When it comes to navigating the world of insurance, understanding fundamental principles is crucial for making informed decisions. This section provides a detailed exploration of essential topics that form the foundation of how various plans and policies work. Whether you’re new to the subject or preparing for a related assessment, grasping these core ideas is the first step in building a strong knowledge base.
Understanding different types of plans and the role of specific elements like premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses is essential. By mastering these concepts, individuals can better evaluate options, compare providers, and ultimately select the most suitable coverage for their needs.
Examining practical scenarios and addressing common questions about eligibility and cost-sharing helps clarify these complex systems. This guide aims to break down the information into easily digestible segments, ensuring that you are well-prepared to answer any questions related to these fundamental topics.
Health Coverage Basics Exam Answers

Understanding the principles of insurance plans and related topics is essential for anyone looking to grasp the fundamentals of the subject. This section will explore key questions that commonly appear in assessments focused on this area. By reviewing these essential concepts, you’ll be able to enhance your knowledge and approach the subject with confidence.
Key Concepts to Focus On

When preparing for a test on this subject, it’s important to understand the different types of plans available and how they work. Focus on terms such as premiums, deductibles, and co-payments, as well as how these elements impact the overall cost of a plan. Additionally, it’s crucial to know how specific plans cater to various groups, such as the elderly or low-income individuals.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While studying for this topic, it’s easy to get confused by complex terminology and policies that may seem similar but have important differences. Pay close attention to the details of each type of plan and avoid mixing up terms related to eligibility, benefits, and costs. It’s also beneficial to familiarize yourself with common mistakes made by others and practice with sample questions to reinforce your understanding.
Understanding Health Coverage Essentials
Gaining a clear understanding of the foundational elements that make up various insurance plans is vital for anyone navigating this field. In this section, we will explore the fundamental components that determine how these plans operate and the factors that influence the cost and benefits of different options.
Key Elements of Insurance Plans
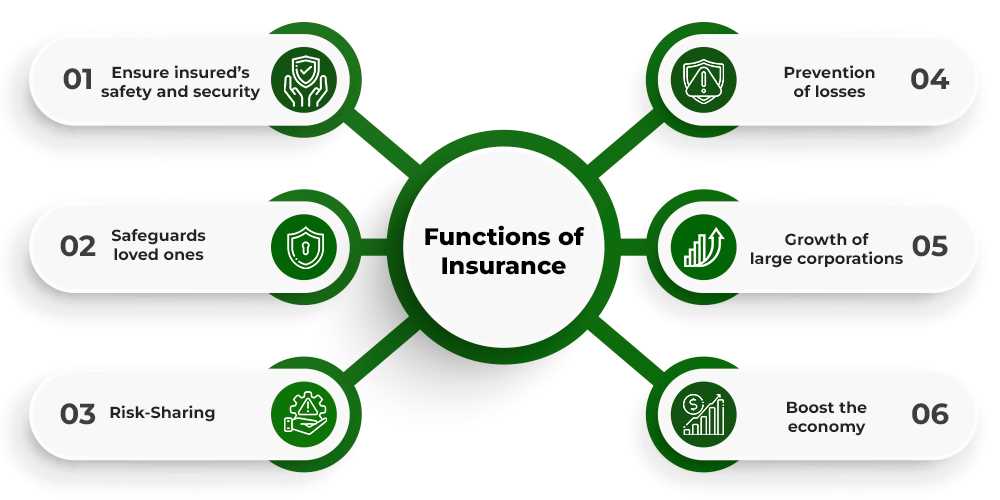
Insurance plans generally consist of several important elements, each affecting the overall structure and cost. It is crucial to be familiar with the following components:
- Premiums – The regular payments made to maintain the plan.
- Deductibles – The amount an individual must pay before the plan starts covering costs.
- Co-payments – A fixed fee paid by the insured for specific services.
- Out-of-pocket maximums – The total amount an individual must pay before the insurance covers all further expenses.
Types of Plans and Their Impact

Different plans offer varying levels of coverage and cost-sharing options. It’s essential to know which type of plan suits your needs best. The main types of plans include:
- Managed care plans – These include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), which emphasize cost management and networks of healthcare providers.
- Fee-for-service plans – These provide flexibility by allowing individuals to choose their healthcare providers, though they tend to have higher costs.
- High-deductible plans – These have lower premiums but require individuals to pay higher out-of-pocket costs before the insurance starts covering expenses.
Key Concepts in Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the critical components of various insurance policies is essential for selecting the right plan. By familiarizing yourself with these core elements, you can make better decisions regarding your options and ensure you are well-prepared to navigate the different types of plans available. Below, we’ll explore the main concepts that shape the structure and costs of these policies.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Premium | The amount paid periodically to maintain an insurance plan. |
| Deductible | The amount an individual must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance begins to pay for services. |
| Co-payment | A fixed amount paid for a specific service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription. |
| Co-insurance | The percentage of costs shared between the insured and the provider after the deductible is met. |
| Out-of-pocket Maximum | The highest amount an individual will pay for covered services in a plan year. |
Each of these elements plays a vital role in determining how much an individual will pay for a policy and how much the insurance provider will cover. Understanding how they interact is key to selecting a plan that meets your financial and healthcare needs.
Types of Health Coverage Explained
There are several different options available when it comes to choosing an insurance plan. Each type of plan offers different levels of care and financial protection, depending on individual needs and preferences. Understanding the differences between these plans can help individuals make informed decisions about which option is most suitable for them.
Common Types of Plans
The following are some of the most common types of insurance policies available:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) – A plan that requires members to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals to see specialists within the network.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) – A more flexible plan that allows individuals to see specialists without referrals and offers coverage both in and out of the network.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) – A plan that requires members to use a network of providers except in emergencies, but does not require referrals.
- Point of Service (POS) – A hybrid plan that combines features of HMO and PPO, where you can choose between in-network and out-of-network providers, though out-of-network services usually come with higher costs.
Other Plan Types to Consider
In addition to the above, there are other plans that may suit specific needs or demographics:
- High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP) – These plans have lower premiums but require individuals to pay a higher deductible before coverage kicks in. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to help save for medical costs.
- Catastrophic Plans – Designed for young, healthy individuals, these plans offer low monthly premiums but high deductibles and are intended to cover worst-case scenarios like serious accidents or illnesses.
- Medicare – A federal program for individuals aged 65 or older, or for certain younger individuals with disabilities, offering various parts to cover hospital care, medical services, and prescription drugs.
- Medicaid – A joint federal and state program that provides coverage for low-income individuals and families, offering a wide range of health services.
By understanding these different types of plans, individuals can better assess which option aligns with their healthcare needs, budget, and long-term goals.
How to Prepare for the Exam
Preparing for a test on insurance-related topics requires a strategic approach to ensure that key concepts are fully understood. To effectively study and perform well, it’s essential to focus on mastering the core principles and terminology, while also familiarizing yourself with the types of questions that may appear. Below are some strategies that will help you prepare efficiently and confidently.
Start by reviewing all relevant materials, including any textbooks, notes, or online resources. Break down the subject into manageable sections, focusing on one concept at a time. This approach helps to avoid feeling overwhelmed and ensures that each area is thoroughly covered.
Practice is crucial for reinforcing your understanding. Look for practice questions or quizzes that simulate the style of the actual test. This will not only test your knowledge but also help you become more comfortable with the types of questions you may face.
Another helpful strategy is to form or join a study group. Discussing topics with others can provide different perspectives and help clarify any areas of confusion. Additionally, teaching others what you have learned is a great way to solidify your own understanding.
Finally, make sure to give yourself enough time to study. Avoid cramming the night before by spreading your study sessions over several days or weeks. Consistent review is key to retaining the information and being able to recall it under exam conditions.
Common Health Coverage Terminology
When navigating the world of insurance plans, understanding the terminology used is essential for making informed decisions. Familiarizing yourself with these key terms will help you better understand the documents, contracts, and policies you encounter. Below are some of the most common terms you are likely to come across and what they mean in simple terms.
Key Terms to Know

The following are important terms that frequently appear when discussing insurance plans:
- Premium – The regular payment made to maintain an insurance plan, typically paid monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Deductible – The amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts to pay for covered services.
- Co-payment – A fixed amount paid by you for a covered service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription, with the insurance covering the rest.
- Co-insurance – The percentage of the cost you share with your insurer after your deductible has been met.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum – The total amount you will be required to pay for covered services in a plan year, after which the insurance pays 100% of the costs.
Other Important Terms
Understanding the following terms can further enhance your knowledge of insurance plans:
- Network – The group of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers that your insurance plan has agreements with to provide care at a lower cost.
- In-Network – Healthcare providers that are part of your plan’s network, offering services at a lower cost to you.
- Out-of-Network – Providers not contracted with your plan, usually resulting in higher costs for services received.
- Pre-authorization – Approval from your insurance plan before certain treatments or services can be provided, to ensure they are covered under your policy.
By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you’ll be better equipped to understand the specifics of your policy and make more informed choices when it comes to selecting or managing your plan.
Importance of Preventive Health Services
Preventive care plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being and avoiding the development of serious conditions. These services focus on identifying health risks early and addressing them before they lead to more significant issues. By prioritizing prevention, individuals can reduce the need for more complex and costly treatments in the future.
Engaging in regular preventive services can lead to early detection of diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, or heart disease, which are more manageable when identified in their early stages. Preventive measures can include routine screenings, vaccinations, wellness check-ups, and lifestyle counseling, all of which are designed to help individuals stay healthy and avoid major medical problems.
In addition to improving health outcomes, preventive care can also help reduce long-term healthcare costs. By addressing risk factors and promoting healthier lifestyles, individuals are less likely to require expensive interventions down the line. This approach benefits not only individuals but also the broader healthcare system by minimizing the burden of treatable or avoidable diseases.
Eligibility Criteria for Health Insurance
Understanding the requirements to qualify for an insurance plan is essential for individuals looking to secure coverage. Different plans have varying eligibility criteria based on factors such as age, income, employment status, and residency. Familiarizing yourself with these factors can help you determine which plans you are eligible for and ensure you select the right one for your needs.
Key Eligibility Factors
The following are some of the main factors that may determine whether an individual qualifies for a specific insurance plan:
- Age – Certain plans, like government-sponsored programs, may have age-related eligibility requirements, such as for seniors or young adults.
- Income Level – Low-income individuals or families may qualify for subsidized plans, while higher-income individuals may have different options available.
- Employment Status – Some plans are employer-sponsored, so eligibility may depend on your job status or whether your employer offers insurance benefits.
- Residency – Eligibility may depend on your legal residency status in a specific country or region, with some plans limited to citizens or permanent residents.
Other Considerations
In addition to the primary eligibility factors, some plans may have additional requirements or conditions, such as:
- Pre-existing Conditions – Some plans may have restrictions or waiting periods for individuals with certain medical conditions, although laws may limit discrimination based on pre-existing conditions in many areas.
- Family Size – Some insurance programs may offer coverage options based on household size or dependent status, influencing the overall cost and availability of the plan.
- Special Programs – Some government programs or non-profit organizations may have specific eligibility criteria based on unique circumstances, such as disability or military service.
By understanding these eligibility criteria, individuals can navigate the complexities of the insurance market more effectively and ensure they have access to the appropriate coverage options.
How Premiums and Deductibles Work
When choosing an insurance plan, two key financial terms to understand are premiums and deductibles. These components determine the amount you will pay for coverage and affect the way your benefits are applied. Knowing how they work can help you make more informed decisions about which plan best suits your needs and budget.
Premiums refer to the regular payments you make to maintain your insurance plan. Typically paid monthly, premiums are the price of having access to the plan’s benefits, regardless of whether you use them. In general, the higher your premiums, the lower your out-of-pocket expenses may be when you need care, and vice versa.
Deductibles are the amounts you must pay out-of-pocket for covered services before your insurer begins to contribute. For example, if your plan has a deductible of $1,000, you must pay that amount for care before the plan starts covering a portion of your medical expenses. Deductibles are often paid annually and can vary widely depending on the plan.
The balance between premiums and deductibles is an important factor to consider. Lower premiums may result in higher deductibles, which means you’ll need to pay more upfront for care before your insurer contributes. Conversely, higher premiums generally mean a lower deductible, which could save you money on healthcare costs throughout the year.
Understanding the relationship between these two components allows you to choose a plan that balances monthly affordability with the potential cost of medical expenses, ensuring that you’re prepared for both expected and unexpected healthcare needs.
Role of Out-of-Pocket Costs in Coverage
Out-of-pocket expenses play a significant role in the overall structure of your insurance plan. These are the costs that you must pay on your own, in addition to regular premiums, when seeking medical services. Understanding how these costs work is crucial for managing your healthcare budget and making sure you can afford the care you need.
Out-of-pocket costs include various types of payments that you are responsible for, such as co-pays, co-insurance, and deductibles. These costs can vary depending on the type of service you receive and whether the provider is in-network or out-of-network. In some plans, certain services like preventive care may be covered without requiring additional payments, but most treatments will involve some level of cost-sharing.
One key factor that affects your out-of-pocket expenses is the out-of-pocket maximum, which is the total amount you are required to pay in a given year. Once you reach this limit, your insurer will typically cover 100% of any additional costs for covered services. This provides a safeguard against catastrophic expenses, ensuring that you do not face unlimited financial responsibility.
The impact of out-of-pocket costs is particularly important for individuals with chronic conditions or those who require frequent medical visits. In these cases, high out-of-pocket expenses can quickly accumulate, making it vital to understand how different plans structure these costs. Balancing the cost of premiums with potential out-of-pocket expenses is essential for finding a plan that fits your financial and healthcare needs.
Understanding Medicaid and Medicare
Medicaid and Medicare are two government programs designed to provide financial assistance for healthcare, but they serve different groups of people and have distinct eligibility requirements. Understanding the differences between these programs is essential for individuals looking to access affordable medical services. Each program offers various benefits and caters to specific needs based on age, income, or disability status.
Medicaid
Medicaid is a program primarily for low-income individuals and families. It is jointly funded by the federal and state governments, with each state managing its own program. Eligibility requirements vary from state to state, but in general, Medicaid provides coverage for:
- Low-income adults, children, and pregnant women
- People with disabilities
- Individuals with limited resources
- Some elderly individuals who meet certain income requirements
Medicaid covers a wide range of services, including hospital care, doctor visits, prescription drugs, preventive care, and long-term care for those who need it. Since the program is state-specific, benefits and coverage details can differ based on where you live.
Medicare
Medicare, on the other hand, is a federal program primarily aimed at individuals aged 65 and older, although it also covers younger individuals with certain disabilities or chronic conditions. Medicare is divided into different parts that offer different types of services:
- Part A – Covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care services.
- Part B – Provides coverage for outpatient services such as doctor visits, preventive care, and medical supplies.
- Part C – Also known as Medicare Advantage, combines Parts A and B and often includes additional benefits like vision and dental care.
- Part D – Offers prescription drug coverage to help offset the cost of medications.
While Medicare is available to those who meet the age or disability criteria, it is important to note that there are premiums, deductibles, and co-payments associated with certain parts of the program. Understanding the costs and benefits of each part is essential to maximizing the value of the program.
Both Medicaid and Medicare provide essential support to millions of people, helping to reduce the financial burden of medical expenses. However, understanding the eligibility requirements, benefits, and coverage options is key to making the best use of these programs.
Health Savings Accounts Overview

A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a financial tool that allows individuals to save money for medical expenses while enjoying tax benefits. These accounts are often paired with high-deductible insurance plans and provide a way to set aside funds specifically for healthcare costs. Understanding how HSAs work, their eligibility requirements, and their benefits is crucial for making the most of this option.
How HSAs Work
HSAs allow individuals to contribute pre-tax income to an account that can be used for qualified medical expenses. These contributions are tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income for the year. The funds in the account grow tax-free, and withdrawals made for qualifying medical expenses are also tax-free. This triple tax advantage–contributions, growth, and withdrawals–makes HSAs a valuable option for saving for healthcare needs.
The money in an HSA can be used for a wide range of medical services, including doctor visits, prescriptions, surgeries, and even dental and vision care. Unlike flexible spending accounts (FSAs), the money in an HSA rolls over from year to year, so it can be accumulated over time for future use.
Eligibility and Contribution Limits
To open an HSA, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible insurance plan, and you cannot be enrolled in other forms of health insurance that offer more comprehensive coverage. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets annual contribution limits for HSAs, which can vary based on whether you are an individual or a family. These limits are updated yearly, so it’s important to stay informed about the maximum amount you can contribute each year.
HSAs are not only useful for those seeking to manage current healthcare expenses, but they can also serve as a long-term savings tool. Because there is no deadline for spending the funds, an HSA can be used as a supplemental retirement savings account, helping you manage medical costs in the future as well.
In summary, an HSA offers individuals a way to save for medical expenses with tax advantages. By understanding the eligibility requirements, contribution limits, and potential uses of these accounts, individuals can make informed decisions about managing healthcare costs both now and in the future.
Impact of Health Coverage on Wellness
Having access to comprehensive insurance options plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. It helps individuals access essential medical services, manage chronic conditions, and prevent potential health issues. When individuals are covered by an effective plan, they are more likely to seek early medical advice, engage in preventive care, and manage their long-term health better. This, in turn, contributes to a higher quality of life and a reduction in the severity of health issues over time.
Preventive Care and Early Detection
Access to appropriate insurance can significantly enhance the ability to undergo regular screenings, vaccinations, and other preventive measures. With proper coverage, individuals are more likely to take part in routine check-ups, which can lead to early detection of conditions that might otherwise go unnoticed. Early intervention can result in more effective treatments, reduced medical costs, and improved outcomes.
Preventive care services like annual physicals, cancer screenings, and immunizations are integral to identifying potential health risks early. People with access to insurance are more likely to receive these services and address emerging issues before they develop into more serious problems.
Managing Chronic Conditions
Chronic illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma require ongoing management. A well-structured insurance plan ensures that individuals with chronic conditions can access the necessary treatments, medications, and specialists to control their symptoms and improve their quality of life. This consistent care can help reduce the risk of complications and hospitalizations, providing individuals with better control over their health.
Without sufficient access to medical services, those with chronic conditions may experience worsening symptoms, leading to a decline in overall well-being. Having the right plan can ensure that necessary treatments are maintained and that individuals stay on top of their health needs, preventing more severe outcomes.
In conclusion, comprehensive insurance options have a profound impact on wellness. By facilitating access to preventive care, early detection, and ongoing management of health conditions, individuals are more likely to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Proper access to care contributes not only to physical well-being but also to emotional and financial stability over time.
Choosing the Right Insurance Plan
Selecting the appropriate insurance option is a vital decision that impacts both your financial stability and overall well-being. The process requires understanding various plan features, such as premiums, deductibles, co-payments, and the specific services covered. A plan that fits your individual or family needs will ensure you receive necessary medical services without overwhelming costs. To make an informed choice, it’s essential to assess your health requirements, budget, and personal preferences.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plan
When evaluating insurance plans, several factors should be taken into account to ensure the plan suits your specific needs:
- Premiums: The monthly cost of the plan. Lower premiums may mean higher out-of-pocket expenses, while higher premiums can lead to lower deductibles and co-pays.
- Deductibles: The amount you pay for covered health care services before your plan starts to pay. Plans with higher deductibles generally have lower premiums.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: Additional costs such as co-payments or coinsurance that you pay when receiving services.
- Network of Providers: The list of doctors, hospitals, and clinics that accept the insurance plan. Make sure your preferred providers are included in the network.
- Coverage Options: The types of services covered, including preventive care, hospital visits, medications, and mental health services.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Whether the plan covers prescription medications and how much you will pay for them.
Comparing Different Plans
To compare different insurance plans effectively, it’s helpful to review a summary of each plan’s benefits. Below is a basic table outlining some key features of common plans:
| Plan Type | Premiums | Deductibles | Co-pays | Out-of-Pocket Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plan A | $250/month | $2,000/year | $20/visit | $5,000/year |
| Plan B | $150/month | $3,500/year | $30/visit | $7,000/year |
| Plan C | $300/month | $1,000/year | $15/visit | $4,000/year |
By comparing the details above, you can evaluate which plan offers the most value for your needs, balancing the monthly premiums with the cost of services. It’s important to consider your typical health care usage and whether you anticipate needing specialized services or frequent medical attention. A well-chosen plan can provide peace of mind and ensure that you are protected against unexpected medical expenses.
Exam Tips for Health Coverage Basics
Preparing for a test on insurance concepts requires a solid understanding of key terms, structures, and processes. It’s essential to focus on the most important aspects, such as policy types, costs, benefits, and eligibility criteria. Effective study strategies include reviewing practice questions, summarizing notes, and breaking down complex concepts into manageable parts. This approach will help ensure that you grasp the foundational elements needed to succeed on the test.
Study Strategies
To effectively prepare for the test, follow these helpful study techniques:
- Understand Key Terms: Ensure you’re familiar with essential vocabulary, such as premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket expenses. Being able to define and explain these terms will be crucial.
- Review Test Materials: Go over any study guides, practice exams, or resources provided by the instructor. These materials often contain the types of questions you will encounter on the actual test.
- Make Summary Notes: Create concise summaries of each topic to reinforce your understanding. Bullet points or mind maps can help visualize connections between different concepts.
- Practice with Mock Tests: Take practice tests under timed conditions to simulate the real exam environment. This will help improve your test-taking skills and time management.
Test-Taking Strategies
During the actual test, the following tips can improve your performance:
- Read Carefully: Take the time to read each question thoroughly. Pay attention to keywords that may help guide your response, such as “always,” “never,” or “most likely.”
- Answer What You Know First: Quickly answer questions that you are confident about. This allows you to focus more on challenging questions later without wasting time.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If you are unsure about a question, try to eliminate the obviously incorrect answers. This increases your chances of choosing the correct option.
- Manage Your Time: Keep track of the time during the test. If you get stuck on a question, move on and return to it later if needed.
By utilizing these study and test-taking strategies, you can approach the test with confidence and increase your chances of success. Remember, consistency and preparation are key to mastering the concepts and performing well.
Frequently Asked Questions About Coverage
When navigating the world of insurance, many individuals have common questions about policies, terms, and costs. Understanding the frequently asked questions can help clarify key aspects and make it easier to choose the right plan. Below, we address some of the most common inquiries related to various plans and their components.
What is the difference between premiums and deductibles?
Premiums are the regular payments made to maintain an insurance plan, typically paid monthly, quarterly, or annually. Deductibles, on the other hand, refer to the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company begins to contribute to your covered expenses. Understanding how both work can help you determine the overall cost of your insurance and how much you may need to pay when receiving services.
How do co-pays and coinsurance work?
Co-pays are fixed amounts that you pay for certain services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions. These are typically low, predetermined amounts that do not change based on the service received. Coinsurance is a percentage of the total cost you are responsible for after meeting your deductible. For example, if your plan includes 20% coinsurance, you’ll pay 20% of the total cost of services, and the insurer will cover the remaining 80%. Understanding these two cost-sharing elements is important for budgeting your expenses.
What is an out-of-pocket maximum?

The out-of-pocket maximum is the maximum amount you will have to pay for covered services in a given year. Once this limit is reached, the insurance company will cover 100% of any additional costs for the rest of the year. This ensures that your financial responsibility is capped, even in the event of significant medical needs.
Can I change my plan during the year?
In most cases, you can only change your insurance plan during certain periods, such as the open enrollment period or if you experience a qualifying life event (e.g., marriage, birth of a child, or loss of other coverage). However, exceptions may apply depending on the type of insurance and the rules in your area.
Are all services covered under a typical plan?
Not all services are automatically covered by every insurance plan. Most policies have specific exclusions, and certain treatments or procedures may not be included. It’s important to carefully review your plan details to understand what is and isn’t covered to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket costs.
By answering these frequently asked questions, you can have a clearer understanding of how various components of an insurance plan work. Being well-informed will help you make better decisions about your financial and healthcare needs.
Challenges in Health Coverage Understanding
Understanding the intricacies of insurance plans can be complex due to various terms, coverage options, and costs involved. Many people find it challenging to navigate the maze of jargon, policies, and differing rules that determine how plans function. This section explores some of the most common difficulties individuals face when trying to grasp the full scope of their plans and how these challenges impact decision-making.
Common Misunderstandings and Confusions
There are numerous aspects of insurance that can cause confusion, from the relationship between premiums and out-of-pocket costs to the limitations on covered services. Here are some common sources of misunderstanding:
- Premium vs. Deductible: People often confuse these two key components. A premium is the regular amount you pay, while a deductible is the amount you need to pay before the insurer starts contributing.
- Service Exclusions: Many individuals overlook or are unaware of exclusions in their plans, which may not cover certain treatments or services.
- Out-of-Pocket Limits: Misunderstanding what counts towards the out-of-pocket maximum can lead to surprises when it comes to paying for medical expenses.
- Co-pays and Coinsurance: The difference between a co-pay and coinsurance can be difficult to grasp, with co-pays being fixed amounts and coinsurance being percentages of total costs.
Breaking Down Plan Structure

To avoid confusion, it is essential to understand how a typical insurance plan is structured. This breakdown helps clarify the various components and their roles:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Premium | The regular payment made to keep the insurance active, usually paid monthly. |
| Deductible | The amount you must pay before your insurance starts covering costs. |
| Co-pay | A fixed amount you pay for a covered service, often at the time of the service. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of the cost you pay after meeting the deductible. |
| Out-of-Pocket Maximum | The maximum amount you will pay in a year before the insurer covers 100% of the costs. |
Understanding each of these components can help demystify the structure of your insurance plan, making it easier to assess and manage your needs. Clarity about how these elements interact is crucial in avoiding costly mistakes and making informed decisions.
Latest Changes in Health Insurance Policies
Recent modifications in insurance regulations and plans have significantly impacted how individuals access and manage their protection against various risks. These changes reflect ongoing efforts to improve affordability, expand coverage options, and ensure fairness within the system. Understanding these adjustments is crucial for both current policyholders and those looking to purchase a new plan. This section explores the key alterations and their implications for users.
One of the most notable changes has been the adjustment of eligibility criteria for specific programs, making it easier for certain groups to qualify for more comprehensive plans. Additionally, there have been updates in the structure of premiums and deductibles, designed to offer more flexibility based on income levels and personal needs.
Another important development is the expansion of preventive services included within many policies. Insurers are now required to cover more preventive care without any additional out-of-pocket expenses, helping individuals maintain their well-being while reducing long-term medical costs. This aligns with a growing focus on proactive health management rather than just treatment of illnesses.
Finally, changes in the regulations governing out-of-pocket expenses have made it easier for consumers to predict and manage their financial responsibilities. New caps on annual spending limits have been introduced, giving policyholders greater financial security in times of medical need.