
The first section of this course introduces foundational knowledge required for anyone pursuing a career in information technology. It covers essential topics that lay the groundwork for understanding computer systems, networks, and the various components that make up modern technology.
Focusing on the core principles, the section emphasizes the importance of recognizing and understanding the different hardware and software elements, their interactions, and how they contribute to the functionality of a computer. By mastering these basic concepts, you will build the skills necessary for further exploration in the IT field.
Additionally, it offers an overview of the most common terminology used in the industry, giving you a strong foundation for communicating and solving technical problems effectively. Mastering this content will not only help you succeed in your studies but also provide practical knowledge that is crucial for real-world applications.
IT Fundamentals Key Concepts and Insights
This section of the course focuses on the foundational knowledge necessary for understanding the core components of modern computer systems. It provides an introduction to the fundamental concepts in IT, covering essential topics such as hardware components, software functions, and basic networking principles. Mastering these elements is crucial for building a solid foundation that will support further studies and hands-on technical work in the field of information technology.
Understanding Core IT Components
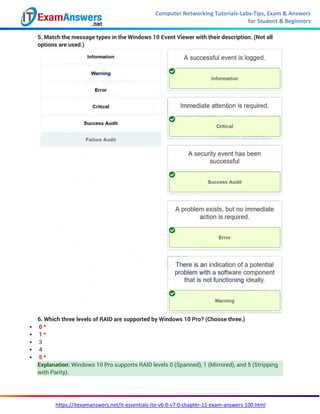
In this section, you will explore the various components that make up a computer system, including processors, memory, storage devices, and input/output interfaces. A solid understanding of these elements allows you to better appreciate how they interact and function together to create a fully operational machine. Learning the roles of each part and how they contribute to the overall system will help you troubleshoot and optimize setups effectively.
Key Terminology and Practical Applications

Additionally, it’s important to familiarize yourself with key industry terms and concepts. Knowing the right terminology will improve your ability to communicate with peers and solve technical issues with precision. In this section, you’ll learn the terms that are crucial for understanding and applying IT knowledge in real-world environments. From the basic setup of a network to the configuration of software tools, these terms will be instrumental in enhancing your technical proficiency.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | The brain of the computer | Executes instructions and processes data |
| Memory | Temporary storage for data | Stores data that the processor needs quickly |
| Storage Devices | Permanent data storage | Stores files, programs, and system data |
| Input/Output Devices | Peripheral devices | Allow interaction with the system (keyboard, mouse, monitor) |
Overview of Chapter 1 Content
The initial section of the course introduces the foundational concepts crucial for understanding the inner workings of information technology. It provides a broad overview of the core principles, focusing on key components that form the backbone of IT systems. This section is designed to give students a strong starting point for further studies and practical applications in the field.
Key topics include a deep dive into the structure and function of computer systems, as well as the essential tools and technologies that drive modern IT environments. By gaining a solid understanding of these elements, learners can build a framework for solving technical problems and working with various technologies efficiently.
Main Concepts Covered
- Introduction to computer hardware and its components
- Overview of software types and their roles in IT systems
- Basic networking principles and how they connect devices
- Understanding operating systems and their functionalities
- Key terminologies used in the IT field
Learning Objectives
- Familiarize with the primary components of computer systems
- Understand the difference between hardware and software
- Learn how networking enables communication between devices
- Gain knowledge of operating systems and their functions
- Build a vocabulary of technical terms used in IT
Key Concepts to Focus On
This section highlights the critical ideas that are essential for building a strong foundation in IT. Understanding these core principles is vital for progressing in the field and solving practical challenges. The concepts covered here are fundamental to working with computers, networks, and software systems, and they form the basis for more advanced studies and technical tasks.
Core Topics to Master
- Understanding hardware components and their functions
- Exploring the role of software in managing system resources
- Basics of operating systems and their interaction with hardware
- Key networking concepts and how devices communicate
- The importance of cybersecurity and data protection
Important Skills to Develop
- Identifying and troubleshooting common hardware issues
- Configuring and managing software environments
- Setting up and maintaining network connections
- Understanding and applying security practices
- Using industry terminology to communicate effectively
Understanding Networking Fundamentals
Networking is the backbone of modern communication, enabling devices to connect, share information, and work collaboratively. This section explores the basic principles that govern the functioning of networks, focusing on the technology that allows devices to communicate effectively. Grasping these concepts is essential for understanding how systems are interlinked and how data flows across different mediums.
Key Networking Components
- Routers: Devices that direct data traffic between networks
- Switches: Used to connect multiple devices within the same network
- Cabling and Wireless Connections: The physical and wireless methods for data transmission
- IP Addresses: Unique identifiers for devices within a network
- Protocols: Rules that govern data transmission, such as TCP/IP
Important Networking Concepts
- LAN (Local Area Network): A network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home or office
- WAN (Wide Area Network): A larger network that connects devices over a wider geographic area
- Subnetting: Dividing a larger network into smaller, more manageable sub-networks
- Wireless Networking: Connecting devices without the use of physical cables
- Network Security: Protecting data and preventing unauthorized access
Basic Computer Components Explained
A computer is made up of various parts, each with a specific role that contributes to the overall performance and functionality of the system. Understanding these components is essential for troubleshooting, upgrading, and optimizing computer systems. This section breaks down the primary hardware elements and their functions, providing a clear view of how they interact to form a fully operational device.
Main Hardware Components
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions
- Memory (RAM): Temporary storage used to hold data and instructions needed by the CPU
- Storage Devices: Permanent storage for files, programs, and system data
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components
- Power Supply: Converts electricity to power the components
How These Components Work Together
These hardware elements work in unison to ensure smooth operation. The CPU processes data, the RAM provides fast access to necessary data, and storage devices keep files for long-term use. The motherboard ensures communication between all these parts, while the power supply keeps everything running.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Central unit that performs calculations and instructions | Executes programs and controls other components |
| RAM | Temporary, high-speed storage | Stores data currently in use for quick access |
| Storage Devices | Permanent data storage (e.g., HDD, SSD) | Stores system files, applications, and user data |
| Motherboard | Main circuit board | Connects and allows communication between components |
| Power Supply | Supplies power to the components | Converts electricity to a usable form for the system |
Common IT Terminology in Chapter 1
Understanding the language of information technology is crucial for success in this field. This section introduces some of the most commonly used terms that form the foundation of IT. Familiarity with these terms will help you communicate effectively and gain a deeper understanding of how systems, networks, and software work together.
The glossary of terms in this section provides a clear definition of essential concepts. From hardware components to networking protocols, these words are key to grasping the technical aspects of IT. Knowing the terminology not only aids in comprehension but also enhances your ability to troubleshoot, configure, and optimize systems.
Key IT Terms to Know
- Operating System (OS): Software that manages hardware and software resources on a device
- IP Address: A unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network
- Protocol: A set of rules that govern data transmission between devices
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects and allows communication between all components of a computer
- Router: A device that forwards data packets between different networks
- RAM (Random Access Memory): A type of volatile memory used to store data temporarily for quick access
- Hard Drive: A storage device that holds data on a permanent basis
Understanding Key Concepts
Mastering these terms will make it easier to navigate technical documentation, collaborate with others, and understand the structure and behavior of modern IT systems. Each term plays a role in the functioning of computers, networks, and software, and having a solid grasp of them will enhance your ability to tackle technical challenges.
Step-by-Step Guide for Test Preparation
Preparing for a technical assessment requires a structured approach to ensure a deep understanding of the material. This guide breaks down the steps you should follow to effectively prepare and increase your chances of success. By focusing on key topics, practicing with relevant exercises, and reviewing concepts, you can build confidence and improve your performance.
Each step in this guide is designed to help you focus your study efforts, organize your time, and reinforce your knowledge. Following this method will ensure that you’re ready to tackle both theoretical and practical aspects of the test with ease.
Preparation Steps to Follow
- Review Core Concepts: Start by revisiting the fundamental ideas and terminology. Ensure that you understand basic concepts such as hardware components, software, and networking protocols.
- Identify Key Areas: Focus on the most important sections of the material. Pay attention to topics that are frequently covered in assessments, such as system configuration and security practices.
- Practice with Quizzes: Test your knowledge with practice quizzes or online exercises. This helps reinforce your understanding and identify areas that need more attention.
- Use Study Resources: Leverage textbooks, online tutorials, or study groups. Collaborating with others can provide different perspectives and fill in knowledge gaps.
- Simulate the Test Environment: Take practice tests under timed conditions to simulate the actual assessment experience. This will help you manage your time and reduce anxiety.
Review and Final Preparation
In the final days before the test, focus on reviewing the material, going over key terms, and understanding how different concepts are connected. Make sure to get plenty of rest, as a clear mind will help you recall information more easily during the test.
Strategies for Success
Achieving success in any assessment requires not just knowledge but also effective strategies to maximize performance. This section provides a set of practical tips to help you approach the test with confidence. By developing a well-thought-out plan and staying focused, you can optimize your results and perform at your best.
Each strategy is designed to guide you through the preparation and actual test-taking process. From time management to understanding question patterns, these approaches are meant to streamline your efforts and reduce stress.
Key Strategies to Follow
- Time Management: Allocate specific time for each section of the test. Prioritize questions based on difficulty and importance to ensure you don’t run out of time.
- Read Questions Carefully: Make sure to thoroughly read each question before answering. Pay attention to keywords and avoid rushing through the text.
- Start with What You Know: Begin by answering the questions you feel most confident about. This will boost your confidence and ensure you gain easy points early on.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Don’t let difficult questions throw you off. Take a deep breath, skip tough questions if necessary, and come back to them later when you’re ready.
- Review Your Answers: If time permits, always go back and double-check your responses. Ensure that you didn’t miss any key details or make careless mistakes.
Final Tips for Test Day
On the day of the test, get enough rest the night before, eat a healthy meal, and stay hydrated. Arrive early to reduce stress, and bring all necessary materials with you. Remember, confidence and preparation are the keys to success, so approach the test with a positive mindset.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chapter 1
In this section, we address some of the most common questions that individuals have when reviewing the first unit of study. Understanding the key concepts, terms, and ideas can sometimes lead to confusion, so this section aims to clarify those doubts. Below are some frequently asked questions and their explanations to help you strengthen your understanding.
Common Inquiries
- What are the primary components of a computer system? The key components of a computer system include the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM), storage devices, motherboard, and power supply. Each part plays a crucial role in the overall operation of the system.
- Why is networking knowledge essential in IT? Networking knowledge is critical as it enables the setup, configuration, and troubleshooting of connections between devices. Understanding protocols, IP addresses, and network topologies is vital for ensuring smooth communication within and between networks.
- What are some common operating systems covered in this section? Common operating systems include Windows, macOS, and Linux. Each has unique features but shares the fundamental purpose of managing hardware and software resources.
Clarifying Common Concepts
- What is the role of the motherboard? The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects all components of the computer. It allows communication between the CPU, memory, and other peripherals, enabling the system to function as a whole.
- How does RAM contribute to system performance? RAM (Random Access Memory) temporarily stores data that is actively being used by the CPU. The more RAM a system has, the more efficiently it can handle multiple tasks and large files without slowing down.
- What is the purpose of a power supply unit? The power supply unit (PSU) converts electrical power from an outlet into a usable form for the computer’s components, ensuring stable and safe operation.
Important IT Vocabulary
Understanding key terms and concepts is essential for mastering the fundamentals of IT. This section covers some of the most important vocabulary that will help you grasp the technical language needed for success. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you will be better equipped to tackle both theoretical and practical challenges in the field.
Key Terms to Know
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The brain of the computer that performs calculations and executes instructions, coordinating the system’s operations.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary storage that holds data currently in use, allowing quick access by the CPU for active processes.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects and allows communication between all the components of a computer system.
- Hard Drive: A permanent storage device used to save data such as files, software, and the operating system.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): A hardware component that connects a computer to a network, enabling communication with other devices.
- IP Address: A unique identifier assigned to each device on a network, used for routing data across the internet or a local network.
Additional Terms for Clarity
- Operating System (OS): Software that manages computer hardware and software resources, providing a user interface to interact with the system.
- Protocol: A set of rules that define how data is transmitted and received across networks. Examples include TCP/IP and HTTP.
- Peripheral: External devices such as printers, monitors, and keyboards that are connected to the computer to extend its functionality.
- Router: A networking device that forwards data between different networks, ensuring correct data paths for communication.
- Firewall: A security system designed to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Study Resources for IT Fundamentals
Effective preparation for any IT course requires a variety of resources to build a solid understanding of the material. This section provides a selection of helpful tools and materials to aid your learning process. By using these resources, you can reinforce your knowledge and gain practical experience to excel in the field.
Recommended Study Materials
- Textbooks and Guides: Comprehensive textbooks provide in-depth coverage of key concepts. Look for books that cover computer hardware, networking, and system management to get a broad understanding.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer video-based courses, often featuring practical demonstrations and interactive quizzes to deepen your knowledge.
- Practice Tests: Taking practice quizzes and mock exams is an effective way to assess your knowledge and get familiar with the format of potential questions.
- Study Groups: Joining online study groups or communities such as those on Reddit or Discord can be a great way to discuss complex topics with peers and exchange valuable tips.
Additional Resources for Hands-On Practice
- Simulation Software: Use virtual labs or simulation tools to practice configuring networks, setting up systems, and troubleshooting common problems without the need for physical equipment.
- Online Forums and Discussion Boards: Websites like Stack Overflow, TechRepublic, and Spiceworks provide community-driven support and solutions to technical problems, where you can learn from real-world scenarios.
- YouTube Tutorials: Many experts and educators share detailed, step-by-step tutorials on YouTube that explain IT concepts with practical demonstrations.
- Vendor-Specific Training: Some companies like Cisco, Microsoft, and CompTIA offer specialized training resources and certifications, providing in-depth learning materials for their technologies.
Essential Tools for Learning IT Fundamentals
Having the right tools is crucial when studying complex IT concepts. The proper resources can enhance your understanding, help you practice key skills, and enable efficient learning. This section outlines various tools that can significantly support your educational journey in mastering core IT topics.
Key Software and Applications
- Virtual Machines: Tools like VirtualBox or VMware allow you to create virtual environments to simulate real-world systems, practice configurations, and run experiments without needing additional hardware.
- Network Simulators: Software such as Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3 can help you visualize and simulate network setups, providing hands-on experience with network configuration and troubleshooting.
- Text Editors: Code editors like Sublime Text, Visual Studio Code, or Notepad++ are valuable for learning programming and scripting, enabling you to write, test, and debug code with ease.
- Disk Imaging Tools: Tools like Clonezilla or Acronis True Image help you back up and manage system images, allowing you to practice system recovery and data management without risking your primary system.
Learning and Practice Resources
- Interactive Learning Platforms: Websites like Codecademy, Khan Academy, and FreeCodeCamp offer interactive lessons that cover a wide range of IT topics, including networking, programming, and security.
- Online Forums: Participating in forums like Stack Overflow, Spiceworks, and TechNet allows you to ask questions, exchange knowledge, and get insights from industry professionals and fellow learners.
- Practice Labs: Platforms such as Labster or the AWS Free Tier provide cloud-based labs where you can practice setting up virtual environments, networks, and other IT services without requiring local hardware.
- Study Apps: Mobile applications like Quizlet or Anki allow you to create digital flashcards to reinforce your knowledge, making it easy to review key terms and concepts on the go.
Practical Applications of IT Knowledge
Understanding the foundational concepts of information technology is essential for applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. Whether you are setting up a network, troubleshooting hardware issues, or developing software, the practical skills gained from mastering IT concepts are crucial in almost every sector. This section explores how IT knowledge is applied in various fields to solve everyday challenges and improve efficiency.
Implementing Network Solutions
- Designing and Configuring Networks: IT professionals apply networking principles to design and build secure, efficient networks for businesses. This involves selecting the right hardware, setting up routers and switches, and configuring firewalls to ensure smooth communication across devices.
- Network Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and resolving network issues such as slow connections or connectivity failures requires a solid understanding of networking protocols, hardware, and software configuration.
Supporting System Management
- System Setup and Configuration: IT knowledge is used to install, configure, and maintain operating systems and software applications, ensuring that systems run efficiently and securely.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Understanding how to set up automated backups and perform data recovery is crucial for protecting sensitive business information and preventing data loss.
Enhancing Security Measures
- Cybersecurity Implementation: IT professionals apply security protocols, encryption, and firewall configurations to protect networks and systems from cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data.
- Risk Management: Knowledge of IT security helps identify potential vulnerabilities and implement measures to mitigate risks, from updating software to conducting regular security audits.
Developing and Maintaining Software
- Software Design: IT knowledge is fundamental in the development of custom software solutions tailored to meet specific business needs. Developers use their understanding of programming languages, algorithms, and databases to create functional applications.
- Software Maintenance: After software is deployed, IT professionals continue to monitor, troubleshoot, and update applications to ensure they function properly and remain compatible with new technologies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Exams
When preparing for assessments, it’s important to recognize and avoid common pitfalls that can negatively impact your performance. Many individuals make errors that could easily be prevented with proper planning, time management, and a clear understanding of the material. In this section, we will highlight some of the most frequent mistakes and offer tips on how to avoid them for better results.
- Failing to Read Instructions Carefully: One of the most common mistakes is not fully understanding the instructions before starting the test. Always take a moment to read the questions carefully to ensure you’re answering them as required.
- Time Mismanagement: Many students underestimate how much time they need for each section. Allocate enough time to each part of the test, and leave time for review at the end.
- Overlooking Key Terms: Focusing too much on memorization and not understanding the underlying concepts can lead to misinterpretation of questions. Pay attention to important terms like “define,” “compare,” or “analyze” to ensure your answers align with what’s being asked.
- Not Reviewing Your Work: After completing the test, make sure to review your answers. Rushed work often contains avoidable mistakes such as missed details or careless errors.
- Skipping Difficult Questions: Some students leave difficult questions for later and run out of time to answer them. It’s better to attempt every question, even if it’s just a guess, as it may earn partial credit.
- Ignoring Practice Material: Skipping practice questions or past tests can leave gaps in your knowledge. Regular practice helps you become familiar with the format and the types of questions you may encounter.
- Overloading on Cramming: Cramming right before the test can be ineffective and lead to unnecessary stress. It’s better to pace your study sessions over time for better retention.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can approach your assessment with confidence and increase your chances of achieving success.
How to Manage Your Study Time
Effective time management is a crucial skill for successful learning. By organizing your study sessions and balancing your time, you can maximize your productivity and reduce stress. The key is to approach your study plan with structure and flexibility, ensuring you allocate enough time for each subject while also allowing breaks to keep your focus sharp.
Set Clear Goals
Before you begin studying, it’s important to define what you aim to accomplish. Setting clear, achievable goals helps keep your efforts focused and allows you to track your progress. Break down larger tasks into smaller, manageable sections, and make sure each study session has a specific objective.
Create a Schedule
One of the most effective ways to manage your study time is by creating a detailed schedule. By dedicating specific times to study, you can ensure that you’re covering all the material you need without feeling overwhelmed. Be realistic about how long tasks will take, and include breaks to avoid burnout.
- Prioritize Important Topics: Focus on areas where you need the most improvement. Use a priority system, such as the Eisenhower Matrix, to distinguish between urgent and less important tasks.
- Avoid Multitasking: Although it may seem efficient, multitasking can lead to distractions and decreased productivity. Concentrate on one task at a time to retain information better and work more efficiently.
- Use Active Study Techniques: Techniques such as summarizing, self-testing, and teaching others are more effective than passive reading. They help reinforce the material and improve retention.
- Track Your Progress: Regularly assess how much you’ve learned and adjust your schedule if necessary. This will help you stay on track and make any necessary changes to your study routine.
By managing your time effectively, you can approach your studies with confidence and make steady progress toward achieving your academic goals.
Test-Taking Tips for IT Essentials
Approaching assessments in the field of information technology requires more than just understanding the material. A strategic approach to answering questions can greatly improve performance and confidence. By preparing effectively, managing time wisely, and adopting the right techniques during the test, you can increase your chances of success.
Understand the Question Format
Before diving into your answers, it’s crucial to understand the format of the questions. Assessments often feature multiple-choice, true/false, and scenario-based questions. Knowing what each type requires can help you approach them more effectively:
- Multiple-Choice: Eliminate obviously incorrect answers to increase your chances of selecting the right one. Pay attention to keywords like “always” or “never” that can change the meaning of the statement.
- True/False: Focus on the wording of the statement. A single word can change the truth value of the statement, so read carefully.
- Scenario-Based: These questions require more than just facts–they test your problem-solving skills. Break down the situation, consider all options, and choose the most logical answer.
Time Management During the Test
Effective time management is essential to completing the test within the allotted time. Here’s how you can ensure that you use your time wisely:
- Start with Easy Questions: Begin with the questions you are most confident about. This will build momentum and save time for more challenging questions later.
- Set Time Limits: If the test is long, allocate a certain amount of time to each section or question. If a question is taking too long, move on and come back to it later.
- Review Your Answers: Leave some time at the end to review your answers. It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re rushing, so a final review can help catch errors.
By applying these strategies, you can approach your assessment with greater ease and confidence, giving yourself the best opportunity to perform well.
Reviewing Chapter 1 for Mastery

Thoroughly reviewing the initial material is key to gaining a solid understanding and mastering the core concepts. This process involves revisiting the content, reinforcing your knowledge, and ensuring you grasp both the foundational concepts and their applications. Effective review strategies can enhance your retention and help you identify areas that need further attention.
Key Areas to Focus On
When revisiting the material, it’s important to focus on the fundamental concepts that are critical to your understanding. Here are the main topics to concentrate on:
- Basic Computer Components: Understanding the core hardware that makes up a computer system is essential. Pay special attention to the functions of the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and power supplies.
- Networking Fundamentals: Review basic networking concepts, including network types, protocols, and the roles of devices like routers and switches.
- Operating System Basics: Familiarize yourself with how operating systems manage hardware, software, and resources, as well as the different types of operating systems.
Strategies for Effective Review
To make your review more effective, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Active Recall: Try to recall key concepts without looking at your notes. This helps strengthen your memory and identify weak areas.
- Practice with Real-World Scenarios: Apply what you’ve learned by solving practical problems or working on mini-projects that involve computer hardware, networks, or operating systems.
- Group Study: Engaging with peers for group study sessions can provide new insights and help clarify any misunderstandings.
Track Your Progress
As you continue your review, it’s important to track your progress. Use tools like self-assessment quizzes or flashcards to test your knowledge. This will allow you to identify areas that need additional focus before moving on to more advanced topics.
| Concept | Review Focus |
|---|---|
| Computer Components | Understand the role of each component and how they interact within the system. |
| Networking Basics | Familiarize yourself with network protocols, devices, and types of networks. |
| Operating Systems | Understand the different types and their functions in managing hardware and software. |
By following these review techniques and focusing on the key areas, you will reinforce your knowledge and ensure that you’re well-prepared for the next step in your learning journey.
Final Thoughts on Exam Preparation
Successfully preparing for an assessment requires not just understanding the material, but also developing a strategic approach. It’s important to stay organized, manage your time effectively, and focus on mastering key concepts. With the right mindset and preparation techniques, you’ll increase your confidence and improve your performance when it matters most.
Effective Strategies for Preparation
To ensure that you’re fully prepared for the upcoming challenge, consider implementing these strategies:
- Consistency: Regular, consistent study sessions are more effective than cramming all at once. Schedule study times in small, focused blocks to reinforce your understanding over time.
- Practice: Doing practice tests or reviewing sample questions is one of the best ways to gauge your readiness. This helps you familiarize yourself with the question format and identify areas where you may need more practice.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Concentrate on areas where you feel less confident. Revisit these topics in depth and work through problems to solidify your understanding.
Maintaining a Positive Mindset
Approaching your preparation with a positive attitude can have a big impact. Believe in your ability to succeed and avoid unnecessary stress. Take breaks when needed to recharge, and maintain a healthy study-life balance to avoid burnout.
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Consistent Study Routine | Helps reinforce knowledge and keeps information fresh. |
| Practice with Sample Questions | Familiarizes you with the format and enhances test-taking skills. |
| Focused Review | Ensures you’re mastering weaker areas before the test. |
By applying these approaches and maintaining a disciplined yet relaxed mindset, you’ll be in a strong position to tackle your test with confidence and success. Good preparation is key, and with the right tools and strategies, you’ll be well-equipped to excel.