
When facing a medical emergency, knowing the correct actions to take can make the difference between life and death. It’s crucial for individuals in the medical field to be well-prepared with the necessary techniques to respond swiftly and effectively in urgent situations. Understanding the fundamental practices for restoring vital functions is an essential part of professional training.
Comprehending how to perform life-saving maneuvers, such as proper chest compressions and the correct use of defibrillators, can significantly impact patient outcomes. These skills not only improve the chances of survival but also ensure that those in distress receive timely and efficient care. The guidelines that govern these procedures are regularly updated to reflect the latest research and best practices in emergency care.
In this section, we explore key knowledge and practical techniques required to master these life-saving procedures. By studying and familiarizing yourself with these principles, you’ll be better equipped to handle emergencies with confidence and precision. Whether you’re preparing for certification or enhancing your skills, understanding these vital steps is the first step toward becoming a more effective responder.
Essential Life-Saving Skills Overview
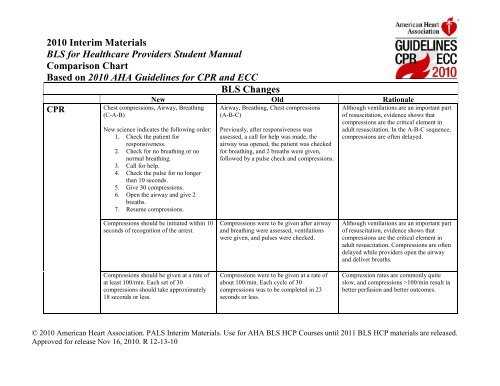
In emergency situations, immediate action can often be the deciding factor between recovery and long-term damage. Knowing how to respond quickly and appropriately to medical crises is an essential skill that can greatly improve survival rates. This section highlights the fundamental principles and key techniques necessary for effectively managing critical incidents in a professional setting.
From the initial assessment of a patient’s condition to performing critical interventions, these skills encompass the core competencies required to stabilize individuals in distress. The ability to assess and manage life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest, choking, and respiratory failure is paramount for ensuring the best possible outcome in emergencies.
Mastering these life-saving procedures equips medical professionals with the confidence and knowledge to act decisively when needed most. Ongoing training and adherence to updated guidelines ensure that responders are well-prepared to face a variety of medical challenges in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Certification Requirements
Gaining certification in life-saving procedures is a critical step for professionals in the medical field. This certification demonstrates an individual’s ability to respond effectively during emergencies, ensuring they are equipped with the essential skills needed to manage various medical crises. To achieve certification, participants must meet specific standards and demonstrate their proficiency in key life-support techniques.
Each certification program has its own set of prerequisites, including a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Participants must complete required training, pass written assessments, and successfully perform hands-on evaluations to prove their competence. In addition, maintaining certification often involves periodic renewal and continuing education to stay current with evolving guidelines and techniques.
Understanding the requirements and preparing for the certification process is crucial for professionals aiming to deliver high-quality emergency care. Meeting these standards ensures that individuals are capable of providing timely and efficient assistance in urgent situations, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Key Skills in Life-Saving Training
To effectively respond to medical emergencies, certain skills are essential for professionals. These abilities ensure that individuals can provide timely, efficient care in critical situations. Mastery of these techniques not only improves survival rates but also builds confidence in high-pressure environments.
Effective Chest Compressions
One of the most vital skills is performing high-quality chest compressions. Proper technique is crucial for maintaining blood circulation during cardiac arrest. The correct depth and rhythm are necessary to maximize blood flow to the heart and brain, which can ultimately save lives.
Use of Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
Another key skill is the ability to operate an automated external defibrillator (AED). AEDs are designed to deliver a shock to the heart, restoring its normal rhythm during a cardiac arrest. Being able to quickly assess the situation and apply the AED is essential for improving patient outcomes in life-threatening conditions.
Common Life-Saving Training Questions Answered

During training in emergency response techniques, many common questions arise regarding the best practices and procedures for managing critical situations. It’s important to clarify these doubts to ensure that professionals are fully prepared to act efficiently in real-life scenarios. In this section, we address some of the most frequently asked questions about emergency intervention and technique application.
What is the Ideal Rate for Chest Compressions?

The recommended rate for chest compressions is 100 to 120 per minute. It’s crucial to maintain this pace to ensure adequate blood circulation during a cardiac arrest. Consistency and depth of compressions are key for optimal results, making the rhythm of compressions an essential factor in successful resuscitation.
When Should I Use an AED?
An automated external defibrillator (AED) should be used as soon as possible if the patient is experiencing cardiac arrest. The device analyzes the heart’s rhythm and delivers a shock if necessary. Immediate use of an AED significantly improves survival chances, so it’s essential to start the process without hesitation.
Importance of High-Quality Chest Compressions

When responding to a medical emergency involving cardiac arrest, performing high-quality chest compressions is one of the most crucial steps in providing effective care. This technique helps maintain blood flow to vital organs, particularly the brain and heart, when the heart stops pumping. Properly executed compressions can significantly increase a patient’s chances of survival until advanced medical assistance arrives.
Maintaining the correct depth, rate, and allowing full chest recoil are essential factors in delivering effective compressions. Inadequate compressions can lead to insufficient blood circulation, reducing the chances of successful resuscitation. Understanding the importance of these factors can make a life-saving difference.
| Key Compressions Factors | Recommended Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Compression Depth | At least 2 inches (5 cm) in adults |
| Compression Rate | 100-120 compressions per minute |
| Recoil | Allow full recoil of the chest between compressions |
| Minimizing Interruptions | Limit pauses to a minimum to ensure continuous circulation |
By following these guidelines, you can maximize the effectiveness of chest compressions and improve outcomes for patients in cardiac arrest. Proper training and frequent practice are essential to mastering this skill and ensuring that you are prepared to act quickly and confidently when needed.
Recognizing Cardiac Arrest Symptoms Quickly
In an emergency situation, quickly identifying the signs of cardiac arrest is critical for taking immediate action. Early recognition allows for the prompt initiation of life-saving measures, which can significantly improve the chances of survival. Understanding the symptoms and knowing how to respond can make all the difference in a crisis.
There are several key indicators to look for when assessing a person who may be experiencing a cardiac arrest:
- Unresponsiveness: The person will not respond to any verbal or physical stimulation.
- Breathing irregularities: Breathing may be absent, irregular, or gasping. This is known as agonal breathing.
- Loss of pulse: The person will not have a detectable pulse at the neck or wrist.
If these signs are observed, it is essential to act quickly. Immediate action, such as starting chest compressions and using a defibrillator, can be life-saving until emergency medical professionals arrive.
It is important to distinguish between cardiac arrest and other medical conditions, as the approach to treatment may differ. For example, in cases of severe heart attack or respiratory failure, symptoms may overlap but require different interventions.
By staying vigilant and learning to recognize these symptoms, responders can ensure that they take the right steps without delay, offering the patient the best chance for recovery.
Step-by-Step Guide to CPR Techniques
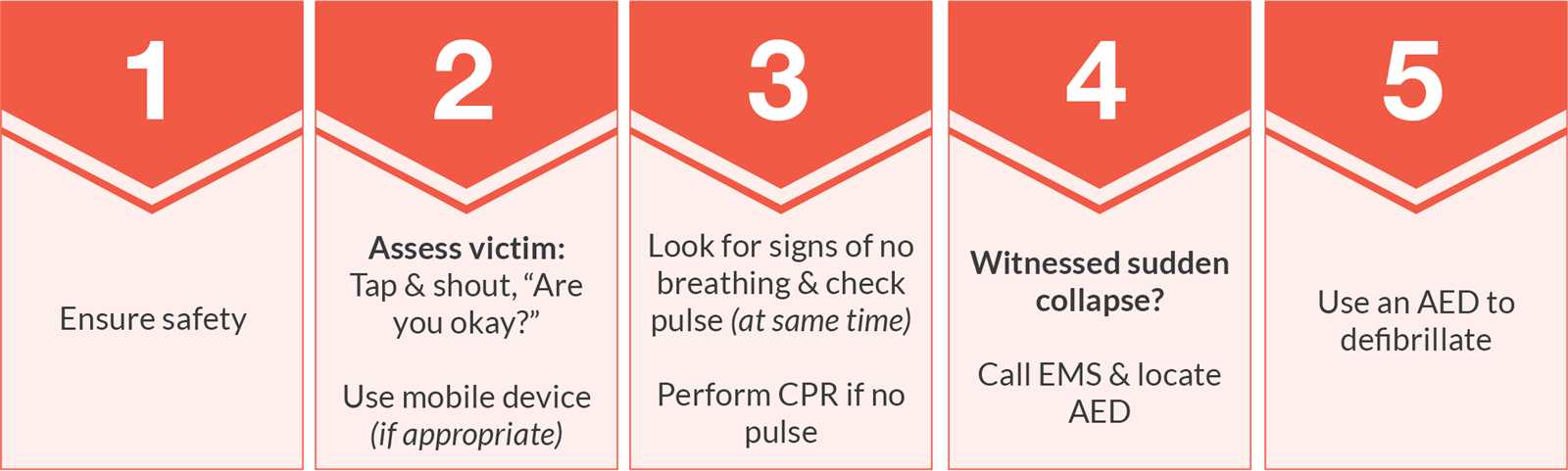
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a crucial skill for anyone who may find themselves in an emergency situation involving cardiac arrest. Performing CPR effectively can significantly improve a patient’s chances of survival by maintaining blood flow to vital organs until professional medical help arrives. This guide provides clear instructions on how to perform CPR correctly, step by step.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Check Responsiveness | Tap the person and shout to see if they respond. If there’s no response, call for help immediately. |
| 2. Open the Airway | Place one hand on the forehead and gently tilt the head back. Lift the chin to open the airway. |
| 3. Check Breathing | Look, listen, and feel for breathing for no more than 10 seconds. If the person isn’t breathing or is only gasping, proceed with CPR. |
| 4. Begin Chest Compressions | Place your hands in the center of the chest, interlock your fingers, and press down hard and fast (about 2 inches deep at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute). |
| 5. Provide Rescue Breaths | After 30 compressions, give 2 rescue breaths by sealing your mouth over the person’s and blowing air into their lungs. |
| 6. Repeat the Cycle | Continue cycles of 30 compressions and 2 rescue breaths until help arrives or the person shows signs of life. |
It’s important to remember that each step should be performed with speed and precision. The faster you can begin chest compressions and provide rescue breaths, the better the outcome for the patient. Always stay focused, and don’t hesitate to call for professional help when needed.
How to Use an AED Effectively
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are life-saving devices designed to restore a normal heart rhythm during a cardiac emergency. Knowing how to use an AED properly can significantly increase the chances of survival for a person experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. The device is simple to operate, but understanding its key functions and steps is essential for effectiveness.
When using an AED, it’s important to follow a clear sequence of actions to ensure proper application. The device analyzes the heart’s rhythm and delivers a shock if necessary, making it a vital tool in emergency response. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you use the AED properly during a critical situation.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Assess the Situation | Confirm the person is unresponsive and not breathing. If needed, call for emergency medical assistance immediately. |
| 2. Turn on the AED | Open the AED case and press the power button to turn the device on. The AED will begin giving you spoken instructions. |
| 3. Attach the Electrodes | Place the AED electrode pads on the person’s bare chest, following the diagram provided on the pads. One pad goes on the upper right side of the chest, and the other on the lower left side. |
| 4. Let the AED Analyze | Allow the AED to analyze the heart’s rhythm. Do not touch the person while the analysis is taking place, as it may affect the results. |
| 5. Deliver a Shock if Needed | If the AED advises a shock, ensure no one is touching the person, then press the shock button to deliver the electrical impulse. |
| 6. Continue CPR | After the shock is delivered, continue chest compressions and rescue breaths. Follow the AED’s prompts for further instructions. |
Remember, even if you are unsure about the steps, the AED provides clear instructions, and it’s designed to be user-friendly. The sooner you begin using the AED, the better the chances of restoring a normal heart rhythm and improving the person’s chances of survival. Always remain calm and focused throughout the process.
Legal Considerations for Healthcare Providers
When providing emergency care, it is essential to be aware of the legal implications associated with offering medical assistance. Healthcare professionals must be informed of the legal protections available to them, as well as the potential risks they may face while performing their duties in emergency situations. Understanding these legal aspects helps ensure that medical interventions are both effective and in compliance with relevant laws.
Duty to Act and Consent
Healthcare professionals are often required to assist in emergencies, particularly when they are on duty. In some cases, there is a legal obligation to intervene, which is referred to as the “duty to act.” This duty ensures that a medical provider responds appropriately in emergency situations. However, consent is also a crucial factor. Before administering care, healthcare workers must obtain the patient’s consent, except in cases where the patient is unconscious or unable to give consent, such as in life-threatening situations.
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan laws are designed to protect individuals, including medical professionals, who provide assistance in an emergency. These laws generally offer immunity from legal liability for actions performed in good faith and without gross negligence. However, it’s important to note that these protections may not apply if the provider’s actions are deemed reckless or outside the scope of standard medical practice.
Understanding and adhering to these legal considerations is critical for healthcare professionals to ensure both patient safety and legal protection. In addition to their medical responsibilities, professionals must navigate legal boundaries to avoid legal repercussions and ensure ethical conduct during emergency care.
Important Changes in BLS Guidelines
Over the years, guidelines for performing life-saving techniques during emergencies have evolved to reflect new research, medical advancements, and a deeper understanding of how to improve outcomes for patients. Staying up to date with these changes is essential for anyone involved in emergency response. Adapting to the updated recommendations can significantly enhance the effectiveness of life-saving interventions in critical situations.
Key Updates in Recent Guidelines
The following are some of the most important changes made in the latest guidelines:
- Compression Depth and Rate: It is now emphasized that chest compressions should be performed at a depth of at least 2 inches and at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. This change was made to ensure that compressions are effective in maintaining circulation to vital organs.
- Compression to Ventilation Ratio: For adults, the recommended ratio of chest compressions to rescue breaths has been updated to 30:2 for both single and multiple rescuers. This adjustment aims to maintain high-quality compressions while still providing adequate oxygenation.
- Hands-Only CPR: Research has shown that performing hands-only CPR (without mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) can be just as effective in some situations, especially when bystanders are unsure about giving rescue breaths. The guidelines now recommend hands-only CPR for untrained responders.
- Defibrillation Timing: The updated guidelines stress the importance of using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) as soon as possible. The faster defibrillation occurs, the higher the chances of survival after a sudden cardiac arrest.
Importance of Staying Informed

These guideline changes reflect the ongoing advancements in emergency care practices. It is crucial for medical professionals and first responders to stay informed about these updates to provide the most effective assistance during emergencies. Regular training and certification ensure that individuals are well-prepared to implement the latest best practices.
What to Expect During the Exam
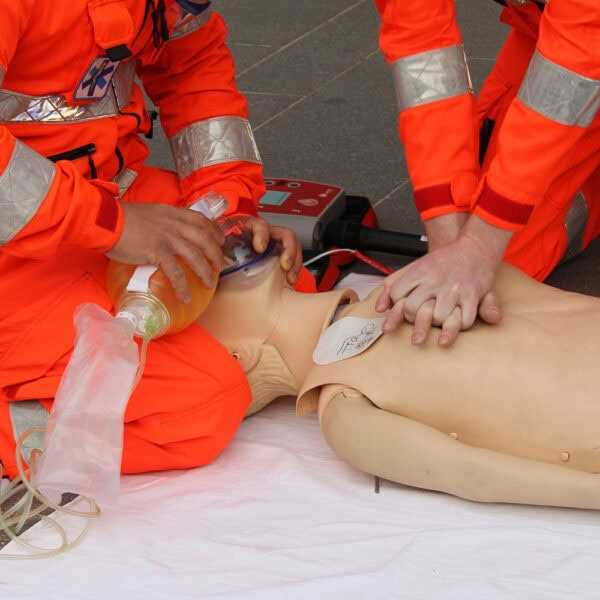
When preparing for an emergency response certification exam, candidates should be ready to demonstrate both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The assessment typically combines written tests with hands-on scenarios to ensure that participants are equipped to perform life-saving procedures effectively in real-world situations. Understanding what to expect during the exam can help candidates feel confident and fully prepared for the challenge.
Theoretical Test
The written portion of the exam focuses on assessing your understanding of essential emergency protocols and guidelines. Expect questions covering a range of topics such as:
- Basic life-saving techniques
- Effective use of emergency equipment
- Identifying and responding to various medical emergencies
- Legal and ethical considerations in emergency care
The exam will likely include multiple-choice, true/false, or short-answer questions that test your grasp of key concepts. It is important to review the most recent guidelines and protocols to ensure you answer accurately.
Practical Skills Evaluation
In addition to the written test, you will be asked to demonstrate your skills in simulated emergency situations. During this part of the exam, you may be required to:
- Perform chest compressions and rescue breaths
- Properly use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
- Manage airway obstruction and administer first aid
You will be evaluated on your ability to perform these procedures effectively, ensuring that your actions are clear, efficient, and according to the latest medical protocols. It’s important to stay calm and focused while performing the skills under time pressure.
With adequate preparation and understanding of the exam format, candidates can approach the evaluation with confidence, knowing that they have the knowledge and skills to pass and provide life-saving care when needed.
Common Mistakes in BLS Training
While learning life-saving techniques, it’s crucial to understand not only the correct methods but also the common errors that can occur. These mistakes can significantly reduce the effectiveness of the intervention and compromise patient outcomes. By recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls, individuals can improve their skills and provide better care during emergencies.
One of the most frequent mistakes during training is inadequate chest compression depth. Many individuals fail to push hard enough, which results in less effective blood circulation to vital organs. Ensuring that compressions reach the recommended depth of at least 2 inches is vital for successful outcomes.
Another common error is performing compressions too slowly. The recommended compression rate is between 100 and 120 per minute. Slower compressions can reduce the circulation of oxygenated blood to the heart and brain, potentially decreasing the chances of survival.
Some trainees also struggle with the timing of chest compressions and rescue breaths. A key part of the technique is maintaining a steady rhythm, following the correct compression-to-breath ratio, especially in the case of performing both methods together. Any inconsistency or hesitation can negatively impact the effectiveness of the procedure.
Additionally, there is sometimes confusion regarding the use of emergency equipment, such as an Automated External Defibrillator (AED). Incorrect placement of pads or failure to follow the AED’s voice prompts can lead to ineffective defibrillation, which may delay vital treatment during a critical moment.
Lastly, another mistake is not practicing enough in realistic scenarios. Hands-on practice is essential for gaining muscle memory and confidence. Without regular repetition in simulated situations, it becomes difficult to perform efficiently under the pressure of a real emergency.
By addressing these common mistakes, individuals can enhance their skills, improve their response times, and be more prepared to manage life-threatening emergencies effectively.
Effective Communication in Emergency Situations

In critical situations, clear and concise communication is essential for ensuring rapid and accurate responses. Whether you’re working in a team or interacting with patients, effective communication can be the difference between life and death. This skill is not only about giving commands but also about ensuring that everyone involved is on the same page, reducing confusion and improving the overall outcome of the intervention.
One of the key aspects of communication in emergencies is staying calm under pressure. In stressful situations, it can be easy to become flustered, but maintaining a clear and calm voice can help convey authority and instill confidence in others. This is especially important when directing bystanders or colleagues who may be unfamiliar with the procedure being carried out.
Another important factor is using direct and simple language. Avoiding medical jargon and speaking in short, clear sentences can ensure that instructions are understood by everyone involved. This is particularly crucial when directing individuals who may not have a medical background or in situations where time is of the essence.
Additionally, it’s important to listen actively and remain open to feedback. In emergencies, new information may constantly emerge, and being receptive to suggestions or concerns can enhance the overall response. Effective communication also involves non-verbal cues, such as eye contact and body language, which can help reinforce your message and provide reassurance to those around you.
Lastly, when working with a team, coordination is key. Assigning specific roles and ensuring that all team members know their responsibilities helps streamline the process and ensures that no critical steps are missed. Clear communication reduces the likelihood of mistakes, enabling the team to work cohesively and efficiently under pressure.
By mastering these communication techniques, responders can improve their ability to handle emergencies effectively, ensuring the best possible outcome for all involved.
How to Prepare for the Test

Preparing for a life-saving skills exam requires focused effort and a clear understanding of the procedures and techniques involved. Whether you’re taking the test for the first time or recertifying your skills, a solid preparation strategy can make all the difference in ensuring your success. The key to doing well is practice, familiarity with the material, and confidence in your abilities to perform under pressure.
Start by reviewing the essential concepts and guidelines related to the techniques. Familiarize yourself with the different steps involved, such as the proper techniques for chest compressions, airway management, and how to operate life-saving equipment like defibrillators. It’s important to know the exact procedures and the reasoning behind them to increase both speed and accuracy during the test.
In addition to understanding the procedures, ensure that you are physically ready for the practical components. Practicing regularly in a controlled environment, such as a training center or with a study group, will help you internalize the movements and gain muscle memory. You should feel comfortable and confident when performing each step, from compressions to administering breaths, and using any necessary equipment. Practice will also help you reduce the chance of mistakes during the real test.
Make use of study materials, including practice exams, instructional videos, and official guidelines. Many organizations provide online resources and mock tests that simulate the actual exam. These resources can help you identify areas where you might need more study or practice, giving you a more focused approach to your preparation. Time yourself during practice sessions to get a feel for the pace you will need to maintain during the test.
Ensure that you know the test format, including any specific requirements or scoring criteria. Some exams have a mix of written assessments and practical skills evaluations. Knowing what to expect in each section will allow you to approach the test with confidence and minimize surprises on the day of the exam.
Finally, stay calm and confident on test day. A calm demeanor can help you focus better and perform tasks more effectively. Trust in your preparation, and remember that practice and knowledge are your best tools for success.
How BLS Training Benefits Healthcare Workers
Life-saving techniques training plays a crucial role in enhancing the abilities of medical staff to respond to emergency situations effectively. This type of education is designed not only to improve patient outcomes but also to provide healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to handle critical moments with confidence. Through practical training and theoretical knowledge, workers are prepared to manage life-threatening events swiftly and correctly.
Here are some key ways that this training benefits medical professionals:
- Improved Response Time: With proper training, workers can react more quickly and decisively during emergencies, significantly increasing the chances of survival for patients.
- Enhanced Confidence: Knowing that you have the right skills and techniques to handle an emergency gives workers the confidence to act immediately and effectively under pressure.
- Increased Safety for Patients: Healthcare workers equipped with emergency response skills are more likely to deliver the correct interventions, reducing the risk of complications or further harm to patients.
- Legal and Ethical Responsibility: Training ensures that professionals are meeting the required standards, helping to avoid legal liabilities and ensuring ethical care in critical situations.
- Team Coordination: In emergency situations, collaboration is key. Workers trained in emergency procedures are better able to communicate and coordinate with colleagues, ensuring a unified and efficient response.
- Preventing Long-Term Damage: Quick intervention can prevent serious long-term consequences for patients, such as brain damage or organ failure, by providing timely and effective care.
Overall, training in life-saving techniques provides essential skills that not only increase the chances of survival but also help healthcare workers feel prepared and capable in high-pressure situations. The benefits extend beyond individual patient care, as these skills contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the healthcare team.
Continuing Education for BLS Professionals
Ongoing learning is essential for anyone working in emergency response roles to maintain proficiency and stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in life-saving techniques. Medical professionals are often required to refresh their skills periodically to ensure they can handle critical situations with the utmost competence. Continuing education programs provide an opportunity to reinforce existing knowledge, learn new methods, and stay current with evolving best practices.
Why Ongoing Education is Crucial
In fast-paced and high-pressure environments, it is vital that professionals remain confident in their ability to perform under stress. Continuing education ensures that these individuals are equipped with the latest knowledge and skills to handle emergencies effectively. Here are some key reasons why ongoing training is necessary:
- Adapting to New Guidelines: As medical guidelines evolve, it is important to keep up with new procedures, techniques, and technologies.
- Refining Skills: Continuous practice and exposure to new scenarios help professionals keep their skills sharp and ensure they are prepared for real-life emergencies.
- Boosting Confidence: Regular learning and assessment help professionals build confidence in their ability to respond to critical incidents promptly and correctly.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many organizations and regulatory bodies require professionals to complete periodic educational sessions to maintain certifications and ensure patient safety.
How to Pursue Ongoing Training
There are several ways that individuals can participate in continuing education to enhance their emergency response capabilities:
- Online Workshops: Many organizations offer online courses that are accessible at any time, allowing professionals to learn at their own pace.
- In-Person Classes: Hands-on training sessions provide valuable opportunities to practice skills and receive feedback from experienced instructors.
- Refresher Courses: These programs are designed specifically for individuals looking to refresh their skills and knowledge after a certain period of time.
- Conferences and Seminars: Attending industry events is a great way to network, exchange knowledge with peers, and stay informed about new trends and practices in the field.
By participating in these educational opportunities, professionals not only enhance their own expertise but also contribute to the overall safety and effectiveness of their teams and patients. Continuing education is an investment in both personal growth and improved patient care.