiovascular system speeds up recovery by improving circulation and nutrient delivery after exertion.
Mastering the fundamentals of this system enables individuals to make informed decisions about physical training, overall health, and performance optimization.
Effective Study Techniques for Beginners

Starting a new subject can be overwhelming, especially when it involves complex concepts and detailed information. However, with the right study methods, beginners can build a strong foundation and gradually develop a deeper understanding. This section outlines practical strategies to enhance learning and retention for those just beginning their studies.
One of the most important aspects of effective studying is to break down the material into manageable sections. Focusing on one concept at a time helps avoid feeling overwhelmed and ensures that you grasp each topic before moving on to the next. Here are some techniques to make your study sessions more productive:
- Active Recall: Test yourself frequently on the material to reinforce memory. Instead of just reading, try to retrieve information from memory to strengthen neural connections.
- Spaced Repetition: Review content at increasing intervals over time. This technique helps improve long-term retention by preventing forgetting.
- Chunking: Group related pieces of information together into larger, more manageable “chunks.” This simplifies the learning process and enhances memory retrieval.
- Concept Mapping: Create diagrams or mind maps that link related ideas and concepts. This visual representation can help clarify complex topics and highlight connections between different pieces of information.
In addition to these techniques, staying organized and setting clear goals for each study session is crucial. Creating a study schedule that balances review and new material can help ensure steady progress. Taking regular breaks is also important for maintaining focus and avoiding burnout.
By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you can build effective study habits that will support your learning journey and lead to greater success in mastering new concepts.
Exploring Muscle Functions and Adaptations
Muscles play a vital role in the body’s ability to perform various physical tasks. Understanding their functions and how they adapt to different conditions is essential for optimizing performance and improving overall strength and endurance. This section explores the mechanisms behind muscle actions and how they change in response to various stimuli.
Key Functions of Muscles
Muscles are responsible for generating force and enabling movement through contraction. Their primary functions include:
- Movement: Muscles work in coordination with bones and joints to produce movement, allowing the body to perform tasks ranging from walking to lifting objects.
- Posture maintenance: Muscles provide support for the body, helping maintain proper posture and balance during static and dynamic activities.
- Heat production: Muscular activity generates heat, which helps regulate body temperature during physical activity.
Muscle Adaptations to Physical Stress

Muscles can adapt to varying levels of stress over time. These adaptations help improve strength, endurance, and efficiency, allowing the body to perform at a higher level. Common adaptations include:
- Hypertrophy: With consistent resistance training, muscle fibers increase in size, leading to greater strength and power output.
- Endurance improvement: Muscles become more efficient at using oxygen and producing energy, which enhances performance during prolonged activity.
- Neuromuscular adaptation: The nervous system becomes better at activating muscles more efficiently, improving coordination and movement precision.
These adaptations are influenced by factors such as intensity, frequency, and type of activity. By understanding the process of muscle adaptation, individuals can tailor their routines to achieve specific fitness goals.
How to Interpret Lab Test Results

Understanding lab test results is crucial for evaluating health and performance. These tests provide valuable insights into the body’s function and can help identify potential issues or areas for improvement. Interpreting these results accurately requires knowledge of the normal ranges, the factors influencing them, and how they relate to an individual’s overall condition.
Key Factors to Consider
When reviewing lab test results, several important factors should be taken into account:
- Normal reference ranges: Each test has a specific reference range, which represents the typical values for a healthy individual. Comparing results against these ranges helps assess whether a test is within normal limits.
- Variations in results: It’s essential to understand that individual factors, such as age, gender, activity level, and diet, can influence test outcomes. Always consider the person’s specific context when interpreting results.
- Trends over time: A single test result may not provide the full picture. It is important to track changes over time to identify patterns or potential health issues.
Interpreting Common Lab Tests
Here is a basic overview of how to interpret some commonly measured parameters in lab tests:
| Test | Normal Range | What It Indicates |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Glucose | 70-100 mg/dL (fasting) | Indicates how well the body is managing blood sugar levels. Elevated levels may suggest insulin resistance or diabetes. |
| Cholesterol | Total: | High cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease. It’s important to monitor both total cholesterol and specific subtypes like HDL and LDL. |
| Creatinine | 0.6-1.2 mg/dL | Creatinine levels reflect kidney function. Elevated levels may suggest impaired kidney function or dehydration. |
| Hemoglobin | 13.8-17.2 g/dL (men), 12.1-15.1 g/dL (women) | Hemoglobin levels indicate how well oxygen is being transported throughout the body. Low levels may indicate anemia. |
Accurately interpreting lab test results requires both technical knowledge and an understanding of the individual’s health context. By carefully analyzing the numbers and considering all relevant factors, you can gain meaningful insights that inform decisions related to health and wellness.
Maximizing Retention Through Case Studies
Case studies are an effective way to deepen understanding and improve long-term retention of complex concepts. By applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, case studies help bridge the gap between learning and practical application. This approach engages learners in critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making, which reinforces memory and enhances the ability to recall information when needed.
When used properly, case studies allow learners to see the practical relevance of the material they study. They provide context, demonstrate how concepts are used in real-life situations, and challenge students to think analytically. Below are some key strategies for making the most out of case study-based learning:
- Active Engagement: Engage with the case study by identifying the core issues, exploring possible solutions, and predicting outcomes. Active participation leads to better understanding and retention.
- Relate to Real-World Situations: Try to connect the case study to your own experiences or similar real-world situations. This personal connection enhances memory and understanding.
- Collaborative Discussion: Discuss case studies in groups to hear different perspectives and deepen your understanding through shared insights.
- Apply the Knowledge: After studying the case, apply the knowledge gained to similar problems or scenarios. Repetition and application are key to reinforcing the material.
Example Case Study
Below is a sample case study that demonstrates how theory can be applied in a practical setting:
| Case Study Topic | Key Concepts | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic Fatigue in an Athlete | Nutrition, Rest, Training Load | Adjust training intensity, improve diet, and incorporate more rest. |
| Cardiovascular Health in Older Adults | Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Exercise Adaptation | Recommend moderate-intensity activities, monitor heart rate, and adjust exercises based on individual capabilities. |
By engaging with these case studies, learners are able to see the direct application of their knowledge, which not only strengthens understanding but also enhances their ability to retain and apply what they have learned in future scenarios.
Understanding Biomechanics for Applied Scenarios

Biomechanics plays a crucial role in understanding how the body moves and interacts with external forces. By analyzing the mechanics of movement, we can optimize performance, prevent injury, and improve overall efficiency in various physical activities. This section explores the application of biomechanical principles in real-world situations, helping learners grasp the significance of these concepts in practical scenarios.
Core Concepts in Biomechanics
In biomechanics, the study of movement is often focused on key principles that explain how forces affect the body during various activities. These principles include:
- Force: The push or pull that causes a change in motion. Understanding how forces work on the body helps in designing safer and more efficient movement patterns.
- Torque: The rotational force that causes movement around a joint. It is essential in activities like lifting, throwing, and rotating movements.
- Leverage: The use of external support or resistance to increase the mechanical advantage. Proper leverage allows for more effective movement with less effort.
Applying Biomechanical Principles in Real-World Scenarios
Applying biomechanical principles to specific scenarios can lead to better performance and fewer injuries. Here are a few examples of how biomechanics can be used in practical situations:
- In Sports: By understanding the optimal angles for jumping, sprinting, or lifting, athletes can maximize efficiency while minimizing strain on the body.
- In Rehabilitation: Biomechanics is crucial for assessing movement patterns and correcting imbalances or weaknesses that could lead to injury.
- In Ergonomics: Proper ergonomic design takes biomechanical principles into account to reduce the risk of strain and injury in the workplace.
Example: Analyzing the Mechanics of a Squat
To demonstrate the application of biomechanics, let’s consider the mechanics involved in a squat, a common movement in various activities. Here are some key biomechanical factors to consider:
- Joint Angles: The angle of the knees and hips during the squat determines the amount of force exerted on the joints. Proper alignment reduces stress on the knees and back.
- Center of Mass: The position of the body’s center of mass affects balance and stability during the squat. Maintaining proper alignment ensures that the weight is distributed evenly across the body.
- Force Distribution: Proper technique ensures that the forces acting on the body are evenly distributed, reducing the risk of injury while optimizing performance.
By understanding and applying these biomechanical principles, individuals can improve both performance and safety in a wide range of physical activities.
Best Resources for Test Preparation
Effective preparation is essential for mastering complex subjects and performing well in assessments. Utilizing the right resources can make a significant difference in how well concepts are understood and retained. This section highlights some of the most useful tools and materials to help learners prepare efficiently and confidently for any evaluation.
Top Study Materials
There are a variety of study materials available that cater to different learning styles. Here are some of the most effective options:
- Textbooks and Reference Books: Comprehensive books provide in-depth coverage of topics and can serve as a solid foundation for understanding fundamental principles.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: These resources offer interactive learning, often with videos, quizzes, and discussions to reinforce concepts.
- Practice Tests: Taking simulated tests helps identify weak areas and boosts confidence by familiarizing students with the format and question types.
- Flashcards: Flashcards are great for quick recall and memorization of key terms, processes, and definitions.
Supplementary Resources
In addition to core study materials, supplementary resources can enhance learning and provide valuable insights:
- Study Guides: These guides offer concise summaries of important concepts, making them an excellent resource for quick reviews and final preparations.
- Podcasts and Audio Resources: Listening to expert discussions or lectures can provide additional context and aid in retention, especially for auditory learners.
- Online Forums and Study Groups: Engaging with peers and experts in online forums or study groups allows for collaborative learning and clarifying doubts.
Recommended Websites and Tools
Many websites offer free or paid resources for efficient studying and test preparation. Here are a few to consider:
- Khan Academy: Offers free courses and tutorials on a wide range of subjects,
Time Management Tips for Exam Day
Managing time effectively during a testing session is crucial for maximizing performance. The ability to allocate appropriate time to each section and maintain focus throughout can make the difference between success and stress. This section provides practical strategies for staying organized and composed on test day, helping you navigate the challenges of limited time.
Prepare a Strategy Beforehand
Before entering the testing environment, it’s important to have a clear strategy. Having a plan will prevent you from wasting precious minutes deciding how to approach each section. Consider the following tips:
- Review the Structure: Familiarize yourself with the format and timing of each section. Knowing how much time you should allocate to each part of the test helps you stay on track.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Tackle the simpler questions first to gain confidence and save time for more difficult ones later.
- Set Time Limits: Assign yourself a specific amount of time for each question or section. Use a watch or clock to stay on pace without getting bogged down in any one part.
During the Test
Once the test begins, staying calm and focused is key. Use the following time management techniques to ensure you make the most of your available time:
- Stay Calm and Confident: If you encounter a difficult question, don’t panic. Move on to the next one and return later if necessary. Keeping a level head will improve your decision-making.
- Keep an Eye on the Clock: Regularly check the time to ensure you’re staying within your allocated limits. Set time checkpoints for different sections or question groups.
- Leave Time for Review: If possible, reserve the last 10–15 minutes to go over your answers. Review your work to catch any mistakes and ensure accuracy.
By employing these time management strategies, you can increase your efficiency and reduce anxiety on test day, giving yourself the best chance for success.