
Achieving a certification in process management is an essential step for professionals looking to enhance their skills in improving business operations. This journey requires a solid understanding of key principles and methodologies that drive continuous improvement within organizations.
For those looking to succeed in the foundational level of this certification, it’s important to familiarize oneself with core concepts that apply to every stage of the process. Mastery of these principles can significantly improve problem-solving abilities and contribute to the overall efficiency of any business environment.
Focused preparation is essential for navigating the complexities of the test and ensuring a comprehensive understanding of how to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. Effective study strategies will make it easier to grasp critical tools, techniques, and frameworks required for success.
6sigmastudy Yellow Belt Exam Answers
Achieving certification in process improvement requires a deep understanding of core methodologies and tools designed to optimize organizational performance. The initial level of this qualification focuses on key principles that form the foundation of continuous improvement and problem-solving techniques. Success in this stage hinges on mastering these essential concepts and applying them effectively in practical scenarios.
To succeed, it’s crucial to become familiar with the various strategies and techniques commonly assessed during the evaluation process. Being able to navigate through questions related to process mapping, statistical analysis, and project management will demonstrate your grasp of these fundamental concepts. Understanding how to approach real-life situations with a structured mindset is equally important for performing well in this challenge.
Effective preparation involves reviewing relevant materials, practicing with sample problems, and becoming comfortable with the type of content likely to appear. This approach ensures that you not only understand the concepts but are also prepared to tackle the questions with confidence and clarity.
Overview of Yellow Belt Certification
Obtaining a foundational certification in process management signifies a professional’s ability to contribute to continuous improvement efforts within an organization. This entry-level qualification provides the necessary skills to understand key principles and frameworks used in business optimization projects. Individuals who achieve this certification demonstrate a solid understanding of the basic tools and methodologies that drive efficiency and quality improvements.
Typically, this level of certification is aimed at those who are new to process improvement and wish to build a strong base before advancing to more complex roles. It focuses on essential concepts like problem-solving, process analysis, and the basics of project management, all of which are critical in driving operational success.
| Key Topics | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Mapping | Understanding how to visualize and analyze workflows to identify inefficiencies. |
| Data Collection | Learning how to gather relevant data for process improvement projects. |
| Problem Solving | Applying systematic approaches to address challenges and improve performance. |
| Project Management | Managing projects efficiently to ensure successful process improvement outcomes. |
Understanding Lean Six Sigma Basics
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology focused on improving organizational efficiency by reducing waste and variation in processes. It combines two powerful approaches: Lean, which aims to eliminate non-value-added activities, and Six Sigma, which focuses on reducing defects and variations. The integration of these methods provides a structured framework for continuous improvement, enabling companies to deliver higher quality products and services while minimizing costs.
Core Principles of Lean

Lean focuses on streamlining operations by removing inefficiencies, enhancing the flow of value through a process. It prioritizes the elimination of waste, defined as any activity that consumes resources without adding value. By focusing on areas such as inventory management, lead times, and overall process flow, Lean helps organizations become more agile and responsive to customer demands.
Key Aspects of Six Sigma
Six Sigma is centered around the idea of minimizing defects in any given process, aiming for near perfection with a target of no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It relies heavily on data-driven decisions, using statistical tools to identify, measure, and control process variations. Understanding the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is fundamental for implementing Six Sigma effectively in any project.
Key Concepts for Yellow Belt Exam
For those pursuing an entry-level certification in process improvement, mastering several foundational concepts is essential. These concepts form the building blocks of effective problem-solving and operational efficiency strategies. Familiarity with these core principles ensures that candidates can apply the methodology in practical situations and demonstrate a solid understanding of key techniques and tools used in business optimization.
Below are some of the crucial topics that are often covered during the certification process:
- Process Mapping: The ability to visualize workflows and identify inefficiencies is fundamental. Understanding how to create and analyze process maps is critical for improving operations.
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant and accurate data is necessary for identifying areas that need improvement. This includes knowing the types of data to collect and the methods for capturing it.
- Basic Statistics: Understanding statistical tools and techniques helps to measure process performance and identify areas for improvement. This includes concepts such as mean, median, standard deviation, and control charts.
- Root Cause Analysis: Being able to identify the underlying causes of problems rather than just addressing symptoms is a key skill in any improvement project.
- Problem-Solving Techniques: Knowing how to apply structured methods such as the 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams helps uncover solutions to recurring challenges.
Mastering these concepts will not only aid in preparing for the certification but also enhance the ability to contribute effectively to process improvement efforts in any business environment.
Common Questions on Process Improvement
When starting out with process improvement, individuals often have several key questions regarding the best practices and methods for achieving significant results. These questions usually revolve around understanding the most effective strategies for streamlining operations, solving problems, and measuring performance improvements. Addressing these common inquiries can help clarify the approach and ensure successful implementation of improvement projects.
How do I identify inefficiencies in a process?
Identifying inefficiencies requires a clear understanding of the existing workflow and the ability to recognize areas where resources are being wasted or where bottlenecks occur. Tools like process maps, value stream mapping, and flowcharts can help visualize the current state of a process. Once inefficiencies are spotted, teams can focus on eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing wait times, and improving overall flow.
What role does data play in process improvement?
Data plays a critical role in assessing the performance of any process and identifying areas that need improvement. By collecting accurate data, teams can measure key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze trends, and make informed decisions. Statistical tools, such as control charts and Pareto analysis, can help interpret this data and guide improvement efforts based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Exam Structure and What to Expect
Understanding the format and expectations of a certification assessment is crucial for success. The evaluation typically focuses on fundamental concepts of process improvement, assessing both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Being familiar with the structure helps candidates approach the test with confidence and ensures they are prepared for the types of questions they will encounter.
The structure of this assessment generally includes multiple-choice questions, case studies, and scenario-based problems designed to test the ability to apply key principles in real-world situations. Candidates should expect questions that cover a wide range of topics, such as data analysis, process mapping, root cause identification, and problem-solving techniques.
Additionally, the assessment is often time-constrained, so effective time management during the test is essential. It’s important to pace yourself, ensuring enough time to read through each question carefully and consider all possible answers. Prior preparation through practice exams or study guides can significantly enhance your readiness for the actual assessment.
Preparation Strategies for Success

Effective preparation is key to performing well in any certification assessment. A structured approach not only boosts confidence but also ensures a thorough understanding of core concepts and practical applications. The following strategies can help guide your preparation and increase your chances of success.
Start by reviewing all relevant materials, focusing on the key principles of process improvement, statistical tools, and problem-solving techniques. It’s essential to have a strong grasp of methodologies such as process mapping, data collection, and root cause analysis, as these are fundamental topics often tested during the assessment.
Practice regularly with sample questions and scenario-based problems to familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you may encounter. This will help you develop critical thinking skills and learn how to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. Additionally, try to create a study schedule that breaks down the content into manageable sections, allowing you to focus on one topic at a time.
Lastly, review your progress periodically and identify areas where you need more practice. Seeking feedback from peers or instructors can also be invaluable in pinpointing weaknesses and reinforcing your understanding. By following these strategies, you’ll be well-prepared for the certification challenge.
How to Study Efficiently for the Exam
Studying efficiently is crucial to mastering the material and performing well in any assessment. To optimize your preparation, it’s important to adopt strategies that allow you to absorb and retain key concepts without feeling overwhelmed. Effective study habits focus on quality over quantity and prioritize understanding over memorization.
Begin by organizing the study material into smaller, more manageable sections. This approach helps break down complex topics into bite-sized chunks, making it easier to focus and understand each part thoroughly. Use a study schedule to allocate specific times for each section, allowing for consistent progress without rushing through the material.
Active learning techniques, such as summarizing key concepts in your own words, can be highly beneficial. This reinforces your understanding and helps identify areas that need further clarification. Additionally, practice with mock questions or scenario-based exercises will enhance your ability to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations. Review these exercises regularly to track your improvement and gain confidence in your abilities.
Lastly, avoid cramming the night before. Give yourself enough time to review the material several times, allowing your brain to consolidate information and retain it for the long term. Regular breaks during study sessions also help maintain focus and reduce fatigue.
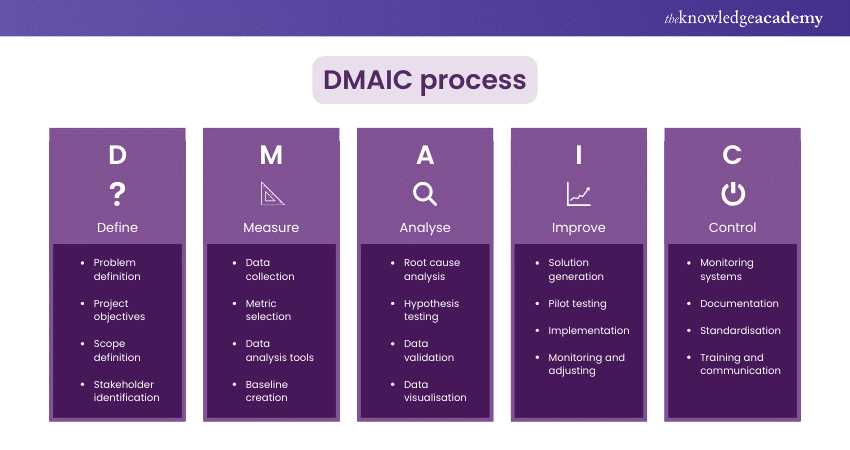
Mastering DMAIC Methodology
The DMAIC methodology is a powerful framework for improving processes and solving complex problems. It provides a structured approach that helps teams systematically analyze and optimize their operations. By mastering each phase of DMAIC, individuals can effectively identify areas for improvement and implement lasting solutions. Understanding and applying this methodology is crucial for anyone involved in process enhancement efforts.
Key Phases of DMAIC
The DMAIC framework consists of five distinct phases that guide the improvement process. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring that the problem is clearly defined, the root causes are identified, and solutions are implemented effectively. Below are the key stages of DMAIC:
- Define: In this phase, the scope of the problem is established, objectives are clarified, and the team is formed. Clear communication of goals ensures everyone is aligned and focused on addressing the right issues.
- Measure: During this phase, data is collected to understand the current process performance. Identifying the key metrics that influence the process is essential for accurate measurement and evaluation.
- Analyze: In this phase, the collected data is analyzed to identify root causes and key issues. Statistical tools and techniques help to uncover the underlying problems that contribute to inefficiency or defects.
- Improve: This stage focuses on developing and implementing solutions to address the identified root causes. Creative thinking and process redesign are often required to eliminate waste and reduce variation.
- Control: The final phase ensures that improvements are sustained over time. Monitoring systems and control plans are put in place to maintain the changes and prevent future issues from arising.
Best Practices for Implementing DMAIC

To successfully apply the DMAIC methodology, there are several best practices to keep in mind:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Always base decisions on solid data and evidence. Using statistical tools will help ensure that the improvements are based on facts rather than assumptions.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involve team members from different departments to gain diverse perspectives and expertise in solving the problem.
- Continuous Monitoring: Even after improvements are made, continuously monitor the process to ensure it remains stable and optimized.
Mastering the DMAIC methodology empowers individuals to approach problem-solving in a logical and systematic way, leading to more effective and sustainable process improvements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Exam
During any certification assessment, it’s easy to make mistakes that can hinder your performance. These errors are often the result of poor preparation, misunderstanding of concepts, or rushing through questions. Identifying and avoiding these common mistakes can greatly improve your chances of success and help you approach the test with confidence.
One of the most frequent mistakes is not fully understanding the question before answering. Rushing through questions without reading them carefully can lead to misinterpretation of the problem, resulting in incorrect answers. It’s crucial to take your time to fully comprehend what is being asked, ensuring that your response addresses the core issue.
Another mistake is overconfidence in memorization. While it’s important to remember key concepts, relying solely on rote memorization can be detrimental. It’s essential to focus on understanding the application of theories and methods rather than just memorizing terms or formulas. This deeper understanding will help you solve complex problems more effectively.
Additionally, neglecting to manage time wisely can lead to unnecessary stress. Some candidates may spend too much time on difficult questions and not leave enough time to answer the rest. Time management is crucial, so it’s recommended to pace yourself and move on if a question is taking too long, returning to it later if necessary.
Lastly, skipping practice and mock tests is a mistake that many make. Without practicing under exam-like conditions, it’s difficult to simulate the pressure of the actual assessment. Regularly taking practice tests helps build familiarity with the format, boosts confidence, and helps identify areas that need improvement.
Tips for Answering Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions are a common format in assessments and require careful attention to detail. While they may seem straightforward, answering them correctly involves strategic thinking. By following a few key tips, you can improve your chances of selecting the correct answer and avoid common pitfalls.
Key Strategies for Success
Here are some essential tips for approaching multiple choice questions with confidence:
- Read the Question Carefully: Always read the question thoroughly before looking at the options. This ensures you understand exactly what is being asked and helps you avoid confusion later.
- Eliminate Clearly Incorrect Choices: Often, multiple choice questions contain one or two answers that are obviously wrong. Eliminate these choices first to narrow down your options.
- Look for Keywords in the Question: Keywords or phrases can help guide you to the correct answer. Pay attention to terms such as “always,” “never,” “most,” or “least,” as they can significantly influence the correct response.
- Don’t Rush: Take your time to consider each option carefully. If you’re unsure, it’s better to skip a question and return to it later with a fresh perspective.
- Trust Your First Instinct: If you’re torn between two answers, trust your initial reaction. Often, your first choice is the correct one, unless you find a strong reason to change it.
Understanding Answer Patterns
Some multiple choice questions may include answer choices that seem similar or tricky. Here’s a guide to understanding common answer patterns:
| Answer Pattern | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| All of the Above | If you’re confident that more than one option is correct, consider selecting “All of the Above.” However, be cautious of this choice when the other answers are extreme or unrelated. |
| None of the Above | If you know that none of the answers are correct, this can be a valid choice. But if one of the answers seems plausible, “None of the Above” is likely incorrect. |
| Extreme Words | Be cautious of answers that include words like “always” or “never,” as they often indicate an overly simplistic answer that is more likely to be incorrect. |
By employing these strategies, you can approach multiple choice questions with greater precision and improve your performance on assessments.
Importance of Data Collection in Projects
Data collection is a critical component of any project, serving as the foundation for informed decision-making and continuous improvement. By gathering relevant information, teams can accurately assess the current state of the project, identify issues, and make evidence-based adjustments to enhance outcomes. Without reliable data, it becomes challenging to measure progress, analyze results, or achieve the desired goals.
Effective data collection not only provides insight into what is happening within a project but also allows for tracking key metrics, forecasting future trends, and pinpointing areas for optimization. It empowers teams to make strategic decisions and take actions that align with the project’s objectives.
Benefits of Data Collection
The role of data collection in project management extends beyond just capturing numbers; it supports a wide range of essential activities:
- Improved Decision Making: With accurate data, teams can assess risks, predict outcomes, and make better decisions that drive project success.
- Performance Measurement: Data allows for the tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure how well the project is progressing toward its goals.
- Problem Identification: Collecting data helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or issues early on, enabling proactive solutions to be implemented.
- Resource Allocation: Data helps teams allocate resources effectively, ensuring that time, money, and effort are directed to the most impactful areas.
Common Methods of Data Collection

There are several ways to collect data throughout a project, depending on the nature of the project and the specific needs of the team. Here are some common methods:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: These tools are useful for gathering subjective data from stakeholders, team members, or customers.
- Interviews: One-on-one interviews provide in-depth qualitative data, often revealing insights that surveys might not capture.
- Observational Studies: Observing processes or behaviors directly can yield valuable data on how work is actually being done and where improvements can be made.
- Automated Data Collection Tools: Software and tools can automate the collection of real-time data, especially in large-scale projects where manual collection would be inefficient.
Ultimately, proper data collection ensures that projects are carried out efficiently, effectively, and in a way that aligns with the goals set at the outset. It forms the backbone of continuous improvement, providing actionable insights that drive ongoing success.
Role of Statistics in Lean Six Sigma
Statistics play a vital role in the Lean Six Sigma methodology, providing the tools and techniques needed to measure, analyze, and improve processes. By leveraging statistical data, teams can identify patterns, assess variation, and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance. The reliance on statistics ensures that improvements are based on objective evidence rather than assumptions, resulting in more accurate and sustainable outcomes.
In Lean Six Sigma, statistical methods help organizations quantify problems, track progress, and validate improvements. The use of data-driven insights allows teams to pinpoint inefficiencies, reduce waste, and achieve higher levels of consistency and quality in their processes.
Key Statistical Tools in Lean Six Sigma
- Descriptive Statistics: This includes tools like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range, which summarize data and provide insights into process performance.
- Control Charts: Used to monitor process stability over time, control charts help identify variations and determine whether a process is in control or needs adjustments.
- Process Capability Analysis: This tool measures the ability of a process to produce products or services within specified limits, helping to assess whether a process meets customer requirements.
- Hypothesis Testing: Hypothesis testing allows teams to determine if changes made to a process have resulted in significant improvements, by comparing data before and after changes.
- Regression Analysis: This technique helps identify relationships between variables and predict outcomes, assisting in understanding how different factors influence process performance.
Benefits of Using Statistics in Lean Six Sigma
Integrating statistics into Lean Six Sigma projects offers several advantages that contribute to process optimization:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Statistics allow for objective decision making, reducing reliance on intuition and guesswork, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
- Improved Process Understanding: Statistical analysis helps teams gain deeper insights into the process behavior, uncovering hidden patterns and sources of variation.
- Efficient Problem Solving: By quantifying problems, teams can pinpoint the root causes more efficiently and implement targeted improvements.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Statistical tools help track process performance, ensuring that improvements are sustained and quality standards are maintained.
Ultimately, the role of statistics in Lean Six Sigma is to provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions, identifying areas of improvement, and ensuring the continuous optimization of processes. By integrating statistical methods into process management, organizations can achieve higher efficiency, consistency, and customer satisfaction.
How to Interpret Process Maps
Process maps are powerful tools that visually represent the flow of activities within a system or process. These diagrams allow teams to understand the sequence of operations, identify potential inefficiencies, and pinpoint areas for improvement. By breaking down complex processes into simple, easy-to-understand visuals, process maps provide valuable insights into how a process functions and where changes might be necessary.
Interpreting a process map effectively requires a clear understanding of the symbols, flow, and relationships between various process steps. The goal is to analyze how each component of the process contributes to the overall outcome and identify areas where changes or improvements can be made to enhance efficiency or quality.
Key Components of a Process Map

When interpreting a process map, it’s essential to be familiar with the key components and symbols that are commonly used to represent process steps and decision points:
- Rectangles: Represent process steps or activities, where work is performed or decisions are made.
- Diamonds: Indicate decision points, where a yes/no or true/false decision is made that will impact the next step.
- Arrows: Show the flow of the process, connecting different steps and illustrating the sequence of activities.
- Ovals: Typically represent the start or end points of the process, defining the boundaries of the flow.
- Circles: Indicate connectors, typically used when a process map continues on another page or section.
Steps to Interpret a Process Map
To successfully interpret a process map, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Identify the Start and End Points: Look for the ovals or other boundary indicators that define where the process begins and ends. This helps set the context for the entire flow.
- Step 2: Follow the Flow: Use the arrows to trace the process flow from start to finish. Pay attention to decision points and the flow paths that emerge from them.
- Step 3: Examine the Process Steps: Review each rectangle to understand the activities performed at each step. Consider how they contribute to the overall process outcome.
- Step 4: Look for Bottlenecks or Inefficiencies: Analyze the process for any areas where delays, repetition, or unnecessary steps occur. These are potential areas for improvement.
- Step 5: Identify Inputs and Outputs: In some process maps, inputs (resources, information) and outputs (products, outcomes) may be clearly defined. Understanding these relationships is key to optimizing the process.
By following these steps, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how a process operates and identify areas for streamlining, reengineering, or enhancing quality. Interpreting process maps is a skill that can help drive continuous improvement initiatives and lead to more efficient, effective processes.
Understanding the Voice of the Customer

The Voice of the Customer (VOC) refers to the insights, feedback, and expectations that customers have regarding a product or service. It is crucial for organizations to actively listen to and understand these needs to improve their offerings, increase satisfaction, and build loyalty. By capturing and analyzing VOC, businesses can gain valuable perspectives that drive decision-making, product development, and process improvements.
Gathering and interpreting customer feedback ensures that an organization’s actions align with customer expectations, ultimately enhancing both the customer experience and business performance. This process involves collecting data through various methods, analyzing it, and using it to guide improvements that meet customer demands effectively.
Methods for Collecting Customer Feedback
There are several ways to collect valuable input from customers, each suited to different contexts and goals. Some of the most common methods include:
- Surveys: Structured questionnaires designed to gather specific information about customer experiences, preferences, and satisfaction.
- Interviews: Direct, often one-on-one conversations with customers to gather in-depth insights into their needs and expectations.
- Focus Groups: Small groups of customers discussing products or services to provide qualitative feedback on their experiences and suggestions.
- Social Media: Monitoring platforms where customers share their opinions, complaints, and praise about a brand or product.
- Customer Support Interactions: Analyzing feedback from customer service channels, including emails, calls, and chats, to identify recurring issues or concerns.
Interpreting Customer Feedback

Once customer feedback is collected, it is important to analyze it effectively to identify patterns, trends, and actionable insights. Here are some strategies to consider when interpreting VOC data:
- Quantify the Data: Use numerical analysis to identify common issues, preferences, and overall satisfaction levels, especially when dealing with large volumes of responses.
- Identify Key Themes: Group similar feedback to uncover broader trends or recurring concerns that can inform areas for improvement.
- Map Customer Journey: Place customer feedback within the context of their entire experience, from initial contact to post-purchase, to understand pain points and opportunities for enhancement.
- Prioritize Issues: Rank feedback based on frequency, impact, and relevance to ensure that the most critical customer needs are addressed first.
By effectively capturing and analyzing the Voice of the Customer, organizations can create customer-centric strategies, drive continuous improvement, and ultimately deliver products and services that better align with customer expectations. This process is a key element in achieving long-term business success and fostering customer loyalty.
How to Apply Continuous Improvement

Continuous improvement is an ongoing effort to enhance products, services, or processes over time. By adopting a systematic approach to improvement, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall quality. The goal is to create a culture where improvement is not seen as a one-time initiative, but as an integral part of everyday operations.
Implementing continuous improvement involves identifying areas for enhancement, setting measurable goals, and consistently making small, incremental changes. These changes, though often subtle, accumulate over time, leading to significant improvements. The key to success lies in fostering a mindset of learning, experimentation, and adaptation across all levels of an organization.
Steps to Apply Continuous Improvement
To effectively implement continuous improvement, organizations can follow these structured steps:
- Identify Opportunities: Start by observing processes and gathering feedback to pinpoint areas that could benefit from improvement. This could involve looking for inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas where customer satisfaction could be enhanced.
- Set Clear Objectives: Once opportunities are identified, set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Clear objectives guide improvement efforts and help measure success.
- Analyze the Process: Understand the current state of the process by collecting data and performing a detailed analysis. Techniques like process mapping or root cause analysis can help identify underlying issues that need to be addressed.
- Implement Changes: Apply small, targeted changes that can have a significant impact. These could involve adjusting workflows, adopting new tools, or refining policies to streamline operations.
- Monitor Progress: Track the results of the changes made. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) and feedback to assess whether the improvements are achieving the desired outcomes.
- Standardize Successful Changes: If a change proves effective, standardize the new process to ensure it is consistently applied. Document the improvements and train relevant teams to sustain the progress.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuous improvement is cyclical. After implementing changes and achieving results, revisit the process to identify new opportunities for enhancement, ensuring the cycle of improvement continues.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
For continuous improvement to be successful, it must be embraced by everyone within the organization. This requires a shift in mindset from simply reacting to problems to proactively seeking ways to improve. Key strategies include:
- Encouraging Employee Involvement: Involve employees at all levels in the improvement process. They are often the ones closest to the work and can provide valuable insights into potential changes.
- Providing Training and Resources: Equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to contribute to improvement initiatives. Offer training on process analysis, problem-solving techniques, and performance measurement.
- Recognizing and Rewarding Improvements: Recognize and celebrate successful improvements, whether big or small. Rewarding employees for their contributions reinforces the importance of continuous improvement and motivates others to get involved.
By embedding continuous improvement into the organization’s culture, businesses can drive long-term success, increase operational efficiency, and foster innovation. The process becomes a natural part of daily operations, helping organizations adapt to changing environments and meet evolving customer needs.
Final Review and Exam Day Tips
As the assessment day approaches, it is important to focus on consolidating your knowledge and preparing mentally for success. A thorough review of the material, along with strategic preparation for the day itself, can greatly enhance your confidence and performance. The goal is to ensure that all key concepts are fresh in your mind and that you are ready to handle the format of the questions with ease.
In this section, we will cover key steps for your final review, along with useful tips to ensure you approach the assessment day feeling prepared and calm. The final review period is an opportunity to focus on areas of improvement, while exam day tips will help you manage your time and reduce stress.
Final Review Tips
The final review process should include a combination of self-assessment and targeted revision. Use the following strategies to make the most of your study time:
- Revisit Key Concepts: Focus on the most important topics and review the foundational principles that you will be tested on. Make sure to revisit areas where you feel less confident.
- Practice with Mock Tests: Take practice questions or mock tests to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you will encounter. This will help you become comfortable with the testing style and identify areas needing more attention.
- Review Mistakes: After completing practice tests, go over your incorrect answers. Understand why your answers were wrong and learn from those mistakes to avoid repeating them.
- Use Visual Aids: Charts, diagrams, and process maps can help you visualize complex concepts. These aids are particularly useful for understanding processes and key methodologies.
- Summarize Important Points: Create summary notes or flashcards that highlight critical information. This will help reinforce your understanding and make it easier to review quickly before the assessment.
Exam Day Preparation Tips
On the day of the assessment, managing your time and maintaining a clear mind are key to success. Follow these tips to ensure a smooth experience:
- Get Adequate Rest: Ensure you get a good night’s sleep before the assessment day. Being well-rested will help you stay focused and alert during the test.
- Eat a Healthy Meal: Have a balanced meal before the test to maintain energy levels. Avoid heavy foods that may make you feel sluggish.
- Arrive Early: Give yourself plenty of time to arrive at the testing location, so you don’t feel rushed. This will help you stay calm and collected.
- Read Instructions Carefully: Take time to read all instructions carefully before starting the assessment. Make sure you understand the requirements and expectations.
- Manage Your Time: Allocate your time wisely during the assessment. Don’t spend too much time on any one question. If unsure, move on and return to it later.
- Stay Calm: If you feel stressed, take a few deep breaths and refocus. Staying calm will help you think clearly and avoid unnecessary mistakes.
Table: Final Review Checklist
| Activity | Purpose | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Review key concepts | Reinforce understanding of essential topics | 1-2 days before |
| Practice with mock tests | Simulate exam conditions | 2-3 days before |