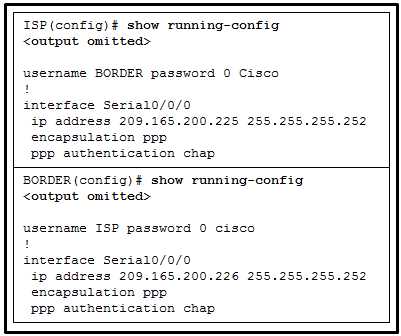
The world of networking encompasses a vast range of essential skills that every professional needs to master. From understanding how devices communicate with each other to configuring network infrastructure, each element plays a crucial role in building robust systems. This section will explore key principles that form the foundation of modern networking technologies.
As the complexity of networks continues to grow, it is vital to have a deep understanding of how to manage and troubleshoot various configurations. Whether it’s working with routers, switches, or different protocols, knowing how to apply the right techniques and solutions is fundamental. The following sections will guide you through important concepts and provide practical insights for success in the field.
Focusing on key aspects of network management, you will learn about essential practices, common pitfalls to avoid, and the steps necessary to ensure smooth operations. By reviewing real-world scenarios and practice questions, you can build confidence in handling various challenges and improve your technical abilities.
Networking Fundamentals and Key Concepts
This section is dedicated to the core principles that play a pivotal role in managing and troubleshooting network environments. By delving into the essential tools, protocols, and configurations, you will be equipped to navigate complex network setups and resolve issues effectively. The insights shared here will help in reinforcing the understanding of important networking topics and preparing for practical applications.
Key Networking Techniques
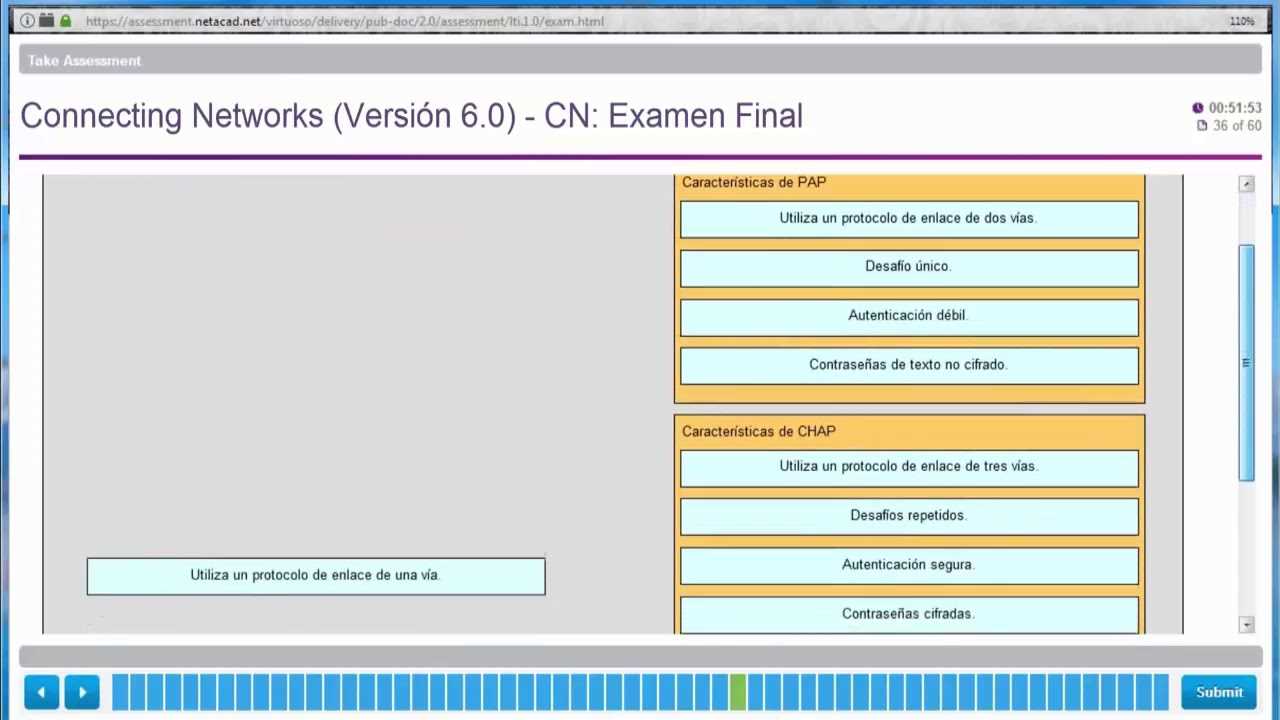
Mastering network configuration and troubleshooting techniques is vital for ensuring network stability and efficiency. It’s essential to understand how devices interact, how information flows, and the role of different networking protocols. The following table highlights some of the most critical networking tasks and their corresponding solutions:
| Task | Solution |
|---|---|
| IP Address Configuration | Verify correct subnet mask and gateway settings. |
| Routing Issues | Check routing tables and verify the correct path is used. |
| Switch Configuration | Ensure VLAN settings are correct and ports are properly assigned. |
| Device Connectivity | Test cables and verify interface statuses on devices. |
| Network Security | Review access control lists (ACLs) and firewalls for proper rules. |
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
Understanding how to approach common network problems is essential for any network professional. By applying systematic troubleshooting steps, it becomes easier to identify root causes and implement solutions quickly. The table below outlines some frequent issues and their corresponding diagnostic steps:
| Problem | Diagnostic Steps |
|---|---|
| Device Not Connecting | Verify physical connections and test the network interface. |
| Slow Network Performance | Check for bandwidth usage, faulty cables, or incorrect routing. |
| IP Conflict | Check for duplicate IP addresses and reassign if necessary. |
| Security Breach | Examine logs for unauthorized access and verify security configurations. |
| Network Segment Isolation | Check for misconfigured VLANs or incorrect switch settings. |
Understanding the Networking Assessment Format
When preparing for a technical certification, it’s essential to understand the structure and expectations of the assessment. This section will provide an overview of how the testing format is organized, what types of questions to expect, and strategies to succeed. Familiarity with the format will help reduce anxiety and improve performance on the actual assessment.
Types of Questions
The assessment typically consists of a variety of question types designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Here are the most common question formats you may encounter:
- Multiple Choice: A question is presented with several possible answers, where only one is correct.
- Drag and Drop: You are required to match items from one list to another, typically to test your understanding of network configurations or protocols.
- Simulation: You may be asked to configure network devices or troubleshoot a scenario based on realistic network setups.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: These questions ask you to complete statements related to networking concepts, testing your recall of key terms.
Structure and Timing
The format is designed to test a broad range of skills, so expect a combination of theoretical questions and practical exercises. The duration of the assessment typically ranges from 60 to 90 minutes, with the following general structure:
- Introduction: Brief instructions on navigating the test platform and understanding the rules.
- Core Topics: Questions covering fundamental networking topics such as routing, switching, and IP addressing.
- Simulated Scenarios: Practical tasks where you must demonstrate your ability to configure and troubleshoot networking equipment.
- Conclusion: A final section to review your performance, with feedback on correct and incorrect answers.
Understanding this structure will allow you to allocate time efficiently and focus on each section based on its difficulty level. With preparation, you can approach the assessment with confidence and clarity.
Key Topics in Chapter 6
This section highlights the essential concepts that are crucial for building a solid understanding of networking fundamentals. The topics covered here form the foundation for more advanced configurations and troubleshooting techniques. Mastering these areas is critical for anyone looking to excel in network management and configuration tasks.
Network Configuration and Setup
One of the core focuses of this section is understanding how to configure and manage network devices effectively. This involves setting up routing tables, IP addressing, and ensuring devices are properly connected and communicating. Key areas include:
- Setting up routers and switches
- Configuring static and dynamic routing protocols
- Managing IP address schemes and subnetting
- Implementing VLANs and network segmentation
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
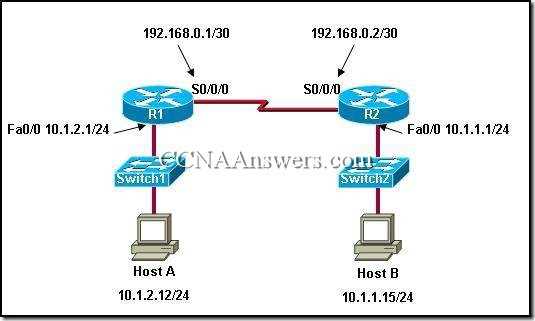
Another critical topic is troubleshooting, which involves identifying and resolving common networking issues. This section equips you with the skills to diagnose problems, from connectivity failures to misconfigured settings. It covers:
- Diagnosing common network connectivity problems
- Utilizing diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute
- Resolving IP addressing conflicts
- Testing and verifying routing paths
By mastering these topics, you will be prepared to handle complex network environments and ensure smooth, efficient operations. The knowledge gained here is foundational for success in any networking role.
Common Questions in Chapter 6 Assessment
When preparing for a technical evaluation, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the types of questions you may encounter. The following section covers some of the most frequently asked questions related to networking concepts. These questions focus on practical knowledge and test your ability to apply key networking principles to real-world scenarios.
Understanding the most common areas of focus can help you prepare efficiently. By reviewing typical questions, you will gain insight into the types of challenges you will face and be able to address them confidently. Below are some examples of common question types and areas that are frequently tested:
- Configuring network devices, including routers and switches
- Identifying and resolving IP address issues, such as conflicts and misconfigurations
- Understanding and implementing routing protocols for data flow
- Diagnosing network connectivity problems and applying troubleshooting techniques
- Configuring VLANs and ensuring correct network segmentation
Being able to answer these questions requires not only theoretical knowledge but also practical skills. By practicing common scenarios and reviewing solutions, you’ll be better prepared to tackle these challenges in any network setup.
How to Prepare for CCNA 4
Successful preparation for a networking certification requires a strategic approach that combines both theoretical study and hands-on practice. The key to mastering the essential concepts is not only understanding the theoretical framework but also gaining experience with real-world network configurations and troubleshooting. This section provides guidance on how to effectively prepare for this level of certification.
The preparation process should focus on a few core areas. Start by reviewing key networking principles such as IP addressing, routing protocols, and device configuration. Once you have a solid understanding of the basics, apply this knowledge by working with simulation tools and lab exercises. This hands-on practice will reinforce your understanding and give you the confidence needed to handle real network environments.
- Study Key Concepts: Review important topics such as network protocols, routing techniques, and device management.
- Practice with Simulations: Use tools like Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3 to simulate real-world network configurations.
- Take Practice Tests: Test your knowledge with practice questions to identify areas where you need improvement.
- Review Troubleshooting Techniques: Understand how to diagnose and solve common network issues through systematic troubleshooting.
- Join Study Groups: Collaborate with others to exchange knowledge and solve complex problems together.
By following this approach and staying disciplined in your studies, you’ll be well-prepared to face the challenges and succeed in the certification process.
Overview of Networking Concepts
Networking is the backbone of modern communication systems, allowing devices to exchange data and share resources. Understanding the fundamental concepts of networking is essential for building and maintaining efficient, secure, and reliable communication infrastructures. This section covers the key principles that govern how networks operate and how various devices interact within these environments.
Core Networking Components
At the heart of any network are several essential components that enable communication between devices. These include:
- Routers: Devices responsible for directing data packets to their destination across different networks.
- Switches: Devices that manage data flow within a local network by connecting devices and forwarding data based on MAC addresses.
- Access Points: Wireless devices that allow mobile devices to connect to a network.
- Cables and Connectors: The physical medium, such as Ethernet cables, used to transmit data across devices.
Key Protocols and Technologies
To ensure data is properly routed, transmitted, and received, various protocols are used. These protocols define how data is packaged, addressed, and delivered across networks. Important protocols include:
- TCP/IP: The foundational protocol suite for most networks, responsible for reliable data transmission across interconnected devices.
- DNS: The system that translates domain names into IP addresses, enabling users to access websites.
- DHCP: A protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses to devices on a network.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Protocols used for accessing web pages and ensuring secure communication on the web.
Mastering these concepts provides a solid foundation for anyone pursuing a career in network administration or support. Understanding how each component and protocol works together ensures efficient and secure network performance.
Practical Tips for Success
Achieving success in technical assessments and certifications requires more than just theoretical knowledge. It demands consistent practice, effective study strategies, and the ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios. In this section, we’ll explore some practical tips that can enhance your preparation and help you perform at your best.
Focus on Hands-on Practice: While understanding the theory is essential, the ability to apply what you’ve learned is crucial. Use simulation tools, virtual labs, and real network setups to practice configurations, troubleshoot issues, and refine your skills. The more hands-on experience you gain, the more confident you’ll be in dealing with practical problems.
Review Key Concepts Regularly: Networking principles can be complex, and it’s easy to forget key details. Make it a habit to review your notes, concepts, and common troubleshooting steps. Regular revision will reinforce your understanding and help solidify the knowledge required for success.
Master Time Management: When preparing for any technical assessment, managing your time effectively is crucial. Break down your study sessions into manageable blocks, focusing on specific topics or skills. During the assessment, make sure you allocate time wisely to each section, leaving room for review at the end.
Join Study Groups: Collaborative learning is a powerful tool. Join study groups or online forums where you can exchange ideas, solve problems together, and share insights. Discussing topics with peers can help deepen your understanding and expose you to different approaches to problem-solving.
Simulate Real-World Scenarios: Try to replicate real-world network problems during your practice. Set up scenarios where you need to configure devices, troubleshoot connectivity issues, or implement protocols under time constraints. This type of practice can help you prepare for unexpected challenges during an actual assessment.
By following these practical tips, you’ll not only strengthen your technical knowledge but also improve your problem-solving abilities, which are essential for succeeding in any networking environment.
Important Networking Protocols to Review
In the field of networking, protocols are the rules and standards that ensure smooth communication between devices. Understanding these protocols is essential for configuring networks, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring data is transmitted correctly and securely. This section focuses on the most important protocols that you should review to build a solid networking foundation.
Here are several key protocols that are fundamental to most network operations:
- TCP/IP: The foundational suite of protocols used for most internet and intranet communications, responsible for reliable data transmission.
- DNS: A system that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, making websites accessible.
- DHCP: This protocol automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, ensuring proper addressing without manual configuration.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (and its secure version) is the protocol used for web browsing, enabling the transfer of data between web servers and clients.
- FTP: The File Transfer Protocol is used for transferring files between computers over a network. It allows both uploading and downloading files.
- SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol is used for monitoring and managing network devices such as routers, switches, and printers.
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is used for sending and receiving email messages across networks.
- ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol is used for diagnostic purposes, such as testing connectivity (e.g., ping commands).
Reviewing and understanding how each of these protocols functions is essential for anyone working with networks. Mastery of these protocols not only ensures efficient data transmission but also helps with troubleshooting, security, and network performance optimization.
Mastering IP Routing for CCNA 4
IP routing is a critical skill for network professionals, enabling the seamless flow of data across different network segments. Whether you’re managing small local networks or large enterprise systems, understanding how routing works is essential for building efficient and secure communication pathways. This section explores the fundamentals of IP routing, key concepts, and practical techniques that will help you master this area of networking.
Basic Routing Concepts
Routing refers to the process of determining the optimal path for data packets as they travel from the source to the destination. There are several core concepts that every networking professional should understand:
- Routing Tables: A router uses a routing table to determine where to forward data packets. The table stores routes to various network destinations.
- Static vs. Dynamic Routing: Static routing requires manual configuration of routes, while dynamic routing protocols allow routers to automatically adjust paths based on network changes.
- IP Addressing: Proper IP addressing is essential for routing, as it ensures that data packets reach the correct destination.
- Subnets and Subnetting: Understanding how to break down large networks into smaller subnets is crucial for efficient routing and optimal network performance.
Key Routing Protocols
Different routing protocols are used to enable communication between routers and determine the best paths for data packets. Some of the most commonly used routing protocols include:
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector protocol that uses hop count as its metric for determining the best path.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): A link-state protocol that uses a more sophisticated metric based on the shortest path and network topology.
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A hybrid protocol that combines the features of both distance-vector and link-state protocols for faster convergence and more efficient routing.
Mastering IP routing requires both theoretical knowledge and practical experience with configuring routers, troubleshooting routing issues, and implementing routing protocols. By focusing on these essential concepts and protocols, you will be well-equipped to design and manage complex networks.
Configuring Network Devices Effectively
Proper configuration of network devices is essential for ensuring reliable communication, optimal performance, and security within a network. Whether it involves routers, switches, or firewalls, configuring these devices correctly is the foundation for a well-functioning infrastructure. In this section, we’ll explore key strategies for configuring network devices effectively, ensuring that each component works harmoniously within the larger network.
Start with Clear Documentation: Before configuring any device, ensure that you have a clear understanding of the network design and requirements. Documenting IP addressing schemes, routing protocols, and security policies is crucial for smooth implementation. This documentation will serve as a guide for troubleshooting and future network expansion.
Use Consistent Naming Conventions: Consistency in device naming and configuration helps maintain clarity across the network. Naming devices logically and uniformly allows for easier management, especially as the network grows. For example, naming switches based on their location or role makes it simpler to identify them during troubleshooting.
Configure Secure Access: Always prioritize security when configuring devices. Set up secure management protocols such as SSH for remote access, disable unused ports, and implement strong password policies. Additionally, using access control lists (ACLs) can help restrict unauthorized access to network devices.
Optimize Performance Settings: Adjust device settings to ensure the network performs efficiently. This may include configuring routing protocols to ensure optimal path selection, implementing Quality of Service (QoS) for traffic prioritization, or adjusting switch port settings to handle the expected traffic load.
Regular Backups and Updates: Always back up your configurations and keep them up to date. Regularly updating firmware and software ensures that devices are protected from security vulnerabilities and benefit from performance enhancements. Backups are essential in case of device failure or network reconfiguration.
By following these best practices for configuring network devices, you can ensure that your network runs smoothly, securely, and efficiently, allowing for easier maintenance and future scalability.
Understanding Troubleshooting Techniques
Effective troubleshooting is a critical skill in networking. When issues arise, it’s essential to methodically identify the root cause and apply solutions quickly to minimize downtime and ensure network stability. This section highlights key techniques and steps to follow when troubleshooting network problems, helping professionals solve issues efficiently and accurately.
The troubleshooting process involves a series of systematic steps that help diagnose and resolve network-related problems. By following a structured approach, you can identify issues such as connectivity problems, performance degradation, or device failures. Understanding how to gather data, isolate problems, and implement solutions is fundamental to resolving any network-related issue.
Basic Troubleshooting Methodology

To troubleshoot effectively, it’s important to follow a well-established methodology. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the common troubleshooting process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify the Problem | Begin by gathering information from users and devices to understand the symptoms of the issue. Is the problem related to connectivity, slow performance, or device configuration? |
| 2. Gather Data | Collect relevant data such as logs, error messages, and diagnostic outputs to better understand the issue. Use tools like ping, traceroute, or device logs to gather additional insights. |
| 3. Isolate the Cause | Analyze the data to narrow down the possible causes. This could involve checking physical connections, verifying configurations, or testing specific devices or protocols. |
| 4. Implement a Solution | Once the cause is identified, apply a solution. This might involve adjusting configurations, replacing faulty hardware, or applying software updates. |
| 5. Test the Solution | Verify that the solution resolves the problem by testing the network for functionality and stability. Ensure that the problem doesn’t recur after the fix has been applied. |
| 6. Document the Process | Document the issue, the steps taken to resolve it, and the final solution. This documentation can help with future troubleshooting and act as a reference for similar problems. |
Common Troubleshooting Tools
Several tools are essential for identifying and solving network issues. These tools help diagnose problems, test connectivity, and analyze network performance. Some commonly used tools include:
- Ping: A simple tool used to test connectivity between devices on the network.
- Traceroute: Used to track the path that data takes between devices, helping identify where communication breakdowns occur.
- NetFlow Analyzer: Monitors network traffic and helps identify bottlenecks or unusual activity that could indicate a problem.
- Packet Sniffer: A tool that captures and analyzes data packets traveling across the network, useful for deep analysis of network issues.
By mastering these troubleshooting techniques and using the appropriate tools, network professionals can resolve issues more quickly and keep networks running smoothly.
Reviewing Case Studies and Scenarios
In any technical field, analyzing real-world examples and scenarios is crucial for reinforcing knowledge and understanding how concepts are applied in practical situations. By reviewing case studies, individuals can gain valuable insights into troubleshooting methods, network configurations, and solutions to common challenges. This approach helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience, offering a clearer perspective on how to handle various network issues effectively.
Case studies and scenarios often present typical network problems faced by professionals. These scenarios challenge individuals to think critically and apply the skills they have learned to resolve issues. By working through these examples, learners can strengthen their problem-solving abilities and deepen their understanding of network management.
Common Types of Scenarios to Review
Some of the most common scenarios presented in case studies include:
- Network Connectivity Issues: Problems related to device communication, such as failure to connect to the internet or problems with internal network traffic.
- Performance Degradation: Situations where network performance is slower than expected, possibly due to bottlenecks, faulty devices, or improper configurations.
- Security Breaches: Cases where unauthorized access or data breaches occur, requiring the implementation of security measures like firewalls or access control lists (ACLs).
- Routing Problems: Issues with data routing, such as misconfigured routing protocols or incorrect path selection that affects network efficiency.
Benefits of Reviewing Case Studies
Engaging with real-world case studies offers multiple benefits for network professionals:
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: By encountering a variety of situations, learners can improve their ability to analyze and resolve complex network problems.
- Better Understanding of Best Practices: Case studies provide practical examples of best practices and effective solutions that can be applied to similar real-world challenges.
- Familiarity with Tools and Techniques: Working through scenarios helps individuals become more comfortable with the tools and troubleshooting techniques commonly used in network management.
- Preparation for Real-World Work: Exposure to common issues faced by network engineers helps prepare learners for the types of challenges they will encounter in professional settings.
Incorporating case studies into learning routines not only reinforces theoretical concepts but also provides the necessary experience to tackle real-world networking challenges confidently and efficiently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
When preparing for technical assessments, it is essential to recognize and avoid common errors that could impact performance. These mistakes often stem from a lack of attention to detail, misinterpretation of questions, or time management issues. By being aware of these pitfalls, candidates can improve their chances of success and better navigate the challenges of the assessment process.
Many test-takers fall victim to avoidable mistakes that can easily be overcome with preparation and focus. Whether it’s rushing through questions, overlooking key instructions, or not applying learned concepts properly, understanding these errors is crucial to performing at your best.
Common Pitfalls to Watch For
- Rushing Through Questions: Many candidates feel pressured to complete the test quickly, leading them to make hasty decisions or overlook important details. It’s crucial to take your time and carefully read each question before answering.
- Misinterpreting Questions: Some questions may seem tricky or worded in an unfamiliar way, which can lead to confusion. Ensure you fully understand what is being asked before choosing an answer, and look for any keywords that could clarify the intent.
- Overlooking Instructions: Instructions provided at the beginning of the test or before specific sections are important for understanding the format and expectations. Failing to follow these can lead to incorrect answers or unnecessary mistakes.
- Skipping Difficult Questions: Some candidates avoid tough questions, thinking they can come back to them later. However, skipping questions may result in incomplete sections or missed opportunities to score points on easier parts of the assessment.
- Not Reviewing Answers: If time allows, always review your answers before submitting the assessment. A fresh look might reveal errors, overlooked details, or changes in your understanding of the question.
Strategies to Avoid Mistakes
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice can help familiarize you with the question format and improve your ability to answer questions accurately. Take mock tests under timed conditions to simulate the real test environment.
- Manage Your Time: Time management is key during the test. Allocate time to each section and keep an eye on the clock to ensure you don’t spend too long on any single question.
- Understand the Key Concepts: Focus on understanding core concepts rather than memorizing answers. This will help you think critically and apply knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Test anxiety can negatively impact your performance. Practice relaxation techniques to stay calm and maintain focus throughout the assessment.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following practical strategies to avoid them, you can increase your chances of performing well and approaching the assessment with confidence.
How to Use Cisco Packet Tracer
Cisco Packet Tracer is a versatile simulation tool designed to help users visualize and practice networking configurations without needing physical equipment. By simulating various network topologies and devices, it allows learners to experiment with router and switch setups, troubleshoot network issues, and test configurations in a controlled environment. This tool is especially useful for hands-on learning and gaining practical experience in network management and design.
Getting Started with Cisco Packet Tracer
To start using Cisco Packet Tracer, follow these basic steps:
- Download and Install: First, download the software from the official Cisco website and complete the installation process.
- Create a New Workspace: Once installed, open the program and start a new project. A blank workspace will appear where you can add devices and create a network layout.
- Choose and Place Devices: Select from a range of devices, such as routers, switches, and end devices, and place them onto the workspace by dragging and dropping them.
Configuring Devices and Connecting Networks
After placing devices in the workspace, you can start configuring them and connecting them to build a functional network:
- Connect Devices: Use the appropriate cables to connect devices. Choose between copper, fiber, or serial cables depending on the connection type.
- Set Up Device Configurations: Configure routers, switches, and other network devices by setting IP addresses, enabling protocols, and adjusting interface settings. Access the configuration window by clicking on a device.
- Test Connections: Once devices are connected, use the built-in testing tools like pings or traceroutes to check network connectivity and ensure proper configuration.
Table of Common Devices in Cisco Packet Tracer
| Device | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Router | Used for routing data between different networks and providing connectivity to the internet or other networks. |
| Switch | Connects devices within the same network, facilitating communication between them by forwarding data packets. |
| PC | Simulates a computer or workstation, allowing you to configure and test network settings like IP addresses and connectivity. |
| Hub | A simple device used to connect multiple devices in a network, often replaced by switches for better efficiency. |
| Wireless Router | Provides wireless connectivity to devices, allowing them to access the network without physical cables. |
By using Cisco Packet Tracer, you can design and simulate complex networks, practice configuring different network devices, and troubleshoot issues before deploying solutions in a real-world environment. It offers a hands-on approach that can help solidify networking concepts and prepare you for various network management tasks.
Study Resources and Materials
When preparing for any certification or technical assessment, having the right study materials is essential. Utilizing a variety of resources can help deepen your understanding of networking concepts and improve your practical skills. In this section, we will explore different types of study materials that can be helpful in mastering the content and excelling in the assessment process.
Recommended Books and Guides
Books and study guides are foundational tools for anyone preparing for a networking certification. Here are some types of materials that can support your learning:
- Official Study Guides: These books are written by experts and often include detailed explanations, practice questions, and real-world scenarios that mirror the material covered in the test.
- Networking Textbooks: Comprehensive textbooks can provide in-depth information on topics such as IP addressing, routing, switching, and network security.
- Practice Question Books: These resources focus on providing a variety of practice questions with detailed answers to help you understand what types of questions might appear in the assessment.
Online Resources and Tools
In addition to traditional books, several online platforms offer excellent study materials and interactive tools:
- Online Forums and Study Groups: Platforms like Reddit, Discord, or specialized networking forums allow you to connect with others, share knowledge, and discuss challenging topics with peers.
- Interactive Labs: Using tools such as Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3, you can practice setting up and configuring networks, simulating scenarios to gain hands-on experience.
- Video Tutorials: Platforms like YouTube and online courses provide video lectures and demonstrations on specific networking concepts, helping you visualize and better understand complex topics.
Practice Exams and Quizzes
Taking practice exams is one of the best ways to gauge your understanding and readiness. Many websites offer free and paid practice exams that replicate the format and difficulty of the actual assessment. These resources can help you identify areas where you need further review and improve your time-management skills during the test.
- Online Quiz Platforms: Websites like Quizlet or ExamCompass allow you to test your knowledge with a variety of questions that cover all aspects of networking.
- Official Practice Tests: Some official certification organizations provide sample tests that are designed to closely match the real exam experience.
By leveraging these diverse study materials, you can gain both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Regularly reviewing and practicing will increase your chances of success and help you approach the assessment with confidence.
Time Management Strategies for the Assessment
Effective time management is crucial when preparing for a technical evaluation. It ensures that you can cover all necessary topics, practice your skills, and approach the test with confidence. Without a structured approach, it can be easy to fall behind or waste time on less important areas. This section outlines some proven strategies to help you manage your time effectively during your preparation and on the day of the assessment.
Prioritize Key Areas of Study
It is essential to allocate more time to topics that are more challenging or that carry greater weight in the evaluation. Focus on the following strategies:
- Identify Weak Areas: Start by assessing which topics you find most difficult and prioritize those in your study sessions.
- Review High-Impact Topics: Some concepts are more likely to appear in the assessment than others. Spend more time reviewing these high-priority areas to maximize your score.
- Break Down Large Topics: If a subject feels overwhelming, break it into smaller, manageable sections. Tackle each section individually to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Plan a Study Schedule
Creating a study schedule helps ensure that you stay on track and cover all the necessary material before the evaluation. Here are a few tips for creating a productive study plan:
- Set Realistic Goals: Divide your time into study blocks and set achievable goals for each session. This will prevent burnout and maintain your motivation.
- Use a Calendar: Mark the study topics you plan to cover on specific dates. Use a digital or physical calendar to keep track of your progress.
- Balance Study with Breaks: Avoid long, uninterrupted study sessions. Take short breaks every hour to refresh your mind and improve retention.
Practice Under Time Constraints
Simulating the test environment by practicing under time pressure is an effective way to build your time management skills. Try the following techniques:
- Timed Practice Tests: Take practice assessments within the allotted time frame. This will help you get accustomed to managing your time efficiently and develop strategies for pacing yourself.
- Time Your Study Sessions: During study sessions, set a timer to work within specific time limits. This approach mimics real-world conditions and helps you develop a rhythm.
- Review After Each Test: After each practice test, analyze how much time you spent on each section. Identify areas where you spent too much time and adjust your approach for the next session.
Stay Calm and Focused During the Assessment
On the day of the evaluation, staying calm and managing stress is just as important as preparation. These strategies will help you maintain focus:
- Read Questions Carefully: Take your time to understand each question before answering. Misreading a question can waste valuable time.
- Don’t Get Stuck: If you encounter a difficult question, move on and come back to it later. Spending too much time on one question can limit your ability to complete the entire assessment.
- Keep Track of Time: Periodically check the clock to ensure you’re staying on pace. Try to complete questions at a steady rate without rushing.
By following these time management strategies, you will be better prepared to handle your study sessions and the actual assessment efficiently. Proper time allocation leads to better focus, less stress, and ultimately a higher chance of success.
Additional Practice for Chapter 6
To truly master the concepts covered in this section, it is essential to engage in targeted practice. Repeatedly testing yourself and applying what you’ve learned in various scenarios helps reinforce your understanding and develop problem-solving skills. This section offers extra practice opportunities to further solidify your knowledge and improve your proficiency.
Practice Activities
The following exercises can enhance your grasp of the material and ensure that you are ready for real-world application:
- Hands-On Lab Activities: Set up simulated networks using available tools, and configure the devices based on the techniques discussed. Real-time practice will deepen your comprehension.
- Scenario-Based Questions: Work through case studies and problem-solving scenarios to test your ability to think critically and apply your knowledge under different conditions.
- Review Previous Exercises: Go back and attempt earlier exercises you have done. Try to complete them in a shorter time frame to simulate exam conditions and track your progress.
Mock Tests
Simulating testing environments can be incredibly beneficial. Complete mock assessments under timed conditions to familiarize yourself with the types of questions that may arise. These tests help you get used to answering questions efficiently and managing your time:
| Test Name | Description | Time Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Timed Practice Test 1 | A full-length test covering all the major concepts from this section. | 60 minutes |
| Focused Topic Test | A shorter test concentrating on specific skills or concepts that require more attention. | 30 minutes |
| Mock Simulation | A hands-on exercise that mimics real-world configuration tasks. | 90 minutes |
Study Groups and Discussions
Collaborating with others in study groups can provide different perspectives on complex topics. Engage in discussions with peers to clarify doubts, share strategies, and deepen your understanding. You can also review and critique each other’s approaches to certain problems.
By completing additional practice activities and testing yourself regularly, you can significantly boost your chances of success. These exercises are designed to strengthen your skills, test your knowledge, and help you become more comfortable with the subject matter.
What to Do After Completing the Exam
Once you have finished the assessment, it is important to take a structured approach to reflect on your performance and plan your next steps. The period immediately after completing any formal evaluation offers an opportunity for both reflection and preparation for the future. By reviewing your experience, you can identify areas for improvement and celebrate your achievements.
The first step is to stay calm and patient. Avoid rushing to conclusions or dwelling on potential mistakes. It is crucial to give yourself time to process the entire experience. Whether or not you feel confident, it’s helpful to keep a balanced perspective.
1. Review Your Performance
Once you have completed the assessment, take a moment to reflect on your responses and the overall process:
- Identify Challenging Areas: Think about any questions or sections that seemed particularly difficult. Did you have enough time to analyze all the material thoroughly? These areas may require further review and practice in the future.
- Assess Time Management: Reflect on whether you allocated your time effectively during the test. Did you spend too much time on any one question? Time management is a skill that can always be improved.
- Track Your Emotions: Notice how you felt throughout the process. Did you experience anxiety or confidence? Understanding your emotional responses can help you prepare better for future assessments.
2. Plan for Follow-Up Action
Based on your reflections, it is time to make a plan moving forward. If you felt confident in your performance, it may be time to prepare for the next stage of your learning journey or move on to practical application. If you encountered challenges, don’t be discouraged:
- Study Further: Focus on the areas where you struggled. Make a plan to revisit those topics and seek additional practice or resources that can help strengthen your knowledge.
- Participate in Discussions: Join study groups, forums, or online communities to exchange insights. Discussing complex topics with others can provide new perspectives and reinforce your understanding.
- Stay Updated: Continuously engage with relevant resources, reading materials, and simulations to stay current with industry trends and best practices.
Ultimately, completing the assessment is just one step in your ongoing development. Use this experience as a stepping stone to further refine your skills, identify growth opportunities, and stay motivated on your learning path. Keep pushing forward, and continue striving for improvement.