
Being prepared to act in critical situations can make all the difference when someone’s life is at stake. Knowing how to respond quickly and effectively can help prevent further harm and even save lives. The ability to perform life-saving procedures is an invaluable skill that can be learned and tested through comprehensive training programs.
Throughout this guide, we will cover key techniques and procedures that are often tested in certifications, ensuring you’re fully equipped to face emergencies with confidence. Whether you’re learning how to handle breathing difficulties or severe injuries, mastering these techniques is crucial to providing immediate help in urgent circumstances.
Understanding the core concepts of emergency medical procedures will give you the foundation needed to make informed decisions under pressure. Practical knowledge combined with theoretical understanding forms the backbone of any effective rescue operation. This section is designed to prepare you for both the theoretical and practical elements of this life-saving training.
CPR Certification Exam Essentials
Acquiring certification for life-saving procedures is a vital step in becoming a capable responder in emergency situations. Understanding the key aspects and procedures tested during the assessment is crucial for success. In this section, we will explore the necessary skills and knowledge required to pass certification evaluations, ensuring you are ready to provide effective help when needed most.
Key Skills to Master
During the certification process, you will need to demonstrate your ability to handle various emergency scenarios. From managing unconscious individuals to ensuring airway clearance, each skill is tested for accuracy and effectiveness. Mastery of these techniques requires both practice and a thorough understanding of proper protocols. The key is to remain calm and focused, applying each step systematically to maximize outcomes.
What to Expect During the Assessment

Assessments are designed to evaluate your competence in practical and theoretical areas. Expect a mix of theoretical questions to test your understanding of the procedures, along with practical exercises where you will need to perform the necessary steps. The key to success is familiarity with the processes, confidence in your actions, and the ability to recall each step under pressure.
Understanding CPR for Adults
When an adult faces a life-threatening situation involving a lack of oxygen or circulation, knowing the appropriate procedures to restore vital functions can be the difference between life and death. This section covers the key techniques used to revive an adult in an emergency, focusing on the correct approach and timing of each action to ensure the best possible outcome.
Steps to Perform for an Adult

The process begins with assessing the situation and ensuring the environment is safe. Once you’ve confirmed the individual is unresponsive and not breathing, it’s time to initiate the critical steps. The most common technique involves chest compressions, combined with rescue breaths, which should be delivered in a steady, rhythmic manner. Ensuring the proper depth and rate of compressions is essential to promoting blood circulation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most frequent errors is improper hand placement or insufficient compression depth, which can drastically reduce effectiveness. Another common mistake is failing to maintain a consistent rhythm, leading to delays in resuscitation efforts. Remember, keeping the airway clear and avoiding interruptions in compressions can significantly improve the chances of recovery.
Key First Aid Concepts to Master
In emergency situations, having a solid grasp of fundamental procedures can help stabilize an individual until professional medical assistance arrives. This section highlights the essential techniques and concepts that form the foundation of immediate care. Mastering these core principles is crucial to ensuring your response is both effective and timely.
Essential Techniques to Learn
Several techniques are fundamental to providing immediate assistance in various emergency situations. These skills must be practiced to ensure confidence and accuracy. Key methods include:
- Controlling bleeding and applying pressure to wounds
- Clearing the airway in cases of choking or obstruction
- Managing burns and preventing further tissue damage
- Recognizing signs of shock and taking appropriate action
Understanding Medical Priorities
In critical situations, knowing how to prioritize care can save lives. Understanding which issues need immediate attention and which can be managed later is key to successful intervention. The following priorities are crucial to any emergency response:
- Ensuring the airway is clear and breathing is restored
- Managing severe bleeding to prevent shock
- Assessing for signs of cardiac arrest and initiating the correct steps
Top Questions in First Aid Tests
When preparing for a certification assessment in emergency care, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the types of questions that assess your knowledge and practical understanding. These questions are designed to evaluate your ability to respond appropriately in life-threatening situations. In this section, we will explore some of the most common queries that are likely to appear in evaluations, helping you prepare effectively.
Test questions typically focus on a range of scenarios, assessing both your theoretical knowledge and your ability to apply it under pressure. Questions often cover areas such as injury treatment, basic life support techniques, and how to handle medical emergencies. Understanding the key principles behind these situations will increase your chances of success.
Examples of typical questions include:
- What steps should be taken if someone is choking?
- How do you manage severe bleeding before medical help arrives?
- What are the signs of shock and how do you respond?
- What should you do if a person is unresponsive but breathing?
These types of questions test your ability to prioritize actions and make life-saving decisions in critical situations. Studying and practicing these scenarios will help ensure you are ready to perform confidently and effectively when needed.
Life-Saving Skills for Emergency Situations

In critical situations, knowing how to act quickly and effectively can be the difference between life and death. Whether it’s managing an injury or providing basic support to someone in distress, the ability to perform the right actions under pressure is vital. This section focuses on the essential skills every individual should master to handle emergencies confidently.
These key abilities not only help stabilize a person but also increase the chances of recovery until professional help arrives. Below are some of the most important techniques you should be familiar with:
Essential Life-Saving Techniques
- Managing Airway Obstruction: Ensuring the airway is clear to allow breathing is a critical first step in any emergency.
- Controlling Severe Bleeding: Applying pressure to wounds and using proper techniques to prevent excessive blood loss.
- Recognizing Cardiac Emergencies: Knowing the signs of heart attacks and how to provide assistance if the heart stops beating.
- Handling Burns: Taking immediate action to cool and protect burn injuries from further damage.
- Preventing Shock: Identifying the signs of shock early and taking steps to stabilize the person.
Important Steps for Immediate Response
In the event of a life-threatening emergency, taking the right steps without hesitation can greatly improve the chances of survival. The following actions are crucial for effective response:
- Assess the scene for safety and ensure you are not at risk.
- Check for responsiveness and breathing before proceeding with any actions.
- Apply life-saving techniques such as clearing the airway or performing chest compressions as needed.
- Stay calm and provide clear information when calling for professional help.
Mastering these life-saving skills is essential for anyone looking to provide immediate assistance in emergencies. Practicing these techniques will ensure you’re prepared to act when needed most.
CPR Techniques for Infants and Children
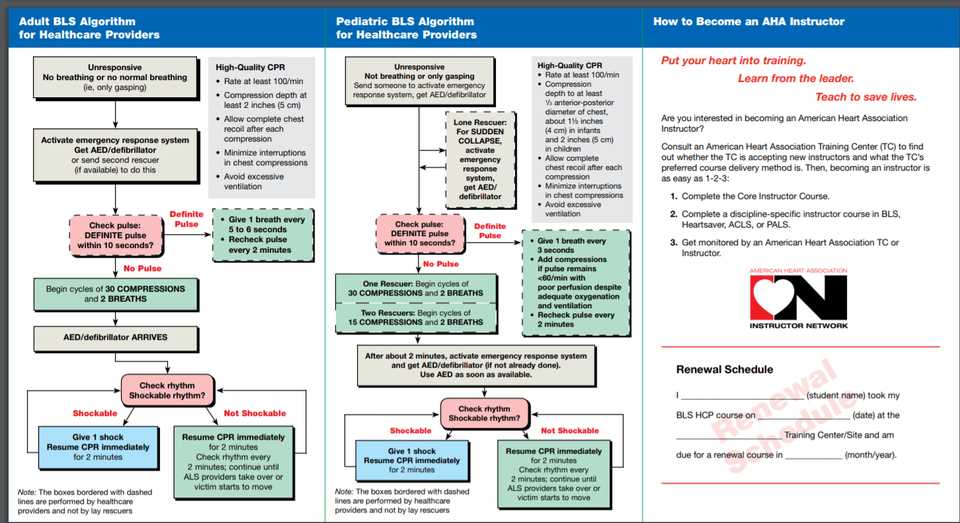
When responding to a life-threatening situation involving an infant or child, it’s essential to understand that the procedures differ from those used with adults. Due to their smaller size and unique physical characteristics, adjustments must be made to ensure proper care. This section will focus on the key techniques used to assist infants and children in critical situations where breathing or circulation is compromised.
For young patients, the most important factors are the depth and force of each action. The goal is to provide just enough pressure to stimulate circulation and restore oxygen flow without causing harm. These techniques should be practiced carefully, as applying too much force or pressure can result in injury.
Here are the main steps for performing emergency care on infants and children:
- Use two fingers for chest compressions in infants, ensuring the depth is about 1.5 inches (4 cm).
- For children, use one or two hands depending on their size, with compressions at a depth of about 2 inches (5 cm).
- Ensure the airway is open, gently tilting the head back and lifting the chin.
- Give rescue breaths using a gentle puff of air, ensuring the chest rises with each breath.
Remember, when dealing with infants and children, less is more in terms of pressure and force. By mastering these techniques, you can provide life-saving support until professional medical help arrives.
Common Mistakes During CPR Practice
While practicing life-saving procedures, it is easy to make mistakes that could affect the outcome of an emergency. These errors often stem from a lack of proper training, nerves, or a misunderstanding of the correct techniques. This section highlights some of the most common mistakes people make when practicing these critical skills and provides guidance on how to avoid them.
Incorrect Hand Placement
One of the most frequent errors during practice is incorrect hand placement. If the hands are positioned too high or too low on the chest, it can lead to ineffective compressions and potential injury. The heel of the hand should be placed on the lower half of the sternum, with the other hand on top, ensuring a firm and stable position.
Insufficient Compression Depth
Another common mistake is not applying enough pressure during compressions. Insufficient depth reduces the effectiveness of the procedure, as blood circulation may not be properly stimulated. For adults, compressions should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) deep, while for children, it should be around 2 inches, and for infants, approximately 1.5 inches (4 cm). Ensure that each compression is deep enough to make a significant impact.
Other errors that may occur include improper timing of compressions and rescue breaths, too many interruptions during the process, or failing to reassess the patient’s condition regularly. By practicing these techniques correctly, you can avoid these pitfalls and provide the best care in emergencies.
Preparing for Your First Aid Exam
When preparing for a certification assessment in emergency care, it’s important to understand the core concepts and techniques that will be tested. A structured approach to studying will ensure you are well-equipped to handle various situations that may arise during the test. This section provides helpful tips and guidance on how to efficiently prepare for your upcoming assessment.
One of the most effective ways to study is to break down the key areas into manageable sections. Focusing on one topic at a time allows for better retention and a clearer understanding of the material. Below is a helpful breakdown of the key areas to focus on while studying for your certification:
| Topic | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Basic Life Support | Learn how to perform life-saving techniques such as chest compressions and rescue breathing. |
| Wound Management | Understand how to control bleeding and treat different types of injuries. |
| Shock Recognition | Identify signs of shock and how to respond effectively. |
| Choking Response | Master techniques for clearing an obstructed airway. |
| Medical Emergencies | Study how to recognize common medical conditions and respond accordingly. |
In addition to studying the theory, practical practice is equally important. Taking part in mock scenarios, either through hands-on training or practice tests, will help reinforce what you’ve learned. Remember to also review any guidelines or manuals provided by the certifying body, as they will often contain essential information that will appear on the assessment.
How to Respond in Cardiac Arrest Cases
When faced with a person experiencing a sudden cardiac emergency, immediate action is crucial. The heart stops beating effectively, cutting off blood flow to vital organs, which can lead to irreversible damage if not addressed quickly. In these situations, every second counts. This section covers the necessary steps to take in order to maximize the chances of survival until professional help arrives.
Recognizing the signs of cardiac arrest is the first step. A person who is unresponsive and not breathing, or only gasping, may be in cardiac arrest. In this case, quick intervention is required. Below are the essential actions to follow:
- Call for Help: Immediately contact emergency services and alert them to the situation. Time is critical.
- Open the Airway: Ensure that the person’s airway is clear by tilting their head back gently and lifting the chin.
- Chest Compressions: Start chest compressions by placing your hands on the center of the chest. Apply firm pressure at the correct depth to help circulate blood.
- Rescue Breathing: If trained, provide rescue breaths by pinching the person’s nose and delivering a breath into their mouth, ensuring the chest rises.
- Defibrillation: If available, use an automated external defibrillator (AED) to deliver a shock, which can help restart the heart.
Remember that the sooner these steps are implemented, the better the outcome. It is important to keep performing chest compressions and rescue breaths until emergency responders take over or the person starts breathing on their own.
The Importance of Quick Action in Emergencies
In critical situations where a person’s life is at risk, swift intervention can make the difference between life and death. Many emergencies, such as sudden cardiac events or severe trauma, require immediate attention to prevent further harm and increase the chances of survival. The faster a responder can take appropriate measures, the better the potential outcome. This section explores the reasons why quick action is essential and the impact it has on saving lives.
Studies show that prompt response during emergencies can significantly improve survival rates. Whether it’s performing life-saving techniques or calling for professional help, every moment counts. Delayed action can lead to complications or worsen the individual’s condition, making the situation more difficult to manage.
The table below outlines how time affects the outcome of common emergency situations:
| Time | Impact |
|---|---|
| 0-4 Minutes | Maximum chance of survival with quick intervention. Brain function and organs are still viable. |
| 4-6 Minutes | Brain damage starts to occur. Intervention is critical to prevent long-term harm. |
| 6-10 Minutes | Severe brain damage may occur. Survival chances decrease without immediate care. |
| 10+ Minutes | High risk of irreversible damage or death. Immediate medical intervention is required. |
Taking immediate action in emergencies allows for a higher chance of recovery and minimizes potential long-term consequences. By being prepared and confident in responding quickly, you can make a significant difference in the outcome of a critical situation.
Basic First Aid Procedures to Know
In any emergency, knowing how to perform essential life-saving procedures can make all the difference. Whether you’re dealing with a simple cut or a more serious injury, understanding basic techniques allows you to provide crucial help before professional medical assistance arrives. This section covers key procedures every responder should be familiar with to effectively manage common medical situations.
Being prepared for various emergencies involves learning how to address injuries and illnesses in the most effective way possible. Below are some of the most important procedures to master:
- Wound Care: Know how to clean and dress cuts, abrasions, and more serious wounds to prevent infection and control bleeding.
- Burn Treatment: Understand how to treat burns, from minor to severe, including cooling the burn and protecting the area from further damage.
- Controlling Bleeding: Be prepared to apply pressure to stop bleeding and, if necessary, use a tourniquet in extreme cases.
- Choking Relief: Learn the techniques to clear an obstructed airway, including the Heimlich maneuver for both adults and children.
- Splinting: Familiarize yourself with how to stabilize broken limbs to reduce pain and prevent further injury before medical professionals can assist.
Mastering these basic procedures increases your ability to respond confidently and effectively in emergencies. The more prepared you are, the more you can help protect others from serious harm or complications while awaiting professional care.
Common CPR Exam Scenarios Explained
During assessments of life-saving skills, it’s important to be familiar with a variety of situations that you might encounter. These scenarios often test your ability to respond quickly and appropriately under pressure. Understanding the different types of emergencies and how to handle them effectively is key to ensuring the best possible outcome. This section explains common scenarios that are often presented during skill evaluations and how to navigate them successfully.
Each situation can vary in terms of severity and the steps required for intervention. Below are some common scenarios you may encounter, along with the actions typically required:
- Unresponsive Adult: In this scenario, the individual is not breathing or is only gasping. Immediate intervention is necessary. The responder should check for responsiveness, call emergency services, and begin chest compressions, followed by rescue breaths if trained.
- Choking Victim: This involves a person who is unable to breathe due to a blocked airway. Perform the Heimlich maneuver or abdominal thrusts to expel the object obstructing the airway.
- Unresponsive Child: Similar to the adult scenario, but the procedure differs slightly. For children, use one hand for chest compressions and be cautious with the depth of pressure applied. Rescue breaths should be administered after each set of compressions.
- Infant with No Pulse: When an infant is unresponsive and not breathing, use two fingers for chest compressions and provide gentle rescue breaths. It’s essential to use less pressure due to the infant’s small body size.
- Electrocution: A person who has been electrocuted may have an irregular heartbeat or no pulse. Ensure the source of electricity is turned off before attempting to assist. Follow standard life-saving protocols based on the victim’s responsiveness.
Understanding the specific needs and responses for each situation will help ensure that you are prepared to react correctly when required. It’s also important to stay calm and focused, as emergencies can escalate quickly, requiring efficient and precise action.
Dealing with Breathing Emergencies Effectively
Breathing difficulties are among the most critical medical emergencies that require immediate attention. Whether caused by an obstruction, an allergic reaction, or a sudden medical condition, quick intervention can be the difference between life and death. Understanding how to recognize breathing problems and how to respond effectively is essential for anyone prepared to handle emergencies.
In the event of a breathing emergency, it is crucial to remain calm and focused. The steps to take depend on the nature of the situation and the person’s age. Below are common scenarios and how to manage them:
Recognizing Signs of Breathing Trouble
Before taking action, it’s important to identify the signs of breathing distress. Common indicators include:
- Labored or rapid breathing
- Weak or irregular breaths
- Blue or pale skin, especially around the lips or fingertips
- Inability to speak or cry in children
Immediate Actions to Take
Once you’ve identified breathing issues, here’s how to respond:
- Clear the Airway: If the individual is choking, perform back blows or abdominal thrusts to clear the airway obstruction.
- Provide Rescue Breaths: If the person is not breathing but has a pulse, perform rescue breaths. Ensure a proper seal over the mouth and nose (or just the mouth for adults) and deliver slow, steady breaths.
- Use an Inhaler or Epinephrine: If the person has a known condition, such as asthma or an allergy, help them administer their inhaler or epinephrine as directed by their medical plan.
- Monitor and Reassure: Keep the person calm and monitor their breathing. If they lose consciousness or stop breathing, begin chest compressions immediately.
Breathing emergencies can escalate quickly, so it’s important to assess the situation promptly and seek professional help as soon as possible. By acting swiftly and effectively, you can significantly increase the chances of a positive outcome.
Key Differences Between CPR and First Aid
In emergency situations, knowing when and how to provide help can make a significant difference. While both are critical for saving lives, the approaches to providing assistance vary in scope, techniques, and situations. Understanding the key differences between these two types of interventions is essential for anyone involved in emergency response.
The primary distinction lies in the focus of each type of intervention. One method is often used to address immediate life-threatening issues, while the other focuses on stabilizing a person or offering temporary relief. Below are the main points of difference:
Scope of Application
The first major difference lies in the breadth of the skills involved:
- Life-Threatening vs. Stabilization: One technique is specifically designed to handle critical situations, like cardiac arrest or respiratory failure, while the other provides general care for a variety of injuries and medical conditions.
- Duration of Intervention: One intervention is typically a brief, immediate action until professional help arrives, while the other can be sustained until the individual receives further medical treatment.
Types of Actions Involved
The methods and procedures used in each situation also differ:
- Rescue Breathing and Chest Compressions: One focuses on restoring normal breathing through techniques such as mouth-to-mouth or chest compressions.
- General Support: The other involves providing support for a range of conditions such as cuts, bruises, fractures, or burns. It includes actions like applying pressure to a wound, immobilizing a limb, or managing shock.
Both approaches are essential in an emergency, but they serve distinct roles. Knowing when to use each method is vital for ensuring the right care is provided in the right circumstances.
Essential Equipment for First Aid Training
Proper training for emergency response situations requires the right tools to ensure effective practice and readiness. Having the appropriate gear allows trainees to simulate real-life scenarios, building the confidence and skills needed to act quickly and correctly in urgent situations. The essential equipment for this type of training is designed to mimic the conditions of actual emergencies and provide hands-on experience.
The following items are commonly used in training courses to ensure participants are prepared for various medical emergencies:
Basic Medical Supplies
These tools form the foundation of most training courses and are used to practice common interventions:
- Bandages and Dressings: Used to control bleeding, dress wounds, and provide support for injuries.
- Gauze Pads: For cleaning and covering wounds to prevent infection.
- Adhesive Tape: Essential for securing bandages or dressings in place.
Mannequins and Simulators
Mannequins and other simulation equipment allow trainees to practice life-saving skills in a controlled environment:
- CPR Mannequins: Used to practice chest compressions and rescue breathing.
- Rescue Simulation Kits: Includes a variety of tools like defibrillators and airway management devices to simulate different emergency conditions.
Using these tools ensures that participants gain hands-on experience and can effectively respond to real-life situations with confidence and accuracy.
What to Expect on a CPR Exam
When preparing for an evaluation focused on life-saving techniques, it’s important to understand the structure and content of the test. Such assessments typically assess a candidate’s ability to respond efficiently in emergency situations, applying learned skills to real-world scenarios. The evaluation combines theoretical knowledge with practical exercises to ensure proficiency in handling critical incidents.
The test usually consists of two key sections: a written portion that covers knowledge of medical emergencies, and a practical part that requires candidates to demonstrate their response techniques. Here’s an overview of what you can expect:
Written Assessment
The theoretical portion often includes multiple-choice or true/false questions, testing your knowledge on various emergency response protocols. Topics may include:
- Basic emergency procedures: Understanding the steps to take in critical situations.
- Life-saving techniques: Knowledge of essential methods like airway management and circulation support.
- Signs of medical conditions: Recognizing symptoms of serious conditions like choking, heart attack, or stroke.
Practical Skills Test
- Performing chest compressions: You’ll practice the correct technique to support blood circulation in someone experiencing a life-threatening condition.
- Rescue breathing: The use of proper methods to ensure the patient’s airway is open and they are breathing.
- Using a defibrillator: Training on the correct application of an automated external defibrillator (AED) when someone’s heart stops.
Success in this type of evaluation requires not only theoretical understanding but also the ability to perform under pressure, demonstrating the essential techniques accurately and efficiently.
Understanding Exam Grading Criteria
When preparing for a certification assessment, understanding the grading system is essential for success. Evaluators look for both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The goal is to ensure that candidates are fully equipped to handle emergency situations effectively. Grading criteria are designed to assess the depth of your understanding, as well as your ability to perform life-saving tasks correctly under pressure.
The evaluation process generally divides into two main components: written knowledge and hands-on demonstration. Each section is graded based on specific criteria to ensure that you can apply techniques appropriately and respond to various medical situations with confidence. Here’s an overview of what evaluators typically look for:
Written Component

The written portion typically consists of multiple-choice or true/false questions. Grading in this section focuses on:
- Knowledge of emergency procedures: Understanding the correct steps to take in various medical emergencies.
- Signs and symptoms: Identifying the symptoms of conditions that require immediate attention.
- Legal and ethical considerations: Being aware of the responsibilities involved when providing assistance to others.
Practical Skills Assessment
The practical segment evaluates your ability to perform techniques that are crucial in an emergency. Grading focuses on:
- Technique accuracy: Correct application of skills such as chest compressions, airway management, and rescue breathing.
- Efficiency: How quickly and effectively you respond to the situation without compromising quality.
- Safety: Ensuring that both the patient and yourself are safe during the process.
Ultimately, the grading process is intended to measure both your knowledge and your ability to apply it effectively in real-life situations. Success in this assessment ensures that you are prepared to assist others in times of crisis.