
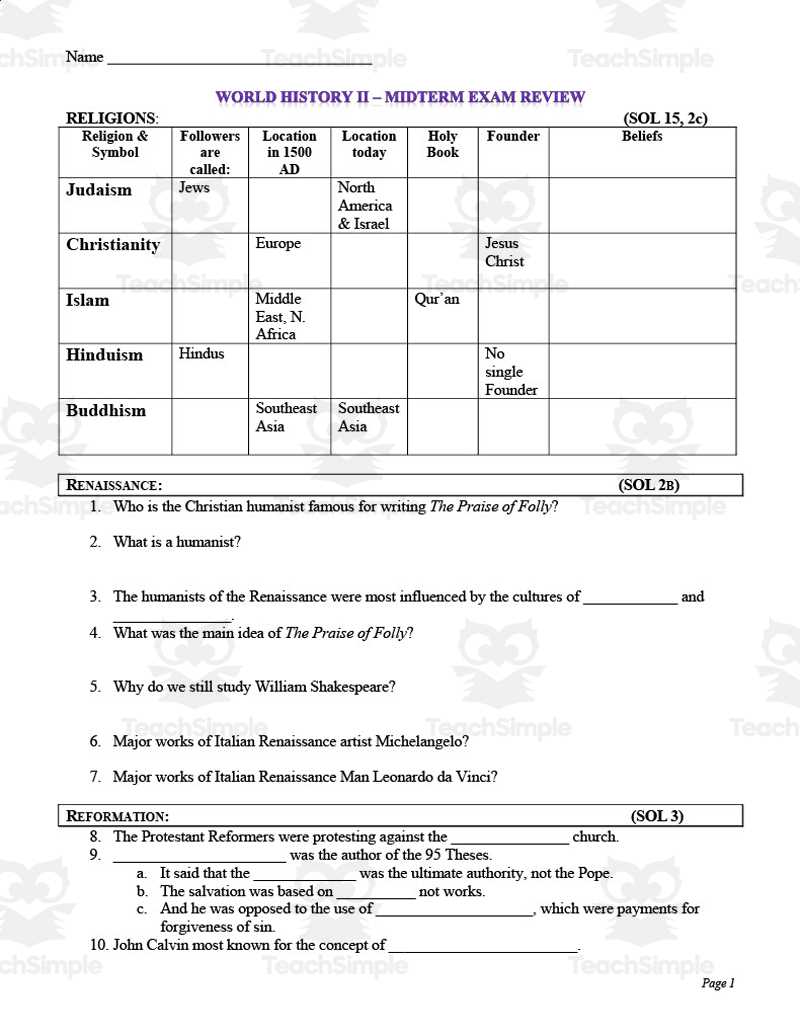
As you prepare to tackle the key topics covered in this course, it’s important to focus on the main events, figures, and movements that shaped the nation’s development. From pivotal moments to influential individuals, understanding these core elements will help you navigate the material effectively.
Through a deeper exploration of political, social, and economic changes, you can gain a clearer perspective on how different periods influenced one another. Reviewing essential concepts will enable you to approach questions with confidence and clarity.
By reflecting on the most significant occurrences and their lasting impact, you can strengthen your understanding of the subject. This section will help you cover the material comprehensively, ensuring you are well-prepared for any challenge that may arise.
US History 2 Final Exam Study Guide Answers

This section focuses on the most crucial topics that you will encounter in the course. Understanding the key moments and figures that defined the nation’s path will be essential to your success. By breaking down significant events and movements, you can get a clearer view of the interconnectedness of the past and how it shapes the present.
In this part of the course, you’ll find an overview of political, social, and economic developments. Recognizing the influence of these factors will help you identify patterns and understand the larger forces at play throughout different periods.
To succeed, it’s important to focus on the major themes and how they relate to one another. By examining the impact of certain decisions and shifts, you can better prepare for various questions and assessments. A strong grasp of these central ideas will help you approach the material with confidence.
Key Topics to Review for Exam
To effectively prepare for the upcoming assessment, it’s essential to focus on the primary subjects and events that have shaped the nation’s path. These key moments represent turning points that influenced not only the country’s future but also its political, economic, and social structures. Familiarizing yourself with these topics will provide a strong foundation for understanding how the past has influenced the present.
Here are some of the most critical areas to focus on for your review:
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Reconstruction Era | Rebuilding the South, Civil Rights Amendments, Freedmen’s Bureau |
| Industrialization | Rise of big business, labor movements, economic shifts |
| World War I | US involvement, military strategies, global impact |
| The Great Depression | Stock market crash, New Deal policies, economic recovery |
| World War II | US entry, wartime economy, post-war influence |
| The Civil Rights Movement | Key leaders, landmark legislation, social changes |
Focusing on these topics will help you gain a comprehensive understanding of the material. Each represents a crucial phase in the nation’s development and will be vital for answering questions related to political, social, and economic changes.
Understanding Major Historical Events
Key events played a defining role in shaping the course of the nation’s development. These pivotal moments reflect the challenges, decisions, and shifts that have impacted the political, economic, and social landscape over time. Grasping the significance of these events allows for a deeper understanding of how the country arrived at its present state.
The American Civil War
The Civil War remains one of the most transformative events in the nation’s history. It not only led to the abolition of slavery but also brought about significant changes in the structure of the government and the relationship between the states and the federal government. Some of the main elements to focus on include:
- Key battles and military strategies
- Major political decisions, such as the Emancipation Proclamation
- The role of figures like Abraham Lincoln and Robert E. Lee
- The war’s aftermath and Reconstruction efforts
The Great Depression
The Great Depression was another critical event that shaped the nation. It was marked by widespread economic hardship, mass unemployment, and the collapse of financial institutions. Understanding the key factors leading to the Depression and the subsequent recovery efforts is essential. Important points include:
- The stock market crash of 1929
- The creation of New Deal programs and their impact
- Social changes during the 1930s
- The role of President Franklin D. Roosevelt in recovery
These events, along with others, represent turning points that offer valuable insights into the ongoing development of the nation. Recognizing their influence will help you understand the broader context and connections between different historical periods.
Important Figures in US History
Throughout the nation’s development, certain individuals have left an indelible mark on its progress. Their actions, decisions, and leadership have shaped political, social, and economic landscapes, influencing the direction of the country. Understanding the roles of these key figures provides crucial insight into the forces that have driven change over time.
Abraham Lincoln
As the 16th president, Abraham Lincoln’s leadership during one of the most turbulent periods in the nation’s past cannot be overstated. His efforts to preserve the Union during the Civil War, along with his role in the abolition of slavery, positioned him as one of the most significant leaders in American history. Key aspects of his legacy include:
- Emancipation Proclamation and the fight for freedom
- His leadership during the Civil War
- His role in shaping the post-war Reconstruction plans
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt’s presidency, which spanned from 1933 to 1945, is marked by his leadership during the Great Depression and World War II. His vision and policies during these crises helped reshape the nation’s approach to government and economics. Essential contributions include:
- New Deal programs and social security reforms
- His leadership during the global conflict of WWII
- Efforts to transform the role of the federal government
These figures, along with others, played pivotal roles in influencing the country’s development and direction. By studying their contributions, you can better understand the broader themes and events that have defined the nation’s journey.
Analyzing Key Political Movements
Throughout the nation’s evolution, several political movements have shaped the direction of policies and governance. These movements reflect the changing ideals, struggles for rights, and shifting power dynamics that have altered the course of American society. Understanding the goals, challenges, and outcomes of these movements is essential for grasping how political decisions have influenced the nation’s development.
The Civil Rights Movement

The Civil Rights Movement, primarily during the 1950s and 1960s, sought to end racial segregation and discrimination against African Americans. Led by prominent figures like Martin Luther King Jr., Rosa Parks, and Malcolm X, this movement brought significant legal and social changes to the country. Some key aspects of the movement include:
- Nonviolent resistance and protest actions
- Landmark events such as the March on Washington
- Passing of crucial legislation like the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Women’s Suffrage Movement
The Women’s Suffrage Movement was a long-fought battle for women’s right to vote, culminating in the 19th Amendment in 1920. This movement, which spanned several decades, involved tireless efforts by leaders such as Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton. Key elements of this movement include:
- Campaigns for equality and women’s political involvement
- Organized protests and demonstrations for voting rights
- Impact of the 19th Amendment on women’s roles in public life
By analyzing these and other political movements, one can better understand how collective action and public pressure have influenced policy changes and shaped modern governance.
Significant Wars and Their Impact
Wars have played a central role in shaping the course of nations, influencing political decisions, social dynamics, and economic strategies. The outcomes of major conflicts often redefine international relations and domestic policies, leaving lasting legacies on countries and their people. Understanding the key wars and their repercussions helps us see how military actions can alter the trajectory of a nation’s development.
The Civil War
The Civil War, fought between the Union and the Confederacy from 1861 to 1865, was a defining conflict in the nation’s path. The war’s consequences went beyond the battlefield, leading to the abolition of slavery, shifts in political power, and deep social changes. The major outcomes include:
- End of slavery and the passage of the 13th Amendment
- Strengthened federal government authority
- Economic transformation in the Southern states
World War II
World War II, spanning from 1939 to 1945, was another pivotal conflict that had profound effects on both the US and the global stage. The war led to significant shifts in global power, and the United States emerged as a dominant world superpower. Some of the major impacts include:
- Economic recovery through wartime production and the rise of the US as an industrial leader
- The creation of the United Nations and the beginning of the Cold War
- Social changes, including increased participation of women in the workforce
| War | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| The Civil War | Abolition of slavery, strengthened Union, and political shifts |
| World War II | Global influence, economic boom, and the rise of the Cold War |
| Vietnam War | Domestic unrest, changes in foreign policy, and military engagement shifts |
Each of these significant conflicts contributed to reshaping national policies, social structures, and international relations, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of war.
Essential Supreme Court Cases
The decisions made by the nation’s highest court have had a profound impact on the legal landscape, influencing the interpretation of the Constitution and setting precedents that shape the law for generations. Landmark rulings often address critical issues that affect individual rights, government powers, and societal norms. Understanding these key cases provides valuable insight into how the legal system has evolved over time and continues to influence everyday life.
Among the most important cases are those that have had far-reaching consequences in areas such as civil rights, government authority, and economic regulation. These decisions are not only critical for understanding legal principles but also for grasping how the court has balanced individual freedoms with national interests.
Some essential cases to consider include:
- Marbury v. Madison (1803) – Established judicial review, affirming the Court’s role in interpreting the Constitution.
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954) – Ended racial segregation in public schools, marking a major victory for civil rights.
- Roe v. Wade (1973) – Recognized a woman’s right to choose an abortion under the Constitution.
- Miranda v. Arizona (1966) – Required police to inform suspects of their rights before interrogation.
- United States v. Nixon (1974) – Limited presidential power, asserting that no one, not even the president, is above the law.
These cases, along with others, have defined the relationship between the individual and the state, offering guidance on everything from freedom of speech to the scope of governmental authority. They continue to shape legal arguments and decisions in courtrooms across the nation.
Economic Shifts Through US History

The economic landscape of the nation has undergone significant transformations over the centuries, driven by both internal and external factors. These shifts reflect changes in production, trade, labor, and technological advancements that have reshaped the workforce and overall economic structure. Understanding these shifts reveals how the economy has adapted to challenges such as war, technological innovation, and shifting global markets.
From the early days of agricultural dependence to the rise of industrial power and the service-driven economy of the modern era, each period has brought distinct changes that impacted individuals and businesses alike. These transitions not only influenced domestic policies but also altered the United States’ position in the global economy.
Key economic shifts include:
- The Industrial Revolution – A period of rapid growth in manufacturing, particularly in the North, that transformed the nation’s economy in the late 19th century.
- The Great Depression – A catastrophic economic downturn in the 1930s that led to widespread unemployment, poverty, and major reforms like Social Security.
- Post-WWII Economic Boom – A time of unprecedented growth, increased consumer spending, and the expansion of the middle class following the end of the Second World War.
- The Rise of Technology and Globalization – The shift toward a technology-driven economy in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, with a focus on information technology, outsourcing, and global trade.
These shifts have left lasting impacts, redefining how Americans work, consume, and engage with the world economy. By analyzing these changes, one can better understand how economic factors continue to shape the nation’s growth and challenges.
Social Changes and Their Effects
Throughout the nation’s development, societal shifts have been a driving force behind transformative changes in culture, politics, and everyday life. These changes often stem from movements advocating for equality, justice, and new social norms. Over time, the collective actions of individuals and groups have reshaped values, influenced policies, and altered the fabric of society in profound ways.
Key social changes have had far-reaching impacts, influencing everything from civil rights to gender roles, education, and family structures. The ripple effects of these changes can still be felt today, as new generations build upon the groundwork laid by those who challenged the status quo.
Some significant social shifts and their effects include:
- The Civil Rights Movement – Brought about significant legislative changes that led to the desegregation of public spaces and guaranteed voting rights for African Americans.
- The Women’s Liberation Movement – Challenged traditional gender roles and pushed for equal rights in the workplace, politics, and education, leading to policy changes like the Equal Pay Act.
- Immigration Reform – Major waves of immigration reshaped the nation’s demographics, bringing cultural diversity and driving debates around citizenship and national identity.
- LGBTQ+ Rights Movement – Advocated for equal rights and recognition for the LGBTQ+ community, culminating in significant legal victories such as the legalization of same-sex marriage.
These shifts have reshaped social dynamics and continue to influence public debates and policies. They highlight the power of collective action in shaping a more inclusive society, where the values of equality, freedom, and justice are continuously reevaluated and pursued.
The Role of the US Constitution

The Constitution serves as the foundational framework for the government, establishing the guiding principles that shape the structure and operation of the nation. It outlines the distribution of powers, protects individual rights, and provides a system of checks and balances to ensure that no single branch of government becomes too powerful. Over time, its interpretation has evolved, adapting to the changing needs of society while remaining a cornerstone of the legal and political system.
At its core, the Constitution defines the relationship between the federal government and the states, guaranteeing certain freedoms and liberties to individuals. It has served as a critical tool for resolving conflicts, ensuring justice, and maintaining stability in the face of societal changes and challenges.
Key aspects of the Constitution include:
- Separation of Powers – Divides the government into three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial, each with distinct powers and responsibilities.
- Checks and Balances – Ensures that no single branch becomes too dominant by allowing each branch to limit the powers of the others.
- Bill of Rights – The first ten amendments, which safeguard individual freedoms such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial.
- Amendment Process – Allows the Constitution to be updated and adapted to reflect evolving societal values and needs.
The enduring relevance of the Constitution lies in its ability to provide a stable yet flexible framework that governs the nation, ensuring that democracy, justice, and equality continue to guide the actions of both the government and the people.
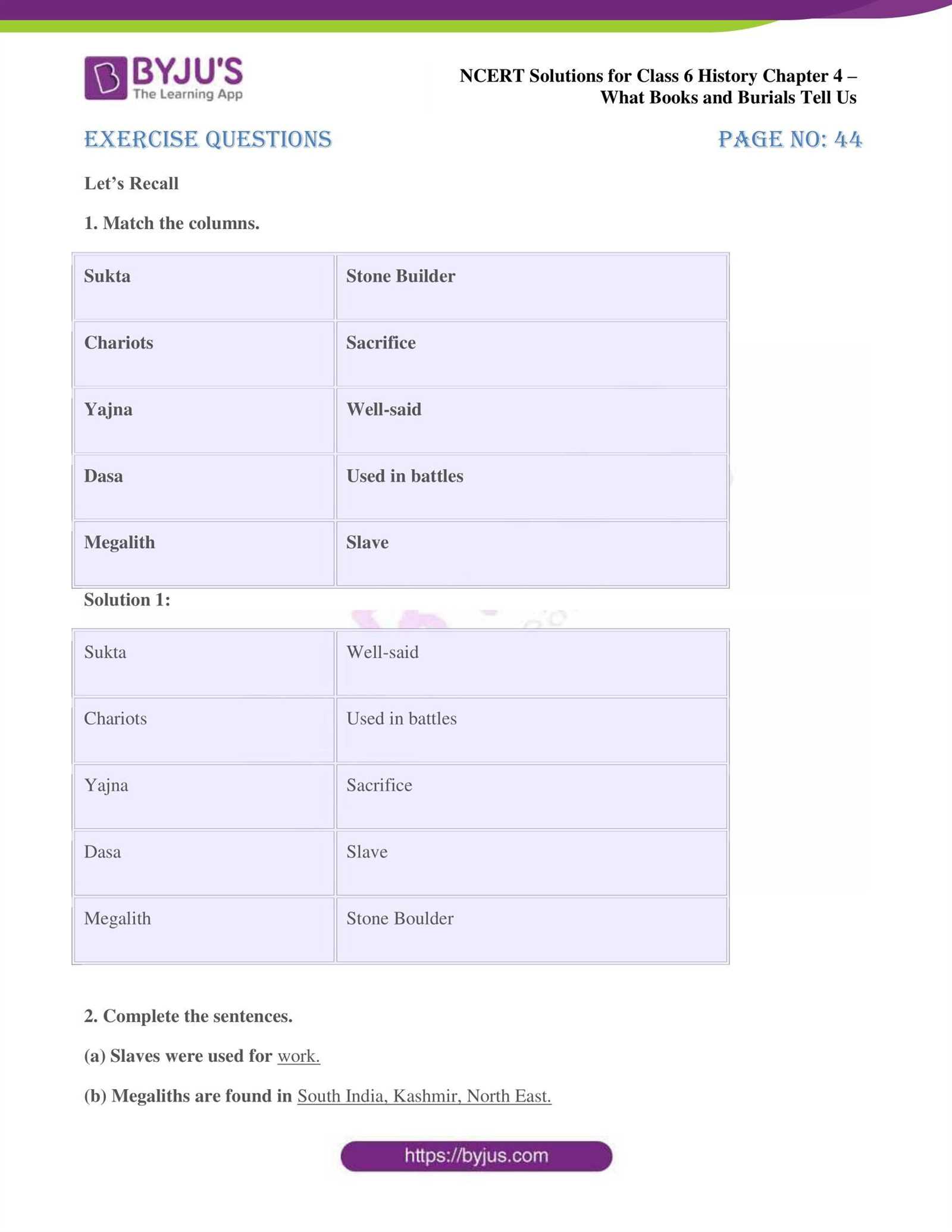
Reconstruction Era Explained
Following the end of the Civil War, the nation entered a period of rebuilding and reconciliation. This era, marked by significant political, social, and economic challenges, focused on integrating the Southern states back into the Union and addressing the rights of newly freed African Americans. The period also involved establishing new laws and policies to promote equality, though it was a time of deep division and resistance in many regions.
At its core, the Reconstruction era sought to redefine the nation’s identity, repair the damages caused by war, and establish a more inclusive society. However, it was also fraught with tension, as differing views on race, politics, and governance created significant obstacles to lasting progress.
Key Events and Policies of the Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction period was shaped by a number of major policies and events that had a lasting impact on the nation. Some of these efforts laid the foundation for civil rights, while others resulted in setbacks and challenges.
| Event/Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| 13th Amendment | Abolished slavery throughout the United States. |
| 14th Amendment | Granted citizenship and equal protection under the law to all persons born or naturalized in the U.S. |
| 15th Amendment | Prohibited denying the right to vote based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude. |
| Freedmen’s Bureau | Provided assistance to freed slaves and poor whites in the South through education, healthcare, and employment support. |
| Black Codes | State laws in the South that severely restricted the rights of African Americans, aiming to maintain a labor force under a system resembling slavery. |
Challenges and Legacy of Reconstruction
While the Reconstruction period made significant strides in ensuring legal rights for African Americans, it was marked by violent opposition and social resistance, particularly in the South. The eventual end of Reconstruction led to the rise of segregation and the disenfranchisement of African Americans for many decades. However, the legacy of the Reconstruction era continues to influence civil rights movements and legal reforms that followed.
Despite its challenges, the Reconstruction period played a crucial role in shaping the future direction of the United States, setting the stage for the eventual expansion of civil rights and the ongoing struggle for racial equality.
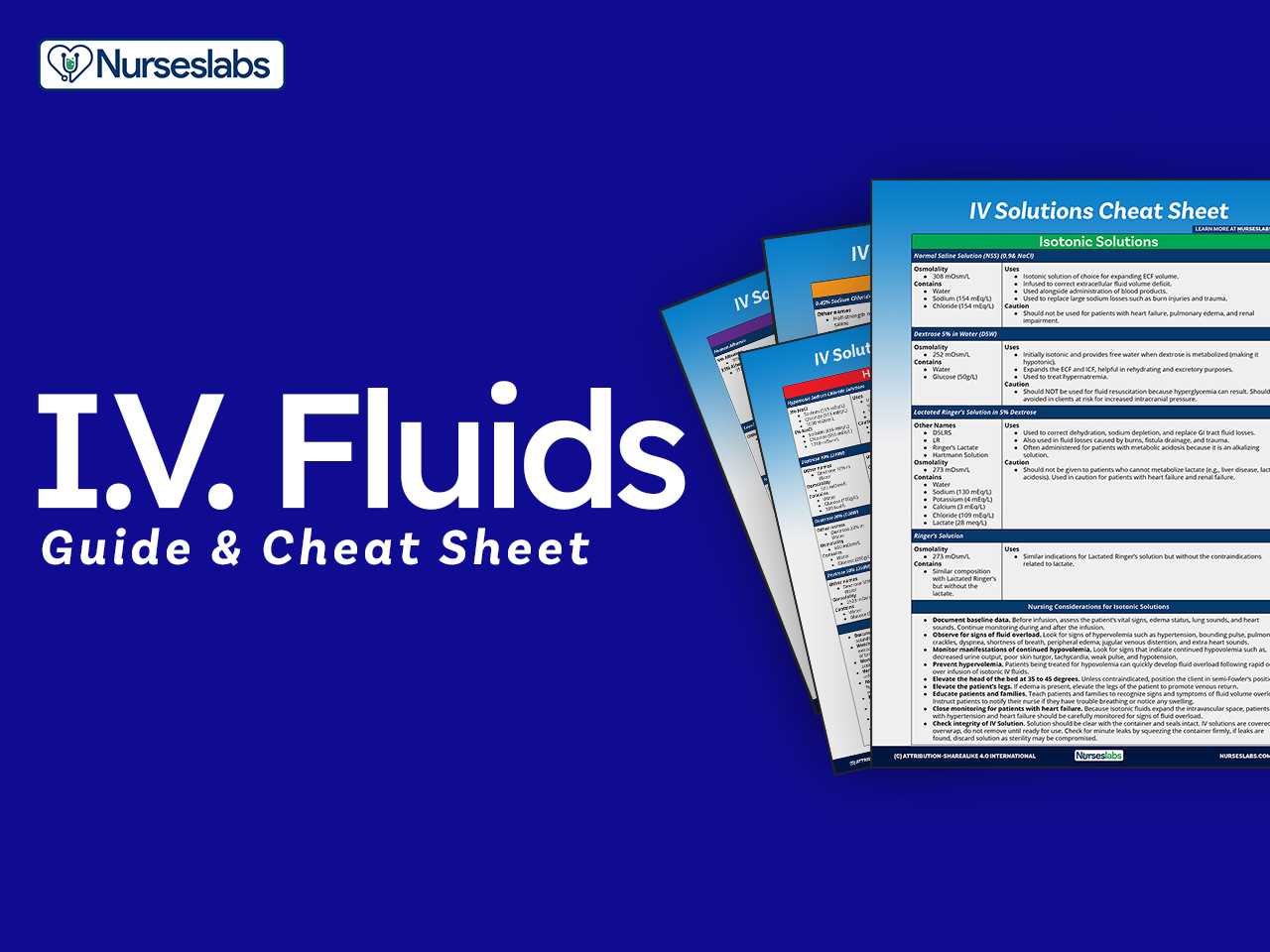
The Great Depression Overview
The period of economic hardship that began in the late 1920s and lasted throughout much of the 1930s had a profound impact on the lives of millions of Americans. This challenging time was marked by widespread poverty, joblessness, and social unrest, as the economy contracted at an alarming rate. As businesses failed, banks collapsed, and unemployment soared, the country faced a deep crisis that reshaped its economic and political landscape.
While the causes of the Great Depression were complex and multifaceted, it is often attributed to factors such as the stock market crash of 1929, banking failures, agricultural overproduction, and global trade disruptions. The resulting economic collapse not only affected individual families but also had far-reaching consequences for the nation’s infrastructure, government policies, and social fabric.
Key Features of the Great Depression
The effects of the Great Depression were felt across various sectors of society. Key characteristics of this period include:
- Mass Unemployment – At the peak of the Depression, unemployment rates reached about 25%, leaving millions of workers without jobs and creating widespread poverty.
- Bank Failures – As banks collapsed due to unpaid loans and a loss of public trust, many Americans lost their savings, further deepening the financial crisis.
- Decline in Industrial Production – Factories shut down, and industrial output plummeted, as demand for goods decreased sharply.
- Stock Market Crash – The stock market crash in 1929 is often seen as the triggering event, sparking the widespread economic downturn.
- Impact on Agriculture – Farmers faced a difficult time with falling crop prices, droughts, and the Dust Bowl, leading to widespread displacement and poverty in rural areas.
Government Response and Recovery Efforts
In response to the crisis, the federal government introduced several relief programs and reforms aimed at stabilizing the economy and providing support to those in need. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal, which included initiatives such as public works projects, financial reforms, and social security programs, played a central role in efforts to revitalize the economy.
While the Great Depression officially ended by the late 1930s, its effects were long-lasting, influencing government policies, economic theories, and social structures for decades to come. The lessons learned during this period continue to shape the nation’s response to economic crises today.
World War II in US Context
The global conflict that began in the late 1930s had a significant impact on the United States, both on the home front and in shaping its position on the world stage. While the country initially maintained a policy of neutrality, various events and pressures eventually led to its active involvement in the war. This period not only altered the course of American foreign policy but also catalyzed major social and economic changes within the country.
The U.S. entered the conflict after the attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941, which prompted a formal declaration of war against the Axis powers. The nation’s military and industrial efforts during the war contributed to a swift recovery from the effects of the Great Depression, as factories converted to war production and millions of Americans were employed in the war effort.
Key Aspects of U.S. Involvement
- Military Mobilization – The U.S. rapidly expanded its armed forces, recruiting millions of soldiers and building a formidable military presence in both the Pacific and European theaters.
- Industrial Production – American factories shifted to producing war materials, such as tanks, aircraft, and munitions, boosting the economy and providing jobs to millions.
- Allied Partnerships – The U.S. formed crucial alliances with nations such as the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, contributing to joint military strategies and resources.
- Home Front Contributions – Civilians played a vital role through war bond purchases, rationing, and working in defense industries, helping to sustain the war effort.
Impact on U.S. Society and Economy

The effects of the war on American society were profound, with lasting changes to its workforce and cultural landscape. Many women entered the workforce in unprecedented numbers, particularly in manufacturing and technical jobs, while African Americans also found new opportunities in wartime industries. The war also catalyzed significant changes in the civil rights movement as returning soldiers demanded equality and fair treatment.
On the economic front, the U.S. emerged from the war as a global superpower, having played a central role in the defeat of the Axis powers. The post-war period saw rapid growth in industrial output and the rise of the U.S. as the world’s dominant economic force. The war also set the stage for the Cold War, as the U.S. and the Soviet Union became the two leading superpowers, each vying for global influence.
Overall, the United States’ involvement in World War II transformed it in ways that shaped its domestic policies, its economic outlook, and its role in global affairs for generations to come.
Cold War Developments and Impact
The Cold War, which began in the aftermath of World War II, was characterized by intense political and ideological rivalry between two major superpowers: the United States and the Soviet Union. This period was marked by both cooperation and confrontation as these nations competed for global influence, leading to a series of significant events that reshaped international relations and had profound effects on domestic policies in the U.S. and other nations.
The rivalry primarily involved military, economic, and cultural strategies rather than direct warfare. Tensions escalated through a series of proxy wars, nuclear arms races, and diplomatic stand-offs, such as the Cuban Missile Crisis. This era also saw the formation of key alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact, which further divided the world into competing spheres of influence.
Key Developments During the Cold War
- Nuclear Arms Race – Both the U.S. and the Soviet Union stockpiled nuclear weapons, leading to fears of mutually assured destruction and global instability.
- Space Race – The competition extended into space exploration, with both countries striving to achieve technological superiority by launching satellites and sending astronauts into orbit.
- Proxy Wars – The Cold War played out in various regions of the world, with both superpowers supporting opposing factions in conflicts in Korea, Vietnam, Afghanistan, and elsewhere.
- Berlin Crisis – The division of Germany and the city of Berlin became a symbol of the broader ideological divide between East and West.
Impact on U.S. Society and Foreign Policy

The Cold War deeply influenced U.S. foreign policy, with an emphasis on containing the spread of communism. This led to military interventions and diplomatic efforts to support democratic nations and undermine communist regimes worldwide. The U.S. also engaged in economic aid programs, such as the Marshall Plan, to stabilize Europe and prevent the rise of communist influence in the aftermath of the war.
Domestically, the Cold War heightened fears of communism, resulting in the Red Scare and the rise of McCarthyism. These events led to widespread government investigations, blacklisting, and political repression aimed at identifying communist sympathizers. The period also witnessed significant developments in U.S. civil rights, as the global competition between the U.S. and the Soviet Union put pressure on the U.S. to live up to its democratic ideals, leading to significant social changes.
| Key Event | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cuban Missile Crisis | 1962 | Brink of nuclear war, leading to a shift toward arms control and diplomacy. |
| Vietnam War | 1955–1975 | U.S. involvement in a failed attempt to stop the spread of communism in Southeast Asia. |
| Berlin Wall Construction | 1961 | Symbolized the division of Europe and marked the height of Cold War tensions. |
| Space Race | 1957–1969 | Competition to achieve space exploration milestones, highlighting technological rivalry. |
Overall, the Cold War left an indelible mark on global politics and U.S. domestic affairs. The tension between the two superpowers led to critical advancements in technology, but also to challenges in international diplomacy and domestic security that continued to shape the world well into the late 20th century.
US Civil Rights Movements
The struggle for equal rights in the United States has been a defining feature of the nation’s social and political landscape, with various groups advocating for the recognition of their fundamental freedoms and opportunities. Over the decades, several movements emerged, each aiming to dismantle systems of inequality and provide greater justice for marginalized communities. These efforts brought about profound legal, social, and cultural shifts that reshaped American society.
The fight for civil rights involved not only legal battles but also protests, acts of defiance, and widespread mobilization across the country. These movements were fueled by the desire for racial equality, gender rights, labor protections, and other essential freedoms that were often denied to large segments of the population. At the heart of these movements were individuals and organizations that challenged the status quo and inspired change through nonviolent resistance, legal advocacy, and public demonstrations.
Key Movements and Milestones

- African American Civil Rights Movement – The most prominent of the civil rights struggles, this movement sought to end racial segregation and discrimination against African Americans, culminating in landmark legislation such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
- Women’s Liberation Movement – Aimed at securing equal rights for women in areas such as employment, education, and reproductive rights, leading to significant legal reforms like the Equal Pay Act of 1963 and Title IX in 1972.
- LGBTQ+ Rights Movement – Focused on achieving equal rights and social acceptance for the LGBTQ+ community, achieving victories such as the legalization of same-sex marriage and the repeal of “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell.”
- Labor Rights Movement – Advocated for fair wages, better working conditions, and the right to unionize, resulting in the formation of unions and the establishment of labor laws that protect workers’ rights.
The efforts of countless activists, both well-known and unknown, were instrumental in pushing forward societal change. From the peaceful protests led by figures like Martin Luther King Jr. to the legal battles fought by groups such as the NAACP, these movements sought to create a more inclusive and just society. They also brought to light the importance of intersectionality, showing how various forms of oppression were interconnected and required collective action to overcome.
The impact of these movements extended beyond legal victories. They transformed cultural norms, shifting public attitudes and creating a more inclusive environment for future generations. While challenges remain, the strides made by these movements serve as a reminder of the ongoing pursuit of equality and justice in the United States.
Tips for Final Exam Success
Achieving success in your academic assessments requires more than just last-minute cramming. To perform well, it is important to follow a structured approach that focuses on understanding key concepts, managing time effectively, and maintaining a calm mindset. By applying the right strategies, you can increase your chances of excelling when it’s time to demonstrate your knowledge.
Effective Preparation Techniques
- Start Early – Begin your preparation well ahead of the assessment period. This allows you to break down the material into manageable chunks and reduces the pressure of cramming at the last minute.
- Create a Study Plan – Outline what topics need to be covered each day. Allocate enough time to review challenging material and ensure that all key subjects are addressed.
- Use Active Learning – Engage with the material in an active manner. Take notes, summarize key points, and ask yourself questions to test your understanding.
- Practice with Past Materials – Reviewing previous tests, quizzes, or practice questions helps you get familiar with the format and pinpoint areas where you need to improve.
Test-Taking Strategies
- Stay Calm and Confident – Anxiety can cloud your thinking. Before the assessment, practice deep breathing exercises and keep a positive attitude to boost your confidence.
- Manage Your Time – During the test, allocate specific time limits for each section or question to ensure that you don’t spend too much time on any one part.
- Read Instructions Carefully – Understand what is being asked in each question. Ensure you address all parts of the question and provide detailed responses where necessary.
- Review Your Answers – If time permits, double-check your responses for accuracy and completeness before submitting your work.
Success in academic assessments doesn’t rely solely on memorizing facts but on understanding the material, managing time effectively, and keeping a calm mindset. By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you will be better prepared to demonstrate your knowledge and perform confidently under pressure.