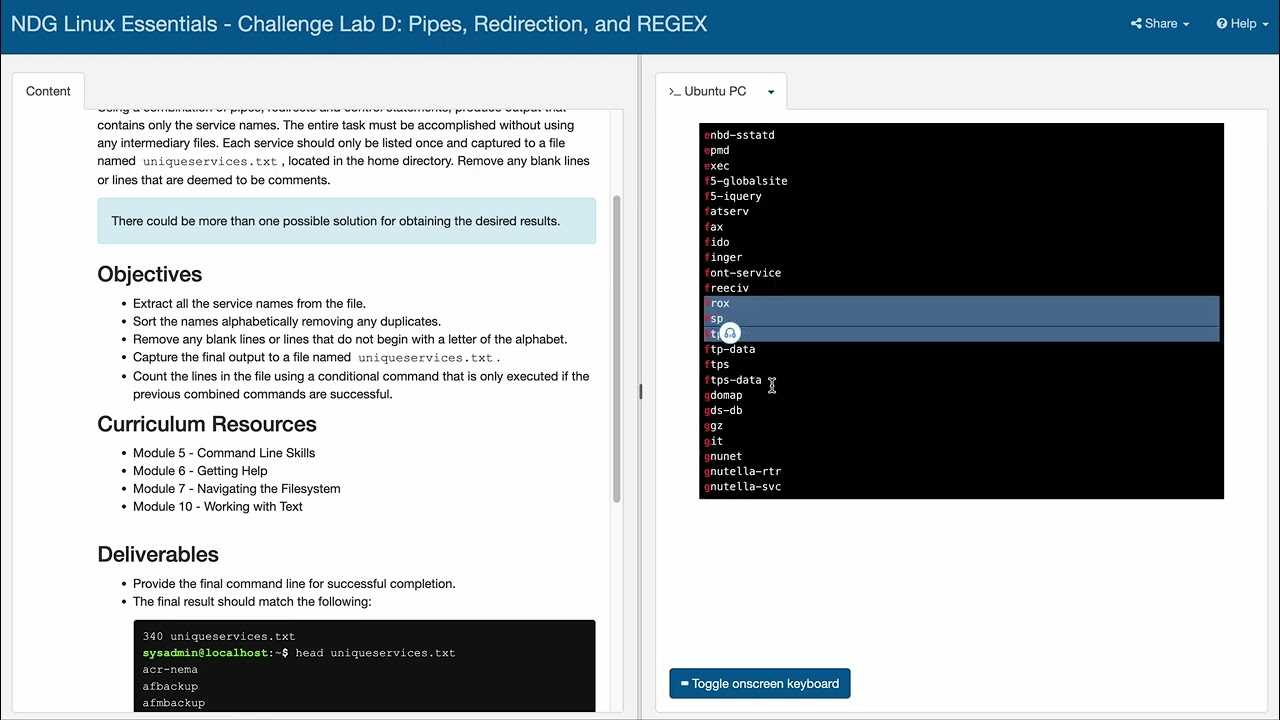
Understanding core principles of operating systems is crucial for anyone looking to build a career in IT support or system administration. The skills gained from this area of study equip professionals with the knowledge to effectively manage and troubleshoot essential system functions. From basic command-line operations to managing system resources, mastering these tasks is foundational for any IT role.
In this section, we dive deep into various topics that cover the essentials of system management. We will explore critical concepts such as file handling, user management, network configurations, and security practices. These topics not only prepare you for practical scenarios but also set the stage for more advanced administrative tasks in the future.
Whether you’re preparing for certification or simply improving your technical expertise, understanding these concepts will significantly enhance your ability to work with operating systems. By the end of this guide, you will be more confident in navigating the system environment and solving problems with efficiency and precision.
NDG Linux Essentials Chapter 6 Exam Answers
This section provides a thorough overview of the key topics covered in the certification process for system administration. It focuses on the essential skills needed for managing and configuring systems, as well as understanding crucial tasks related to file management, user permissions, and basic network configurations. By mastering these concepts, you will enhance your ability to perform critical tasks in any IT environment.
Here is a summary of the core areas to focus on when preparing for the related assessment:
| Topic | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| System Management | Basic command-line operations, system processes, and resources |
| File Handling | Creating, deleting, and managing files and directories |
| User and Group Management | Adding/removing users, assigning permissions, and managing groups |
| Networking Concepts | Configuring basic network settings and troubleshooting network issues |
| System Security | Understanding user authentication, password policies, and file permissions |
By reviewing these areas and understanding their practical applications, you will be better prepared to successfully tackle the challenges presented during the assessment process. This guide will help clarify the essential concepts and provide useful tips to approach the test with confidence and precision.
Key Topics Covered in Chapter 6
In this section, we explore the fundamental concepts that are essential for managing and configuring systems effectively. The focus is on practical skills that help administrators handle daily tasks, troubleshoot issues, and ensure that systems run smoothly. A solid understanding of these areas is crucial for anyone looking to excel in system administration.
File System Management plays a central role, where users learn how to navigate and manipulate files, create directories, and organize data efficiently. Understanding how to work with various file types and permissions is key to securing and maintaining system integrity.
User and Group Administration is another critical aspect. This includes adding and removing users, assigning appropriate permissions, and managing group memberships to control access to system resources. Proper management ensures the security and efficiency of the operating system.
Basic Networking concepts are also covered in depth. This involves configuring network interfaces, understanding IP addresses, and troubleshooting connectivity issues. These skills are essential for maintaining seamless communication between systems and the broader network.
By mastering these key areas, individuals will develop the necessary skills to manage both individual systems and larger networks effectively, ensuring that everything operates securely and efficiently.
Essential Linux Commands for Chapter 6
To efficiently manage and configure systems, mastering key commands is essential. These commands allow administrators to interact with the system, manage files, handle users, and troubleshoot network issues. Understanding these tools is crucial for performing basic administrative tasks with confidence and precision.
File Management and System Navigation
cd is used to change the working directory, allowing users to navigate through the file system. ls displays a list of files and directories, which is essential for verifying directory contents. Additionally, commands like cp (copy), mv (move), and rm (remove) are frequently used for managing files and directories efficiently.
User and Permission Management
Managing users and controlling access is vital for system security. The useradd and usermod commands allow administrators to add and modify users. To set file permissions, chmod is used to define read, write, and execute permissions for users and groups. chown is another important command to change ownership of files and directories.
By mastering these commands, administrators can effectively control system resources, ensuring smooth operation and security of the system environment.
Understanding File System Structure
A solid understanding of how the file system is organized is crucial for managing and navigating operating systems. The file system structure determines how data is stored, accessed, and organized within the system. This knowledge allows administrators to manage storage effectively, locate files, and troubleshoot related issues.
Directory Hierarchy
At the core of any system’s structure is its directory hierarchy. The root directory, typically represented by /, is the starting point from which all other files and directories branch. Subdirectories are organized in a tree-like structure, allowing easy navigation and management of files. Common directories such as /home, /etc, and /var serve specific purposes, such as storing user data, configuration files, and system logs, respectively.
File Types and Attributes
Files in a system can be categorized into different types, such as regular files, directories, and symbolic links. Understanding these types helps in determining how they should be managed. Each file also has attributes, such as permissions, ownership, and timestamps, which define who can access the file and what operations can be performed on it.
By mastering the file system structure, administrators can effectively manage resources, organize files, and ensure the system runs efficiently and securely.
Linux User and Group Management
Managing users and groups is a critical aspect of system administration. This process involves creating and organizing user accounts, setting appropriate permissions, and ensuring secure access to system resources. Proper management helps maintain a secure environment, controlling who can access and modify different parts of the system.
User Account Management
User accounts are essential for controlling access to the system. The useradd command is used to create new users, while usermod allows modifications to existing accounts. Administrators can set various parameters, including the user’s home directory, login shell, and password. passwd is used to set or change the password for a user, ensuring secure access to the system.
Group Management and Permissions

Groups are an efficient way to manage multiple users who require similar access to resources. The groupadd command creates new groups, while groupdel removes them. By adding users to specific groups, administrators can control which users have access to certain files or directories. Permissions can be managed using commands like chmod and chown to set read, write, and execute privileges for users and groups.
Effective management of user accounts and groups ensures that the right individuals have appropriate access to system resources, thereby enhancing both security and efficiency.
File Permissions and Ownership Explained
Managing file permissions and ownership is a crucial part of securing a system. By controlling who can access or modify files, administrators ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized users. Proper permission settings help maintain the integrity of files and directories while allowing legitimate users to perform necessary tasks.
Understanding File Permissions
Permissions determine who can read, write, or execute a file. These permissions are set for three types of users: the owner, the group, and others. The key permissions are:
- Read (r) – Grants permission to view the contents of the file.
- Write (w) – Grants permission to modify the contents of the file.
- Execute (x) – Grants permission to run the file as a program.
Permissions are represented numerically, with the following values:
- Read = 4
- Write = 2
- Execute = 1
For example, a permission value of 755 means that the owner has read, write, and execute permissions (7), while the group and others have read and execute permissions (5).
File Ownership
Each file and directory has an associated owner and group, which determine who can modify or access them. Ownership is critical for ensuring that only authorized individuals or groups can make changes. The chown command is used to change the owner and group of a file or directory, while chgrp changes the group associated with a file.
- Owner – The user who has control over the file.
- Group – A collection of users who share similar permissions to the file.
- Others – All other users who are not the owner or part of the group.
By properly configuring both permissions and ownership, system administrators can protect files and ensure that the right users have the appropriate access.
Networking Concepts for Linux Essentials

Networking is a critical aspect of modern system administration, enabling devices and systems to communicate and share resources. A solid understanding of networking concepts is essential for configuring network settings, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and ensuring reliable communication between systems. This section covers key networking concepts relevant to system administrators.
Basic Networking Terms
Before diving into network configurations, it’s important to understand the fundamental terms that define how systems communicate:
- IP Address – A unique identifier assigned to each device on a network, allowing it to send and receive data.
- Subnet Mask – Defines the range of IP addresses that are within the same network, helping route traffic appropriately.
- Gateway – A device that routes traffic from one network to another, typically connecting a local network to the internet.
- DNS (Domain Name System) – Translates human-readable domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into IP addresses.
Common Networking Commands
Several commands are essential for configuring and troubleshooting network settings:
- ip – Used to display and configure IP addresses, routes, and other network parameters.
- ifconfig – Displays or configures network interfaces, often used for troubleshooting network connections.
- ping – Sends a network request to a device to check if it is reachable and measure the round-trip time.
- netstat – Shows network connections, routing tables, and network statistics to help diagnose network issues.
Configuring Network Interfaces
To set up network connections, administrators must configure network interfaces. This involves setting the correct IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Network interfaces can be configured manually or automatically using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Understanding how to configure static IP addresses versus DHCP is essential for managing different network environments.
By mastering these networking concepts and tools, administrators can ensure that systems are properly configured, troubleshoot network problems effectively, and maintain secure and reliable network communication.
Exam Preparation Tips for Chapter 6
Preparing for a test requires focused study and a solid understanding of key concepts. For effective preparation, it’s important to familiarize yourself with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. A strong grasp of the material, combined with hands-on experience, will help you perform well on the assessment.
Start by reviewing the core topics and key commands that are frequently tested. Practice using the tools and commands in a controlled environment, as hands-on experience is crucial for solidifying your knowledge. Don’t just memorize commands–understand their purpose and how they fit into real-world scenarios. Additionally, pay attention to file management, user permissions, and network configuration, as these are often areas of focus.
Use study materials such as practice tests, online resources, and tutorials to reinforce your learning. These resources can provide a variety of question types, helping you become comfortable with the format of the assessment. Group study sessions can also be beneficial, allowing you to discuss challenging concepts with peers and clarify any doubts.
Finally, ensure that you manage your time wisely during the exam. Focus on answering the questions you are most confident about first, and then return to more challenging ones later. Stay calm, read each question carefully, and apply your knowledge to solve problems effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
When preparing for and taking any technical assessment, it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can affect your performance. Even with the best preparation, making certain mistakes can lead to avoidable errors. By being mindful of these mistakes, you can increase your chances of success and ensure a smoother testing experience.
Overlooking Instructions
One of the most common errors is failing to carefully read and understand the instructions. Whether it’s a multiple-choice question or a practical task, not following the directions can result in lost points. Pay close attention to the requirements of each question, especially when specific commands or formats are requested. Misinterpreting the task can lead to unnecessary mistakes.
Rushing Through Questions
Another frequent mistake is rushing through the assessment. Time management is key, but it’s just as important to avoid hurrying through questions without fully understanding what is being asked. Take your time to think through each question and double-check your answers before submitting. Skimming questions or answers too quickly can cause you to overlook small but critical details.
By staying calm and focused, reading all instructions thoroughly, and managing your time effectively, you can avoid these common mistakes and improve your performance on the test.
How to Manage Files with Commands
File management is a crucial skill for any system administrator or user working with command-line interfaces. Mastering the ability to manipulate, move, copy, and delete files through simple commands ensures efficient management of data within a system. Understanding these core commands allows for streamlined workflows and the ability to automate tasks for greater productivity.
Basic File Operations
To begin managing files effectively, it’s important to understand a few fundamental commands:
- cp – This command is used to copy files from one location to another. It can also be used to copy entire directories with the -r option.
- mv – Use this command to move files or rename them. The destination path is specified to move files between directories.
- rm – This command removes files from the system. For directories, the -r option is used to remove them recursively.
- touch – Create a new empty file or update the timestamp of an existing file.
Working with Directories
Managing directories is just as important as managing files themselves. Use the following commands to work with directories:
- mkdir – Create a new directory at the specified location.
- rmdir – Delete empty directories from the system.
- ls – List the contents of a directory. The -l option provides detailed information such as file permissions and size.
These basic file and directory management commands are essential tools for navigating and maintaining a file system. Whether you are organizing files, backing up data, or setting up complex directory structures, mastering these commands is key to effective system administration.
Understanding Process Management in Linux
Efficient process management is essential for maintaining the smooth operation of a system. The operating system relies on processes to execute programs and perform tasks. Understanding how processes are handled allows administrators to monitor system resources, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance. This section covers the basics of process management, including how to list, control, and terminate processes effectively.
Each process running on the system is assigned a unique identifier known as a Process ID (PID). The system keeps track of these processes to manage their execution, prioritize tasks, and allocate system resources. Users can interact with processes using a variety of commands to inspect, control, or modify their behavior.
Here are some important commands for process management:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ps | Displays information about the currently running processes. |
| top | Provides a dynamic, real-time view of system processes, including resource usage. |
| kill | Used to terminate processes by specifying their PID. |
| nice | Adjusts the priority of a process to influence its execution order. |
| bg | Resumes a paused process in the background. |
| fg | Brings a background process to the foreground. |
By using these commands, users can efficiently manage processes, monitor resource consumption, and ensure optimal system performance. Whether you’re troubleshooting a system slowdown or adjusting the priority of critical processes, a strong understanding of process management is fundamental to system administration.
System Services and Their Importance
System services play a vital role in maintaining the overall functionality of a computing environment. These background processes or daemons ensure that critical tasks such as network connectivity, file system access, and system monitoring are consistently managed without user intervention. Understanding and managing these services is essential for maintaining a stable and secure system.
In any modern operating system, there are various services running at any given time. These services can range from simple utilities that handle print jobs or manage user authentication, to more complex processes that provide web or database services. Proper service management helps ensure the system runs smoothly, optimizes performance, and maintains security.
Key System Services
Here are a few common types of system services and their functions:
- Network Service – Ensures that the system can connect to and communicate over networks. Examples include services like DNS (Domain Name System) or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
- Web Server Service – Handles the serving of web content. Services like Apache or Nginx manage web traffic and deliver web pages to users.
- Database Service – Manages the storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data. Databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL often run as background services.
- Logging Service – Collects system logs to help monitor system health, security, and troubleshooting efforts. Examples include the syslog service or journald in some systems.
- Security Services – Responsible for monitoring system security, enforcing user access control, and protecting the system from unauthorized access. Services like SSH or firewall daemons fall into this category.
Managing System Services
Managing these services typically involves starting, stopping, or restarting them as needed. Many systems offer tools like systemctl (on systems using systemd) or service (for older systems using SysVinit) to control these processes. For instance, administrators can check the status of a service, restart it if necessary, or disable it if it’s not required for operation.
Keeping services running smoothly is crucial for system reliability and security. Inadequate service management can lead to slow performance, network issues, or even security vulnerabilities. As such, knowing how to monitor and adjust system services is an important skill for administrators and users alike.
Security Basics for Linux Users
Maintaining the security of a system is crucial for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. For users interacting with a multi-user or networked environment, it is essential to follow basic security practices to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of both the system and its users.
System security involves managing user access, ensuring proper configurations, and applying regular updates to fix potential vulnerabilities. By following a few fundamental guidelines, users can significantly reduce the risks associated with using their devices in a connected world.
Key Security Practices for Users
- Use Strong Passwords – Always choose complex and unique passwords for your user accounts to prevent unauthorized login attempts. Avoid using easily guessable phrases or reusing passwords across multiple sites or systems.
- Regularly Update Software – Keep all system software, including applications and services, up to date. This ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched, and your system is protected from exploitation.
- Implement User Access Controls – Limit user permissions based on the principle of least privilege. Users should only have access to the files and applications necessary for their tasks.
- Use Firewalls – Configure firewalls to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. By blocking unwanted traffic, firewalls help prevent malicious actors from accessing your system.
- Enable Encryption – Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This adds a layer of protection, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
Common Security Tools
- SSH (Secure Shell) – A secure protocol for accessing remote systems, SSH ensures encrypted communication between devices, preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- SELinux or AppArmor – Security modules that help enforce security policies and isolate applications to prevent malicious activities.
- ClamAV – A popular open-source antivirus tool for detecting and removing malicious software on your system.
By following these basic security practices, users can significantly reduce the chances of falling victim to cyber threats. Securing a system is an ongoing process, and vigilance is key to ensuring long-term protection.
How to Troubleshoot Common Errors
When working with a system, encountering errors is inevitable. These issues can range from minor glitches to significant failures that impact productivity. Understanding how to effectively diagnose and resolve common problems is essential for maintaining system stability and ensuring smooth operations.
Troubleshooting involves identifying the root cause of a problem, analyzing relevant system logs, and applying appropriate solutions. By following a systematic approach, users can quickly resolve most issues without requiring extensive technical support.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Approach

1. Check for Recent Changes: Often, errors arise after changes have been made to the system. Whether it’s a software installation, an update, or a configuration change, revisiting recent modifications can help pinpoint the cause of the issue.
2. Review System Logs: System logs provide valuable insights into what occurred before and after the error. Tools like journalctl or dmesg allow users to access detailed logs that can reveal the source of the problem, whether it’s related to hardware, software, or permissions.
3. Verify System Resources: Check whether the system is running low on memory, disk space, or CPU resources. Resource shortages can cause unexpected crashes and performance issues. Commands like top, free, and df can help monitor system health.
Common Error Types and Solutions
- Permission Denied: This issue often occurs when a user lacks the necessary rights to perform an action. To fix this, check the file permissions and modify them with the chmod command or change the file owner using chown.
- Missing Dependencies: If an application fails to start due to missing libraries or packages, you can resolve it by installing the required dependencies using package managers like apt, yum, or dnf.
- Service Not Starting: If a service fails to start, it could be due to incorrect configuration or missing files. Review the service status with systemctl status and check for error messages in the logs to determine the cause.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Network problems can often be resolved by verifying the system’s IP configuration, testing connectivity using tools like ping, and checking firewall settings.
By applying these troubleshooting steps and keeping a methodical approach, most common errors can be quickly identified and resolved. Understanding the tools available and knowing where to look for information will empower users to solve issues more efficiently and with greater confidence.
Useful Tools for System Admins
System administrators rely on a variety of tools to manage, monitor, and maintain systems efficiently. These tools help automate tasks, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the smooth operation of servers and networks. Understanding how to use these utilities can drastically improve productivity and system reliability.
From monitoring system performance to managing user access and analyzing logs, there are countless tools available. Below are some of the most widely used tools for system administrators, each serving a specific purpose to simplify daily management tasks.
Key Tools for System Administrators
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| top | Displays real-time system resource usage, including CPU, memory, and processes. Useful for diagnosing system performance issues. |
| htop | An interactive version of top that offers a more user-friendly interface and additional features such as process tree view and process search. |
| df | Shows disk space usage for file systems. Useful for monitoring available disk space and ensuring that the system doesn’t run out of storage. |
| du | Reports disk usage for directories and files, helping administrators track which files or directories are consuming the most space. |
| netstat | Provides information about network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics. Essential for diagnosing network issues. |
| ss | A tool similar to netstat, but faster and more efficient. It shows socket statistics and is useful for monitoring network performance. |
| systemctl | Used to manage services and system states. It’s essential for controlling daemons, starting, stopping, and checking service statuses. |
| journalctl | Accesses system logs generated by the systemd service manager. Vital for troubleshooting and checking system logs for errors. |
| grep | A powerful search tool used to search through files or output. It’s extremely useful for filtering logs or other text data based on patterns. |
| chmod | Used to change file permissions. Essential for managing user and group access to files and directories. |
By mastering these tools, system administrators can improve their ability to manage systems efficiently, identify problems quickly, and ensure smooth, continuous operation of services and applications. The right combination of tools can save time, reduce errors, and automate repetitive tasks, making the administrator’s role much more manageable.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Exam Answers
Preparing for a technical assessment requires not only theoretical knowledge but also practical skills. In this section, we will break down key strategies and approaches to help you effectively navigate through the various questions. Understanding each concept and how it applies to real-world scenarios will be crucial to performing well in the evaluation.
By following a structured approach, you can tackle each question with confidence. Whether it involves configuration, command usage, or troubleshooting, having a step-by-step process allows you to stay organized and minimize mistakes. The following steps will guide you in approaching the exam questions methodically.
Step-by-Step Approach
- Understand the Requirements: Carefully read each question to ensure you understand what is being asked. Take note of keywords and concepts that should guide your response.
- Break Down Complex Questions: For questions involving multiple steps or commands, break them down into smaller, manageable tasks. This helps you focus on one part at a time and reduces the chances of missing critical details.
- Recall Key Commands: Be familiar with the most common commands used for system management, file handling, and user permissions. Recalling these commands quickly will give you an edge during the assessment.
- Check for Logical Flow: Ensure that the steps you plan to take or describe in your answers make logical sense. A well-structured response is more likely to earn full marks than one that is disorganized or incomplete.
- Test and Verify (if possible): If the question involves practical skills, such as configuration or troubleshooting, try to verify your approach before finalizing your answer. This ensures you have chosen the correct method.
- Provide Clear Explanations: While commands are important, explaining the reasoning behind your choices can demonstrate your understanding. Ensure your answers are not just technical but also provide context for why certain steps are necessary.
Additional Tips for Success
- Manage Your Time: Allocate time for each section based on its complexity. Avoid spending too much time on a single question.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: During the exam, stay focused and calm. If you get stuck on a question, move on to the next one and return to it later with a fresh perspective.
- Review Your Work: If time permits, review your answers before submitting. Check for any missed details or errors in the commands or procedures.
Following this structured approach will ensure you are well-prepared and able to answer each question thoroughly and confidently. Keep practicing and refining your skills to increase your chances of success in the evaluation.