
In the world of finance, certain professionals are entrusted with ensuring that financial institutions adhere to regulations, maintain stability, and protect the interests of depositors. These individuals play a crucial role in overseeing the operations of financial entities, identifying potential risks, and verifying compliance with established standards. Their responsibilities go beyond simple checks; they analyze financial health, investigate irregularities, and ensure that institutions operate within the legal framework set by authorities.
These inspectors use a variety of tools and techniques to assess the operational practices of financial organizations. They are trained to recognize early warning signs of instability, which could lead to larger issues such as insolvency or violations of the law. The findings from these investigations are integral in shaping policies, enforcing standards, and maintaining trust in the financial system.
Through their work, these professionals contribute to a safer, more secure financial environment for both businesses and consumers. By ensuring adherence to financial laws and regulations, they help preserve the integrity of the entire system, fostering transparency and accountability across the industry.
FDIC Bank Examiner Overview
Individuals who oversee the financial operations of institutions are tasked with ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and identifying potential risks. These professionals perform detailed assessments to ensure organizations maintain their financial stability and operate within the rules established by regulatory bodies. Their role is vital in preventing financial disruptions and ensuring that these entities continue to function effectively while safeguarding public trust.
Key Functions of Financial Oversight Professionals
These professionals are responsible for evaluating the operational practices, internal controls, and financial health of institutions. Their duties involve inspecting records, conducting interviews with management, and reviewing compliance with federal and state laws. Based on their findings, they provide recommendations for improvement or corrective actions when necessary. Their evaluations help to mitigate the risk of financial mismanagement or fraud.
Process and Methodology
The process followed by these professionals typically includes a combination of on-site inspections and off-site analyses. During inspections, they assess financial statements, audit reports, and operational procedures to identify areas of concern. Off-site, they analyze trends, compare performance metrics, and monitor compliance with established regulations. Both methods ensure a comprehensive review of each institution’s practices.
| Key Area | Methodology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Health | Review of financial statements and performance | Identify solvency and liquidity risks |
| Operational Controls | On-site inspections, interviews with staff | Ensure adherence to internal policies and regulations |
| Legal Compliance | Analysis of legal documents and regulatory adherence | Ensure full compliance with laws and guidelines |
Key Responsibilities of FDIC Examiners
Professionals in charge of overseeing financial institutions have a broad range of responsibilities aimed at ensuring compliance with legal frameworks, identifying potential risks, and safeguarding the stability of the financial system. These individuals work to maintain a transparent, efficient, and accountable environment by assessing how financial organizations operate and whether they adhere to regulatory standards. Their role extends beyond basic audits to include detailed assessments that inform broader regulatory actions.
Risk Identification and Mitigation
One of the most crucial tasks of these professionals is identifying financial risks within an organization. They evaluate the institution’s financial health, looking for signs of instability, such as irregular cash flow or significant financial discrepancies. Through thorough reviews of financial documents, they pinpoint areas where risk is highest and suggest appropriate corrective actions. Their ability to spot early warning signs helps prevent larger issues from developing, ensuring long-term stability.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring that financial entities comply with relevant regulations is another key responsibility. These professionals thoroughly assess compliance with federal and state laws, focusing on adherence to required capital levels, reporting standards, and consumer protection guidelines. After each assessment, they produce comprehensive reports outlining their findings and recommendations. These reports are essential for decision-makers who rely on them to enforce regulations and protect public interest.
Additional Tasks: In addition to risk analysis and compliance checks, these specialists also conduct interviews with senior management, evaluate internal controls, and assess the overall management of the institution. They may also follow up on previous recommendations to ensure corrective actions have been taken.
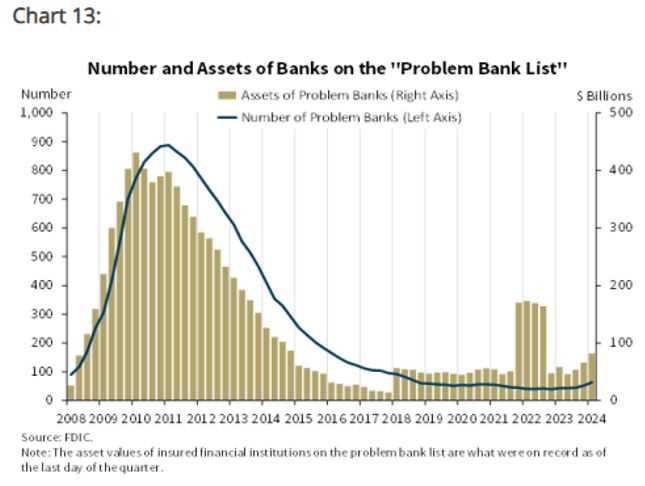
Importance of Bank Inspections
Regular inspections of financial institutions are crucial to ensuring that these organizations operate within the boundaries of the law, manage risks effectively, and remain financially sound. Without proper oversight, financial entities may engage in risky practices that could jeopardize their stability and the broader financial system. Inspections provide a necessary mechanism for monitoring performance, preventing fraud, and upholding public trust in the financial sector.
Ensuring Financial Stability
One of the primary reasons for conducting thorough inspections is to guarantee the stability of financial entities. These evaluations help to detect issues such as undercapitalization, poor management practices, or inadequate risk management strategies. By identifying such weaknesses early, inspectors can recommend corrective actions before the problems escalate into more severe financial crises, thus safeguarding the institution’s long-term viability.
Building Public Confidence
Routine oversight also plays an essential role in maintaining public confidence in the financial system. When institutions are regularly checked for compliance with laws and regulations, it reassures consumers, investors, and regulators that the system is functioning properly. This transparency helps to prevent panic and ensures that individuals and businesses alike feel secure in their financial dealings.
How FDIC Examiners Ensure Financial Stability
Financial oversight professionals play a critical role in maintaining the overall stability of the financial system. By conducting in-depth assessments, they are able to detect potential risks and vulnerabilities that could threaten the stability of financial entities. Through these evaluations, they ensure that institutions remain solvent, follow proper risk management practices, and adhere to regulations that protect both the economy and consumers.
Risk Detection and Prevention
One of the primary methods used by these professionals to ensure stability is identifying risks before they develop into serious issues. They thoroughly examine financial reports, audit results, and operational procedures to pinpoint areas of concern such as liquidity shortfalls or excessive leverage. Early identification of these risks allows for timely interventions, preventing financial distress or even failure.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Standards
Adhering to established regulations is essential for maintaining a balanced and secure financial system. These professionals ensure that institutions comply with industry laws that govern capital requirements, lending practices, and consumer protection. They evaluate whether these entities meet minimum standards set by regulators and recommend corrective actions when necessary, thus preventing actions that could lead to instability.
Systemic Risk Mitigation: By conducting regular evaluations, these experts help minimize systemic risks–those that could impact the wider financial system. Through their oversight, they create an early-warning system that helps detect trends that might have larger economic consequences, ensuring that regulatory bodies can respond swiftly to potential threats.
Qualifications Needed for FDIC Examiners
Professionals who conduct financial oversight must possess a combination of education, experience, and specific skills to effectively evaluate the health and operations of financial institutions. The role requires a deep understanding of finance, regulatory frameworks, and risk management practices. These individuals are tasked with identifying risks, ensuring compliance with regulations, and providing insights that help maintain the stability of the financial system.
Educational Background
A strong foundation in finance, accounting, or economics is essential for those seeking a career in financial oversight. A bachelor’s degree in these fields is typically required, though advanced degrees such as an MBA or a Master’s in Finance can be beneficial. Knowledge of financial statements, market trends, and financial modeling is crucial for assessing an institution’s performance and identifying potential areas of concern.
Relevant Experience and Skills
Practical experience in financial analysis, risk management, or auditing is highly valued. Professionals often begin their careers in roles such as financial analysts, auditors, or compliance officers before transitioning to oversight positions. In addition to technical expertise, strong communication skills are necessary to write detailed reports, present findings, and collaborate with institution leadership to implement recommendations. Critical thinking and problem-solving abilities are also essential to address complex financial issues.
Certifications: Many professionals in this field pursue certifications such as the Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) or Certified Public Accountant (CPA), which demonstrate a commitment to maintaining high standards of expertise and knowledge in the field of financial oversight.
Role in Identifying Banking Risks
Professionals responsible for overseeing financial institutions are integral in identifying and mitigating risks that could undermine the stability of these organizations. By conducting thorough assessments, they evaluate various aspects of an institution’s operations, identifying potential threats that could affect its financial health. Their role is to pinpoint vulnerabilities early, providing recommendations to prevent financial instability or regulatory violations.
Types of Risks Identified
These specialists focus on a wide range of potential risks, ensuring that financial entities operate within acceptable safety margins. The most common types of risks they assess include:
- Credit Risk: The risk of borrowers failing to repay loans or meet financial obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: The risk that an institution will not have enough liquid assets to meet short-term obligations.
- Operational Risk: The risk arising from failed internal processes, systems, or human error.
- Market Risk: The risk of financial loss due to changes in market conditions, such as interest rates or foreign exchange fluctuations.
- Compliance Risk: The risk of failing to adhere to regulations and laws, potentially leading to legal consequences or penalties.
Methodologies for Risk Identification
To detect these risks, financial oversight professionals utilize various tools and methodologies, including:
- Financial Statement Analysis: Reviewing balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports to identify potential liquidity or solvency issues.
- Stress Testing: Simulating extreme market conditions to determine how well an institution can handle adverse scenarios.
- Internal Audits: Conducting detailed reviews of internal processes and controls to identify operational weaknesses.
- Compliance Reviews: Verifying adherence to applicable regulations and industry standards to mitigate legal or regulatory risks.
By identifying these risks early on, these professionals help institutions take proactive measures to safeguard against potential financial crises and maintain long-term stability.
Tools Used by FDIC Examiners
Professionals responsible for overseeing financial institutions rely on a range of specialized tools to conduct thorough assessments. These instruments help ensure a comprehensive review of an institution’s financial health, operations, and adherence to regulations. By utilizing both software and manual techniques, they are able to analyze vast amounts of data, identify risks, and provide actionable insights that support effective decision-making.
| Tool | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Statement Analysis Software | Programs that automate the analysis of financial documents. | Quickly identify discrepancies, liquidity issues, and financial trends. |
| Stress Testing Models | Simulations designed to model the impact of extreme market conditions on institutions. | Assess how institutions would fare during financial crises or market volatility. |
| Risk Management Dashboards | Interactive tools that aggregate risk data from various sources. | Provide real-time insights into risk exposure and operational effectiveness. |
| Compliance Tracking Software | Systems that monitor adherence to regulations and standards. | Ensure that institutions meet legal and regulatory requirements. |
| Audit Tools | Programs used to track and evaluate internal audits and controls. | Identify internal control weaknesses and prevent fraud or operational inefficiencies. |
These tools are critical in conducting detailed reviews and providing reliable assessments. They enable professionals to process large volumes of data efficiently, ensuring a more accurate understanding of an institution’s operational practices and financial health.
Examination Process Explained
The process of assessing the financial health and operational integrity of a financial institution involves a series of systematic steps. These steps are designed to thoroughly evaluate the institution’s compliance with regulatory standards, its financial practices, and its overall stability. The goal of the evaluation is to identify potential risks, ensure the institution is operating efficiently, and provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
Preparation and Planning
The examination process begins with thorough preparation. Before setting foot in the institution, professionals review prior examination reports, financial statements, and other relevant documents. They also gather information about the institution’s current operations, key personnel, and any known issues or risks. This planning phase is crucial for identifying areas that require special attention and setting the scope of the review.
On-Site Evaluation

Once on-site, the team conducts an in-depth review of the institution’s operations. This involves interviews with management, examining financial records, and reviewing compliance procedures. Professionals assess various risk factors, including credit, liquidity, and operational risks. They also evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls, ensuring that the institution is following proper procedures and regulations to protect its assets and customers.
After completing the on-site evaluation, a final report is compiled, which includes findings, observations, and recommendations for corrective actions if needed. This report is then shared with the institution’s leadership, and follow-up actions are determined based on the severity of the issues identified.
Common Challenges Faced by Examiners
Professionals conducting financial reviews often face a variety of challenges that can complicate their work. These challenges can stem from internal factors within the institutions being reviewed, external economic conditions, or the complexity of regulations and industry standards. Effectively overcoming these obstacles is essential for ensuring a thorough and accurate evaluation of financial health.
Limited Access to Information
One of the primary challenges is the limited access to critical data or documents. Institutions may not always be forthcoming with all the information needed for a complete review, particularly if they are concerned about the implications of certain findings. Lack of transparency or inadequate record-keeping can hinder the assessment process, requiring professionals to work harder to obtain the necessary details to perform their duties.
Complex Financial Structures

Modern financial institutions often operate with complex structures, including diverse portfolios, intricate investment strategies, and global operations. Understanding and evaluating these complex systems requires advanced technical knowledge and considerable time. Moreover, assessing risks in such environments can be challenging, as small changes can have significant ripple effects on overall stability.
Despite these challenges, professionals continue to refine their methodologies, adapt to new technologies, and improve their skills to ensure effective assessments and timely identification of potential risks.
How Examiners Assess Compliance
Evaluating whether a financial institution adheres to regulatory requirements is a critical part of the oversight process. Professionals tasked with these reviews use a variety of methods to ensure that the institution operates within the framework of laws and industry standards. This involves examining internal policies, operational procedures, and transaction records to identify potential violations or areas of concern.
To assess compliance, these professionals begin by reviewing the institution’s policies and procedures to ensure they align with current regulations. This includes evaluating how the institution handles customer data, financial transactions, and reporting practices. Next, they examine whether the institution is adhering to industry-specific laws, such as anti-money laundering (AML) rules and consumer protection standards.
Another key aspect of the compliance assessment involves verifying that the institution maintains accurate and up-to-date records. Professionals will audit transaction histories, internal reports, and other relevant documents to detect discrepancies, potential fraud, or any regulatory breaches. Interviews with key personnel may also be conducted to gauge their understanding of compliance requirements and ensure they are being followed effectively across all departments.
By taking a comprehensive approach to evaluating compliance, these professionals help ensure that financial institutions meet the necessary legal standards, ultimately safeguarding the interests of clients, shareholders, and the broader financial system.
Impact of FDIC Findings on Banks
The results of financial reviews can have significant consequences for institutions. When these assessments identify deficiencies or areas of concern, it can trigger a range of responses, from corrective actions to regulatory penalties. The findings not only influence an institution’s operations but can also impact its reputation, customer trust, and long-term financial stability. Understanding these effects is essential for institutions to navigate the complex landscape of compliance and regulatory oversight.
Potential Consequences for Institutions
When an assessment uncovers serious issues, it may lead to a variety of outcomes. These could include mandatory corrective measures, operational changes, or financial adjustments. In extreme cases, findings may result in legal actions or restrictions on certain business activities, such as lending or investment practices. While the primary goal of the evaluation is to improve financial health, the consequences can also strain resources and impact the institution’s strategic direction.
Long-Term Impact on Reputation and Operations
The reputation of an institution can take a hit if serious issues are found during reviews. Even if the problems are resolved, negative publicity or public perception may linger, affecting customer confidence and investor interest. In some cases, financial institutions may be required to disclose the results of their assessments, which could further damage their standing in the market. This underscores the importance of maintaining a strong compliance culture and proactive internal controls to avoid such outcomes.
| Impact | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Action | Legal consequences, penalties, or restrictions on operations. |
| Operational Adjustments | Internal restructuring, procedural changes, or personnel shifts. |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of customer trust, investor confidence, and market position. |
| Increased Oversight | More frequent reviews, heightened scrutiny, or closer monitoring. |
In conclusion, the findings of financial reviews have far-reaching implications, not only for an institution’s compliance but also for its financial health, operational efficiency, and reputation in the market. Addressing any identified issues quickly and comprehensively is key to minimizing negative impacts and maintaining long-term stability.
FDIC Examiner Training Requirements
Professionals involved in financial oversight must undergo extensive training to effectively assess the health and operations of financial institutions. This training ensures they are well-equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to evaluate compliance, identify risks, and recommend corrective actions when needed. The process typically involves a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, and continuous learning to stay updated with evolving regulations and industry standards.
The training program covers various key areas such as financial analysis, regulatory frameworks, risk management, and investigative techniques. Trainees are taught how to review financial statements, audit internal controls, and assess the adequacy of systems designed to ensure regulatory compliance. Additionally, they gain a deep understanding of legal and ethical standards, which are crucial when carrying out inspections and handling sensitive information.
In addition to classroom training, professionals also engage in practical, on-the-job experiences, which allow them to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings. Mentorship programs and peer reviews further support their development, helping them refine their skills and learn from experienced colleagues.
Continuous professional development is also a critical aspect of the training process. As regulations and financial landscapes evolve, professionals must stay up to date on new laws, technologies, and industry trends. This ongoing education ensures they remain effective and informed throughout their careers, capable of addressing emerging challenges and maintaining high standards of oversight.
Relationship Between FDIC and Banks
The relationship between regulatory authorities and financial institutions is one of oversight and compliance. These authorities play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and security of the financial system by monitoring institutions and enforcing regulations designed to protect both the public and the economy. The oversight process involves periodic reviews, audits, and assessments to ensure that these entities adhere to legal and financial standards set by the government and industry bodies.
Collaboration and Support
While the relationship is primarily supervisory, there is also an element of support. Financial institutions receive guidance on best practices, legal compliance, and risk management strategies. In many cases, authorities work closely with these entities to identify potential issues before they become serious problems. By fostering open communication and collaboration, institutions are better equipped to address challenges and align their operations with evolving regulations.
Regulatory Enforcement and Compliance

Enforcement is another key aspect of this relationship. When an institution fails to meet the required standards, the authorities have the power to implement corrective actions, such as imposing fines, mandating operational changes, or restricting certain business activities. These measures help ensure that institutions do not jeopardize their financial stability or expose clients to unnecessary risks. However, these interventions are always aimed at improving the overall health of the financial system and protecting public trust.
FDIC Examiners and Consumer Protection
One of the primary roles of financial oversight professionals is to ensure the protection of consumers within the financial sector. This involves monitoring the practices of institutions to ensure they are operating fairly, transparently, and in accordance with consumer protection laws. These professionals work to prevent abusive practices, safeguard consumer rights, and maintain the integrity of the financial system. Their work is essential in maintaining public trust and ensuring that consumers can access services without fear of exploitation.
Through regular assessments, professionals identify potential risks to consumers, including fraudulent activities, predatory lending, and unfair fees. They evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls, ensuring that financial institutions comply with regulations that protect individuals from harmful business practices. In cases where violations are detected, corrective measures are taken to address the issue and prevent future harm.
Ensuring Fairness and Transparency
Transparency is a key component of consumer protection. These professionals ensure that consumers have access to clear, accurate information about the products and services offered. This includes ensuring that terms, fees, and conditions are disclosed in an understandable manner, allowing consumers to make informed decisions. By focusing on fairness and transparency, they help maintain a healthy financial environment where individuals are empowered and informed.
Advocating for Consumer Rights
In addition to overseeing institutions, these professionals also act as advocates for consumers, ensuring that their rights are respected and upheld. They address complaints, investigate potential violations, and take necessary actions to ensure institutions are held accountable. Their work ultimately helps to create a safer and more equitable financial landscape for all individuals.
Reporting and Documentation by Examiners
Accurate reporting and thorough documentation are essential components of the oversight process. After evaluating financial institutions, the professionals involved are responsible for compiling their findings into detailed reports. These documents serve as official records of the assessments conducted and help ensure transparency and accountability within the financial system. The reporting process is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the review process and supporting future regulatory actions.
Key Elements of Reporting
The documentation provided after an assessment typically includes the following key elements:
- Findings: A clear summary of the observations made during the evaluation, including any risks, issues, or discrepancies discovered.
- Compliance Assessment: A review of how well the institution adheres to industry regulations, including consumer protection laws and financial reporting standards.
- Recommendations: Suggested actions to rectify any identified issues or to improve operational practices to ensure compliance with applicable standards.
- Risk Analysis: An analysis of the potential financial risks or vulnerabilities discovered during the review, with an emphasis on mitigating these risks.
Documentation Process
The documentation process is not only about reporting findings but also about ensuring that all steps taken during the review are thoroughly recorded. This includes:
- Interviews and Surveys: Records of conversations with institution staff, customers, and other relevant stakeholders.
- Data Collection: Compiling financial data, audit results, and other key metrics necessary for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Follow-up Actions: Documentation of any corrective measures that are proposed or implemented, ensuring they align with regulatory expectations.
These records are vital for future assessments, as they allow for a clear understanding of past evaluations and provide a basis for continuous improvement in the financial sector.
Legal Framework Surrounding FDIC Examinations
The legal foundation for financial oversight is built on a framework of regulations and statutes designed to maintain the stability and integrity of financial institutions. This structure defines the responsibilities and powers of regulatory bodies, ensuring they have the authority to conduct comprehensive reviews and enforce necessary corrective measures. The legal guidelines set clear boundaries for assessments, protecting both the institutions under review and the broader financial system from potential risks.
Key Regulations and Statutes
Several key pieces of legislation govern the regulatory process and provide a basis for inspections and oversight:
- Federal Deposit Insurance Act: This act establishes the role of federal regulators in overseeing institutions to ensure public confidence in the financial system.
- Bank Holding Company Act: It provides regulations related to financial groups, setting standards for corporate governance and financial soundness across entities.
- The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act: A comprehensive statute that introduced numerous financial regulations, increasing accountability in the financial sector.
- The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act: This law focuses on protecting consumers’ private financial information, and regulators must ensure compliance during evaluations.
Enforcement and Compliance

Regulatory authorities have a legal obligation to enforce compliance with these laws through a variety of tools, including:
- Sanctions and Penalties: Legal consequences for institutions found to be non-compliant with applicable regulations.
- Corrective Actions: Regulatory bodies can mandate institutions to take specific steps to address deficiencies or operational failures identified during evaluations.
- Transparency Requirements: Financial institutions must disclose key information to regulators, ensuring open communication and accountability in operations.
The legal framework ensures that evaluations are not only conducted fairly and effectively but also in a way that upholds the safety and stability of the entire financial ecosystem.
Future Trends for FDIC Examiners
As the financial landscape evolves, so too must the methods and practices employed to ensure its stability. The future of regulatory assessments is shaped by technological advancements, changing market conditions, and evolving consumer expectations. In response to these shifts, those responsible for overseeing financial institutions must adapt and adopt new strategies to remain effective. The continued integration of modern tools and an increased focus on data-driven decision-making will play a crucial role in shaping the future of financial oversight.
Technological Innovations

Technological advancements are expected to streamline and enhance the evaluation process, making it more efficient and accurate. Key trends include:
- Data Analytics: The use of big data and predictive analytics will enable a deeper understanding of financial trends, risks, and operational patterns within institutions.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will assist in identifying potential vulnerabilities by analyzing large volumes of data quickly and more precisely, improving the accuracy of assessments.
- Blockchain Technology: With its potential for secure, transparent record-keeping, blockchain could revolutionize the way transactions and institutional activities are monitored and verified.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity and Risk Management

As cybersecurity threats continue to rise, future regulatory reviews will place a stronger emphasis on evaluating the resilience of financial systems against cyberattacks. This will involve:
- Risk Assessment Models: Implementing more robust models to assess the potential impact of cybersecurity risks and ensure institutions have the necessary defenses in place.
- Enhanced Compliance Checks: Financial institutions will face increased scrutiny over their ability to protect sensitive data and comply with privacy regulations.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and the integration of automated tools to track ongoing risk factors, ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
These trends will redefine how financial oversight is conducted, creating a more agile and informed approach to maintaining the stability of the financial system.
Key Skills for Aspiring FDIC Examiners
To succeed in the field of financial oversight, aspiring professionals must develop a diverse set of skills that combine technical knowledge, analytical ability, and interpersonal acumen. These abilities are essential for navigating the complex regulatory landscape and ensuring that financial institutions operate in a sound and ethical manner. Understanding financial statements, risk management, and compliance standards are just the beginning. The ability to effectively communicate findings, think critically under pressure, and adapt to new challenges are all equally important in this field.
Essential Technical and Analytical Skills
In-depth technical knowledge is the cornerstone of any financial oversight role. Key skills include:
- Financial Analysis: The ability to assess financial statements, balance sheets, and income statements is critical. Understanding financial health indicators and identifying potential areas of concern is essential.
- Risk Management Knowledge: Familiarity with risk assessment models and frameworks will help professionals identify and mitigate financial threats.
- Regulatory Knowledge: A thorough understanding of the legal and compliance standards governing financial institutions is vital for evaluating adherence to laws and regulations.
- Attention to Detail: Precision is key when reviewing documents, transactions, and data. A meticulous approach helps ensure that no discrepancies go unnoticed.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Strong communication skills are just as critical as technical expertise in this field. These abilities are crucial for effectively engaging with stakeholders and presenting findings:
- Clear Reporting: The ability to write clear, concise reports and document findings accurately is essential. This ensures that any issues are communicated effectively to relevant parties.
- Negotiation and Conflict Resolution: Professionals must often navigate complex situations, requiring diplomacy and negotiation skills when addressing concerns with financial institutions.
- Collaboration: Working as part of a team, both within regulatory bodies and with external institutions, is common. Effective collaboration fosters a productive work environment and leads to more thorough assessments.
Developing a balance of technical expertise and communication abilities is key to excelling in this role. These skills not only aid in completing evaluations but also in maintaining strong professional relationships within the financial sector.