
When preparing for a certification in emergency response, understanding the core concepts and techniques is essential for success. Whether you’re looking to provide help in critical situations or aiming to meet professional standards, a solid foundation in life-saving practices can make all the difference.
Key skills and techniques are tested to ensure you’re ready to react swiftly and effectively when faced with an emergency. From recognizing signs of distress to performing life-saving measures, each step you take can be crucial in saving a life.
As you go through the training, it’s important to focus on the practical application of these skills, as well as the theory behind them. Being familiar with the necessary steps and knowing how to execute them under pressure is the key to achieving success and gaining confidence in your abilities.
Understanding the Certification Test Format

For anyone pursuing a certification in emergency response techniques, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the assessment. The certification process is designed to evaluate both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that candidates can effectively handle critical situations when they arise. Understanding the format of the test will help you approach your preparation with confidence and focus.
Types of Questions and Skills Assessed
The test typically consists of multiple-choice questions that assess your knowledge of emergency protocols, as well as hands-on practical scenarios that simulate real-life situations. It is essential to understand the key concepts and techniques involved in emergency response, as these will form the foundation of both the written and practical components of the assessment.
Timing and Structure of the Test
Each section of the certification is carefully timed to ensure that you are able to demonstrate both quick thinking and accuracy under pressure. The written portion will challenge your knowledge of the essential steps involved in providing aid, while the practical part will require you to perform specific actions correctly, under observation, to demonstrate your readiness for real-world situations.
Key Skills Tested in Emergency Response Certification
During the certification process, candidates are assessed on their ability to perform crucial life-saving actions under pressure. The key skills tested are designed to ensure that individuals can provide immediate assistance in critical situations. These skills not only include technical knowledge but also the ability to stay calm and act swiftly when every second counts.
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Proper technique for performing chest compressions to maintain circulation in a victim’s body during emergencies. |
| Airway Management | Ensuring that the airway is open to allow proper breathing and oxygen flow to the lungs. |
| Rescue Breathing | Delivering breaths to a victim who is not breathing, ensuring that air reaches the lungs effectively. |
| Use of AED | Knowledge and correct usage of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) to restore a normal heart rhythm. |
| Scene Safety | Assessing the environment for safety before providing aid to ensure both the rescuer and victim are not at risk. |
Essential Steps in Life-Saving Techniques for Certification

When preparing for certification in emergency response, mastering the key steps involved in delivering life-saving assistance is crucial. These steps are designed to ensure that the victim receives the best possible chance of survival. Each action must be performed with precision and confidence, as these techniques can make the difference between life and death.
First, assessing the situation is the first step in providing effective assistance. Ensuring the safety of both the victim and the rescuer is paramount before moving forward with any intervention. Once the scene is secure, the next crucial step is to check the victim’s responsiveness and breathing.
If the victim is unresponsive and not breathing, immediate action is needed. Start by performing chest compressions to maintain blood circulation, followed by rescue breathing if necessary. This combination helps to deliver oxygen to the body’s vital organs until professional help arrives. Additionally, utilizing an AED as soon as possible can help restore normal heart rhythm in cases of cardiac arrest.
Each step must be performed quickly and effectively to ensure the best possible outcome in an emergency. Consistent practice and thorough understanding of these life-saving techniques are essential for those pursuing certification, as proficiency in these skills is a critical part of the process.
Common Mistakes During Life-Saving Training
During training for emergency response, it’s easy to make mistakes, especially when under pressure. Understanding these common errors and how to avoid them can significantly improve your performance when it counts. Being aware of what can go wrong helps you fine-tune your skills and build confidence in real-life situations.
Top Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Chest Compression Depth | Ensure compressions are deep enough (about 2 inches) to circulate blood effectively, but not too deep to cause injury. |
| Delayed Action | Start immediately with chest compressions if the victim is unresponsive and not breathing. Delaying action can be critical. |
| Inconsistent Chest Compressions | Maintain a steady rhythm at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. Stopping too often reduces effectiveness. |
| Improper Hand Placement | Place hands correctly, one on top of the other, on the lower half of the chest. Incorrect placement can reduce compression efficiency. |
| Failure to Open Airway Properly | Use the head-tilt, chin-lift method to ensure the airway is clear before giving rescue breaths. |
Practicing for Success
By practicing the correct techniques and being mindful of common mistakes, you increase your ability to perform life-saving actions when necessary. Regular training and feedback help ensure that each action is executed efficiently and effectively, reducing errors when you face a real emergency situation.
How to Prepare for Life-Saving Certification
Preparing for a life-saving certification requires a combination of theory and practical skills. The process involves understanding critical procedures, mastering essential techniques, and ensuring you can perform under pressure. With the right approach, you can increase your chances of passing the assessment and being fully prepared for real-world emergencies.
Study the Key Concepts and Techniques
Before taking the certification, it’s important to thoroughly review the core concepts and procedures you will be tested on. This includes understanding how to assess an emergency situation, the steps to follow in providing assistance, and the correct application of techniques like chest compressions, rescue breathing, and the use of an AED. Focus on mastering the foundational principles that guide emergency response.
Practice Hands-On Skills Regularly
The practical component of the certification is just as important as the written test. Make sure to practice the hands-on skills repeatedly until they become second nature. Work with a training partner or attend practice sessions to refine your techniques. Additionally, use manikins and other training tools to simulate real-life situations, which will help you stay calm and perform effectively under pressure.
CPR Techniques for Different Age Groups

When providing life-saving assistance, it is important to adjust techniques based on the age of the individual in need. Each age group–whether an infant, child, or adult–requires specific methods to ensure the most effective intervention. Understanding these variations is essential for providing proper care in emergencies.
Techniques for Infants
Infants require a more delicate approach due to their small size and developing bodies. The following steps should be followed when performing emergency procedures on an infant:
- Chest Compressions: Use two fingers in the center of the chest, just below the nipple line, applying gentle but firm pressure at a depth of about 1.5 inches.
- Rescue Breathing: Cover the infant’s mouth and nose with your mouth, providing small, gentle breaths to avoid over-inflating the lungs.
- Airway Opening: Use a gentle head-tilt, chin-lift method to open the airway, being careful not to overextend the neck.
Techniques for Children
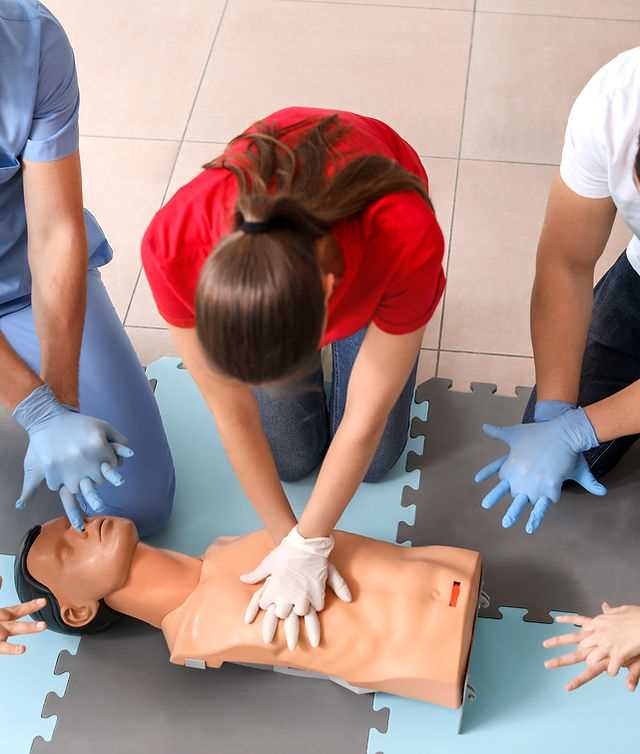
For children, the techniques are similar to those for adults but adjusted for their smaller bodies. The following steps should be taken into account when providing assistance:
- Chest Compressions: Use one or two hands, depending on the size of the child, compressing the chest at least 2 inches deep.
- Rescue Breathing: Give breaths in a manner similar to adults, but be mindful to adjust the volume based on the child’s size and age.
- Use of AED: If an automated external defibrillator is available, use pediatric pads if possible, or adult pads if necessary, placing them appropriately on the child’s chest.
Techniques for Adults
For adults, life-saving techniques involve more direct force and volume, as their bodies are fully developed. The following steps are recommended for adult victims:
- Chest Compressions: Place both hands on the center of the chest and compress at least 2 inches deep, with a steady rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Rescue Breathing: Provide strong, full breaths while ensuring the victim’s chest rises with each breath.
- Use of AED: If an AED is available, use adult-sized pads and follow the device’s instructions to administer shocks if needed.
Importance of Chest Compressions in Life-Saving Techniques
Chest compressions are a vital part of life-saving techniques and play a crucial role in maintaining circulation when the heart has stopped. Performing effective chest compressions ensures that oxygen-rich blood continues to circulate through the body, particularly to the brain and other vital organs. This action can significantly improve a victim’s chances of survival, especially when performed immediately and correctly.
Why Chest Compressions Are Essential
Chest compressions are important for several reasons, including:
- Maintaining Blood Flow: Effective compressions help maintain blood flow to the brain and heart, which are critical in the initial moments of cardiac arrest.
- Oxygenation of Organs: By performing compressions, the heart pumps blood through the body, delivering essential oxygen to the organs until professional help arrives.
- Preventing Brain Damage: Timely chest compressions can help reduce the risk of irreversible brain damage by ensuring that the brain receives a continuous supply of oxygenated blood.
Key Techniques for Effective Chest Compressions
To maximize the effectiveness of chest compressions, the following techniques must be followed:
- Proper Depth: Ensure that the chest is compressed at least 2 inches deep for adults, and about 1.5 inches for infants, to effectively circulate blood.
- Correct Rate: Maintain a compression rate of 100-120 compressions per minute to keep the blood flowing at an adequate pace.
- Full Recoil: Allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions to ensure the heart is refilled with blood before the next compression.
Mastering the technique of chest compressions is a critical skill in emergency response, as it can make the difference in saving a life during a cardiac emergency.
Rescue Breathing: What You Need to Know
Rescue breathing is an essential technique for providing life-saving support when a person is not breathing or is not breathing adequately. It involves delivering air into the victim’s lungs to ensure that oxygen continues to circulate throughout the body, particularly to vital organs like the brain and heart. This process is often combined with chest compressions to optimize the chances of survival in emergency situations.
When to Perform Rescue Breathing
Rescue breathing should be performed in situations where the victim is unresponsive and not breathing, or if they are breathing irregularly. Key indicators include:
- No Breathing: The victim shows no signs of breathing, or breathing has completely stopped.
- Irregular Breathing: The victim’s breaths are shallow, gasping, or very slow, which may indicate a lack of oxygen in the body.
- Unresponsiveness: The person does not respond to verbal or physical stimuli and is not showing signs of life.
Steps for Performing Rescue Breathing
Here are the steps you need to follow when performing rescue breathing:
- Check for Breathing: Ensure that the person is not breathing or is only gasping. Check for no more than 10 seconds.
- Open the Airway: Gently tilt the person’s head back and lift the chin to open the airway.
- Give Rescue Breaths: Pinch the person’s nose shut, cover their mouth with yours, and give a breath that lasts about 1 second, ensuring the chest rises.
- Repeat as Needed: Continue giving one breath every 5-6 seconds for an adult, or more frequently for infants and children, until the person starts breathing independently or emergency help arrives.
It’s important to combine rescue breathing with chest compressions, especially in situations like cardiac arrest, to keep blood circulating while restoring the victim’s oxygen levels.
Assessing Breathing and Heartbeat Accurately

Accurate evaluation of respiratory and cardiac functions is essential in emergency situations to determine the necessary steps for providing effective assistance. Recognizing the signs of normal and irregular patterns can significantly impact the speed and quality of care delivered to the individual in need. This process involves a careful and timely approach, focusing on subtle changes that may indicate life-threatening conditions.
To properly assess these vital functions, it is important to remain composed and observant. The process begins with monitoring the chest for any visible rise and fall, indicating the presence of breath. Simultaneously, detecting the pulse helps in understanding the condition of the circulatory system. Both of these observations provide critical information about the person’s current state and guide further intervention.
It is also crucial to differentiate between normal, shallow, and irregular patterns. Shallow or absent breathing, along with weak or absent pulses, may signal the need for immediate medical intervention. Ensuring accuracy in these assessments is vital to deciding the next course of action, whether that involves starting life-saving measures or calling for advanced care.
Role of AED in CPR Procedures

An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) plays a critical role in emergency situations where an individual experiences a sudden cardiac arrest. The device is designed to deliver a controlled electric shock to the heart, potentially restoring a normal rhythm and significantly improving the chances of survival. It is an essential tool used in conjunction with basic life support techniques to stabilize the patient until advanced medical care arrives.
How AED Enhances Survival Chances
The use of an AED increases the likelihood of a successful recovery by providing timely defibrillation, which can restore the heart’s rhythm in cases of arrhythmia. The device guides the user with clear, simple instructions, making it accessible even to those with limited medical training. Early defibrillation, along with continuous support, is key to preventing irreversible damage to the heart and other vital organs.
Steps Involved in Using an AED
- Turn on the AED and follow the device’s audio or visual prompts.
- Place the electrode pads on the patient’s chest as directed by the machine.
- The AED will analyze the heart rhythm and determine if a shock is necessary.
- If a shock is advised, the AED will instruct you to clear the area before delivering the shock.
- After delivering the shock, continue with the monitoring and provide additional life-saving measures as necessary.
By combining the use of an AED with effective life-saving practices, it is possible to increase the survival rates of those experiencing sudden cardiac emergencies, emphasizing the importance of quick, coordinated actions.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in CPR
When performing life-saving procedures, it is essential to understand the legal and ethical responsibilities involved. Providing assistance in an emergency situation can have profound implications, both for the individual receiving help and the person offering it. Being aware of the potential risks and obligations can help ensure that care is given appropriately while protecting all parties involved.
Legal Protection for Rescuers
One of the key legal principles surrounding emergency assistance is the concept of Good Samaritan laws. These laws are designed to protect individuals who offer aid in good faith during an emergency. As long as the responder acts within their level of training and does not intentionally harm the individual, legal protections generally apply. However, performing actions outside of one’s training or failing to follow protocols could result in legal consequences.
Ethical Responsibilities
Ethically, it is important to provide care without hesitation while respecting the dignity and rights of the individual. Consent is a critical consideration, as performing certain interventions on someone who is conscious or has not consented can lead to ethical dilemmas. In cases where the individual is unconscious and unable to provide consent, the ethical principle of implied consent typically applies, assuming the person would wish to receive help if able to decide.
Additionally, there is an ethical duty to continue providing care until professional help arrives or the situation is otherwise resolved. This includes acting within one’s abilities, seeking additional assistance when necessary, and refraining from abandoning the individual in need.
CPR Myths and Misconceptions Explained
In emergency situations, many individuals may rely on widely circulated beliefs and misunderstandings about life-saving techniques, which can sometimes lead to confusion or even harm. Dispelling these myths is crucial for ensuring that proper methods are used when responding to someone in need of immediate assistance. Understanding the truth behind these misconceptions can help individuals feel more confident and effective when providing aid in critical moments.
One common myth is the idea that performing these life-saving measures can cause harm, leading to people hesitating to act. In reality, the risks of not intervening far outweigh the potential harm caused by taking action. Another misconception is that the procedures are too complicated or require advanced skills, deterring people from trying them at all. However, these techniques are simple and can be easily performed by anyone with basic training.
It is also often believed that the individual must be completely still or unconscious for help to be effective. However, even if the person is breathing or moving slightly, immediate action can still make a difference. Misunderstandings like these can prevent timely intervention, delaying the necessary steps to save a life.
Tips for Retaining CPR Knowledge Long-Term
Maintaining knowledge and skills for life-saving techniques over time requires consistent practice, review, and engagement. Often, people may forget key procedures or lose confidence if they don’t regularly refresh their understanding. By integrating effective strategies into daily life, individuals can ensure that they remain prepared to respond quickly and correctly in an emergency.
One of the most effective ways to retain knowledge is through periodic review and repetition. Practicing techniques in a controlled environment or participating in refresher courses can significantly enhance muscle memory and mental readiness. Additionally, learning through various methods, such as videos, hands-on training, and group activities, can reinforce understanding.
| Method | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Practice | Helps maintain muscle memory and confidence in performing techniques accurately. |
| Refresher Courses | Provides updated information and an opportunity to practice in a real-life context. |
| Group Training | Encourages teamwork and exposes individuals to different perspectives and techniques. |
| Interactive Learning | Engages different senses, making the knowledge more memorable and applicable. |
By committing to these practices, individuals can ensure they retain essential life-saving skills, remaining confident and capable when faced with an emergency.
What to Expect After the Certification Assessment
Once you’ve completed the certification assessment, there are several key steps and outcomes to anticipate. This process is designed to evaluate your knowledge and skills, and depending on your performance, the next steps may include receiving official certification, additional training, or feedback on areas for improvement. Understanding what happens next can help you feel more prepared and confident in your progress.
Receiving Your Results
After completing the assessment, you will typically receive your results within a specific timeframe. In many cases, the results are provided immediately or within a few days. If you pass, you will be awarded a certificate acknowledging your competency in the required areas. If further practice or study is necessary, feedback will be given, often highlighting areas where improvement is needed.
Next Steps After Passing the Assessment

Once you pass the assessment, you may be required to maintain your certification through periodic refreshers or continuing education. These requirements ensure that your skills stay current and that you are prepared to handle real-life situations effectively. You may also be encouraged to participate in additional training to deepen your knowledge and reinforce practical techniques.
Choosing the Right CPR Course for You

Selecting the appropriate training program is crucial to ensure you gain the knowledge and skills necessary to respond effectively in emergency situations. With many courses available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one suits your needs best. Understanding the key factors that differentiate these programs will help you make an informed decision and be well-prepared to assist others when needed.
Assess Your Needs
Before choosing a course, consider your specific goals and the type of environment in which you may need to apply these skills. For instance, if you work in a healthcare setting, a more advanced program may be required. On the other hand, a basic life-saving course could be sufficient for those looking to assist family members or co-workers. Clarifying the level of expertise required for your situation is the first step toward selecting the best option.
Understand the Course Structure
Each program has a different structure, ranging from in-person classes to online modules. Some courses focus more on theory, while others prioritize hands-on practice. It is important to choose a program that aligns with your learning style. If you prefer practical experience and direct guidance, an in-person class may be more beneficial. Alternatively, online courses offer flexibility if you need to learn at your own pace, though they might not offer the same level of interaction and practice.
Check for Certification and Accreditation
Ensure that the course you select provides an official certification upon completion, as this will serve as proof of your competency in the subject. Accreditation from recognized organizations can also indicate the quality and credibility of the program. It is important to verify that the course meets recognized standards and is widely accepted by employers and institutions.
How CPR Certification Can Save Lives
Being certified in life-saving techniques can be the difference between life and death in emergency situations. Having the knowledge and skills to assist someone experiencing a medical crisis provides an opportunity to intervene before professional help arrives. With the proper training, individuals are empowered to act swiftly and effectively, potentially improving the chances of survival for those in need of urgent care.
Immediate Action in Critical Moments
When someone is in distress due to a medical emergency such as cardiac arrest or respiratory failure, every second counts. Certified individuals are trained to recognize the signs of these conditions and respond appropriately, whether by performing chest compressions, clearing airways, or using an automated defibrillator. These early interventions are vital in maintaining circulation and oxygen flow to the brain and other vital organs, preventing irreversible damage.
Confidence to Act in High-Stress Situations
One of the greatest benefits of certification is the confidence it instills in participants. In stressful, high-pressure situations, many people hesitate or feel unsure about taking action. Certification removes this uncertainty by providing clear guidelines and techniques, which increases the likelihood that individuals will step forward when help is needed. This confidence can be life-saving, especially when there is no one else around to assist.
By becoming certified, you not only enhance your ability to save lives but also contribute to a safer environment for everyone around you.
Post-CPR Exam: Next Steps in Certification
After completing a life-saving training assessment, the next steps are crucial in ensuring that the knowledge and skills gained are recognized and maintained. Certification marks the official acknowledgment of competency in emergency procedures, but there are additional actions and responsibilities to consider to ensure preparedness and proficiency in real-life situations.
Upon successful completion, individuals typically receive a certificate that validates their ability to perform essential life-saving actions. However, to keep this certification current, additional training and periodic refreshers are often required. It is important to understand the necessary steps to maintain certification and continue to be an effective responder when emergencies arise.
| Next Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Certification Awarded | Once you pass the assessment, you will receive an official certificate proving your ability to perform life-saving techniques. |
| Continuing Education | To keep your skills up to date, consider taking periodic refresher courses that cover new techniques and updates to procedures. |
| Skills Practice | Reinforce your knowledge by practicing the procedures regularly, either through drills or hands-on training sessions. |
| Certification Renewal | Most certifications require renewal after a set period, typically every 2-3 years, to ensure ongoing competency. |
By following these steps, you ensure that you remain well-prepared and ready to act confidently in critical situations, potentially saving lives when every second counts.