Preparing for academic evaluations requires a blend of strategic planning, mastery of concepts, and focused practice. Navigating complex topics can feel overwhelming, but breaking them down into manageable parts makes the process much smoother. Understanding key principles is essential for building a strong foundation and tackling challenges effectively.
This article delves into practical strategies, analytical techniques, and insightful resources to help you succeed. Whether it’s honing your critical thinking or enhancing problem-solving abilities, this guide provides the tools you need to approach your studies with confidence. Explore proven methods to refine your skills and achieve remarkable outcomes in assessments.
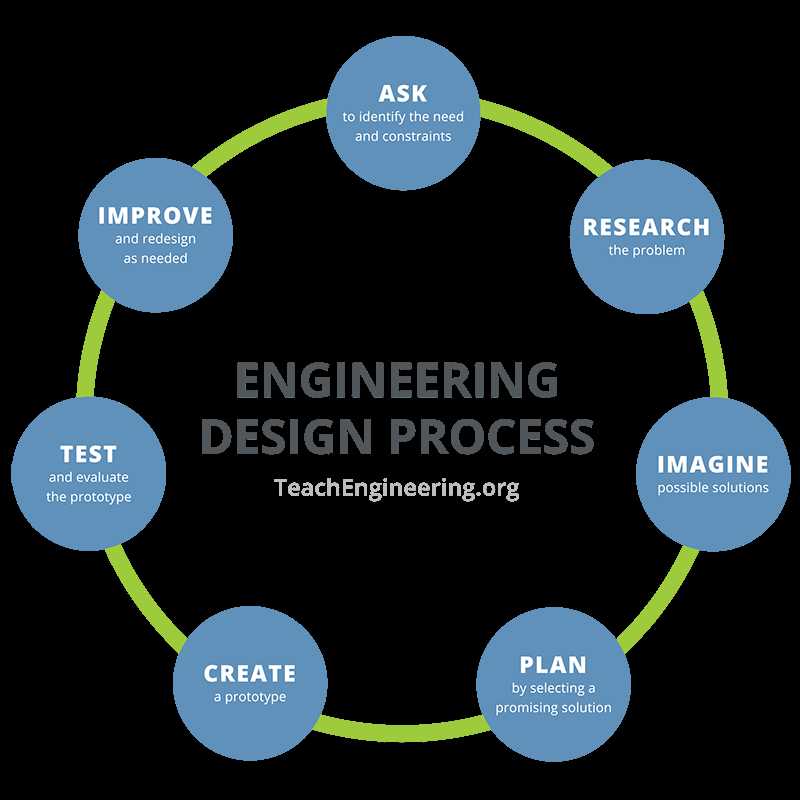
Mastering the Basics of Engineering Design
Understanding foundational concepts is essential for solving complex challenges. Building a strong grasp of basic principles allows you to approach tasks with clarity and develop innovative solutions. This section explores the essential components that form the bedrock of effective problem-solving and project execution.
Core Principles to Focus On

- Identifying Objectives: Clearly define what needs to be achieved before starting any task.
- Breaking Down Problems: Divide larger challenges into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Optimizing Processes: Focus on efficiency and accuracy in each step of the workflow.
Practical Skills to Develop
- Visualization: Train your ability to mentally map out solutions and workflows.
- Critical Thinking: Analyze situations logically to identify the best course of action.
- Adaptability: Stay flexible and adjust approaches as new information emerges.
By mastering these foundational elements, you can tackle projects and assessments with confidence, ensuring both efficiency and effectiveness in your approach.
Essential Skills for Problem-Solving
Effective solutions begin with a clear understanding of the challenge at hand. Developing a structured approach and honing critical abilities can transform complex scenarios into manageable tasks. This section highlights the core competencies necessary to approach issues methodically and achieve optimal results.
Critical Thinking and Analysis

- Identifying Root Causes: Look beyond surface issues to uncover the underlying problems.
- Evaluating Alternatives: Compare multiple solutions to determine the most effective path forward.
- Prioritizing Tasks: Focus on addressing the most impactful aspects first.
Practical Application Techniques
- Observation: Pay attention to details that might influence outcomes or reveal hidden issues.
- Team Collaboration: Share perspectives and leverage collective expertise for innovative solutions.
- Resilience: Embrace challenges as opportunities to learn and refine strategies.
By cultivating these skills, you can approach obstacles with confidence and precision, ensuring that each step contributes meaningfully toward a successful resolution.
How to Prepare for Final Assessments
Effective preparation requires a balance of strategic planning and focused practice. By organizing your time, utilizing available resources, and reinforcing your understanding of key concepts, you can approach evaluations with confidence and clarity. This section outlines practical steps to ensure a productive study experience.
Creating a Study Plan
- Set Clear Goals: Outline what you need to achieve and prioritize topics based on importance.
- Break Down Material: Divide subjects into smaller sections for manageable study sessions.
- Allocate Time Wisely: Dedicate specific periods to each topic to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Maximizing Learning Efficiency
- Practice Regularly: Reinforce knowledge by solving sample problems or reviewing past assignments.
- Engage Actively: Participate in discussions, ask questions, and seek clarification on challenging areas.
- Use Reliable Resources: Refer to credible guides and materials to deepen your understanding.
Adopting these strategies can help you build confidence and ensure that you are well-prepared to handle even the most challenging assessments effectively.
Understanding Core Design Principles
Grasping the essential concepts behind effective problem-solving lays the groundwork for innovative and efficient solutions. These principles serve as the framework for analyzing challenges and implementing strategies that lead to successful outcomes. This section provides an overview of the foundational ideas that guide thoughtful and systematic approaches.
Key Elements of Structured Thinking
At the heart of successful approaches lies a set of guiding principles that ensure clarity and consistency. These elements focus on functionality, efficiency, and adaptability in addressing challenges.
| Principle | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Form and Function | Balance between aesthetics and usability | Ensuring solutions are visually appealing and practical |
| Consistency | Uniformity in processes and elements | Maintaining coherence in all stages of execution |
| Scalability | Ability to adapt to future needs | Designing with potential growth or changes in mind |
Practical Applications of Core Ideas
- Problem Framing: Clearly define the scope and objectives to focus efforts effectively.
- Iterative Testing: Refine solutions through repeated evaluation and adjustments.
- Feedback Integration: Use input from peers or stakeholders to enhance outcomes.
By understanding and applying these core ideas, you can build a foundation for consistently achieving results that are both effective and sustainable.
Effective Study Methods for Exams
Preparing for evaluations requires more than just reviewing notes. It involves adopting strategies that help retain information, improve understanding, and build confidence. This section explores techniques that can make study sessions productive and focused, ensuring better outcomes.
Organized Planning: Structuring your preparation time is crucial for comprehensive coverage of topics. Break down subjects into manageable sections, set clear objectives for each session, and allocate time wisely. An organized schedule reduces stress and maximizes efficiency.
Active Engagement: Passive reading often leads to limited retention. Instead, engage with the material by summarizing concepts in your own words, discussing ideas with peers, or creating visual aids like mind maps. This active involvement helps solidify knowledge.
Practice Makes Perfect: Reinforce your understanding by solving practice problems or taking mock assessments. This not only familiarizes you with the format of questions but also highlights areas needing improvement. Regular practice ensures steady progress.
By integrating these methods into your preparation routine, you can approach your assessments with greater clarity and confidence, leading to success in achieving your goals.
Breaking Down Complex Engineering Challenges
When faced with a difficult problem, it’s essential to approach it systematically. Breaking down large, complex issues into smaller, manageable components allows for better understanding and more efficient problem-solving. This section discusses how to deconstruct a challenge and develop strategies to address each part effectively.
Identifying the Core Problem: The first step in solving any challenge is to clearly define the central issue. By identifying the root cause, you can focus your efforts on resolving the most critical aspect, rather than getting sidetracked by secondary factors.
Breaking the Problem into Segments: Once you understand the core issue, divide the challenge into smaller, more manageable parts. Addressing one section at a time allows for a step-by-step approach and prevents feeling overwhelmed.
Utilizing Available Resources: Don’t hesitate to use all available resources, including reference materials, expert advice, and practical tools. Each piece of information can contribute to a more well-rounded solution, helping you tackle each segment of the problem more effectively.
By using a structured approach, complex problems become easier to manage and solve, enabling more effective solutions and quicker resolutions.
Key Tools for Successful Design Projects
For any successful project, having the right tools at your disposal is crucial. These tools help streamline the workflow, enhance collaboration, and ensure that objectives are met efficiently. In this section, we’ll explore the essential tools that are commonly used throughout the course of a project.
Planning and Organization
- Project Management Software: Tools like Trello, Asana, and Microsoft Project help keep tasks organized, track deadlines, and assign responsibilities.
- Time Management Tools: Apps such as Toggl and Clockify assist in tracking work hours, ensuring that each part of the project is given adequate time.
Collaboration and Communication
- Cloud-Based File Sharing: Tools like Google Drive and Dropbox allow teams to share files easily and access them from anywhere, enhancing collaboration.
- Team Communication Platforms: Slack and Microsoft Teams provide instant messaging, video calls, and file sharing, all in one platform.
Design and Visualization Tools: Tools like AutoCAD and SketchUp enable designers to create detailed models and blueprints. These tools are vital for translating concepts into tangible visuals.
Testing and Prototyping Tools: Prototyping software like Fusion 360 or tools for physical prototyping like 3D printers help visualize and test solutions before full implementation.
By leveraging these tools, teams can enhance productivity, reduce errors, and create more effective solutions for any project.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Exams
When preparing for and taking assessments, students often fall into several common traps that can hinder their performance. Recognizing these mistakes beforehand and understanding how to avoid them can greatly improve your chances of success. In this section, we’ll highlight frequent errors and offer strategies to steer clear of them.
Rushing Through Questions: One of the most common errors is rushing through questions without thoroughly reading them. This can lead to misunderstandings and careless mistakes. It’s important to read each question carefully and take time to plan your response before writing.
Skipping Difficult Questions: It’s easy to skip over challenging questions, but this can result in missed opportunities for points. Instead, try to answer all questions, even if it means coming back to the more difficult ones after you’ve completed the easier ones.
Strategies for Avoiding Common Mistakes
| Mistake | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Rushing | Take your time and review your answers before submitting. |
| Skipping Questions | Attempt every question, even if it’s just a rough answer to come back to. |
| Not Managing Time | Allocate time to each section and stick to it to avoid running out of time. |
Not Managing Time: Failing to pace yourself during the assessment can result in unfinished sections. A proper time management strategy, including setting specific time limits for each section, can ensure that all areas of the test are covered.
Overthinking the Answers: Overcomplicating answers can lead to confusion and errors. Stick to clear, straightforward responses based on your knowledge, and avoid second-guessing yourself.
By avoiding these common mistakes and applying sound strategies, you can improve your performance and increase your chances of achieving the best results possible.
How to Analyze Real-World Design Problems
Solving complex issues in the real world requires a structured approach that begins with a deep understanding of the problem. Breaking down the problem into manageable parts, identifying the root causes, and considering practical solutions are key steps in developing effective solutions. In this section, we will explore the process of analyzing and addressing challenges that arise in real-world scenarios.
Steps to Analyze and Approach Challenges
- Identify the Problem: Clearly define the issue at hand. Understanding the core of the problem is essential before moving forward with any solution.
- Gather Relevant Information: Collect data and insights that will help you understand the context and constraints surrounding the challenge.
- Break Down the Problem: Divide the issue into smaller, more manageable components. This makes it easier to address each aspect systematically.
- Brainstorm Possible Solutions: Consider multiple potential solutions to the problem, keeping in mind the limitations and available resources.
- Evaluate and Test: Assess each solution, test its feasibility, and analyze the results before moving forward.
Key Factors to Consider
- Feasibility: Can the solution be implemented with available resources, time, and technology?
- Impact: What is the potential outcome or effect of the solution, both in the short and long term?
- Constraints: Are there any limitations, such as budget or regulations, that could affect the solution’s success?
By following these steps and considering the critical factors, you will be better equipped to approach and solve real-world challenges effectively. This methodical approach will allow for thoughtful and sustainable solutions to complex issues.
Time Management Strategies for Students
Effective time management is essential for academic success and personal well-being. Managing your time properly can help balance multiple tasks, meet deadlines, and reduce stress. In this section, we will explore practical strategies that can help students stay organized, prioritize their responsibilities, and achieve their goals.
Key Time Management Techniques
- Prioritize Tasks: Start by identifying the most urgent and important tasks. Focus on completing them first before moving on to less critical assignments.
- Create a Schedule: Plan your day, week, or month in advance. Allocate specific time blocks for studying, attending classes, and personal activities.
- Break Tasks into Smaller Steps: Breaking large tasks into smaller, manageable parts makes them less overwhelming and helps you stay focused.
- Use Time-Tracking Tools: Utilize planners, calendars, or apps to keep track of deadlines, appointments, and study sessions.
- Avoid Procrastination: Set clear goals and avoid delaying tasks. Starting early gives you more time to handle unexpected challenges.
Tips for Maximizing Productivity
- Stay Organized: Keep your workspace and materials organized to avoid wasting time searching for resources.
- Eliminate Distractions: Find a quiet place to study and limit distractions from your phone, social media, or other interruptions.
- Take Breaks: Allow yourself short breaks during long study sessions to refresh your mind and avoid burnout.
By implementing these strategies, students can enhance their productivity, reduce stress, and successfully manage their academic responsibilities. Effective time management not only helps with studies but also contributes to a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Exploring Case Studies in Engineering
Case studies provide valuable insights into how complex problems are addressed in real-world projects. These examples allow individuals to learn from past experiences, apply theoretical knowledge, and explore practical solutions to various challenges. By examining detailed accounts of specific projects, students and professionals can gain a deeper understanding of methodologies, strategies, and the impact of decision-making processes.
Key Aspects of Case Study Analysis
- Problem Identification: Every case study begins with recognizing a central challenge or issue. Understanding the core problem is critical to formulating effective solutions.
- Solution Development: The case study details the approach taken to address the problem. This may involve brainstorming ideas, testing prototypes, or implementing innovative techniques.
- Implementation: Case studies often include the execution of the proposed solutions and the processes involved in bringing a project to fruition.
- Results and Evaluation: Analyzing the outcomes is crucial. Case studies highlight both successes and failures, offering lessons that help avoid future mistakes.
- Lessons Learned: Every case study provides valuable insights that can improve future projects. Reflecting on these lessons helps enhance decision-making and problem-solving skills.
Benefits of Studying Case Studies
- Practical Application: Case studies bridge the gap between theory and practice, allowing individuals to see how concepts are applied in the real world.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing case studies encourages critical thinking and helps develop problem-solving abilities by evaluating different approaches.
- Improved Decision Making: Learning from the successes and failures of past projects can enhance an individual’s ability to make informed decisions in future situations.
Exploring case studies in various fields provides a broader perspective on how challenges are faced and overcome. These real-world examples are essential tools for learning, offering valuable knowledge that can be applied to similar problems in the future.
Practical Tips for Exam Confidence
Building confidence for assessments involves both mental preparation and effective study strategies. By adopting the right techniques, students can improve their performance, reduce anxiety, and approach tests with a clear, focused mindset. Confidence comes from consistent practice, understanding the material, and developing a positive attitude towards the process.
Preparation Strategies
- Start Early: Begin reviewing material well in advance to avoid last-minute cramming. Spreading out your study sessions helps reinforce knowledge over time.
- Practice Actively: Actively engaging with the material, such as taking practice tests, solving sample problems, and discussing concepts with peers, strengthens understanding.
- Stay Organized: Break down the material into smaller sections and tackle them one by one. Keeping a study schedule and setting achievable goals boosts focus and productivity.
- Teach Others: Explaining concepts to someone else helps reinforce your own understanding and can highlight any areas needing further review.
Maintaining Calm and Focus
- Rest and Recharge: Ensure you get enough sleep before the assessment. A well-rested mind is more alert and better equipped to retain information.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Breathing exercises or short mindfulness sessions can calm nerves and reduce stress, helping you stay focused during the assessment.
- Visualize Success: Positive visualization can boost your confidence. Imagine yourself performing well and staying calm during the entire process.
By preparing strategically and maintaining a calm, positive attitude, you can approach any challenge with greater confidence and assurance, ultimately improving your chances for success.
The Role of Creativity in Engineering

Creativity plays an essential role in problem-solving and innovation. It allows individuals to approach challenges from different perspectives, offering novel solutions to complex issues. While technical knowledge is crucial, the ability to think outside the box and apply imaginative thinking can lead to groundbreaking solutions that improve processes, products, and systems. This intersection of creativity and problem-solving is where true innovation thrives.
Creative thinking is not just about coming up with artistic ideas, but about being able to see patterns, make connections, and imagine new possibilities within constraints. It involves rethinking traditional methods, exploring alternative approaches, and developing unique ways to solve problems. Creativity drives progress by pushing boundaries and challenging existing norms.
| Creative Thinking Skills | Application in Problem Solving |
|---|---|
| Idea Generation | Helps generate multiple solutions to a problem, increasing the likelihood of finding the best one. |
| Pattern Recognition | Allows for identifying underlying patterns that can inform more efficient solutions. |
| Adaptability | Enables the ability to adjust solutions as new information or challenges arise. |
| Cross-Disciplinary Thinking | Integrates knowledge from various fields, leading to novel solutions that may not emerge from a single perspective. |
By embracing creative thinking, individuals can break free from conventional solutions, enhancing their ability to tackle even the most challenging tasks. Innovation is born from this combination of technical skill and creative insight, making it an invaluable asset in any field.
Applying Logical Thinking in Design Tasks
Logical thinking is a fundamental aspect of tackling complex challenges. It involves breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable components and approaching them systematically. This method of reasoning allows individuals to identify patterns, establish relationships, and create structured solutions. By relying on logic, one can efficiently navigate through various tasks and ensure that each decision is well-supported by data and clear rationale.
When facing design-related tasks, applying logic helps in organizing ideas, testing hypotheses, and evaluating alternatives. It ensures that all steps are taken in a coherent and methodical manner, reducing the risk of errors and inefficiencies. Logical approaches also facilitate communication, as they present solutions that can be easily explained and justified.
Through logical thinking, one can prioritize tasks, analyze possible outcomes, and assess the effectiveness of different strategies. This process not only streamlines the workflow but also fosters a more confident decision-making process, allowing individuals to approach design tasks with clarity and precision.
How to Interpret Engineering Questions
When faced with a complex problem, understanding the question is crucial to formulating a correct and effective solution. Interpreting the task correctly requires a methodical approach, which involves carefully analyzing the problem, identifying key elements, and recognizing the underlying goals. This approach ensures that the task is broken down logically, and all aspects are addressed thoroughly.
Steps to Decode the Problem
- Read the Question Carefully: Before attempting to solve, take the time to fully read the problem statement. Look for important details, keywords, and constraints.
- Identify the Objective: Determine the main goal of the question. What is being asked for? Is it a design, calculation, analysis, or recommendation?
- Break Down the Information: Organize the given data and figure out what is known and what needs to be solved. Clarify any unfamiliar terms or concepts.
- Look for Patterns: Often, the solution involves recognizing familiar structures or principles that can be applied to similar problems.
- Prioritize Constraints: Ensure that any constraints or limitations mentioned in the problem are fully understood, as they will influence the design or solution process.
Effective Strategies for Clarification
- Rephrase the Question: Restating the question in your own words helps to solidify your understanding and ensures clarity.
- Identify Key Terms: Pay attention to technical jargon, units of measurement, and specific terminology used in the problem. Research any unfamiliar terms if necessary.
- Draw Diagrams: Visual aids, such as diagrams or sketches, can help clarify complex problems and assist in organizing your thoughts.
By following these steps and strategies, one can interpret any problem more effectively, ensuring that the approach and solution align with the task at hand.
Strategies to Excel in Group Projects
Successful collaboration in team-based tasks requires a balance of effective communication, clear role distribution, and focused effort. By leveraging each member’s strengths and maintaining strong coordination, the group can achieve its goals efficiently and with greater creativity. Applying the right strategies can transform a challenging project into a rewarding experience.
Effective Communication and Collaboration

- Set Clear Expectations: At the start, define each person’s responsibilities and ensure that everyone understands the overall project goal. Clear expectations help avoid confusion later.
- Regular Check-ins: Schedule meetings to discuss progress, share updates, and address any concerns. Regular communication ensures the team stays on track and aligned.
- Active Listening: Pay attention to others’ ideas and feedback. Actively listening promotes a healthy environment for creativity and problem-solving.
Managing Time and Resources
- Break Down the Project: Divide the task into smaller, manageable steps. Assign deadlines for each part to maintain steady progress and avoid last-minute rushes.
- Leverage Team Strengths: Assign tasks based on individual strengths and expertise. When each member contributes where they excel, the group performs more efficiently.
- Use Collaborative Tools: Utilize platforms for document sharing, communication, and project management. These tools streamline collaboration and help keep the project organized.
By adhering to these strategies, a team can not only complete the task but also ensure that the process is smooth, enjoyable, and leads to a successful outcome.