
Success in any comprehensive assessment requires a solid understanding of key concepts, events, and figures. This section is designed to help you consolidate knowledge and prepare effectively for your upcoming challenge. By focusing on critical themes, you can approach your preparation with confidence and clarity.
Strategic preparation is the key to mastering a wide range of material. This guide will help you navigate through essential topics, emphasizing significant milestones, influential individuals, and pivotal moments that shaped the world. By organizing your study sessions around these core elements, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Whether you are reviewing past content or reinforcing new material, adopting a focused approach will ensure that you are well-prepared. Keep in mind that effective study habits and time management are just as important as the content itself. Approach each topic systematically, and make sure to prioritize areas that are more challenging to ensure a well-rounded grasp of the material.
World History Final Exam Review Packet
When preparing for a comprehensive assessment of past events, it is essential to focus on the most significant concepts and developments that have influenced societies throughout time. The aim is to understand the key moments that shaped political, social, and economic structures globally. By organizing your study into manageable sections, you can more easily grasp complex topics and create a strong foundation for your knowledge.
Understanding critical themes and analyzing influential figures will allow you to connect different periods and recognize patterns across various civilizations. Studying the major transformations–whether through revolutions, discoveries, or conflicts–will deepen your understanding of how the world evolved. Concentrate on the underlying factors that caused changes and the long-term effects they had on societies and cultures.
While preparing for this type of assessment, consider reviewing the essential skills needed for interpreting primary sources, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, and understanding historical context. In addition, practicing with past materials and summarizing key points can be highly beneficial for reinforcing your knowledge and boosting confidence.
Key Topics to Focus On

To effectively prepare for any comprehensive assessment, it’s important to prioritize the core concepts that have shaped civilizations throughout time. Identifying the key subjects will help you focus on the most impactful developments, figures, and events. By honing in on these critical areas, you’ll build a strong understanding of how different cultures evolved and interacted over time.
Focus on significant moments that triggered change, such as revolutions, innovations, and the rise and fall of empires. Pay attention to the political, economic, and social systems that defined societies and the individuals who influenced these structures. Understanding the connections between different regions and how global events shaped one another is also crucial for a comprehensive grasp of the material.
Important Dates and Events
To truly understand the course of human development, it’s essential to recognize the significant moments that have altered the direction of societies. Certain events marked turning points, changing the trajectory of nations, economies, and cultures. These milestones are often linked to key figures, conflicts, discoveries, and political movements that shaped the world.
Focusing on these pivotal occurrences helps put into context the broader trends and shifts that influenced later developments. Whether it’s the founding of powerful empires, the signing of crucial treaties, or the initiation of transformative movements, remembering these key dates is vital for a comprehensive understanding of past achievements and struggles.
Understanding Historical Movements
Throughout time, various movements have emerged that drastically reshaped societies, challenging the status quo and driving change. These movements often began with the efforts of a few individuals or groups but evolved into larger forces that transformed politics, economics, and culture. Understanding the core principles and motivations behind these movements is essential to grasp how civilizations progressed and adapted.
Key Movements to Explore

- Revolutions – These often marked the overthrow of oppressive systems, whether through political, social, or economic means.
- Enlightenment – A period of intellectual transformation that emphasized reason, individualism, and skepticism of authority.
- Industrialization – A movement that changed economies from agricultural to industrial, affecting labor, urbanization, and global trade.
- Nationalism – The rise of national identity and the push for independence or unification of states.
- Colonialism and Imperialism – The expansion of empires, resulting in cultural exchanges, exploitation, and conflict across regions.
Influential Figures and Their Impact

- Napoleon Bonaparte – His leadership changed the political landscape of Europe and spread revolutionary ideals.
- Karl Marx – His writings inspired numerous socialist movements and challenged capitalist structures.
- Martin Luther – Sparked the Protestant Reformation, challenging the authority of the Catholic Church and reshaping religious practice.
- Mahatma Gandhi – Led non-violent movements for independence and social reform in India, influencing global protest strategies.
Major World Leaders and Their Impact
Throughout time, certain individuals have shaped the course of events through their leadership, decisions, and vision. These influential figures left lasting marks on their nations and the world at large, whether through political reforms, military strategies, or cultural shifts. By understanding their actions and motivations, we gain insight into the forces that propelled societies forward or led to significant transformations.
Key Leaders and Their Contributions

| Leader | Impact | Region |
|---|---|---|
| Alexander the Great | Expanded his empire across three continents, spreading Greek culture and establishing a legacy of Hellenistic civilization. | Europe, Asia, Africa |
| Winston Churchill | Guided the UK through WWII, advocating for resilience, democracy, and post-war rebuilding. | Europe |
| Queen Elizabeth I | Strengthened England’s naval power and established it as a dominant force in global trade and exploration. | Europe |
| Nelson Mandela | Led the fight against apartheid in South Africa, promoting equality, reconciliation, and peace. | Africa |
| Genghis Khan | Unified the Mongol tribes and created one of the largest empires in history, influencing global trade and cultural exchanges. | Asia, Europe |
Leadership Styles and Legacy
These leaders displayed a variety of leadership styles, from militaristic to diplomatic, yet their influence often transcended their immediate context. Their ability to inspire loyalty, execute strategies, and navigate complex challenges shaped the destinies of entire civilizations. The decisions made by these figures continue to influence contemporary politics, society, and culture in profound ways.
Significant Wars and Conflicts
Throughout human civilization, numerous battles and confrontations have altered the course of nations and reshaped global dynamics. These conflicts, whether driven by territorial disputes, ideological differences, or the desire for resources, have had profound effects on societies. Understanding the causes and consequences of these wars allows us to better comprehend the social, political, and economic shifts that followed.
From ancient sieges to modern confrontations, each major conflict has contributed to the evolution of military tactics, international diplomacy, and the balance of power. The outcomes of these struggles often determined the fates of empires, influenced the rise of new states, and left legacies that continue to shape global relations.
Cultural and Scientific Achievements
Throughout time, human creativity and intellect have driven remarkable advancements in both cultural expression and scientific discovery. These achievements have had a lasting impact on societies, shaping everything from art and literature to technology and medicine. By studying these contributions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the innovations that have transformed our way of life and the legacy they leave behind.
| Achievement | Impact | Period |
|---|---|---|
| Invention of the Printing Press | Revolutionized the spread of knowledge, enabling mass communication and education. | 15th Century |
| Renaissance Art | Redefined artistic expression with innovations in perspective, human anatomy, and emotion in visual art. | 14th–17th Century |
| Development of the Scientific Method | Transformed the approach to scientific inquiry, laying the foundation for modern science. | 17th Century |
| Medical Advancements (e.g., Vaccination) | Improved public health and extended life expectancy through innovations in disease prevention. | 18th–19th Century |
| Electricity and Magnetism Discoveries | Led to the creation of technologies that revolutionized energy, communication, and industry. | 18th–19th Century |
Revolutionary Ideas in History

Throughout the course of human development, certain ideas have sparked profound change, challenging traditional structures and leading to shifts in societal norms and power. These transformative concepts have altered the way individuals think, interact, and organize themselves, often bringing about new systems of governance, social justice, or scientific understanding. By examining these revolutionary ideas, we gain insight into the forces that have shaped civilizations.
| Idea | Originator | Impact | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Separation of Powers | Montesquieu | Laid the groundwork for modern democratic systems with checks and balances. | 18th Century |
| Natural Rights | John Locke | Influenced the development of human rights and the foundation of democratic governments. | 17th Century |
| Evolutionary Theory | Charles Darwin | Revolutionized biological sciences by introducing natural selection as the driving force of evolution. | 19th Century |
| Non-Violent Resistance | Mahatma Gandhi | Promoted civil disobedience and non-violent protest as a method for achieving social and political change. | 20th Century |
| Communism | Karl Marx | Introduced the theory of class struggle, which later inspired movements for workers’ rights and socialist revolutions. | 19th Century |
Political Systems Through the Ages
Across civilizations, different structures of governance have emerged to organize societies, distribute power, and maintain order. These systems, ranging from monarchies to republics, have shaped the rights of individuals and the functioning of states. The evolution of political systems reflects changes in societal values, technological advancements, and philosophical beliefs, illustrating the diversity of approaches to governance throughout time.
Early Forms of Government
In ancient societies, political systems were often based on the concentration of power in the hands of a single ruler or a small elite. Kingdoms and empires, led by monarchs or emperors, dominated much of the early political landscape. These systems were largely autocratic, with rulers possessing absolute authority over lawmaking, military decisions, and religion.
Modern Political Structures
The emergence of democracy, particularly in the modern era, introduced the concept of political power shared by citizens. Republics, constitutional monarchies, and socialist states each developed their own methods for balancing authority and individual rights. These systems brought with them new ideas about representation, the rule of law, and social contracts that continue to shape global politics today.
Economic Developments and Theories
Throughout the course of human civilization, economic systems have evolved, driven by changes in trade, production, and technology. From simple barter systems to complex global markets, these developments have shaped societies’ structures and their people’s ways of life. Understanding the various economic theories that emerged alongside these transformations allows us to grasp the underlying forces that govern wealth distribution and resource allocation.
Early Economic Systems
In the earliest stages of civilization, economies were based on subsistence agriculture and bartering, where goods and services were exchanged directly. As societies expanded, trade networks grew, and early forms of currency began to emerge, facilitating more efficient exchanges. The rise of empires and kingdoms saw the development of complex systems of taxation, resource management, and state-controlled economies.
Classical Economic Theories
As societies moved into the modern age, influential economic theories began to take shape, exploring the roles of markets, governments, and labor. Classical economists like Adam Smith introduced the idea of the “invisible hand,” advocating for free markets and minimal government intervention. Meanwhile, thinkers such as Karl Marx offered critiques of capitalism, proposing alternative models based on the collective ownership of resources and the redistribution of wealth.
Understanding Historical Geography
The physical layout of the land, its resources, and its strategic location has always played a pivotal role in shaping the development of societies. Geography influences not only the movement of people, goods, and ideas but also the rise and fall of civilizations. By studying past geographical contexts, we can better understand the economic, political, and cultural forces that influenced historical events and human actions.
Geography and Civilization Development

The relationship between geography and the growth of ancient civilizations is evident in the ways that regions with fertile land, access to water, and favorable climates became centers of power. River valleys like those of the Nile, the Tigris-Euphrates, and the Indus River supported agriculture, which allowed societies to flourish and trade. On the other hand, geographical barriers, such as mountains or deserts, often limited contact between different cultures, leading to isolation or the development of unique traditions.
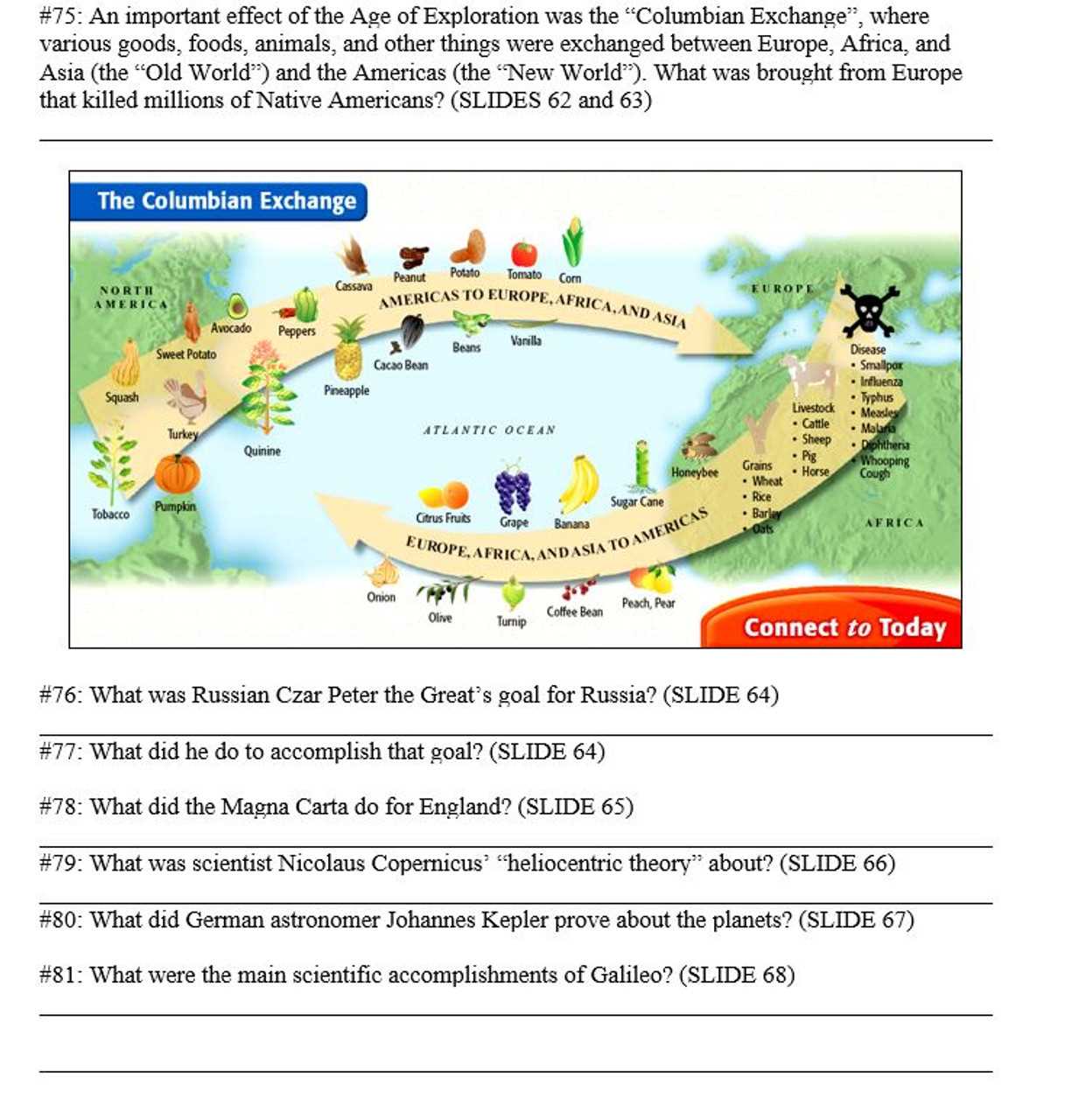
Geopolitical Strategies and Conflict
Throughout history, the location of nations or empires has influenced their geopolitical strategies and decisions. The control of key trade routes, access to natural resources, or proximity to other powerful states often determined the nature of diplomatic relations, alliances, and conflicts. Geography has thus been a driving factor in shaping military campaigns, territorial expansion, and the establishment of borders that still exist today.
Social Structures Across Time
Throughout human existence, societies have organized themselves into distinct social hierarchies, each with its own norms, roles, and power dynamics. These structures have varied widely across cultures and periods, yet they all share a common purpose: to organize people in ways that promote stability, order, and economic productivity. Understanding these structures offers insights into the development of social, political, and economic systems across different civilizations.
Early Social Hierarchies
In ancient civilizations, the organization of society was often rigid, with clear divisions between different classes. These divisions were typically based on factors like birth, wealth, or occupation. Some of the earliest social structures included:
- Monarchies: Kings or emperors at the top, with religious leaders and nobles holding significant power.
- Slavery: In many ancient societies, enslaved people formed the bottom tier of the social pyramid, performing the most labor-intensive work.
- Class-based systems: Merchants, artisans, and farmers often made up the middle class, while priests, scribes, and warriors held higher status.
Social Mobility and Change
Over time, changes in technology, economy, and philosophy brought about shifts in social mobility and class structures. In the medieval period, for example, feudalism defined much of European society, with rigid roles for peasants and lords. However, the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods led to greater opportunities for education and individual achievement, challenging the established social orders.
Modern societies, especially those influenced by democratic and capitalist ideals, have witnessed significant transformations in social structures. Today, many nations focus on reducing class distinctions and increasing opportunities for mobility through education and policy reforms.
Religious Movements and Beliefs

Religious movements and beliefs have played a central role in shaping the cultural, social, and political landscapes throughout human history. They provide individuals with a framework for understanding the world, their place in it, and the forces that govern life. These belief systems have not only influenced personal behavior but also shaped civilizations, often leading to the formation of institutions, the establishment of laws, and the development of moral and ethical codes.
Major Religious Movements
Throughout the centuries, various religious movements have emerged, each offering distinct perspectives on spirituality, ethics, and the nature of existence. Some notable movements include:
- Monotheistic Religions: The belief in one supreme deity, such as in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, has had a profound impact on societies across the globe.
- Eastern Philosophies: Traditions like Hinduism, Buddhism, and Confucianism focus on the search for enlightenment, karma, and the balance of nature.
- Reformation Movements: The Protestant Reformation, led by figures like Martin Luther, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church, leading to the rise of new denominations.
The Impact of Religious Beliefs on Society
Religious movements have often acted as catalysts for change, not only influencing personal beliefs but also shaping laws, governance, and cultural practices. In many societies, religious institutions held immense power, guiding the moral compass of the people and providing social services like education and healthcare. Furthermore, the spread of religious ideas has often led to the formation of empires and the expansion of cultures through missionary work and conversion.
Despite the diversity of religious beliefs, many of these systems share common themes such as the search for moral truth, the importance of community, and the quest for understanding the divine. These common threads have fostered both unity and conflict throughout history, as differing belief systems sometimes collided, leading to both cooperation and division among societies.
Technological Innovations in History
Throughout the ages, technological innovations have been pivotal in shaping civilizations, transforming industries, and advancing human capabilities. These breakthroughs often emerge as solutions to specific challenges, but their effects ripple across societies, influencing every aspect of life–from communication and transportation to medicine and warfare. The progression of technology reflects humanity’s desire to enhance productivity, improve quality of life, and push the boundaries of what is possible.
Key Technological Breakthroughs

Several inventions and innovations stand out for their far-reaching impact on society. Some of the most significant include:
- The Printing Press: Revolutionized the spread of knowledge by making books more accessible, fueling the Renaissance and the Reformation.
- The Steam Engine: A key driver of the Industrial Revolution, it powered factories, trains, and ships, reshaping global economies.
- The Telephone: Changed communication by allowing instant voice contact across long distances, laying the foundation for the modern telecommunications industry.
- The Internet: Has revolutionized global connectivity, transforming everything from social interactions to commerce and education.
Impact of Technology on Society

Technological innovations have not only enhanced efficiency but have also introduced new social dynamics. The creation of labor-saving machines, for example, increased production and lowered costs but also led to shifts in employment patterns and the nature of work. Furthermore, as technology has advanced, it has created new opportunities for global interaction, democratized information, and sparked significant cultural shifts.
However, these advancements are not without their challenges. They often require societal adaptation, whether in terms of policy, ethics, or environmental impact. As new technologies emerge, the task of balancing progress with responsibility becomes ever more critical, highlighting the need for thoughtful innovation and sustainable practices.
Art and Architecture Through the Ages
Throughout time, visual and structural creations have been powerful expressions of human thought, culture, and society. Art and architecture have not only captured the aesthetic values of different civilizations but have also been tools for communicating political power, religious beliefs, and societal ideals. These creations serve as lasting records of human achievement and reflect the evolution of technical skills, materials, and design philosophies.
Major Artistic Movements
Various artistic movements have left a profound impact on the development of cultures. Some of the key movements that shaped the artistic landscape include:
- Renaissance Art: Focused on the revival of classical antiquity, it emphasized perspective, realism, and humanism. Famous artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo played pivotal roles in this period.
- Baroque Art: Known for its dramatic use of light and shadow, Baroque art often conveyed emotion and grandeur, seen in works by artists like Caravaggio and Rembrandt.
- Impressionism: A break from tradition, this movement focused on capturing moments of everyday life with bold, expressive brushstrokes. Artists like Claude Monet and Edgar Degas pioneered this style.
- Modernism: Challenged past conventions and explored new forms of expression, often using abstract and geometric shapes. Pablo Picasso and Wassily Kandinsky were central figures in this movement.
Architectural Marvels Across Eras

Just as art has evolved, so too has architecture. Major civilizations have left behind monumental structures that not only served practical purposes but also symbolized their values and beliefs:
- The Pyramids of Egypt: These massive structures are enduring symbols of ancient Egyptian power, reflecting both their architectural innovation and religious significance.
- The Parthenon: A symbol of classical Greek civilization, this temple is celebrated for its harmonious proportions and influence on Western architectural design.
- The Colosseum: This iconic Roman amphitheater showcases Roman engineering ingenuity, used for public spectacles and events that held social and political significance.
- The Great Wall of China: A remarkable feat of engineering, this wall stretches thousands of miles and represents the strategic and defensive capabilities of ancient China.
The study of art and architecture reveals much about the societies that produced them, offering insights into their values, technologies, and aesthetic tastes. From ancient monuments to modern skyscrapers, these creations remain integral parts of the cultural fabric, inspiring generations long after their construction.
Preparation Strategies and Tips
Successfully preparing for a comprehensive assessment requires more than just reviewing material–it involves effective planning, focused practice, and a well-organized approach. Establishing a study routine, utilizing various resources, and honing test-taking skills are key factors in achieving a strong performance. The following strategies and tips can help guide your preparation and ensure that you are ready for any challenge.
Effective Study Habits
Building a productive study routine is essential for long-term success. Consider the following strategies:
- Create a Schedule: Plan your study sessions well in advance. Break down the material into manageable sections and allocate specific times for each topic to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Prioritize Key Topics: Focus on areas that are most important or challenging. Review class notes, textbooks, and past materials to identify key concepts and themes that are likely to appear in the assessment.
- Active Learning: Engage with the material by summarizing, questioning, and teaching the content. This approach helps reinforce understanding and retention of the material.
Test-Taking Techniques
On the day of the assessment, applying effective test-taking strategies can significantly impact your performance:
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before starting, make sure to read all directions thoroughly to avoid unnecessary mistakes.
- Time Management: Allocate time for each section or question and keep track of time throughout the test. This will prevent rushing through any part of the assessment.
- Answer Strategically: Start with questions that you find easier, then move on to the more challenging ones. If unsure about an answer, mark it and return to it later.
By combining effective study techniques with efficient test-taking strategies, you can feel more confident and prepared. Consistent practice, focused effort, and smart planning will set you on the path to success.