
In this section, we explore essential principles that explain how individuals interact with one another and make decisions in group settings. The focus is on uncovering the forces that shape actions, thoughts, and feelings within various social environments.
Throughout, we delve into the underlying mechanisms that influence how people form perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs. Understanding these patterns is crucial for analyzing everyday interactions and gaining deeper insights into human behavior.
By examining key factors such as conformity, group influence, and interpersonal relationships, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the elements that drive individual and collective behavior. This exploration will help clarify the psychological forces that shape both personal and social dynamics.
Unit 14 Social Psychology Study Guide Answers

This section provides a comprehensive overview of key concepts that explain how individuals think, behave, and interact within groups. It offers an in-depth look at the various factors that influence decision-making, relationships, and perceptions in everyday life.
By examining theories and research, this part aims to clarify the essential components of human interactions and provide a deeper understanding of how individuals respond to external influences. The following subsections will break down these concepts into manageable insights.
Understanding Group Dynamics

Group behavior plays a crucial role in shaping individual actions. Whether in a team, family, or community setting, understanding the mechanisms behind group influence is essential. Factors such as group cohesion, leadership, and roles within a group structure significantly impact behavior. Recognizing how these elements interact allows for a clearer picture of why people behave differently when in groups compared to when they are alone.
The Power of Perception and Attitudes
People’s perceptions and attitudes towards others strongly influence their actions and interactions. These attitudes can be shaped by various factors, including cultural background, personal experiences, and societal norms. Exploring how individuals form attitudes and how these beliefs guide their behavior is essential for understanding social interactions and decision-making processes.
Overview of Social Psychology Concepts
This section introduces essential ideas that explain how individuals think, feel, and act in relation to others. These fundamental principles shape how we engage in various social environments, influencing everything from personal choices to group behavior. Understanding these concepts helps explain why people behave differently in different situations and how their actions are influenced by the surrounding environment.
Throughout this overview, we will explore key factors such as perception, attitude formation, and the roles played by group interactions in shaping individual behavior. These insights are vital for understanding the complex nature of human relationships and the forces that drive our actions within society.
The Role of Attitudes and Beliefs
Our views and beliefs play a crucial role in guiding behavior and decision-making. Whether positive or negative, these internalized perceptions often shape our responses to people and situations around us. Understanding how attitudes are formed and how they impact social interactions is vital for interpreting behavior in various contexts.
Influence of Group Dynamics
Group membership profoundly affects individual behavior. Whether in a family, workplace, or community, the presence of others can influence personal decisions, beliefs, and actions. Group norms, peer pressure, and leadership all contribute to shaping how individuals behave within collective settings. Examining these influences is key to understanding how people adapt their behavior in different group contexts.
Key Theories in Social Psychology
This section focuses on fundamental theories that explain how individuals interact with each other and how their behavior is shaped by both internal and external influences. These theories provide a framework for understanding why people act in certain ways in various social contexts and offer insights into the underlying psychological processes that guide human behavior.
By exploring these key concepts, we can better understand the mechanisms that drive human interactions, from the formation of beliefs to the influence of others on individual choices. These theories help us interpret everyday behavior and offer valuable perspectives on how we function within groups and societies.
Understanding Social Influence and Behavior
Human behavior is deeply influenced by the presence and actions of others. From conformity to persuasion, individuals often adjust their thoughts, feelings, and actions based on external factors. This section explores the various ways in which group dynamics, societal norms, and peer pressure shape individual choices and behaviors.
Conformity is one key concept that explains how individuals align their behavior with that of a group. People may change their attitudes or actions to fit in or avoid conflict, even if they privately disagree with the group. Obedience is another significant factor, where individuals comply with authority figures, sometimes overriding their own moral judgments to follow orders.
Understanding these forces is essential for interpreting actions in both personal and public settings. Whether in a family, workplace, or community, the influence of others plays a pivotal role in shaping how individuals behave in various situations.
Factors Affecting Group Dynamics
Group behavior is influenced by various internal and external factors that shape interactions, decision-making, and the overall functioning of the group. Understanding these elements is crucial to interpreting how groups form, maintain cohesion, and navigate conflicts.
Several factors contribute to the way individuals behave within a group:
- Group Size: Larger groups tend to have more diverse opinions and may experience greater difficulty in reaching consensus, while smaller groups may have more cohesive decision-making.
- Group Roles: The roles individuals take on within a group can significantly affect dynamics. Leadership, task assignments, and responsibilities shape how group members interact and contribute to the group’s success.
- Norms and Expectations: Each group develops specific expectations regarding behavior. These norms influence how members communicate, collaborate, and resolve conflicts.
- Group Cohesion: The strength of bonds between group members can determine how well the group functions. High cohesion often leads to increased cooperation, while low cohesion may cause fragmentation.
- Communication Patterns: Open and effective communication is essential for positive group dynamics. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, inefficiency, and conflict.
These factors interact in complex ways, creating unique dynamics in each group. Understanding them is essential for fostering healthy, productive group interactions and overcoming challenges in both professional and personal settings.
Role of Attitudes in Social Interaction
Individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are significantly shaped by their attitudes toward others, situations, and concepts. These mental frameworks guide how people perceive and react to their environment, affecting how they interact within social settings. Attitudes influence both verbal and nonverbal communication, making them a key factor in establishing relationships and navigating social situations.
Attitudes can be positive, negative, or neutral, and they can have a direct impact on social interactions. For example, a person’s attitude toward a group or an individual can determine how they approach conversations, form relationships, or resolve conflicts. Understanding the role of these mental dispositions helps to explain variations in how people connect with one another.
Factors That Shape Attitudes

Attitudes are not formed in isolation; they are influenced by various factors:
- Personal Experiences: Past interactions and events can strongly shape an individual’s outlook and reactions in future social encounters.
- Family and Culture: The values and beliefs imparted by family and culture significantly influence the way people view the world and interact with others.
- Social Influence: The opinions and behaviors of peers and authority figures often shape an individual’s attitudes, especially in group settings.
- Media and Society: Exposure to media messages, societal trends, and public figures can modify people’s attitudes on various issues.
Impact of Attitudes on Interaction

Attitudes not only determine how individuals perceive others but also how they behave toward them. Positive attitudes can foster trust, cooperation, and harmonious relationships, while negative attitudes often lead to misunderstandings, hostility, or avoidance. A person’s overall attitude plays a vital role in shaping the dynamics of social interactions, whether in professional, familial, or casual settings.
In summary, understanding the power of attitudes in guiding behavior allows individuals to improve their social interactions and build stronger, more effective relationships.
Conformity and Obedience Explained
Human behavior is often influenced by external pressures to fit in or follow authority, leading individuals to adjust their actions and beliefs accordingly. These processes–conformity and obedience–help to explain why people sometimes act in ways that align with group norms or commands from authority figures, even if it goes against their own preferences or moral judgments.
Conformity involves changing one’s behavior to match the expectations or norms of a group, often to gain acceptance or avoid conflict. On the other hand, obedience refers to following direct instructions from an authority figure, sometimes without questioning the morality or reason behind those orders. Both of these mechanisms are essential for understanding how individuals adapt their actions in response to their environment.
Key Differences Between Conformity and Obedience
While both conformity and obedience involve adjusting behavior, the key distinction lies in the source of influence:
| Factor | Conformity | Obedience |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Influence | Peer pressure or group norms | Commands from an authority figure |
| Motivation | Desire to fit in or avoid social rejection | Following orders or instructions |
| Outcome | Behavior change to align with group | Behavior change to comply with authority |
Examples of Conformity and Obedience
Examples of conformity include individuals dressing in a certain style because it is popular within their peer group or adjusting opinions to align with the majority in a social setting. Examples of obedience are more commonly seen in hierarchical structures, such as employees following the orders of a supervisor or soldiers carrying out commands from their superiors, sometimes even in extreme or unethical situations.
Both conformity and obedience are powerful forces in shaping behavior, demonstrating how deeply individuals can be influenced by the groups and authority figures around them.
Impact of Social Identity on Behavior
Our sense of belonging to particular groups significantly influences how we think, feel, and act. From family and friends to professional networks and cultural communities, the groups we identify with shape our behaviors and attitudes in powerful ways. These group affiliations help define who we are, affecting how we interact with others and how we perceive ourselves within society.
When individuals strongly identify with a group, they tend to adopt the values, norms, and behaviors associated with that group. This can lead to both positive outcomes, such as increased cooperation and support, and negative outcomes, such as in-group bias or exclusion of others. The influence of social identity can be seen in various aspects of life, including decision-making, conflict resolution, and even political beliefs.
Analyzing Social Perception and Judgment
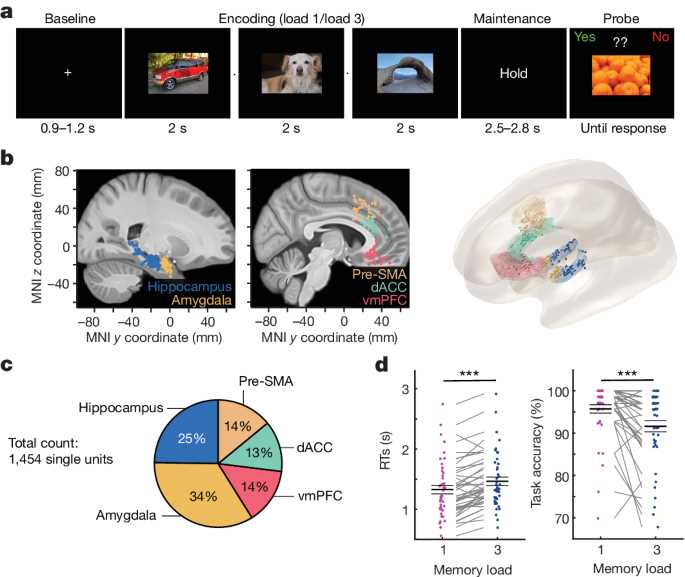
How we interpret and evaluate others plays a crucial role in shaping our interactions and relationships. Our perception of people, events, and situations is influenced by a range of factors, including prior experiences, cognitive biases, and cultural influences. This section delves into the process by which individuals form impressions of others and make judgments based on limited information.
Social perception refers to the process of understanding and making sense of the behaviors and intentions of others. Judgment, on the other hand, involves forming opinions or conclusions about people, often based on stereotypes or assumptions. Together, these processes significantly impact how we navigate social interactions and form attitudes about those around us.
Key Factors Influencing Perception and Judgment

Several factors contribute to how we perceive and judge others:
- First Impressions: Initial encounters tend to leave a lasting impact. The first impression formed can strongly influence subsequent perceptions and interactions.
- Cognitive Biases: Biases such as the halo effect, confirmation bias, and fundamental attribution error can distort our judgments, leading us to make inaccurate assumptions about others.
- Attractiveness and Appearance: Physical appearance plays a significant role in shaping judgments, with people often making assumptions about someone’s personality based on their looks.
- Cultural Influences: Cultural background and norms can affect how we interpret behaviors and understand the intentions of others, sometimes leading to misunderstandings in cross-cultural interactions.
Impact of Social Perception on Relationships

The way we perceive and judge others can influence our relationships, both positively and negatively. Accurate perceptions can foster trust and cooperation, while misjudgments can lead to conflict or alienation. Being aware of our biases and striving for more objective assessments of others can improve social interactions and strengthen relationships.
Social Cognition in Everyday Life
In our daily interactions, we constantly process information about the world and the people around us. These mental processes, often operating automatically, help us navigate social situations and make decisions quickly. Whether we’re interpreting the behavior of others or forming judgments about situations, the way we think about and understand the world plays a pivotal role in shaping our daily experiences.
Social cognition encompasses the mental processes we use to interpret, analyze, and recall information about others. It influences how we interact with people, how we understand their intentions, and how we make decisions in social contexts. From deciding how to respond in a conversation to determining how to act in a group, social cognition is at the heart of our everyday behavior.
How We Process Information in Social Settings
When interacting with others, our brains work to process and evaluate information efficiently. We rely on several strategies to make sense of social situations:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Heuristics | Simple rules or mental shortcuts that help us make quick decisions, often based on past experiences or limited information. |
| Attributions | The process by which we explain others’ behaviors, attributing actions to internal dispositions or external factors. |
| Confirmation Bias | Tendency to search for, interpret, or focus on information that confirms our existing beliefs and expectations. |
Social Cognition in Daily Interactions
Our understanding of social cues, such as body language or tone of voice, allows us to adapt and respond appropriately in different situations. The way we interpret others’ actions can influence our behavior, leading to smoother interactions or potential misunderstandings. In a professional setting, for example, reading nonverbal signals accurately can help build rapport, while in a personal relationship, understanding the emotions of others can strengthen bonds and reduce conflict.
Ultimately, our ability to process and interpret social information shapes how we navigate the world. By becoming more aware of how we think about and respond to others, we can improve our interactions and enhance our social experiences.
Prejudice and Discrimination in Society
Throughout history, certain groups of people have faced unfair treatment based on characteristics such as race, gender, or social class. These biases often stem from deeply ingrained beliefs that lead individuals to form negative judgments about others, affecting their behavior and interactions. The result is not only individual harm but also widespread inequalities in society.
Prejudice refers to preconceived negative attitudes or stereotypes about individuals based on their group membership. Discrimination occurs when these biased attitudes translate into actions that harm others or treat them unfairly. These issues are pervasive and can manifest in various forms, from subtle microaggressions to overt acts of injustice. Both prejudice and discrimination have significant consequences, reinforcing societal divisions and perpetuating injustice.
Impact of Prejudice and Discrimination
The effects of biased attitudes and unfair treatment are felt on both an individual and societal level:
- Psychological Effects: Individuals who experience prejudice or discrimination may suffer from stress, lower self-esteem, and diminished mental health.
- Social Inequality: Discrimination can lead to unequal access to resources, opportunities, and rights, exacerbating social divisions and perpetuating poverty and marginalization.
- Economic Disparities: Discriminatory practices in hiring, promotion, and pay can limit economic mobility and create persistent wealth gaps between different groups.
Addressing Prejudice and Discrimination
Efforts to reduce prejudice and discrimination require both individual and collective action. It involves fostering empathy, challenging harmful stereotypes, and advocating for policies that promote equality and inclusion. Education plays a key role in this process, helping to raise awareness of biases and encouraging more fair and just treatment of all individuals, regardless of their backgrounds.
Attraction and Relationship Formation
Human connections are a fundamental part of life, and the process of forming relationships is influenced by various factors. Attraction plays a key role in determining who we feel drawn to and can shape the course of interactions, whether personal or professional. Understanding the elements that drive attraction helps explain how relationships develop and evolve over time.
Attraction is not just about physical appearance; it encompasses a range of emotional, psychological, and social elements. People are often drawn to others who share similar interests, values, and experiences. Other factors, such as proximity and repeated exposure, also contribute significantly to the formation of relationships. Over time, these initial connections can develop into meaningful bonds, whether they are friendships, romantic relationships, or professional partnerships.
Factors Influencing Attraction
There are several key elements that influence the way we form connections with others:
- Physical Attractiveness: While physical appeal can grab attention, it is often only one of many factors that contribute to lasting attraction.
- Similarity: People are more likely to be drawn to others who share similar interests, beliefs, and values, fostering a sense of mutual understanding.
- Proximity: The more often we interact with someone, the more likely it is that we will develop feelings of attraction toward them.
- Reciprocity: Mutual liking and the exchange of positive feelings can help build and reinforce relationships.
Stages of Relationship Development
Relationships typically evolve in stages, with each phase contributing to a deeper bond between individuals:
- Initiation: The first stage involves meeting and forming an initial impression of the other person, often based on surface-level factors like appearance or behavior.
- Exploration: During this phase, individuals begin to share personal information and discover common interests, which can deepen the connection.
- Commitment: As trust and understanding grow, relationships may evolve into committed partnerships, where both individuals invest more emotionally and practically.
- Maintenance: Long-term relationships require ongoing effort to nurture and sustain, often involving open communication and shared goals.
Exploring Aggression in Social Contexts
Aggression is a behavior that often arises from interactions within groups and environments, manifesting in various forms such as verbal confrontations, physical actions, or hostile attitudes. While aggression can be driven by individual factors, its expression is heavily influenced by the context in which it occurs. The dynamics of social settings, such as group pressures, cultural norms, and perceived threats, all contribute to how and when aggressive behaviors are triggered. Understanding these influences is key to addressing and managing aggression in both personal and collective situations.
In social contexts, aggression can be seen as both a response to specific situations and a learned behavior that evolves over time. Factors such as frustration, environmental stress, and social comparisons play significant roles in increasing the likelihood of aggressive actions. Additionally, the way aggression is reinforced or punished in a community can either escalate or reduce its occurrence. Exploring the factors that contribute to aggression within social settings is crucial for developing strategies to reduce its negative impact.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Frustration | When individuals face barriers or obstacles in achieving their goals, frustration can lead to hostile reactions. |
| Group Dynamics | In group settings, peer pressure and collective behavior can heighten aggressive tendencies, particularly in competitive environments. |
| Cultural Influence | Norms and values within a culture may either condone or discourage aggressive actions, influencing how individuals behave in various situations. |
| Media Exposure | Exposure to violence in media can desensitize individuals to aggression, making it more acceptable or normal in their daily lives. |
| Deindividuation | In large groups or anonymous settings, individuals may feel less accountable for their actions, increasing the likelihood of aggressive behavior. |
In summary, aggression in social contexts is shaped by a variety of internal and external factors, including emotional states, group dynamics, and cultural influences. By examining how these elements interact, we can better understand the roots of aggressive behavior and explore ways to reduce its impact on individuals and communities.
Helping Behavior and Altruism
Helping behavior refers to actions taken to assist others in need, often driven by empathy, moral values, or a sense of responsibility. Altruism, a related concept, involves selflessly acting for the benefit of others, sometimes even at a personal cost. These behaviors play an essential role in maintaining social harmony and cooperation, and they are often influenced by the environment, personal experiences, and situational factors. Understanding why people help others–and what motivates them to act selflessly–is key to fostering a supportive and caring society.
Factors Influencing Helping Behavior
Helping behavior can be influenced by a variety of psychological, social, and situational factors. Some of the key elements that affect whether individuals choose to assist others include:
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others often leads people to offer help when someone is in distress.
- Social Norms: Cultural expectations and moral guidelines can motivate individuals to act in ways that align with societal standards, such as helping those in need.
- Group Membership: People are more likely to assist others who belong to the same group or community, based on a sense of shared identity.
- Personal Experience: Those who have previously received help or faced hardship may be more inclined to help others in return.
Altruism and Its Impact

Altruism represents a higher level of helping behavior, where individuals act out of a genuine desire to improve the well-being of others, often without expecting anything in return. Altruistic actions have been linked to positive psychological outcomes, such as a sense of fulfillment and increased life satisfaction. In addition, altruism fosters stronger social bonds and creates a ripple effect, encouraging others to act in similar ways.
Despite its many positive aspects, altruism is not always guaranteed, as individuals may hesitate to help due to factors like fear of rejection or uncertainty about the outcomes. However, in situations where people feel a strong sense of moral obligation or empathy, they are more likely to engage in altruistic acts. Understanding the motivations behind helping behavior and altruism can help communities create environments that encourage cooperation and mutual support.
Social Psychological Research Methods
Research in this field seeks to explore human behavior, group dynamics, and the factors that influence interactions within society. To understand how individuals think, feel, and act in various social contexts, researchers use a variety of methods to gather and analyze data. These methods help draw conclusions about the underlying psychological principles and mechanisms that drive behaviors, attitudes, and perceptions. The most commonly used approaches include experiments, surveys, observational studies, and case studies, each offering distinct advantages and limitations.
Experimental research allows scientists to manipulate variables and establish cause-and-effect relationships. In contrast, surveys offer a broader view of population trends, while observational techniques enable the study of behaviors in natural settings. Case studies provide in-depth insights into specific individuals or groups. By employing these methods, researchers can form conclusions that guide future theories and practical applications within the field.
The choice of method depends on the research question and the specific context of the study. Each approach offers a different lens through which to view the complexities of human behavior and interaction.
Application of Social Psychology in Real Life
The insights gained from examining human behavior in group settings extend far beyond academic theory. They influence various aspects of our everyday lives, from the way we interact with others to how we make decisions and respond to external influences. Understanding the forces that shape attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors has practical implications in diverse areas such as education, business, healthcare, and even law enforcement.
One of the primary applications of these principles is in improving communication and teamwork within organizations. By recognizing the impact of group dynamics, leaders can foster more effective collaboration and reduce conflicts. Similarly, the ability to influence attitudes and behaviors is crucial in marketing, where companies utilize persuasive tactics to reach potential customers.
Key Areas of Application
- Education: Enhancing teacher-student interactions and developing strategies for conflict resolution.
- Healthcare: Understanding patient behavior to improve treatment compliance and healthcare outcomes.
- Law Enforcement: Applying principles to reduce prejudice, enhance community relations, and prevent conflicts.
- Marketing: Using insights on persuasion and consumer behavior to design effective advertising strategies.
By applying the concepts of behavior and group interaction to real-world problems, individuals and organizations can address societal challenges, improve interpersonal relations, and create a more cooperative environment in various fields.
Challenges in Social Psychology Research
Research in the field of human behavior presents a range of unique obstacles, largely due to the complexity of human interactions and the variability of external factors. Unlike controlled lab experiments, real-world environments introduce a multitude of variables that can be difficult to account for. This unpredictability often complicates the drawing of definitive conclusions, making it essential for researchers to use nuanced methods to capture the full range of human behaviors.
One major challenge is ensuring that research findings are generalizable across different groups of people. Cultural, societal, and individual differences can lead to variations in how people react to similar situations, which makes it difficult to apply results from a specific study to a broader population. Moreover, ethical concerns around participant consent and privacy can limit the types of experiments that can be conducted, especially those that involve sensitive issues or vulnerable groups.
Key Issues in Research
- Ethical Concerns: Balancing the need for authentic data with the protection of participants’ rights and well-being.
- Generalization: Difficulty in applying findings from a small, specific sample to a wider population.
- Complexity of Variables: Accounting for the many external influences that affect human behavior in real-life settings.
- Replication Crisis: The challenge of replicating studies to ensure reliability and validity of results.
These challenges require careful consideration and innovative methods to ensure the integrity and applicability of research. Despite these difficulties, advancements in research methodologies and ethical guidelines continue to enhance the understanding of human behavior and its complexities.