In this section, we dive deep into the essential concepts and skills that form the backbone of modern network infrastructure. It focuses on key elements that every aspiring network professional must master. Whether you are troubleshooting devices or designing networks, understanding these foundational topics is crucial for success in the field.
The material covers a variety of important areas such as routing, switching, and IP configuration. These concepts are vital for ensuring that communication between devices is efficient and secure. A solid grasp of these subjects not only helps with certifications but also provides the real-world knowledge needed to address everyday networking challenges.
By carefully studying and applying the principles discussed here, you’ll gain the confidence to approach complex network scenarios with clarity. It’s not just about memorizing facts; it’s about building a strong understanding that can be applied in practical settings.
Chapter 3 Network Essentials Insights
This section focuses on the key topics that form the foundation of a strong networking career. It explores various networking protocols, device configurations, and troubleshooting methods that are integral to network design and maintenance. By understanding these concepts, professionals can ensure that network operations are smooth, efficient, and secure.
Understanding Network Routing and Switching
Routing and switching are at the heart of any network. In this part, you’ll learn about the fundamental principles of routing paths and how data packets travel across different networks. Configuring routers and switches correctly ensures that information reaches its intended destination without unnecessary delays or errors. Mastering these skills is essential for anyone seeking to build and manage reliable networks.
IP Addressing and Subnetting Techniques
IP addressing and subnetting are crucial for organizing and managing a network’s resources. Proper subnetting allows for efficient use of available IP addresses while ensuring that network traffic is directed correctly. Understanding the theory behind subnetting, along with practical techniques for calculation and configuration, is a core skill for network professionals. With these techniques, network designers can create scalable, efficient, and secure network architectures.
Understanding Key Networking Concepts
In this section, we explore the core ideas that shape the structure and functionality of modern networks. A solid understanding of these concepts is essential for anyone working in network administration or design. From the basics of data transmission to advanced device configurations, mastering these principles is the first step towards building efficient and secure networks.
Networking Protocols play a central role in enabling devices to communicate effectively. These protocols define the rules for data exchange, ensuring that information is sent and received in a predictable manner. Understanding how these protocols operate and interact is crucial for troubleshooting and optimizing network performance.
Another important aspect is IP addressing and subnetting, which allows for efficient network management. These techniques help organize network resources, ensuring that devices are easily identifiable and can communicate without conflicts. Proper implementation of these concepts ensures that network infrastructure is scalable and reliable.
Finally, device configuration is key to ensuring that routers, switches, and other network hardware function as intended. Proper setup of these devices is essential for maintaining network stability and security. Understanding how to configure these devices for different scenarios enables network administrators to create robust and secure infrastructures.
Top Questions from Networking Section
This section highlights some of the most commonly asked questions that test your understanding of core networking concepts. These questions cover a broad range of topics, from routing principles to IP configuration, helping you assess your grasp of key networking skills. Being familiar with these types of questions will not only aid in practical application but also prepare you for real-world network challenges.
One area often tested involves routing protocols. Understanding how different protocols operate and their applications in various network environments is essential. Questions in this area may focus on how routers determine the best path for data and the role of different routing protocols in optimizing network traffic.
Another frequently asked topic revolves around subnetting and IP addressing. These questions evaluate your ability to properly configure networks, allocate IP addresses, and manage subnets for efficient use of network resources. Correctly answering these types of questions demonstrates your ability to design scalable and effective network infrastructures.
Common Mistakes in Networking Concepts

When learning about network fundamentals, many individuals make common errors that can hinder their understanding and progress. These mistakes often stem from misunderstandings of core principles or from rushing through configuration tasks without fully grasping their implications. Avoiding these pitfalls is crucial for developing a strong networking skill set.
One frequent mistake involves misconfiguring IP addresses and subnets. This can lead to network connectivity issues, where devices are unable to communicate with each other due to incorrect address allocation. Ensuring that IP addresses are properly assigned and subnets are correctly calculated is essential for a functioning network.
Another common error occurs when dealing with routing protocols. Many learners mistakenly assume that all protocols function the same way, without fully understanding their unique features and applications. It’s important to grasp the differences between protocols like RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, as each serves a specific purpose in network routing.
Essential Networking Protocols
In any network environment, understanding the fundamental protocols is crucial for ensuring efficient communication between devices. These protocols dictate how data is transmitted, routed, and secured across networks. Mastering the key protocols enables network professionals to build reliable infrastructures and troubleshoot connectivity issues effectively.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the most widely used protocols, ensuring reliable communication by establishing connections and managing data flow between devices. TCP is essential for most internet activities, including web browsing and file transfers, because it guarantees that data is received accurately and in the correct order.
Internet Protocol (IP) serves as the addressing system for devices on a network. IP addresses are used to uniquely identify each device, enabling them to send and receive data. Understanding how to configure and manage IP addresses is essential for any network professional, as it is the foundation of network routing and communication.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automates the assignment of IP addresses to devices within a network. This protocol simplifies network management by dynamically allocating addresses, reducing the chances of configuration errors and ensuring that devices can easily join the network.
How to Approach Networking Problems
When faced with complex networking scenarios, having a systematic approach can significantly improve your ability to find solutions. By breaking down each problem into smaller, more manageable steps, you can tackle even the most challenging issues with confidence. Here are some strategies to effectively address networking problems and ensure accurate resolutions.
- Understand the Problem: Carefully read through the question or issue to make sure you fully comprehend what is being asked. Pay attention to any network configurations, device details, or specific requirements mentioned.
- Identify Key Concepts: Recognize the networking principles involved, such as IP addressing, routing protocols, or subnetting. Identifying the core concepts will guide you towards the right approach.
- Break Down the Scenario: Divide the problem into smaller components, such as analyzing network diagrams, reviewing device configurations, and isolating potential causes of issues.
- Use Logical Steps: Apply a step-by-step method for troubleshooting. For example, start by verifying physical connections, then check configurations, and finally examine protocols and routing paths.
By following this structured approach, you can ensure that each problem is addressed in a systematic manner, leading to a clear and efficient solution. Whether you are working on network design or troubleshooting existing setups, staying organized and focused is essential for success.
Review Tips for Networking Concepts
Preparing for a network fundamentals assessment requires more than just memorizing facts. It’s about understanding the underlying concepts and applying them effectively. To maximize your study efforts, focus on critical areas, practice troubleshooting scenarios, and ensure you’re comfortable with key protocols and configurations. Here are some valuable tips to help you review and sharpen your skills before the test.
| Review Tip | Focus Area | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Understand the Basics | Networking protocols, IP addressing | Review common protocols like TCP, IP, and DHCP. Practice subnetting and IP address configuration. |
| Hands-on Practice | Device configuration | Set up routers and switches, configure basic settings, and practice troubleshooting scenarios. |
| Use Study Guides | Key concepts and commands | Work through practice questions and labs to reinforce your knowledge and identify weak areas. |
| Stay Calm and Confident | Problem-solving strategies | Approach each question systematically. Break complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. |
These tips will help you strengthen your understanding, improve your practical skills, and enhance your confidence during the review process. With a focused approach and plenty of practice, you will be well-prepared to tackle the networking challenges ahead.
Strategies for Success in Networking Concepts
Achieving success in mastering fundamental network principles requires a combination of practical experience, thorough understanding, and effective study techniques. By employing the right strategies, you can improve both your comprehension and performance in this area. Below are several key approaches to help you excel in your networking journey.
- Master Core Concepts: Focus on understanding the foundational topics such as IP addressing, routing protocols, and subnetting. Build a solid grasp of how these concepts work together within a network environment.
- Hands-on Practice: Set up a lab environment, either virtually or with physical devices, to practice configuring routers, switches, and other network devices. Real-world experience will reinforce your theoretical knowledge.
- Use Study Resources: Leverage textbooks, online resources, and practice labs to reinforce your understanding. Utilize quizzes and practice exams to identify areas that need improvement.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Break down complex problems into smaller parts. Approach each challenge step-by-step, ensuring you understand the rationale behind each solution.
- Join Study Groups: Engage with peers or online communities to discuss difficult topics and share insights. Collaborative learning can provide different perspectives and deepen your understanding.
By following these strategies, you will be well-equipped to tackle the challenges ahead and succeed in mastering networking concepts. Focus on consistent practice, review, and problem-solving to build a solid foundation for your future networking career.
Core Routing and Switching Topics
Understanding the fundamental principles of routing and switching is essential for building and maintaining efficient networks. These core topics form the foundation of network design and management, enabling devices to communicate effectively across various layers of a network. A strong grasp of routing protocols, network topologies, and switching techniques is necessary for troubleshooting and optimizing network performance.
Routing Protocols
Routing protocols are used to determine the most efficient path for data to travel across a network. There are several key protocols to focus on, such as RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, each designed for specific network sizes and configurations. Understanding how these protocols operate and their differences is vital for selecting the right one based on network requirements. Additionally, knowledge of static routing and dynamic routing is essential for managing traffic flow and ensuring data reaches its destination.
Switching and VLAN Configuration
Switching plays a crucial role in directing data to the correct destination within a local area network (LAN). It involves forwarding frames based on MAC addresses. Understanding concepts like VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and how they segment network traffic for security and efficiency is key. Additionally, mastering STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) ensures redundancy and prevents network loops, which are critical for maintaining a stable and reliable network environment.
Mastering routing and switching topics will equip you with the skills needed to design, configure, and maintain a robust network infrastructure that meets the demands of modern communication and data exchange.
Subnetting Practice for Networking Fundamentals
Subnetting is a crucial skill for network design, as it allows for efficient utilization of IP addresses and enhances network performance. Understanding how to divide a network into smaller subnets is key to managing large-scale networks. This section focuses on practical exercises to help you master subnetting and prepare for common challenges in network management. By practicing these exercises, you will gain confidence in addressing real-world networking problems.
Subnetting Basics
Before diving into more complex subnetting scenarios, it’s important to grasp the fundamental concepts, such as the use of subnet masks, network address, and broadcast address. These elements are essential in determining how an IP address range can be split into smaller, functional networks. Each subnet mask defines how many addresses are available for hosts within a specific subnet, and understanding this calculation is crucial for efficient subnet design.
Practice Exercises
Here are a few practical examples to solidify your subnetting skills:
- Exercise 1: Given the network address 192.168.10.0/24, how would you divide it into four subnets? What is the new subnet mask?
- Exercise 2: For the network 10.0.0.0/8, calculate the range of valid IP addresses for the subnet 10.0.1.0/24.
- Exercise 3: What is the first usable host address and the last usable host address in the subnet 172.16.50.0/26?
By working through these subnetting exercises, you will develop a deep understanding of how to calculate network boundaries, identify available host addresses, and troubleshoot subnetting issues. Mastering subnetting is essential for network efficiency, scalability, and security.
Explaining Network Devices
Network devices play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of data across different segments of a network. These devices are responsible for routing, switching, and securing communication between various systems. Understanding how each device functions and interacts within the network is essential for maintaining efficient, scalable, and secure network operations. This section breaks down the key network devices that are vital for modern networking environments.
Routers
Routers are responsible for directing data packets between different networks. They examine the destination address of a packet and determine the most efficient path for the packet to travel. Routers operate at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, making them essential for connecting local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs) or the internet. They also perform functions such as IP address assignment, network address translation (NAT), and traffic filtering.
Switches
Switches operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) and are responsible for forwarding frames within a local network. They use MAC addresses to determine the correct destination for data and ensure efficient communication between devices on the same network. By creating dedicated paths for data to travel, switches help reduce network congestion and enhance overall performance. Managed switches can also provide additional features such as VLAN segmentation and port security.
Understanding how these devices work individually and together is vital for building and maintaining a network that can handle increasing demands while ensuring reliability and security. Familiarizing yourself with the functions of routers, switches, and other network devices will help optimize performance and troubleshoot network issues more effectively.
IP Addressing and Subnetting Questions

Proper IP addressing and subnetting are crucial skills for network design, as they allow administrators to efficiently manage and allocate network resources. Mastering these concepts ensures that networks can scale, operate securely, and provide the necessary connectivity. In this section, we will explore a set of practical questions designed to strengthen your understanding of IP addressing and subnetting techniques. These exercises focus on real-world scenarios to help you develop problem-solving skills in network management.
IP Addressing Questions
IP addressing involves assigning unique identifiers to each device within a network. Understanding how to work with both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses is essential for managing a modern network. Below are some practice questions to test your knowledge:
- Question 1: What is the network address for 192.168.10.45/24?
- Question 2: Convert the IP address 200.100.50.25 into its binary format.
- Question 3: How many usable host addresses are available in the 172.16.0.0/22 network?
Subnetting Questions
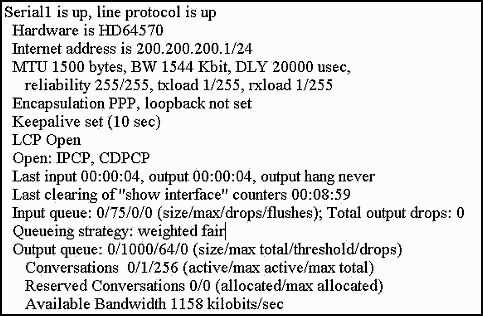
Subnetting allows for the division of a larger network into smaller, more manageable subnets. Below are some questions that focus on subnetting, challenging you to calculate network sizes and address ranges:
- Question 1: Given the IP address 10.0.0.0/8, how would you subnet it into 8 equal parts? What are the new subnet masks?
- Question 2: For the network 192.168.20.0/25, list the valid host IP range.
- Question 3: What is the subnet mask for the network 192.168.10.0 with 512 subnets?
These questions test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills in IP addressing and subnetting. By solving them, you will sharpen your ability to design and manage IP networks effectively.
Commonly Tested Network Commands
In the world of networking, proficiency with key commands is essential for managing devices and troubleshooting various network-related issues. Knowing the most commonly used commands allows administrators to efficiently configure, monitor, and maintain network infrastructure. This section focuses on the core commands that are frequently tested in network configuration and management scenarios.
Configuration Commands

Configuration commands allow network engineers to set up and modify devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls. These commands are foundational for establishing network settings and ensuring proper operation. Some of the most commonly used configuration commands include:
- enable: Elevates the user’s privilege level to allow access to privileged EXEC mode.
- configure terminal: Enters global configuration mode for device configuration.
- interface: Specifies the interface to be configured, such as Ethernet or serial ports.
- ip address: Assigns an IP address to an interface on the device.
- hostname: Sets the device’s hostname, which helps identify it in the network.
Diagnostic and Monitoring Commands
Diagnostic commands help network administrators identify issues with network connectivity, performance, and device status. These commands are essential for troubleshooting and maintaining a healthy network. Some of the most common diagnostic commands are:
- ping: Tests connectivity between devices by sending ICMP echo requests.
- show ip interface brief: Displays the status of interfaces and their IP addresses.
- traceroute: Identifies the path packets take to reach a destination, helping diagnose routing issues.
- show running-config: Displays the current configuration of the device, useful for verifying settings.
- show version: Provides information about the device’s software version and hardware details.
By mastering these essential commands, you will be better equipped to manage and troubleshoot network devices, ensuring a more stable and efficient network environment.
Time Management for Chapter 3
Effective time management is crucial when tackling complex technical concepts and problem-solving tasks. In a fast-paced learning environment, allocating sufficient time to each topic while maintaining focus is key to mastering the material. This section offers guidance on how to efficiently manage time while studying challenging networking concepts and configurations.
Creating a Study Plan
Having a structured approach to studying is essential for staying on track and covering all necessary material. A well-organized study plan helps divide your time wisely across various topics, allowing for comprehensive understanding without feeling overwhelmed. Here are a few tips for creating an efficient study schedule:
- Set clear goals: Break down the material into smaller, manageable sections and set specific learning goals for each session.
- Prioritize challenging topics: Identify areas where you need more practice and allocate more time to those concepts.
- Use timed sessions: Study in focused blocks of time, such as 30-45 minute intervals, with short breaks in between.
- Review regularly: Set aside time for periodic reviews to reinforce your understanding and prevent forgetting key concepts.
Maximizing Study Efficiency
To make the most out of your study time, it’s important to adopt strategies that increase focus and minimize distractions. Here are several tips for maximizing your productivity:
- Eliminate distractions: Find a quiet space and minimize interruptions, such as turning off notifications on your devices.
- Practice time-bound questions: Simulate time-limited scenarios to improve your problem-solving speed and accuracy.
- Work on practice tests: Doing mock exercises will help familiarize you with the types of tasks you may encounter, while also improving your pacing.
- Review mistakes: After completing practice questions, analyze any errors and learn from them to avoid repeating the same mistakes.
By managing your time effectively, you can ensure that you cover all necessary topics while reinforcing key concepts, ultimately leading to greater success in your learning process.
Troubleshooting Scenarios
Effective troubleshooting is a critical skill in networking, requiring a systematic approach to identify and resolve issues. This section focuses on common issues that arise during networking tasks and provides strategies to diagnose and fix them. Understanding these scenarios will help build confidence when addressing problems and improve overall problem-solving abilities.
Identifying Common Network Failures
Network failures can range from minor connectivity issues to more complex configurations. The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the symptoms of the problem, such as slow performance, dropped connections, or lack of network access. Here are a few common network issues:
- Incorrect IP Configuration: Misconfigured IP addresses, subnet masks, or gateways can cause devices to be unable to communicate properly.
- Physical Layer Problems: Faulty cables, connectors, or damaged network interfaces can result in loss of connectivity.
- Routing Failures: Misconfigured routing tables or incorrect static routes may prevent packets from reaching their destination.
- Firewall or ACL Issues: Improperly configured firewalls or access control lists can block necessary traffic, causing communication failures.
Steps to Resolve Network Issues
When addressing network problems, following a methodical approach helps minimize confusion and speeds up resolution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing and fixing common issues:
- Gather Information: Start by collecting data about the network configuration, symptoms, and error messages.
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure all cables and devices are properly connected and powered on. Look for obvious signs of hardware failure.
- Verify IP Configuration: Use commands like ipconfig or show ip interface brief to verify the IP settings of the devices involved.
- Test Connectivity: Use tools like ping or traceroute to test connectivity and pinpoint where the failure occurs in the network.
- Review Logs and Configurations: Check device logs, routing tables, and ACL configurations to identify misconfigurations or issues.
- Apply Fixes: Once the problem is identified, apply the appropriate solution, whether it be reconfiguring IP settings, replacing faulty hardware, or adjusting routing protocols.
By following these steps, you can systematically troubleshoot and resolve common network issues, improving the performance and reliability of your network.
Preparing for Exam Day
Effective preparation for the testing day is key to success. The goal is to ensure that all the necessary knowledge is well understood, and you’re mentally and physically ready for the challenge. Preparation should include both review of the material and strategies to manage the test itself. By following a structured approach, you can feel more confident and perform at your best when the time comes.
Reviewing Key Concepts
The night before the test, it’s important to focus on reviewing key topics that are likely to appear. This is not the time for learning new material, but rather for reinforcing what has already been studied. Make sure to focus on the following:
- Key Protocols: Refresh your understanding of networking protocols, IP addressing, and subnetting, as these are foundational topics.
- Common Network Devices: Review the functions and configurations of routers, switches, firewalls, and other network components.
- Troubleshooting Methods: Familiarize yourself with common troubleshooting tools and techniques that could be tested.
- Routing and Switching Principles: Ensure you understand the fundamentals of routing and switching, including static and dynamic routing protocols.
Managing Time and Stress
Test day is not just about knowledge, but also about managing your time and stress. Proper time management can make a significant difference in how effectively you can complete the test. Here are a few tips:
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Get a Good Night’s Sleep | A well-rested mind performs better. Avoid last-minute cramming and aim for a full night’s sleep. |
| Arrive Early | Arriving early reduces stress and gives you time to settle in before the test begins. |
| Read Questions Carefully | Ensure you fully understand each question before answering. Take time to read instructions and options carefully. |
| Stay Calm | Stay calm and composed throughout the test. If you encounter a difficult question, move on and return to it later. |
By managing your time and mental state, you will be in a better position to focus on the task at hand and perform well. Preparation is not just about the material, but about setting yourself up for success on the big day.
How to Use Practice Exams Effectively
Practice tests are an essential tool in preparing for any certification or knowledge assessment. They help simulate the actual test environment, identify weak areas, and improve time management skills. When used strategically, practice tests not only boost your confidence but also enhance your ability to recall information under pressure. However, simply taking practice tests is not enough; it’s important to approach them with a clear plan in order to maximize their effectiveness.
Strategic Approach to Practice Tests
To get the most out of practice tests, follow a structured approach. Here are some key strategies:
- Start with a Diagnostic Test: Begin by taking a diagnostic test to assess your current knowledge level. This will help you identify areas that require more attention.
- Focus on Weak Areas: After taking a few practice tests, review your mistakes carefully. Spend extra time on the topics where you scored poorly and aim to improve your understanding of those areas.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Take practice tests under timed conditions. This will help you become familiar with the pressure of completing questions within a certain timeframe, and improve your pacing.
Reviewing and Learning from Mistakes
Merely completing practice tests is not enough; reviewing your performance is critical for learning. Pay attention to the questions you answered incorrectly and understand why your answers were wrong. Look for patterns in the mistakes, such as misunderstanding certain concepts or making simple errors. Use this feedback to adjust your study plan and reinforce areas where you need improvement.
- Analyze Incorrect Answers: Break down each incorrect answer and determine whether it was due to a lack of knowledge or a misunderstanding of the question.
- Track Progress: Keep a record of your scores over time. This will allow you to see your improvement and identify which topics still need work.
- Revisit Difficult Topics: Return to challenging concepts and use a variety of study methods, such as flashcards, diagrams, or discussions with peers, to deepen your understanding.
By approaching practice exams with a strategic mindset and focusing on learning from mistakes, you can use them to effectively prepare for the real assessment. Remember, practice tests are not just a tool for gauging progress–they are an opportunity to refine your knowledge and improve your test-taking skills.
Key Points to Remember
Mastering key concepts is critical for success in any technical field. In the context of network fundamentals, understanding core topics provides a solid foundation for more advanced learning. This section focuses on the most important takeaways from the material, offering a guide to what should be remembered and applied during assessments. These essential concepts will aid in building a deeper understanding and ensure that you’re well-prepared for practical application.
Core Networking Concepts
At the heart of any networking framework are a few fundamental concepts. These principles serve as the building blocks for configuring and managing networks. Understanding these will allow you to troubleshoot, design, and optimize network performance.
- IP Addressing: Understand the different types of IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6), subnets, and how addressing impacts routing and communication within a network.
- Routing Protocols: Gain familiarity with common protocols such as OSPF, EIGRP, and RIP. Know how they differ in terms of convergence, scalability, and security.
- Subnetting: Master subnetting as it is crucial for network design. Be able to divide networks into smaller subnets to optimize performance and address management.
Important Tools and Commands
Knowing the right tools and commands to use can make troubleshooting and configuration tasks easier. Familiarize yourself with the most common commands used in network management and configuration.
- Ping: Use ping to check connectivity between devices in the network. It is a simple yet powerful tool for troubleshooting.
- Traceroute: Traceroute helps determine the path data takes from source to destination, useful for diagnosing routing issues.
- Show Commands: The ‘show’ commands on routers and switches provide a wealth of information, from interface statistics to routing tables.
By keeping these key points in mind, you’ll be better prepared for working with network devices, configuring systems, and addressing common challenges in network environments. Focus on understanding these principles, as they are essential for mastering more complex networking topics.