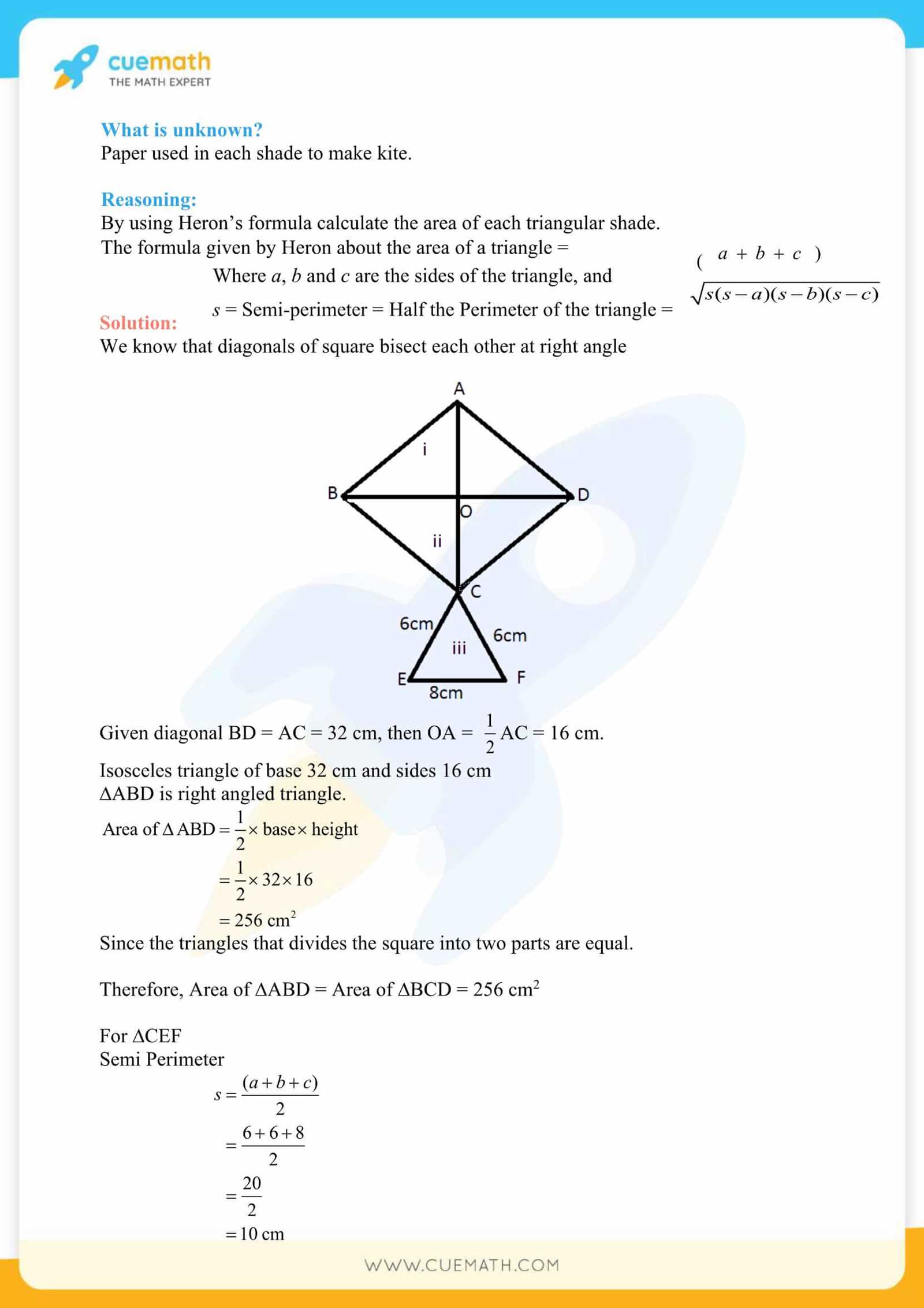
Mastering the techniques and problem-solving methods in advanced coursework requires a clear understanding of complex concepts. This section focuses on providing detailed solutions to a variety of exercises that challenge your grasp of the subject matter. By reviewing these examples, you’ll enhance your comprehension and ability to tackle similar questions in assessments.
Throughout this guide, we’ll break down various problem types, offering insights into the most effective ways to approach each. Whether it’s interpreting data sets, evaluating results, or applying formulas, the key is practicing with precision. The solutions presented will give you a solid foundation to build on as you prepare for your final evaluation.
AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test C Answers
This section provides solutions and explanations for the exercises presented in the advanced coursework, focusing on key techniques and methodologies. Understanding how to interpret complex problems is crucial for success. By reviewing each step, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to apply the concepts to real-world scenarios.
Through detailed breakdowns of various questions, this guide aims to clarify common challenges students face. It highlights strategies for approaching data analysis, evaluating results, and utilizing relevant formulas. The step-by-step approach will help reinforce important concepts and ensure you’re prepared for similar problems in future assessments.
Understanding Key Statistical Concepts
Grasping fundamental ideas is essential for tackling complex problems in advanced coursework. A solid foundation in core principles will guide you through the process of solving various exercises. From understanding data distribution to making informed predictions, mastering these concepts is key to success.
Core Principles to Focus On
Key concepts like measures of central tendency, variability, and correlation lay the groundwork for deeper problem-solving. These elements form the basis of understanding how data behaves and how it can be analyzed effectively.
Applying Core Principles in Problems
Once you understand the basic concepts, applying them to real-world situations will test your ability to think critically. These principles help in interpreting results, making informed decisions, and identifying patterns in data.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Central Tendency | Measures like mean, median, and mode that summarize data with a single value. |
| Variability | How spread out the values in a data set are, often measured by range, variance, and standard deviation. |
| Correlation | Shows the relationship between two variables, indicating strength and direction of the relationship. |
Approaching the Test with Confidence
Success in any advanced assessment is largely determined by your approach and mindset. Preparing effectively allows you to feel in control, making it easier to navigate through challenges. With the right strategies, you can tackle each problem with clarity and composure.
To build confidence before the exam, it’s important to establish a structured preparation plan. This helps ensure that all necessary topics are reviewed thoroughly, leaving you ready for any type of question. Focus on mastering core techniques, and practice applying them to varied scenarios.
Key Strategies for Confidence
- Understand the Problem Types: Identify common question formats and practice solving them repeatedly.
- Review Key Formulas: Having important equations and principles readily available helps reduce stress during the assessment.
- Time Management: Allocate specific time to each section to ensure that all questions are addressed.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: Keeping a clear mind allows for better problem-solving even when under time constraints.
Preparing Your Mindset
- Visualize Success: Mentally walk through solving problems and achieving positive outcomes.
- Focus on Understanding, Not Memorization: This approach encourages deeper learning and better retention of material.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Practice under timed conditions to replicate the exam environment and improve focus.
How to Interpret Test Questions Effectively
One of the most important skills for performing well in assessments is the ability to understand and interpret the questions accurately. Being able to quickly identify key components within each question allows you to focus on the most relevant information and apply your knowledge effectively. A clear approach to reading and analyzing the prompt can significantly improve your response quality and efficiency.
Breaking Down the Question
Start by carefully reading each question and identifying its main objective. Look for keywords that indicate the type of response required, whether it’s a calculation, explanation, or interpretation. Understanding the intent behind the question will help you narrow down what is being asked and how to structure your answer.
- Identify Key Terms: Highlight or underline important phrases like “calculate,” “explain,” or “compare.”
- Understand the Context: Look at any accompanying data or scenarios that provide additional insights into the question.
- Focus on Action Words: These will guide the way you approach solving the problem.
Effective Strategies for Answering
Once you’ve broken down the question, think about how best to apply your knowledge. Start by recalling related concepts and techniques that can be used to address the problem. It may also help to organize your thoughts logically before writing your response.
- Use Process of Elimination: If it’s a multiple-choice question, eliminate the clearly incorrect answers first to narrow down your options.
- Show Your Work: Whenever possible, outline your steps or reasoning to demonstrate a clear thought process.
- Double-Check Your Interpretation: If unsure, re-read the question to confirm you’ve understood it correctly before proceeding.
Breaking Down the Test Format
Understanding the structure of an assessment is crucial for effective preparation. Familiarity with the format allows you to manage your time wisely and approach each section with confidence. Recognizing the various types of questions and how they are framed will enable you to strategize your responses and optimize your performance.
Types of Questions
Assessments typically feature a mix of question types that test different skills and areas of knowledge. Knowing what to expect helps you focus on the appropriate strategies for each format. Here are some common question types you might encounter:
- Multiple-Choice: These questions provide several options, and you’ll need to choose the correct one based on your understanding of the material.
- Short Answer: These questions require concise, direct responses that demonstrate your grasp of the concepts.
- Open-Ended: You’ll need to explain your reasoning, walk through your process, and often provide detailed solutions.
Time Allocation and Strategy
Each section of the assessment may have varying levels of difficulty, and managing your time is essential to ensure you address all the questions. Prioritize questions that are more straightforward or familiar, allowing extra time for the more challenging ones.
- Quick Review: Start by quickly scanning the entire exam to get a sense of the question distribution and overall difficulty.
- Time per Section: Allocate a specific time limit to each section, ensuring that no part of the exam is left incomplete.
- Read Carefully: Take your time to read each question fully, as misinterpreting a prompt can lead to unnecessary mistakes.
Analyzing the Data Interpretation Section

The ability to analyze and interpret data is a crucial skill when approaching complex problems. In this section, you’ll encounter various forms of data presentation, such as tables, charts, and graphs, each designed to assess how well you can extract meaningful insights. Understanding how to read and interpret these visual aids is key to answering the questions effectively.
Key Steps for Interpreting Data
When analyzing data, it’s important to take a methodical approach to ensure that you’re extracting the correct information. Follow these steps to ensure accuracy in your interpretation:
- Examine the Data Type: Identify whether the data represents a categorical or numerical variable, as this will affect how you analyze it.
- Identify Patterns and Trends: Look for any obvious trends or patterns within the data that may help answer the question.
- Note Key Values: Pay attention to outliers, averages, and ranges that may provide important context for your answer.
- Cross-Check Information: If multiple data sets are provided, compare and contrast them to draw conclusions more accurately.
Approaching Graphs and Tables
Graphs and tables are powerful tools for presenting data, but they can be overwhelming if not approached correctly. Here’s how to break down these elements effectively:
- For Graphs: Focus on the axes, labels, and scales. Make sure you understand what each axis represents and how to read the values correctly.
- For Tables: Pay attention to column and row headings to understand the relationships between the variables. Identify any trends in the rows or columns that could indicate patterns.
- For Pie Charts: Note the proportion of each segment and how they relate to the total data set. Compare these proportions to answer the related questions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on Test C
When tackling an advanced assessment, it’s easy to make simple errors that can impact your overall score. Being aware of common mistakes allows you to take proactive steps to avoid them and ensure a more accurate and efficient performance. By recognizing these pitfalls, you can refine your approach and minimize avoidable errors.
Common Errors to Watch For
There are several frequent mistakes that can occur during an assessment. These errors may stem from misinterpreting questions, overlooking important details, or rushing through sections without proper checks. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Rushing Through Questions: It’s easy to feel pressed for time, but rushing can lead to careless mistakes. Always double-check your work before submitting.
- Misreading Key Information: Pay close attention to keywords like “most,” “least,” or “exactly” as they often change the nature of the question.
- Skipping Units of Measurement: Always include the correct units in your answers, as omitting them can lead to point deductions.
- Incorrect Interpretation of Graphs: Ensure you fully understand the data representation in graphs and charts before answering related questions.
Effective Strategies for Avoiding Mistakes
Adopting effective strategies can help you steer clear of errors and approach each question with a clearer focus. Here are some methods to consider:
- Take Time to Review: Before moving on to the next section, take a moment to ensure that your answers are complete and correct.
- Practice Regularly: The more you familiarize yourself with the question format, the less likely you are to overlook key details.
- Read Questions Carefully: Ensure you fully understand each prompt and what it is asking before attempting to answer.
Quick Reference for Common Mistakes
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Rushing Through Questions | Review answers before submitting to catch careless errors. |
| Misreading Keywords | Pay close attention to qualifying words like “exact,” “only,” or “greater.” |
| Overlooking Units | Always include and check units in numerical answers. |
| Incorrect Graph Interpretation | Carefully analyze axes, labels, and scales in graphs and charts. |
Steps to Solve Probability Questions
Solving probability-related questions requires a clear and systematic approach. By following a structured method, you can break down complex problems into manageable steps, ensuring that you address all relevant factors and make accurate calculations. Understanding the key concepts and applying the correct formulas will help you arrive at the right solution with confidence.
Step 1: Understand the Problem
The first step is to thoroughly read and comprehend the problem. Take note of the given information, including the total number of possible outcomes, and identify what is being asked. Understanding the context of the problem is essential before proceeding with any calculations.
- Read Carefully: Identify any specific conditions or restrictions provided in the question.
- Define the Event: Determine what specific event or outcome you are trying to calculate the probability for.
- Clarify Assumptions: Make sure you understand any assumptions regarding independence, repetition, or conditional events.
Step 2: Apply the Correct Formula

Once you fully understand the problem, apply the appropriate probability formula. The formula you use will depend on whether the problem involves independent events, conditional probability, or combinations of events. Some of the most common formulas include:
- For Independent Events: P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
- For Conditional Probability: P(A | B) = P(A and B) / P(B)
- For Mutually Exclusive Events: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
Step 3: Calculate and Simplify
Now that you have the correct formula, it’s time to plug in the known values and calculate the probability. Be mindful of simplifying fractions, converting percentages, or adjusting your answer to fit the required format. Accuracy in this step is key to getting the right result.
- Perform Calculations: Carefully perform any necessary arithmetic to arrive at the correct probability value.
- Simplify Your Result: If the answer is a fraction, simplify it. If it’s a decimal, round to the required number of places.
- Double-Check: Review your calculations to ensure you haven’t missed any steps or made an error.
Guidelines for Answering Confidence Interval Questions
When faced with questions involving estimation, the concept of a confidence interval plays a critical role in providing an interval estimate for a population parameter. These problems often require a careful analysis of data, as well as a clear understanding of the process used to construct and interpret confidence intervals. Following a systematic approach will help you avoid common mistakes and ensure that your answers are accurate and well-supported.
Step 1: Identify the Key Information
Before proceeding with any calculations, make sure you identify all relevant information given in the problem. Typically, a confidence interval problem will provide the sample mean, sample size, standard deviation, and the desired level of confidence (such as 95% or 99%). Ensure that you understand the relationship between these variables and their role in constructing the interval.
- Sample Mean: This is often the point estimate and represents the average of the observed data.
- Standard Deviation: This measures the spread or variability of the data within the sample.
- Sample Size: The number of observations in the sample, which impacts the width of the confidence interval.
- Confidence Level: Indicates how confident you can be that the population parameter lies within the interval.
Step 2: Apply the Correct Formula
Once you have gathered the necessary information, the next step is to apply the appropriate formula for constructing the confidence interval. The general formula for a confidence interval is:
Confidence Interval = Sample Mean ± (Critical Value) * (Standard Error)
The critical value depends on the desired confidence level, and the standard error is the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. Be sure to select the correct distribution (z-distribution or t-distribution) based on the sample size and whether the population standard deviation is known.
- Critical Value: This value corresponds to the z-score or t-score associated with the desired confidence level.
- Standard Error: Calculated as the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size (n).
Step 3: Interpret the Interval
After calculating the confidence interval, it’s important to interpret the result correctly. A confidence interval provides a range of plausible values for the population parameter, not a definitive value. For example, a 95% confidence interval suggests that if you were to take many samples, 95% of the intervals would contain the true population parameter.
- Meaning of the Interval: Understand that the interval gives a range where the true parameter is likely to fall with a specified level of confidence.
- Precision of the Estimate: A wider interval indicates less precision, while a narrower interval reflects a more precise estimate.
Tips for Working with Regression Problems
Regression problems often involve analyzing the relationship between two or more variables to predict outcomes or identify trends. These types of problems require a solid understanding of the underlying principles of model fitting, as well as the ability to interpret results accurately. Approaching regression problems with a clear strategy will help ensure that you make correct predictions and avoid common pitfalls.
Step 1: Understand the Variables
Before diving into any calculations, it’s essential to identify the variables involved and their roles. The dependent variable (often called the response) is the one you’re trying to predict, while the independent variable (or predictor) is used to explain or predict changes in the dependent variable. Understanding the relationship between these variables is key to forming an effective regression model.
- Dependent Variable: This is the outcome you’re trying to predict or explain.
- Independent Variable: These are the factors you believe influence the dependent variable.
- Linearity: Ensure that the relationship between the variables is approximately linear for a linear regression model.
Step 2: Fit the Model
Once you’ve identified the variables, the next step is to fit the regression model to your data. This process involves determining the best line or curve that minimizes the error between the observed data points and the predicted values. The most common method for fitting a linear regression model is using the least squares method.
- Choose the Correct Model: Decide whether a linear or nonlinear model is appropriate based on the data and the relationship between variables.
- Check for Outliers: Outliers can skew the results and affect the accuracy of your model. Be sure to assess the residuals and investigate any unusual data points.
- Assumptions: Ensure that the assumptions of the regression model, such as homoscedasticity and normality of residuals, are met for reliable results.
Step 3: Interpret the Results
After fitting the model, it’s crucial to interpret the results to make meaningful conclusions. The most common output includes the regression equation, R-squared value, and p-values for each predictor. The regression equation provides the estimated relationship between the variables, while the R-squared value indicates how well the model fits the data.
- Regression Equation: The equation shows how changes in the independent variable affect the dependent variable.
- R-Squared Value: This value tells you how much of the variation in the dependent variable is explained by the model.
- P-Values: These values help assess the significance of each predictor in the model. A low p-value suggests a strong relationship between the predictor and the outcome.
Understanding Hypothesis Testing Questions
In statistical analysis, testing assumptions about a population is a crucial step in drawing meaningful conclusions from data. This process typically involves comparing sample data against a specific claim or expectation. To effectively approach these questions, one must develop a clear understanding of the components involved, such as formulating competing hypotheses, selecting the right test, and interpreting the results in context.
The core of hypothesis testing lies in setting up two opposing hypotheses: one that represents no effect or no difference (the null hypothesis), and another that suggests a difference or effect exists (the alternative hypothesis). By testing these hypotheses against the sample data, we determine if the evidence is strong enough to support the alternative hypothesis or if the null hypothesis should remain valid.
Key Steps in Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing follows a well-established series of steps to ensure that conclusions are drawn appropriately. These steps help to systematically evaluate the evidence and make an informed decision.
- Formulate Hypotheses: Define both the null hypothesis (H₀) and the alternative hypothesis (H₁).
- Choose a Significance Level: Determine the probability threshold (α), commonly set to 0.05 or 0.01, to decide when to reject the null hypothesis.
- Select the Right Test: Depending on the type of data and sample size, choose the appropriate statistical test (e.g., z-test, t-test, chi-square test).
- Perform the Test: Calculate the test statistic based on the sample data and compare it to the critical value(s).
- Make a Decision: Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on the comparison of the test statistic and the significance level.
- Interpret Results: Draw conclusions in the context of the problem and assess the evidence for or against the initial claim.
Critical Values and P-Value
To determine whether to reject the null hypothesis, it’s important to understand how critical values and p-values come into play. Critical values define the cutoff points for the test statistic, beyond which the null hypothesis would be rejected. On the other hand, the p-value quantifies the probability of observing data as extreme as the current sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
| Significance Level (α) | Description |
|---|---|
| 0.05 | 5% probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true (Type I error). |
| 0.01 | 1% probability of making a Type I error. |
When the p-value is less than the chosen significance level (α), it indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, leading to its rejection. Conversely, if the p-value is greater than α, there is insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis, meaning the claim stands.
How to Tackle Sampling and Surveys
When working with data, one of the first steps is selecting a representative group from a larger population to study. The accuracy of your conclusions relies heavily on how well the sample reflects the entire population. Whether you are conducting a survey or gathering data for an experiment, it is essential to approach sampling with precision and care. This ensures the reliability of the results and prevents bias from distorting the findings.
To begin, it is important to understand that different sampling techniques can have varying degrees of accuracy. Random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling each have their own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the correct method depends on the specific goals of your research and the nature of the population being studied. A poorly chosen sampling technique can lead to misleading conclusions, so it’s crucial to match the sampling method to the research objectives.
Types of Sampling Methods
There are several strategies for selecting a sample, each offering unique advantages depending on the context of the study. Understanding the differences between these methods helps in selecting the most appropriate one for your research.
- Random Sampling: Every individual in the population has an equal chance of being selected. This method is widely used to reduce bias and ensure fairness in selection.
- Stratified Sampling: The population is divided into subgroups, or strata, and samples are drawn from each group. This ensures that specific subgroups are accurately represented.
- Cluster Sampling: The population is divided into clusters, and a random sample of clusters is selected. This method is often used when it’s difficult to create a list of the entire population.
- Systematic Sampling: A sample is selected at regular intervals from a list of the population. This method is simple but may introduce bias if there is a hidden pattern in the population.
Effective Survey Design
Once you have chosen the appropriate sampling technique, the next challenge is designing the survey itself. A well-constructed survey can provide valuable insights, but poorly phrased questions or a biased sample can lead to inaccurate results. It is important to carefully consider how questions are worded, the order in which they appear, and the type of response options offered.
For instance, open-ended questions allow participants to express their thoughts in their own words, while closed-ended questions limit responses to predefined options. Both types have their place in survey design, but it’s important to choose the right one based on the type of information you wish to gather. Additionally, be mindful of potential biases introduced by question framing or the sample’s composition.
Key Formulas to Remember for Test C
When preparing for any exam involving data analysis, mastering the fundamental equations is crucial. These formulas are the backbone of many questions and help in solving a wide range of problems efficiently. Whether it’s calculating probabilities, determining relationships between variables, or estimating population parameters, understanding the key formulas will significantly enhance your performance.
In this section, we will outline some of the most important formulas that will help you navigate various problem types. These equations are essential tools for interpreting data, making predictions, and testing hypotheses. Make sure to practice applying these formulas to different scenarios to increase your confidence and accuracy on the exam.
Key Formulas for Data Analysis

- Mean (Average): The mean is the sum of all values divided by the number of values.
Formula: x̄ = Σx / n
- Variance: The variance measures how far each number in the set is from the mean.
Formula: σ² = Σ(x – x̄)² / n
- Standard Deviation: The standard deviation is the square root of the variance.
Formula: σ = √σ²
- Z-Score: The Z-score indicates how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean.
Formula: z = (x – x̄) / σ
Key Formulas for Hypothesis Testing
- Confidence Interval: A range of values used to estimate a population parameter.
Formula: CI = x̄ ± Z * (σ / √n)
- Test Statistic for Proportions: Used for testing hypotheses about population proportions.
Formula: z = (p̂ – p) / √(p(1-p) / n)
- T-Test for Means: Used to test hypotheses about the population mean when the sample size is small.
Formula: t = (x̄ – μ) / (s / √n)
- P-Value: The p-value helps determine the significance of the test result.
Formula: P-value = P(T ≥ t) or P(T ≤ t)
These formulas provide the foundation for solving many of the problems you will encounter. Ensure that you are comfortable with each of them and practice applying them in various contexts to improve both your speed and accuracy during the exam.
Explaining the Use of p-Values
In the realm of hypothesis evaluation, understanding how to interpret evidence is essential. The p-value plays a key role in assessing whether the observed results are statistically significant. It helps determine the strength of the evidence against a null hypothesis, offering insight into how likely the results are due to chance alone.
A p-value is essentially a measure of the probability that the observed data, or something more extreme, would occur if the null hypothesis were true. The lower the p-value, the stronger the evidence against the null hypothesis, suggesting that the observed result is less likely to be due to random variation. Conversely, a higher p-value indicates weaker evidence against the null hypothesis.
Understanding the Meaning of p-Values
- p-value This typically indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, suggesting that the result is statistically significant. Researchers often use this threshold to decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
- p-value ≥ 0.05: A p-value above this threshold generally suggests weak evidence against the null hypothesis, meaning the observed data could easily occur by chance. In this case, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
- p-value ≈ 0.01: A p-value in this range is often seen as providing moderate evidence against the null hypothesis, but it may not always be sufficient to reject it depending on the context and the research question.
Factors That Influence p-Values
- Sample Size: Larger sample sizes tend to produce more reliable p-values because they provide a clearer picture of the underlying population. Small sample sizes may lead to p-values that are harder to interpret due to higher variability.
- Effect Size: The magnitude of the effect being tested can also impact the p-value. A small effect might yield a large p-value, suggesting that the effect is not significant, whereas a large effect is more likely to produce a smaller p-value.
- Significance Level (α): The chosen significance level, often set at 0.05, acts as a threshold to determine whether a result is significant. If the p-value is lower than α, the null hypothesis is rejected.
In summary, the p-value is a fundamental concept in hypothesis testing, providing a way to quantify the evidence against the null hypothesis. While it is a useful tool, it should not be interpreted in isolation but rather alongside other factors, such as the context of the study, sample size, and effect size, to make well-informed conclusions.
Time Management Strategies During the Test
Efficiently managing time during an assessment is crucial for maximizing performance. When faced with a series of questions under time constraints, how you allocate your minutes can significantly impact your results. Having a structured approach ensures that you complete all tasks to the best of your ability while avoiding unnecessary stress.
The key to success is recognizing the types of questions and understanding how long you should spend on each one. By planning your approach, you can prevent getting stuck on difficult items and ensure that you have time to review your work.
Prioritize Based on Difficulty
Begin by quickly scanning the entire assessment to identify questions that are either straightforward or time-consuming. By identifying the easier questions first, you can tackle them quickly and build confidence. Save the more challenging questions for later, once you’ve secured points from the simpler ones.
Set Time Limits for Each Section
- Set an overall time limit: Divide the total amount of time you have by the number of sections or questions to determine how long you can spend on each one. Stick to this limit as closely as possible.
- Allocate extra time for review: Set aside 5-10 minutes at the end to go back over your answers, ensuring that you’ve not overlooked any details or made careless mistakes.
- Skip and return: If you come across a particularly tricky question, move on and return to it later. This way, you don’t waste time getting frustrated or stuck.
Practice Makes Perfect
Before the actual assessment, simulate timed conditions by taking practice sessions. This will help you get accustomed to managing time under pressure and allow you to refine your pacing strategy. The more you practice, the more confident and efficient you will become in your approach.
In summary, effective time management during an assessment requires a combination of planning, prioritization, and practice. By allocating your time wisely and staying focused, you can approach each question with a clear strategy, maximizing your ability to perform well under time constraints.
Reviewing Practice Questions and Solutions
Engaging with practice problems and thoroughly reviewing solutions is an essential part of preparing for any assessment. It allows you to understand the underlying concepts, identify areas of weakness, and improve problem-solving skills. Instead of merely memorizing answers, focusing on the approach to each question can deepen your comprehension and help you apply knowledge effectively.
Approach to Reviewing Solutions
Once you have worked through practice problems, it’s important to carefully examine the solutions. This review process should involve more than just checking if your answers were correct. Instead, focus on the following aspects:
- Understanding the reasoning: Look at how each solution is built. Pay attention to the steps taken, the rationale behind them, and how the correct answer is derived.
- Identifying common mistakes: If your answer was incorrect, trace where your approach went wrong. Did you misinterpret the question? Were there calculation errors? Learning from your mistakes is key to improving.
- Recognizing patterns: Many questions will follow similar patterns or require the same core concepts. Identifying these patterns can save time during the actual assessment.
Making the Most of Practice Sessions
To truly benefit from practice, focus on creating a structured review plan. Here are a few strategies to make the most of your sessions:
- Review a variety of problems: Work through problems of different types to get a well-rounded grasp of the material. The more diverse your practice, the better prepared you will be.
- Set time limits: Practice under timed conditions to simulate the real assessment environment. This helps you manage your time and work efficiently under pressure.
- Reflect after each session: After completing a practice session, take some time to reflect on your performance. Consider the areas where you were confident and those that need more attention.
In summary, reviewing practice questions and solutions is not just about confirming answers but about deepening your understanding of concepts, identifying mistakes, and refining your approach to problem-solving. By making this an integral part of your preparation, you’ll be better equipped to handle similar questions on the actual assessment.
Final Preparation Tips for Test Success
As the assessment approaches, it’s important to implement strategies that maximize your performance. Effective preparation goes beyond just reviewing material; it involves creating a focused plan, managing your time efficiently, and taking care of your physical and mental well-being. By following these final preparation tips, you can approach the assessment with confidence and clarity.
Organizing Your Final Study Session
In the final days before the assessment, it’s essential to organize your study routine for maximum effectiveness. Focus on the most important concepts while making sure you understand the underlying principles behind each type of question. Consider the following steps:
- Prioritize key concepts: Focus on the areas where you feel less confident or where you have struggled in the past. Target these topics for review to reinforce your understanding.
- Use active recall: Instead of passively reading notes, actively quiz yourself on the material. This improves memory retention and helps solidify important concepts.
- Work on practice problems: Solve problems under timed conditions to simulate the actual experience. This will help you become more efficient and comfortable with the types of questions you’ll face.
Managing Stress and Maintaining Focus
In the days leading up to the assessment, it’s important to manage stress and maintain focus. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Take regular breaks: Study in intervals, taking short breaks between sessions. This helps prevent burnout and keeps your mind fresh.
- Sleep well: Prioritize a good night’s sleep, especially the night before the assessment. A rested mind performs significantly better than a fatigued one.
- Stay hydrated and eat well: Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for cognitive function. Avoid excessive caffeine or sugary foods that may cause energy crashes.
Final Review Checklist
Before you begin the assessment, ensure that you’ve completed all the necessary preparations. The following checklist can help you stay on track:
| Task | Status |
|---|---|
| Review key concepts | ✔️ |
| Complete practice problems under timed conditions | ✔️ |
| Get a full night’s rest | ✔️ |
| Stay hydrated and eat a balanced meal | ✔️ |
| Maintain a positive mindset | ✔️ |
By following these final preparation strategies, you’ll be ready to tackle the assessment with confidence and clarity. Remember to stay calm, manage your time effectively, and approach each question with a clear and focused mind.