Preparing for advanced assessments in business finance requires a deep understanding of various analytical techniques. These tests often challenge candidates to apply their knowledge of economic principles, accounting methods, and model-building strategies. To excel, it’s essential to approach these evaluations with a structured mindset and practical skills that go beyond memorization.
The process involves dissecting real-world scenarios and constructing coherent models that can predict business performance under different conditions. Success in these assessments hinges on the ability to demonstrate a comprehensive grasp of accounting documents, understand their interrelationships, and skillfully manipulate the data to derive meaningful insights. Building proficiency in these areas is critical for anyone looking to succeed in corporate finance roles or investment banking positions.
Effective preparation requires mastering key concepts such as cash flow analysis, profitability metrics, and risk evaluation. A strategic approach to studying will ensure that candidates can confidently navigate through complex tasks and present well-supported conclusions in a clear, logical manner. Those who develop a solid foundation will be well-equipped to tackle even the most challenging problems that arise during these assessments.
Financial Analysis Assessment Success
Achieving success in high-level business analysis assessments requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. Candidates are tasked with constructing detailed models, interpreting complex data, and demonstrating an in-depth understanding of various financial documents. The key to excelling lies in the ability to synthesize this information efficiently while maintaining accuracy and clarity in the analysis.
To navigate these challenges effectively, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the most common types of calculations and decision-making tools used in corporate finance. The process of preparing for such evaluations involves mastering the relationships between different accounting reports and applying this knowledge to solve real-world problems.
| Key Concept | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow Management | Understanding cash inflows and outflows | Used to determine liquidity and solvency |
| Profitability Metrics | Assessing company performance | Helps in evaluating operating efficiency |
| Risk Assessment | Evaluating potential financial risks | Important for investment and financial decisions |
| Balance Sheet Analysis | Reviewing assets, liabilities, and equity | Essential for determining a company’s financial position |
By mastering these core principles, candidates will be well-prepared to tackle any challenge presented during the assessment process, offering clear, concise, and accurate financial insights. Preparing in this way not only improves exam performance but also builds a foundation for practical application in real business environments.
Understanding the Assessment Structure
Success in high-level business evaluations requires familiarity with their structure and expectations. These assessments are designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application in corporate finance. Candidates are asked to solve problems, interpret data, and demonstrate a clear understanding of various key concepts. Knowing what to expect can significantly improve preparation and performance.
The structure of these evaluations typically involves multiple components, each focusing on different aspects of financial analysis. Understanding the layout and the skills being tested in each section helps candidates prepare more effectively and manage their time efficiently during the test.
- Case Studies: Real-world business scenarios that require building models, making assumptions, and calculating outcomes based on provided data.
- Multiple Choice Questions: Questions that assess theoretical knowledge and the understanding of financial concepts, metrics, and key terms.
- Practical Exercises: Hands-on tasks that involve manipulating financial data and documents to derive insights or make recommendations.
- Time Constraints: Most assessments are timed, so it’s crucial to manage your time wisely across different sections.
Each component is designed to test a specific skill set, from data analysis to decision-making. Practicing each type of task will not only build confidence but also ensure you are well-equipped to handle whatever may come up during the assessment.
Key Concepts in Financial Analysis
In order to succeed in advanced business evaluations, understanding fundamental principles is essential. These principles form the foundation for building robust models, interpreting data, and making informed decisions. From assessing profitability to managing cash flow, each concept plays a critical role in analyzing a company’s financial health. Mastery of these key areas will enhance both performance in assessments and practical application in real-world scenarios.
| Concept | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow Management | Tracking the movement of cash in and out of a business | Critical for assessing a company’s liquidity and solvency |
| Profitability Analysis | Evaluating a company’s ability to generate profit relative to its revenue | Helps determine operational efficiency and financial sustainability |
| Risk Assessment | Identifying potential financial risks and their impact | Key for making informed investment and strategic decisions |
| Leverage Ratios | Measuring the proportion of debt used in financing | Essential for understanding financial risk and capital structure |
| Valuation Techniques | Methods for estimating the value of a company or asset | Vital for investment analysis and mergers & acquisitions |
Each of these concepts is interrelated, and mastering them enables more accurate assessments of financial performance. Understanding how to apply them in various scenarios is critical for both completing assessments and executing sound business decisions.
Common Mistakes in Financial Models
When constructing models, even the smallest errors can lead to inaccurate results and misleading conclusions. Many candidates make similar mistakes that can significantly affect their ability to analyze and interpret data properly. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for improving both model accuracy and efficiency. Avoiding common mistakes ensures that the results are reliable and aligned with real-world scenarios.
1. Incorrect Assumptions
One of the most frequent errors in financial analysis is using inaccurate assumptions about future performance, such as revenue growth rates, cost projections, or market conditions. These assumptions are often based on outdated information or overly optimistic forecasts, which can distort the entire model. It’s important to base assumptions on credible data and conservative estimates to maintain realism in the model.
2. Failure to Link Key Statements
Another common issue is failing to properly link financial reports, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. These documents are interconnected, and neglecting to establish accurate links between them can result in inconsistencies and errors. Ensuring proper relationships between variables across statements is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the analysis.
Attention to detail and understanding the flow of data between different sections of the model is vital to avoid miscalculations. It’s essential to verify that all assumptions and formulas are consistent across all elements of the model.
Essential Excel Skills for the Assessment
Excel is the primary tool for creating and analyzing financial models, and mastering its features is essential for success in advanced business evaluations. The ability to use Excel effectively can make the difference between a well-constructed model and one full of errors. Understanding key functions and shortcuts is not only crucial for efficiency but also for ensuring the accuracy of your results.
1. Advanced Formulas and Functions
In any financial analysis, using the right formulas is essential for quick calculations and accurate results. Functions like VLOOKUP, INDEX/MATCH, SUMIF, and NPV are frequently used in constructing models. Mastering these formulas will help you link different sections of your analysis, calculate key metrics, and automate complex calculations. It’s important to understand not only how to use these functions but also when and why they should be applied.
2. Data Management and Visualization
Efficiently managing and organizing large datasets is a critical skill. Excel’s data tools, such as PivotTables, Data Validation, and Conditional Formatting, allow you to summarize, analyze, and present data in a clear and organized way. Learning how to filter and manipulate data for better visualization can improve both the presentation and interpretation of financial information. Additionally, mastering charts and graphs will help communicate insights effectively.
Proficiency in these areas will not only improve the speed and accuracy of your analysis but also ensure that your models are both professional and easy to understand. Whether you’re building complex models or analyzing data, these Excel skills are indispensable for excelling in the assessment process.
How to Approach Financial Reports
When analyzing a company’s performance, it’s essential to approach its financial documents with a strategic mindset. These reports provide a wealth of information that, when interpreted correctly, can reveal valuable insights about a business’s health, profitability, and future prospects. The key is understanding how to read and assess each report to uncover trends, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
1. Understand the Interconnections
The primary financial documents are all interconnected. The income statement shows profitability over a period, the balance sheet provides a snapshot of financial position, and the cash flow statement highlights liquidity. It is crucial to recognize how changes in one report affect the others. For example, net income from the income statement directly impacts the cash flow statement and the retained earnings on the balance sheet. A comprehensive understanding of these relationships will help you better interpret the data as a whole.
2. Focus on Key Metrics

Rather than getting lost in the details, focus on the key metrics that matter most for analysis. Profit margins, return on equity, liquidity ratios, and debt-to-equity ratios are essential indicators of a company’s financial health. Pay attention to trends in these numbers over time and compare them to industry benchmarks. Identifying strengths and weaknesses in these key areas can guide your decision-making process and provide a clearer view of the company’s financial outlook.
Approaching financial reports with this structured analysis enables a more efficient and accurate understanding of a business’s performance, paving the way for more informed strategic decisions.
Tips for Efficient Time Management
Effective time management is crucial when tackling complex tasks that require both speed and accuracy. Whether working under a deadline or managing multiple components simultaneously, organizing your time ensures you can cover all necessary areas without missing key details. By implementing smart strategies, you can optimize your workflow and maintain focus throughout the process.
1. Prioritize Key Tasks
Start by identifying the most important elements of the task at hand. Focus on high-priority items that will have the most significant impact on the overall outcome. Break down the work into smaller, manageable sections, and tackle the most difficult or time-consuming tasks first. This approach helps prevent last-minute rushes and ensures critical components are completed early on.
2. Use Time Blocks
Divide your available time into dedicated blocks for specific tasks. For example, allocate a fixed amount of time for data analysis, another for financial calculations, and separate time for reviewing your work. Time-blocking minimizes distractions and ensures each part of the process receives adequate attention. Be disciplined in sticking to the set limits for each block to maintain a steady pace throughout.
Consistency is key–by practicing these strategies regularly, you will naturally improve your efficiency and confidence when working on time-sensitive projects.
Best Resources for Preparation
Preparing for an advanced business assessment requires the right set of resources to help you build a strong foundation and master the necessary skills. The right materials not only guide your study but also give you practical insights into the process. Whether you prefer structured lessons, self-paced practice, or expert advice, there are a variety of resources that can support your preparation journey.
1. Online Courses and Tutorials
Many online platforms offer comprehensive courses designed to cover all aspects of business evaluation and model building. These structured lessons provide detailed explanations, real-world examples, and practical applications. Some popular options include:
- Coursera – Offers courses from top universities with hands-on practice.
- Udemy – Provides affordable, on-demand video lessons on key financial skills.
- LinkedIn Learning – Features courses focusing on Excel, financial analysis, and more.
2. Practice Questions and Mock Assessments
Practicing with questions that simulate the actual assessment conditions is crucial for improving speed and accuracy. These resources often come with detailed explanations, helping you understand why certain approaches are correct. Some platforms to consider are:
- Investopedia – Offers a range of quizzes and tutorials on various finance topics.
- Financial Modeling Prep – Provides free resources and templates for financial model practice.
- Wall Street Oasis – Features mock tests and community-driven resources.
3. Study Guides and Reference Books
Books and study guides written by industry experts offer in-depth coverage of the key topics. These are great for building foundational knowledge and gaining a deeper understanding of the concepts. Recommended books include:
- Investment Banking by Joshua Rosenbaum – A comprehensive guide on valuation and modeling techniques.
- The Financial Modeller’s Guide to Excel by Danielle Stein Fairhurst – Focuses on Excel techniques used in finance.
- Financial Analysis and Modeling Using Excel and VBA by Chandan Sengupta – A great resource for advanced learners.
By utilizing a combination of these resources, you can ensure thorough preparation and gain confidence in your ability to handle complex financial analysis tasks.
Mastering the Income Statement Analysis

Analyzing the income statement is crucial for understanding a company’s profitability over a specific period. This financial document provides key insights into how well a company generates revenue and controls its expenses. A thorough analysis helps identify trends, assess performance, and determine areas that need attention. Mastering this analysis is essential for making informed decisions regarding business operations and investment strategies.
When conducting an income statement analysis, it is important to focus on key performance indicators such as revenue, gross profit, operating income, and net income. Examining these metrics allows you to gauge the company’s ability to turn sales into profit and manage costs effectively. Additionally, comparing these figures over multiple periods can reveal underlying trends that may not be apparent in a single report.
Moreover, evaluating profit margins, both gross and net, provides insight into the company’s operational efficiency and cost management. A declining gross margin could indicate rising costs of goods sold, while a shrinking net margin may reflect increased operating expenses or taxes. By mastering these aspects, you can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health and its potential for future growth.
Cash Flow Statement and Its Importance
The cash flow report is an essential financial document that shows how money moves in and out of a business during a specific period. It highlights the company’s liquidity by focusing on cash inflows and outflows, which are critical for understanding its ability to pay bills, invest in new projects, and fund operations. Unlike other financial documents, which may reflect accounting profits, this report provides a clearer picture of the actual cash available for use.
1. Assessing Liquidity
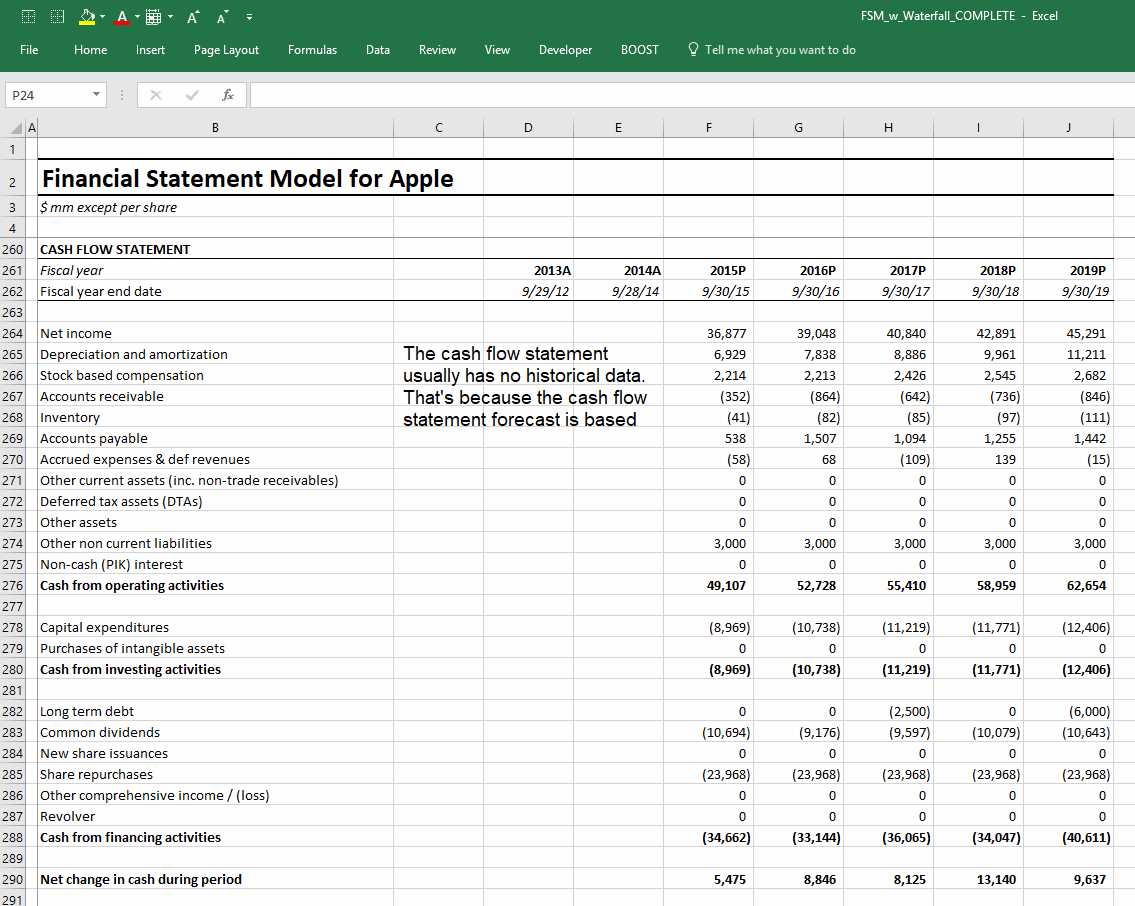
One of the primary functions of the cash flow report is to assess a company’s liquidity. While other financial reports may show profitability, they do not necessarily reflect the cash a business has on hand to cover immediate expenses. By analyzing cash inflows from operations, investments, and financing, you can evaluate whether the company has sufficient cash to meet short-term obligations and continue its operations smoothly.
2. Identifying Operational Efficiency
Another key benefit of the cash flow statement is that it helps identify how well a company’s core operations are generating cash. The operating activities section of the report provides insight into whether the business is effectively converting its revenue into actual cash. A healthy cash flow from operations is a sign of a well-managed company that can sustain its business without relying too heavily on external financing or credit.
Understanding and analyzing this report enables businesses, investors, and stakeholders to make better-informed decisions, ensuring that the company remains financially stable and prepared for future growth opportunities.
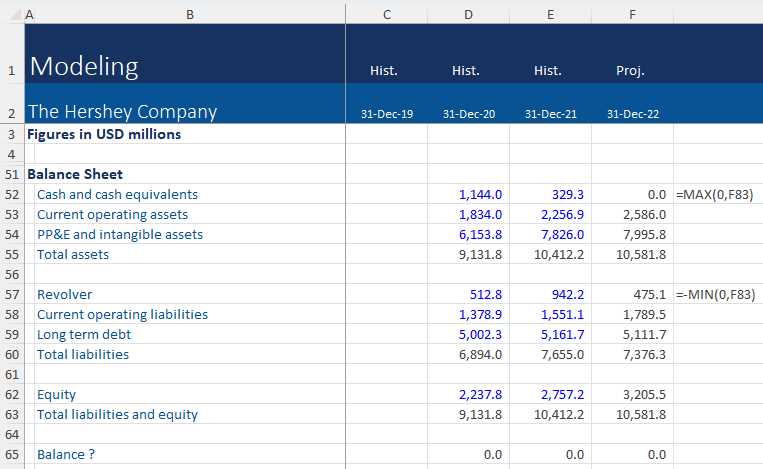
Balance Sheet: Critical Insights
The balance sheet is one of the most fundamental financial documents, offering a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It helps assess the overall financial health and stability of a business by showing what the company owns and owes. Analyzing this report provides valuable insights into the company’s ability to meet its obligations, its financial structure, and how effectively it utilizes its resources to generate value.
Key areas to focus on when analyzing a balance sheet include the relationship between assets and liabilities, the level of equity, and the company’s ability to finance operations. This information is essential for determining risk, making investment decisions, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Key Sections of the Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is divided into three main sections:
| Assets | Liabilities | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Current and Non-Current Assets | Current and Non-Current Liabilities | Owner’s Equity |
| Cash, Receivables, Inventory | Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt | Common Stock, Retained Earnings |
Assets represent everything a company owns or is owed, liabilities represent what it owes, and equity represents the owner’s claims on the business after all liabilities have been subtracted. Analyzing these components can help determine the company’s solvency and whether it is in a position to finance future growth or investments.
Evaluating Liquidity and Leverage

Liquidity ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio, provide insights into the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations using its current assets. On the other hand, leverage ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio help assess the level of debt compared to the company’s equity, offering insights into its risk profile and financial structure.
By carefully analyzing the balance sheet, stakeholders can gain a clear understanding of a company’s financial position, operational efficiency, and long-term viability in a competitive market.
Building a Strong Financial Model
Creating a robust financial model is essential for making informed decisions about a business’s future. It involves constructing a structured, logical representation of a company’s financial performance, typically with the aim of forecasting outcomes and assessing potential scenarios. A well-designed model helps identify key drivers of business performance, evaluate risks, and estimate the impact of various strategies. It is a critical tool for investors, executives, and analysts to predict future financial health and make strategic decisions.
To build a strong model, it is important to start with clear objectives and a solid understanding of the business. The model should reflect the unique dynamics of the company and its industry while providing a framework for both operational and strategic planning. Accuracy in data input and consistency in assumptions are crucial for ensuring reliable outputs.
One of the foundational elements of a good model is the ability to integrate various components like income, balance sheet, and cash flow projections. Linking these elements together allows for seamless analysis and better insights into a company’s financial situation. Additionally, sensitivity analysis, scenario planning, and stress testing are vital in assessing how changes in key variables could affect the model’s predictions.
Overall, a well-built financial model serves as a powerful tool for both understanding a company’s current financial state and predicting its future. Whether used for internal planning or external analysis, it enables better decision-making and provides a foundation for growth and stability.
Interpreting Financial Ratios Accurately
Understanding and interpreting financial ratios correctly is a crucial skill for assessing the health and performance of a business. Ratios provide valuable insights into different aspects of a company’s operations, such as profitability, liquidity, and efficiency. However, it is essential to approach these metrics with a critical eye, recognizing that they are just one piece of the puzzle and should be viewed in context. Misinterpretation of ratios can lead to inaccurate conclusions and poor decision-making.
When analyzing these indicators, it is important to compare them to industry benchmarks, historical performance, and competitor data. For example, a high profit margin may seem positive, but if it is significantly above industry standards, it could suggest pricing issues or unsustainable cost management. Similarly, a low current ratio might indicate liquidity problems, but it could also reflect efficient asset management, depending on the company’s business model.
Furthermore, understanding the limitations of each ratio is critical. Some ratios are more relevant to certain industries, and their implications can vary depending on the company’s size, stage of growth, or financial structure. For instance, a high debt-to-equity ratio might be acceptable in capital-intensive industries, whereas it might raise red flags in others.
Ultimately, accurate interpretation of financial ratios requires a combination of analytical skills, industry knowledge, and an understanding of the broader economic environment. By considering all of these factors, analysts and decision-makers can gain a deeper, more nuanced understanding of a company’s financial standing and make more informed, strategic decisions.
How to Handle Complex Scenarios
Dealing with intricate situations is an essential part of analyzing business data and making strategic decisions. These scenarios often involve multiple variables, interdependencies, and uncertainties that require careful attention and structured thinking. The key to managing complex cases effectively is breaking them down into smaller, more manageable parts while maintaining a clear focus on the overall objectives.
One of the most effective ways to approach complicated situations is to establish a solid framework. This helps to identify the core issues and prioritize areas that need immediate attention. Some key steps include:
- Clarify the objectives: Determine the primary goals of the analysis or decision-making process. Understanding what you are trying to achieve will help focus your efforts.
- Gather relevant data: Ensure that all necessary information is collected, accurate, and up to date. Incomplete or outdated data can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Identify key variables: Highlight the main drivers in the scenario. These could be financial factors, market conditions, or internal company dynamics.
- Assess risks and assumptions: Recognize the assumptions being made in the analysis and evaluate potential risks. This will help in anticipating challenges and preparing for different outcomes.
- Test various outcomes: Use scenario analysis or sensitivity testing to understand how different variables might impact the situation. This helps in preparing for a range of possible results.
Additionally, maintaining flexibility and being ready to adjust your approach is crucial. Complex scenarios often evolve, and being able to adapt to new information or changing conditions is essential for achieving the best outcomes.
By staying organized, methodical, and open-minded, you can navigate through complex situations more effectively and make well-informed decisions that align with your strategic goals.
Common Challenges in Financial Analysis
Analyzing business performance and making accurate predictions can be complex, with various obstacles arising along the way. Whether it’s dealing with incomplete data, forecasting future trends, or interpreting various financial indicators, challenges are inevitable. However, recognizing these hurdles early can help in formulating strategies to overcome them and enhance the quality of the analysis.
Some common difficulties encountered during the evaluation process include:
Data Quality and Availability
- Incomplete Data: Insufficient or missing data can significantly hinder the accuracy of your analysis. Gaps in critical information can lead to misinterpretations or skewed results.
- Data Consistency: Variations in data sources, formats, or definitions across periods or departments can create confusion and make comparisons difficult.
- Outdated Information: Using outdated data can mislead analysts, especially in industries where conditions change rapidly, leading to inaccurate conclusions.
Complexity in Interpretation
- Multiple Variables: Financial indicators often interact with one another, making it challenging to isolate the effect of a single variable on performance.
- Estimating Future Outcomes: Forecasting future performance involves many assumptions and uncertainties. Small changes in assumptions can have large impacts on results, making predictions difficult.
- Subjectivity in Analysis: Personal biases can influence the interpretation of data, leading to conclusions that are not fully objective or reliable.
Despite these challenges, the key to successful financial analysis lies in a disciplined approach. By ensuring data accuracy, understanding the interrelationships of financial variables, and maintaining objectivity in interpretation, analysts can mitigate these common obstacles and provide valuable insights.
How to Review Your Work Effectively

Reviewing your analysis and calculations is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your work. While it may seem like a simple task, effective review requires a structured approach and attention to detail. By following a few key strategies, you can identify errors, improve the clarity of your work, and enhance your overall analytical process.
To conduct an efficient review, consider the following steps:
- Take a Break Before Reviewing: After completing your work, step away for a brief period. This pause helps you return with a fresh perspective, making it easier to spot mistakes or inconsistencies.
- Check the Structure and Logic: Ensure that your analysis flows logically and that all assumptions are clearly outlined. Check if each step leads naturally to the next and if your conclusions are supported by the data.
- Focus on Key Figures: Pay special attention to the main calculations and metrics. Cross-check important numbers and formulas to make sure there are no discrepancies.
- Use Tools and Automation: Leverage built-in features of your software, such as audit tools and formula tracing, to identify errors or inconsistencies. These tools can help you pinpoint areas that require further inspection.
- Get a Second Opinion: If possible, ask a colleague or mentor to review your work. A second set of eyes can often catch errors you might have overlooked.
By adhering to these best practices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of mistakes and ensure that your work is thorough and precise. An effective review process not only enhances the quality of your analysis but also improves your overall proficiency in handling complex tasks.
Post-Exam Tips and Career Insights
After completing an assessment, it is essential to take time to reflect on both your performance and the skills gained throughout the process. The experience offers more than just the immediate outcome; it can be a valuable learning opportunity that provides insight into areas for improvement and future growth. How you handle this phase can significantly impact your professional trajectory and help you refine your approach to future challenges.
Once the assessment is over, here are a few strategies to make the most of the experience:
- Analyze Your Performance: Take the time to review your results and pinpoint areas where you excelled and areas for improvement. Understand the mistakes you made, why they occurred, and how you can avoid them in the future.
- Seek Feedback: Reach out to peers or mentors for constructive feedback. Understanding how others approached the same tasks can provide you with new perspectives and valuable techniques that can be applied moving forward.
- Continue Learning: The completion of any challenge should be seen as just one step in your ongoing professional development. Invest in resources, whether through courses, books, or practical experience, to enhance your expertise further.
- Build a Network: Connect with colleagues and professionals in your field. Networking is a powerful tool that opens doors to new opportunities and insights that can propel your career forward.
- Stay Resilient: Remember that setbacks are part of growth. Use the experience to build resilience and a positive mindset, which are invaluable in both professional and personal development.
In the long run, mastering your technical abilities is crucial, but developing soft skills such as problem-solving, time management, and communication will differentiate you as a well-rounded professional. Take what you’ve learned from this process and apply it to advance in your career, keeping a focus on both immediate and long-term objectives.