
Preparing for a test in healthcare-related subjects requires a solid understanding of key terms and concepts that are fundamental to the field. These terms form the backbone of communication in various medical settings, from clinical environments to patient care and diagnosis. Familiarity with this vocabulary can significantly enhance your ability to comprehend complex materials and perform well under pressure.
The ability to understand and accurately apply these terms is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in health-related professions. Effective learning methods, such as regular practice and repetition, can help solidify your knowledge. The focus should be on grasping both the meanings and practical uses of words and phrases, not just memorizing definitions.
In this section, we will explore strategies and resources that will assist you in navigating through the vast array of terms. You will find tips on how to manage your preparation efficiently, improve retention, and gain confidence in your understanding. A systematic approach will not only help you succeed but also ensure that you are well-equipped for your future professional endeavors.
Medical Vocabulary Mastery for Success
Achieving proficiency in healthcare language is essential for anyone aiming to succeed in a profession that relies heavily on accurate communication and understanding. Mastering the core language of the field will not only help you grasp complex concepts but also enable you to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. This section focuses on effective methods to strengthen your command over critical terms, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any challenges ahead.
Essential Terms and Concepts
A strong foundation begins with learning the fundamental building blocks. These terms are used frequently in medical settings and encompass a variety of aspects, from anatomy and physiology to treatments and diagnoses. To excel, focus on these key areas:
- Anatomical Terms – Understanding the names and functions of body parts is crucial for clear communication.
- Common Procedures – Familiarize yourself with the vocabulary associated with common medical interventions.
- Abbreviations and Acronyms – Many healthcare professionals rely on shorthand for efficiency. Knowing these abbreviations can save time and improve comprehension.
Effective Learning Strategies

Once you’ve identified the core concepts, it’s important to adopt strategies that maximize retention and recall. Here are a few methods to help reinforce what you’ve learned:
- Regular Practice – Frequent review of terms and their meanings is crucial for solidifying knowledge.
- Contextual Learning – Practice using terms in real-life scenarios, whether through case studies or discussions with peers.
- Utilizing Flashcards – Create a set of flashcards to test your memory and reinforce key concepts.
By consistently applying these strategies and dedicating time to review, you will strengthen your understanding and become more confident in your ability to navigate complex material with ease.
Overview of Healthcare Language Basics

Understanding the language used in healthcare is fundamental for anyone pursuing a career in the medical field. This specialized vocabulary serves as the foundation for effective communication among professionals and between providers and patients. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the basic structure and components of this language to navigate the field with confidence.
The language of healthcare is built on a combination of roots, prefixes, and suffixes that provide a concise way to describe body functions, diseases, and treatments. Mastery of these elements is key to both understanding and conveying important information in medical settings. A systematic approach to learning these components allows for clearer and more accurate communication across a variety of scenarios.
By grasping the basics, you will be able to quickly decode complex terms and better understand the documentation and instructions encountered in your professional journey. This foundational knowledge paves the way for more advanced concepts and enhances overall proficiency in the field.
Key Prefixes and Suffixes You Should Know
In the world of healthcare language, prefixes and suffixes play a crucial role in shaping the meaning of words. These small components can significantly change the context of a term, making them essential to understand for clear and accurate communication. By learning the most common prefixes and suffixes, you can easily interpret complex terms and understand their meanings more efficiently.
Prefixes are added to the beginning of a word, often altering its meaning to indicate direction, location, time, or degree. Suffixes, on the other hand, are attached to the end of a word and usually define a condition, procedure, or disease. Mastery of these elements will enhance your ability to decode unfamiliar terms quickly.
Common Prefixes
- Hyper- – Means excessive or above normal (e.g., hypertension – high blood pressure).
- Hypo- – Means deficient or below normal (e.g., hypoglycemia – low blood sugar).
- Sub- – Means under or below (e.g., subcutaneous – beneath the skin).
- Pre- – Means before (e.g., preoperative – before surgery).
Common Suffixes
- -itis – Indicates inflammation (e.g., arthritis – inflammation of the joints).
- -ectomy – Refers to the removal of a part (e.g., appendectomy – removal of the appendix).
- -pathy – Refers to disease or condition (e.g., neuropathy – disease of the nerves).
- -ology – Refers to the study of (e.g., oncology – the study of cancer).
By familiarizing yourself with these prefixes and suffixes, you will be able to break down complicated medical terms into understandable parts, making it easier to recall their meanings and use them correctly in your studies and professional practice.
Common Healthcare Root Words Explained
At the core of healthcare language lie root words, which provide the foundation for many complex terms. These root words are essential for understanding the meaning of more complicated medical expressions, as they often refer to key aspects of the body, conditions, or processes. Recognizing these roots allows for quicker comprehension of unfamiliar terms and better communication in clinical settings.
By learning these common roots, you can break down words into smaller, more manageable parts, each carrying its own meaning. This not only makes it easier to interpret various terms but also aids in remembering them for future use. Below are a few of the most frequently encountered root words in healthcare.
Common Root Words
- Cardi- – Refers to the heart (e.g., cardiology – the study of the heart).
- Derm- – Pertains to the skin (e.g., dermatitis – inflammation of the skin).
- Osteo- – Refers to bones (e.g., osteoporosis – condition of weakened bones).
- Neuro- – Relates to the nerves or nervous system (e.g., neurology – the study of the nervous system).
- Hemat- – Pertains to blood (e.g., hematology – the study of blood).
Understanding these basic root words will help you decipher more complex terms by recognizing familiar patterns. This knowledge serves as a key tool in mastering the language of healthcare and communicating effectively within the field.
How to Memorize Complex Terms Efficiently
Memorizing intricate vocabulary can be challenging, especially when dealing with long or unfamiliar words. However, using effective techniques can make this process smoother and more manageable. By applying strategies that focus on repetition, association, and organization, you can enhance your ability to retain and recall complex terms more easily.
One of the most powerful ways to memorize terms is by breaking them down into smaller, more digestible parts. Understanding the meaning of each component–such as prefixes, suffixes, and root words–can help make complex terms easier to remember. Additionally, creating associations between the terms and real-world concepts or visual imagery can reinforce memory retention.
Effective Memorization Techniques
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Chunking | Breaking large amounts of information into smaller, manageable units for easier recall. |
| Mnemonics | Using memory aids such as acronyms or rhymes to create associations with the terms. |
| Visualization | Creating mental images or diagrams related to the terms to aid in retention. |
| Spaced Repetition | Reviewing terms at increasing intervals to reinforce memory over time. |
By consistently applying these strategies and remaining patient with the process, you will find that retaining complex vocabulary becomes more manageable. The key is to stay organized, use diverse techniques, and give yourself time to absorb the information fully.
Tips for Understanding Healthcare Abbreviations
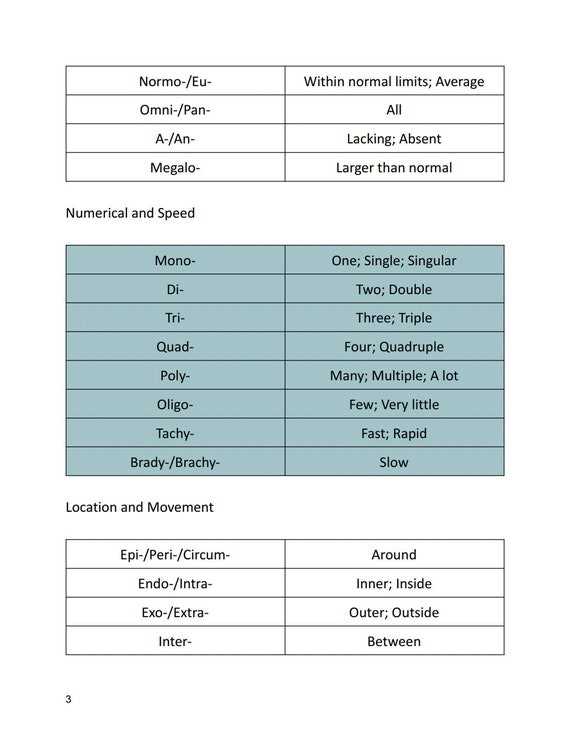
Abbreviations are an essential part of the healthcare field, used to streamline communication and save time. However, the wide variety of abbreviations can be overwhelming, especially for those new to the field. Understanding these shorthand terms is vital for both professionals and students in ensuring accurate interpretation of medical records, prescriptions, and instructions.
Learning to decode abbreviations is not just about memorizing them, but about understanding their context and purpose. By familiarizing yourself with common abbreviations and the principles behind their use, you can improve your ability to read and understand documents in a healthcare setting. Below are a few tips to help you navigate this challenge more effectively.
Helpful Strategies
- Learn the Common Abbreviations – Start by focusing on the most frequently used abbreviations in healthcare settings, such as BP for blood pressure and HR for heart rate.
- Understand the Context – The meaning of an abbreviation can change based on its context. Always consider the surrounding information to help clarify the intended meaning.
- Use Flashcards – Create a set of flashcards with the abbreviation on one side and the full term on the other to reinforce your memory.
- Practice Regularly – Familiarize yourself with these abbreviations by reviewing materials and practicing with quizzes or examples.
Common Abbreviations to Know
- IV – Intravenous
- Rx – Prescription
- Dx – Diagnosis
- OTC – Over-the-counter
- QID – Four times a day
By consistently applying these strategies and focusing on learning the most common abbreviations, you’ll enhance your ability to understand and use these shorthand terms effectively, ensuring clear communication and minimizing the risk of errors in the healthcare environment.
Practice Questions to Test Your Knowledge
One of the most effective ways to reinforce your understanding of key concepts is through practice. By testing yourself with questions related to the vocabulary and principles you’ve learned, you can identify areas of strength as well as topics that may require further review. Regular practice helps solidify your knowledge and boosts your confidence when applying what you’ve learned in real-world scenarios.
Below are a series of practice questions designed to test your understanding of the material. These questions cover a variety of topics and will help you gauge your familiarity with important terms and concepts. Use this as a tool to track your progress and improve your retention.
Test Your Knowledge
| Question | Your Answer |
|---|---|
| What does the prefix “hypo-” mean? | ____________________ |
| Which suffix indicates a surgical procedure to remove a part? | ____________________ |
| What is the root word for “heart”? | ____________________ |
| What does “cardiology” refer to? | ____________________ |
| Which abbreviation stands for “prescription”? | ____________________ |
By answering these questions, you can get a better sense of your proficiency with the material. Take your time and review the answers to ensure a deeper understanding. Repeating this exercise periodically will help strengthen your knowledge and prepare you for applying these concepts in practical situations.
Breaking Down Anatomy and Physiology Terms
Understanding the language of the body can be a challenge due to its complexity and specialized nature. However, by breaking down the terms into smaller components, such as prefixes, suffixes, and root words, it becomes easier to decipher their meanings. This approach not only simplifies the process of learning but also helps to remember complex concepts by recognizing patterns and relationships within the language.
In this section, we will explore how to deconstruct anatomy and physiology terms effectively. Whether you’re dealing with the names of organs, systems, or processes, understanding the structure of these words will give you the ability to comprehend and recall them more easily.
Breaking Down Complex Terms
- Prefix – Often indicates location, number, or time (e.g., hyper- meaning “excessive” or “above,” as in hypertension).
- Root Word – The core of the term that provides the primary meaning (e.g., cardio meaning “heart,” as in cardiovascular).
- Suffix – Typically describes a condition, procedure, or disease (e.g., -itis meaning “inflammation,” as in arthritis).
Common Anatomy and Physiology Terms
- Cardiovascular – Relating to the heart and blood vessels.
- Neurology – The study of the nervous system.
- Gastroenterology – The study of the stomach and intestines.
- Respiratory – Pertaining to the lungs and breathing process.
By understanding how these terms are built, you can begin to see connections between different parts of the body and their functions. This method not only aids in memorization but also improves overall comprehension of the subject matter.
Important Terms for Diagnosis
In the healthcare field, accurate diagnosis is crucial, and having a solid understanding of the key terms used in this process is essential. These terms help healthcare professionals communicate effectively about conditions, symptoms, and treatments. Recognizing and understanding these terms ensures that both diagnosis and subsequent care are based on precise information.
Whether describing symptoms, procedures, or conditions, the language used for diagnosis is often technical, but it follows a clear and structured format. This section focuses on the most important terms that are frequently encountered when identifying and classifying diseases or health conditions. Familiarizing yourself with these terms can significantly improve comprehension and communication in clinical settings.
Common Diagnostic Terms
- Acute – A condition that comes on quickly and is severe in nature.
- Chronic – A condition that persists over a long period, often for life.
- Benign – A condition that is not harmful or cancerous.
- Malignant – A condition that is harmful and often cancerous.
- Symptom – A sign or manifestation of a condition experienced by the patient.
- Sign – An objective indication of a condition, typically observable or measurable by a healthcare provider.
Key Prefixes for Diagnosis
- Pre- – Refers to something occurring before (e.g., preoperative means before surgery).
- Post- – Refers to something occurring after (e.g., postpartum means after childbirth).
- Hypo- – Indicates a deficiency or below normal level (e.g., hypotension refers to low blood pressure).
- Hyper- – Indicates excess or above normal level (e.g., hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar).
By mastering these essential terms, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the diagnostic process, allowing you to interpret clinical information more accurately and communicate more effectively in healthcare environments.
Terms Related to Treatment Procedures
In healthcare, understanding the various procedures used to treat conditions is essential for both patients and practitioners. These procedures can range from simple interventions to complex surgeries, and the language used to describe them is precise and structured. Familiarity with these terms helps ensure that the correct treatments are applied and understood across different healthcare settings.
This section covers key terms associated with treatment methods, from diagnostic tests to therapeutic procedures. Recognizing these terms will give you a clearer picture of how healthcare professionals approach treatment, as well as what patients might experience during their care.
Common Treatment Procedures
- Surgery – A medical procedure involving an incision to treat or diagnose a condition.
- Radiotherapy – The use of radiation to treat cancerous growths.
- Chemotherapy – A treatment that uses drugs to destroy or control cancer cells.
- Physical Therapy – A treatment designed to improve movement and function through exercise and rehabilitation.
- Dialysis – A procedure used to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood in patients with kidney failure.
Key Procedures and Their Suffixes
- -ectomy – Refers to the surgical removal of a part of the body (e.g., appendectomy means removal of the appendix).
- -plasty – Refers to the surgical repair or reconstruction of a part of the body (e.g., rhinoplasty is surgery to reshape the nose).
- -otomy – Refers to cutting or making an incision into an organ or tissue (e.g., laparotomy refers to a surgical incision into the abdomen).
- -scopy – Refers to the use of an instrument to examine or view a part of the body (e.g., arthroscopy is the examination of a joint using a small camera).
By mastering these terms, you will gain a better understanding of the wide range of treatments available, as well as how healthcare professionals describe and perform these procedures to improve patient outcomes.
How to Interpret Health Records and Charts
Health records and charts contain critical information about a patient’s condition, treatment, and progress. They serve as the primary means of communication between healthcare professionals, ensuring that the care provided is consistent and informed. Understanding how to read and interpret these documents is essential for both healthcare workers and patients.
In this section, we will explore the key components of health records and charts, including how to identify important data points, interpret abbreviations, and understand medical notes. Gaining proficiency in this area will enhance your ability to make informed decisions and communicate effectively within the healthcare system.
Key Elements in Health Records
- Patient Information – Includes personal details such as name, age, and medical history.
- Progress Notes – Describes the patient’s condition and the care provided, including observations and treatments.
- Test Results – Provides information about laboratory tests or imaging studies conducted, helping to diagnose conditions.
- Treatment Plans – Outlines the proposed steps for managing the patient’s condition, including medications, therapies, or surgeries.
- Medications – Lists drugs prescribed, along with dosages and instructions for use.
Common Abbreviations and Symbols
- Rx – Prescription or treatment.
- BP – Blood pressure.
- HR – Heart rate.
- PRN – As needed, usually for medications.
- STAT – Immediate or urgent action required.
By becoming familiar with these components and terms, you will be able to confidently interpret health records, ensuring that you understand the key details that guide patient care.
Strategies for Preparing for Your Assessment
Preparing for a major evaluation requires effective planning, organization, and practice. The key to success lies in understanding the material, knowing how to approach different types of questions, and managing your time effectively. By adopting specific techniques and strategies, you can increase your chances of performing well and reduce the stress often associated with assessments.
This section covers practical strategies to help you prepare for your upcoming assessment. From reviewing key concepts to mastering test-taking techniques, these approaches will help you build confidence and improve your understanding of the content.
Effective Preparation Techniques
- Active Review – Engage with the material actively by summarizing key points, creating flashcards, or teaching the content to others.
- Practice with Mock Tests – Simulate the actual test environment by taking practice quizzes or tests. This will help you familiarize yourself with the format and timing.
- Break Down the Content – Break the study material into smaller sections and focus on one topic at a time. This reduces overwhelm and improves retention.
- Group Study – Join or form a study group to discuss difficult concepts. Collaborative learning often helps reinforce knowledge.
- Use Visual Aids – Diagrams, charts, and mind maps can help visualize complex concepts, making them easier to understand and recall.
Time Management and Focus
- Create a Schedule – Set aside dedicated time each day for focused preparation. Consistent, manageable sessions are more effective than cramming.
- Avoid Multitasking – Limit distractions by focusing on one task at a time. This will improve your concentration and efficiency.
- Take Regular Breaks – Studying for long periods without breaks can lead to burnout. Take short breaks to recharge and maintain focus.
By following these strategies and sticking to a well-structured plan, you’ll be well-equipped to perform your best when it’s time for the assessment.
Utilizing Flashcards for Quick Learning
Flashcards are an effective tool for reinforcing knowledge and retaining important concepts in a quick and manageable way. Whether you’re looking to memorize terms, definitions, or key facts, this method allows for active recall, which is essential for long-term retention. The repetitive nature of flashcard practice also helps with reinforcing your memory, ensuring that key information is readily accessible when needed.
In this section, we will explore how flashcards can be used effectively for fast learning and recall, offering strategies and tips to maximize their usefulness.
Benefits of Flashcards
- Active Recall – Flashcards engage your brain in active recall, which strengthens your ability to retrieve information from memory.
- Portability – Flashcards can be taken anywhere, making it easy to review on the go, whether you’re commuting or on a break.
- Quick Sessions – Flashcard sessions can be short, allowing for consistent, focused practice without overwhelming yourself.
- Self-Testing – By testing yourself regularly, you can track your progress and identify areas that need further attention.
How to Create Effective Flashcards
- Keep It Simple – Write concise information on each card, focusing on a single fact, term, or concept to avoid confusion.
- Use Both Sides – On one side, write a question or term; on the other, write the answer or definition to test your recall.
- Use Images or Mnemonics – Visual aids or memory techniques can help make difficult concepts easier to remember.
- Review Regularly – Consistent review is key. Use a spaced repetition system to ensure you’re reinforcing your memory over time.
By incorporating flashcards into your routine, you can create a powerful tool for quick and effective learning, helping you retain crucial information in a fraction of the time.
Best Online Resources for Exam Prep
In the digital age, preparing for assessments has never been easier, thanks to a wide array of online tools and platforms. These resources offer a variety of methods to reinforce your knowledge, ranging from interactive quizzes and practice questions to detailed explanations and expert-led courses. Leveraging these online resources can significantly boost your preparation and improve your performance.
In this section, we’ll highlight some of the best online platforms that can aid you in mastering essential concepts and ensuring thorough preparation for your upcoming evaluation.
Top Online Resources
| Resource | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Khan Academy | Free educational platform with comprehensive courses and practice exercises. | Interactive exercises, video lessons, progress tracking. |
| Quizlet | Customizable flashcards for a wide range of subjects. | Flashcards, practice tests, study games, community-shared sets. |
| Coursera | Online courses from top universities and institutions. | Video lectures, assignments, peer interactions, certification. |
| Memrise | Platform focused on language and vocabulary building with spaced repetition. | Interactive learning, spaced repetition, video content, mobile-friendly. |
| ProProfs Quiz Maker | Quiz platform with pre-made and custom quizzes. | Custom quizzes, instant feedback, learning analytics. |
By incorporating these online tools into your preparation routine, you can ensure that you’re not only reinforcing key concepts but also diversifying your learning methods to keep things fresh and engaging. Whether you prefer self-paced learning, interactive challenges, or expert-led courses, these resources provide a wide range of options to support your journey towards success.
How to Handle Time Management During Tests
Time management is a crucial skill to develop when preparing for and completing any assessment. Efficiently allocating time during a test can make the difference between finishing all questions and feeling rushed. Understanding how to manage your time allows you to approach each section with confidence and reduces the likelihood of errors caused by anxiety or poor pacing.
In this section, we’ll explore practical strategies to help you optimize your time during a test, ensuring that you can tackle every question effectively without feeling overwhelmed.
Key Strategies for Time Management
- Familiarize Yourself with the Test Format – Before taking the test, review the structure and type of questions. Knowing what to expect allows you to allocate your time accordingly.
- Prioritize Easier Questions – Start with questions you find easiest. This helps you gain momentum and ensures that you don’t run out of time on questions you can easily answer.
- Set Time Limits for Each Section – Set an approximate time limit for each section or question. Use a watch or timer to track your progress, ensuring you stay on schedule.
- Avoid Overthinking – If you’re unsure about a question, don’t spend too much time on it. Move on and return to it if time permits.
- Leave Some Time for Review – Always allocate a few minutes at the end to review your answers. This allows you to catch mistakes and ensure that you haven’t missed anything important.
By implementing these time management strategies, you can approach the assessment with a clear plan in mind. Staying calm and organized during the test will help you perform at your best and reduce stress.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Medical Terminology Exams
When preparing for assessments that test your understanding of specialized language, avoiding common pitfalls is essential to performing well. Many learners struggle not because they lack knowledge but because they make simple mistakes under pressure. Recognizing these mistakes can help you approach your assessments more effectively and confidently.
This section will highlight some of the most frequent errors people make during these types of tests and provide tips for overcoming them. By understanding these pitfalls, you can focus your efforts on strengthening your knowledge while avoiding missteps that could impact your results.
Frequent Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

- Misunderstanding Root Words and Prefixes – Often, students confuse similar-sounding prefixes or roots. It’s crucial to grasp the meanings of each component to avoid incorrect interpretations.
- Skipping Over Instructions – Many learners rush to start answering questions and overlook specific instructions, which can lead to misinterpretation of the tasks. Always take a moment to carefully read instructions before answering.
- Overlooking Minor Details – In complex assessments, small details like spelling or punctuation can make a significant difference. Double-check your responses for accuracy and clarity.
- Not Managing Time Properly – Running out of time is a common issue. Ensure you pace yourself throughout the test, spending an appropriate amount of time on each section without getting stuck on challenging questions.
Improvement Tips
- Practice with Flashcards – Regularly test yourself with flashcards to reinforce your knowledge and avoid confusion between similar terms.
- Take Breaks During Study Sessions – Resting your mind during long study sessions helps maintain focus and prevents burnout.
- Review Mistakes – After practicing, go back to review any mistakes made and understand why they happened. This helps solidify your learning.
By being aware of these common mistakes and implementing the suggested strategies, you can avoid unnecessary errors and improve your performance. A clear understanding and careful preparation are key to success in any specialized assessment.