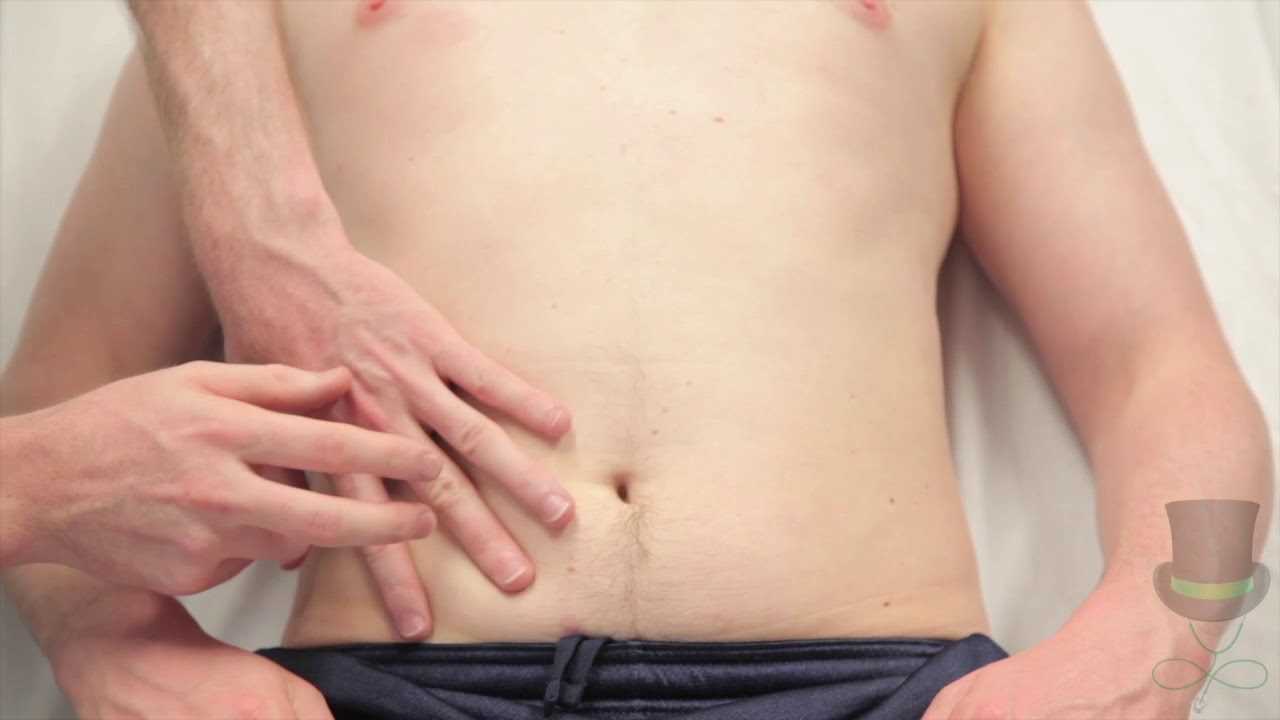
When evaluating the internal organs, one of the most valuable methods is assessing sounds produced within the body. These auditory signals help medical professionals detect a range of conditions and irregularities that may not be immediately visible. Mastering the ability to interpret these sounds can be an essential skill in clinical practice.
The process involves tapping specific areas of the body to produce sounds that indicate the underlying state of organs or tissues. These sounds vary based on factors like fluid levels, tissue density, or air pockets. Understanding how to properly apply this technique and interpret the results is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
In this section, we will explore how this diagnostic method works, its significance in clinical practice, and the key sounds that can provide insights into the patient’s condition. With a focus on practical applications and clinical relevance, you will gain a deeper understanding of this essential examination tool.
Abdominal Exam Percussion Techniques
Assessing internal organ conditions through sound is a key part of physical examination. By tapping specific areas of the body, a clinician can identify various abnormalities that may not be immediately visible. This approach provides valuable insight into the state of underlying tissues, helping to guide further diagnostic steps.
To perform this technique effectively, the examiner uses the pads of the fingers to gently tap over the surface of the body, listening carefully to the resulting sounds. These sounds can vary significantly depending on factors such as organ density, fluid accumulation, or the presence of air pockets. Understanding how to interpret these auditory cues is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Proper technique involves selecting the correct areas to tap, applying the right amount of pressure, and using an appropriate rhythm. The results are then analyzed, with clinicians looking for distinct sounds that could indicate conditions like liver enlargement, fluid buildup, or bowel obstruction. Mastery of these techniques allows healthcare professionals to gain a clearer understanding of what’s happening inside the body.
What is Abdominal Percussion
This diagnostic method involves tapping on the body’s surface to produce sounds that reflect the condition of internal structures. The variations in the sounds heard during this procedure can provide crucial information about the underlying organs and tissues. The technique is widely used to identify abnormalities that may not be detectable through other means.
During this process, the examiner uses their fingers to apply gentle taps, listening carefully to the resulting auditory feedback. The nature of the sounds–whether dull, resonant, or tympanic–offers insights into issues like fluid retention, organ enlargement, or the presence of gas. It is a non-invasive tool that can guide further clinical investigation without requiring advanced imaging techniques.
By interpreting the sounds correctly, healthcare professionals can gain valuable information to diagnose conditions like ascites, bowel obstructions, or liver disorders. Proper technique and a keen ear are essential to ensure the results are accurate and reliable.
Importance of Percussion in Diagnosis
Sound-based diagnostic techniques play a crucial role in evaluating the health of internal organs. By tapping on the body’s surface and listening to the resulting sounds, medical professionals can gather valuable information about the state of underlying tissues. This method helps to uncover hidden abnormalities, guide further investigation, and inform treatment decisions.
Uncovering Hidden Conditions
Using sound to assess internal structures allows clinicians to detect issues that may not be immediately apparent. Abnormalities such as fluid buildup, organ enlargement, or air pockets often manifest as distinct sounds when tapped. These auditory clues can prompt further tests or immediate interventions, ensuring that potentially serious conditions are not overlooked.
Non-invasive and Efficient Diagnostic Tool
One of the key advantages of this method is that it is non-invasive, making it suitable for a wide range of patients. Unlike imaging techniques that may require expensive equipment or patient preparation, sound assessment provides quick and effective results. It is a valuable first step in the diagnostic process, especially when time is of the essence.
Steps to Perform Abdominal Percussion
To effectively assess internal conditions through sound, a specific technique must be followed. The process involves careful positioning of the patient, controlled tapping, and focused listening to the resulting noises. These steps are crucial for obtaining accurate readings and diagnosing potential issues within the body.
The first step is to position the patient comfortably, typically lying on their back with the abdomen exposed. The examiner should ensure a quiet environment to better hear the sounds produced. Using the middle or index finger, the examiner gently taps the surface of the abdomen, avoiding excessive force, and listens for different tones that indicate underlying conditions.
The technique requires consistency in both pressure and rhythm. It is important to tap in a systematic manner, starting from one region and moving across the abdomen to assess all areas. Each sound should be carefully noted, as variations in tone can suggest the presence of air, fluid, or solid masses. This method allows healthcare professionals to gather important diagnostic information through a simple, non-invasive procedure.
Common Percussion Sounds and Their Meaning
During a physical examination, different sounds heard when tapping the body can reveal a great deal about the underlying organs and tissues. These auditory cues provide important diagnostic information and can help differentiate between healthy and abnormal conditions. Understanding the meaning behind each sound is crucial for accurate clinical assessments.
Types of Sounds and Their Implications
Each type of sound heard during the tapping process offers distinct clues about what’s happening inside the body. Some common sounds include:
- Resonance: A hollow, drum-like sound typically heard over normal air-filled organs, such as the lungs and the intestines.
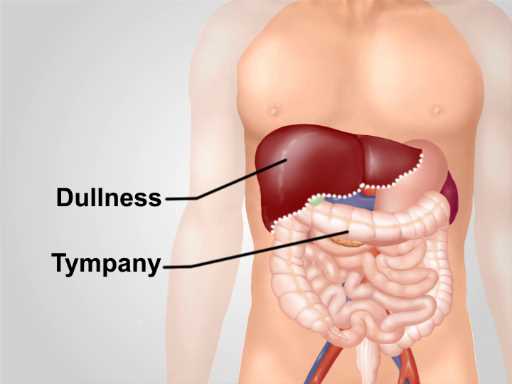
- Dullness: A thudding sound indicating a solid organ or mass, such as the liver or spleen, or the presence of fluid in the abdomen.
- Tympany: A high-pitched, drum-like sound usually heard over areas filled with gas, like the stomach or intestines.
- Hyper-resonance: A louder, lower-pitched sound, often indicating excess air or gas, such as in cases of bowel obstruction.
Significance of Different Tones
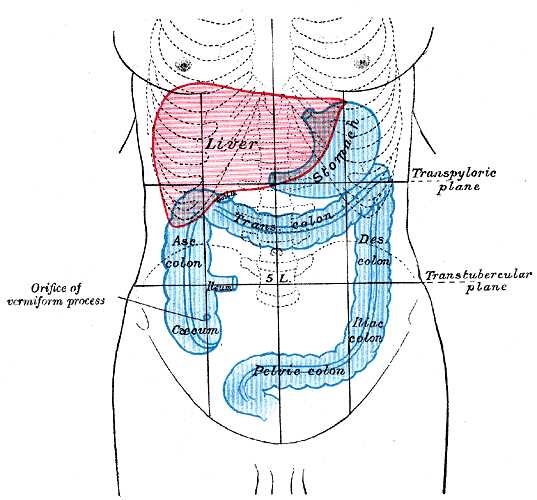
The interpretation of these sounds helps in diagnosing various conditions. For example, dullness may suggest the presence of fluid or solid masses, while tympany can indicate gas-related issues. By identifying and distinguishing these sounds, medical professionals can make informed decisions about further investigations or treatments.
Identifying Tympany and Dullness
When tapping the body, two distinct sounds can provide crucial information about the underlying internal conditions: tympany and dullness. These auditory cues are essential for diagnosing various issues, as they reflect differences in the composition and contents of the organs or spaces being assessed.
Recognizing Tympany
Tympany is a high-pitched, drum-like sound that is typically heard over air-filled structures. It suggests that the area being tapped contains gas or air, as seen in the stomach and intestines. This sound is often normal in healthy individuals, but its presence in unexpected areas could indicate conditions like bowel obstruction or excessive gas buildup.
Recognizing Dullness
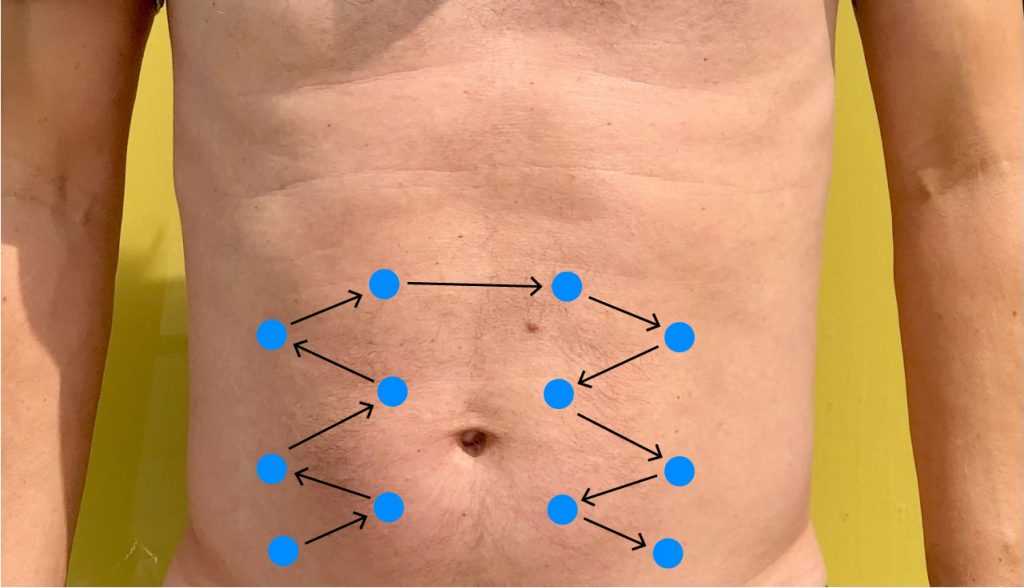
Dullness, on the other hand, is a lower-pitched, thudding sound heard when tapping over solid or fluid-filled areas. It often occurs over organs like the liver or spleen, as well as regions with fluid accumulation, such as in cases of ascites. The presence of dullness may signal abnormal conditions, such as organ enlargement, masses, or fluid retention.
Tips for Accurate Percussion Results
Obtaining reliable and precise results when assessing internal conditions through sound requires proper technique, preparation, and awareness of potential pitfalls. A few key guidelines can help ensure the accuracy of your findings, allowing you to confidently interpret the sounds and make informed decisions about the patient’s health.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Ensure a Quiet Environment | Perform the assessment in a calm, quiet setting to avoid interference from external noises, which can make it difficult to hear subtle sounds. |
| Consistent Pressure | Apply a consistent amount of pressure when tapping. Too much force can dampen the sound, while too little may not produce a clear tone. |
| Systematic Approach | Tap each area in a systematic manner to ensure that all regions are properly assessed, making it easier to identify any irregularities. |
| Use the Correct Technique | Use the middle finger of one hand to tap on the finger placed lightly on the surface of the body, avoiding excessive force or rapid movements. |
| Assess Multiple Areas | Check multiple regions for a more comprehensive assessment. Different sounds in different areas can provide more accurate insights into the patient’s condition. |
By following these tips, you can enhance the reliability of your results and improve your diagnostic abilities, ensuring that you are hearing the correct tones and interpreting them properly.
When to Use Percussion in Abdominal Exams
Sound assessment is a valuable diagnostic tool that can be used in various clinical scenarios to identify internal issues. Knowing when to apply this technique is essential to ensure it provides useful information. This method is particularly effective in detecting conditions related to organ size, fluid accumulation, or air presence.
It is typically employed when a healthcare provider suspects an abnormality in the abdominal area. For example, if a patient presents with symptoms like bloating, pain, or discomfort, this technique can help identify causes such as fluid retention or gas buildup. Additionally, it is useful when there is a concern about organ enlargement or the presence of masses.
Furthermore, this approach can be used as part of routine assessments to confirm or rule out certain conditions. It serves as a quick and non-invasive step before more invasive procedures or imaging are considered. By incorporating sound assessment, clinicians can gather important clues that guide further evaluation and treatment.
How Percussion Helps Detect Fluid Build-up
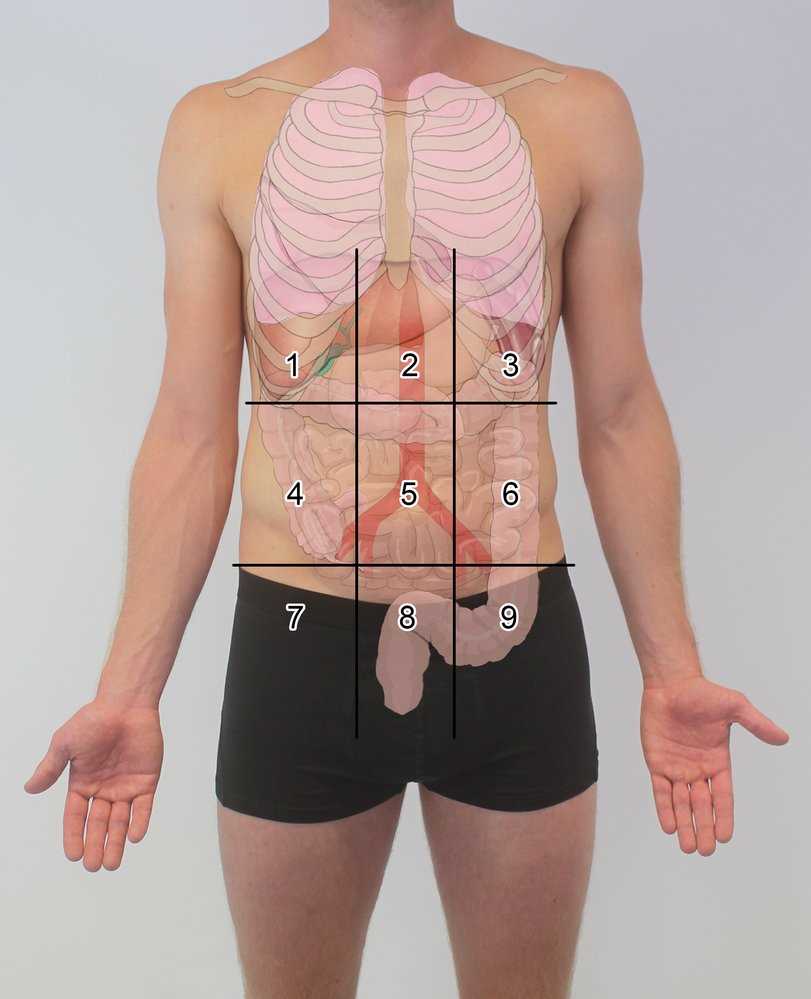
Sound assessment is a key technique for identifying fluid accumulation in the body, especially in areas like the abdomen. By tapping over different regions, healthcare professionals can detect variations in sound that indicate the presence of excess fluid. This method provides valuable insights into conditions like ascites, where fluid collects in the abdominal cavity.
When fluid accumulates in the body, it alters the normal sounds produced during tapping. Typically, areas with fluid will produce a dull or muffled sound, which differs from the resonant tones heard over air-filled spaces. By carefully assessing these differences, clinicians can pinpoint regions where fluid may be present.
Assessing Fluid Distribution
In cases of significant fluid build-up, the sound changes across the affected area. By listening for these differences, it becomes easier to gauge the extent of the fluid retention and whether further diagnostic steps, like imaging, are necessary. This technique is particularly useful in patients with liver disease, heart failure, or other conditions that can cause fluid accumulation.
Evaluating Bowel Gas with Percussion
When assessing the condition of the digestive system, the presence of gas in the intestines can provide important diagnostic clues. By using sound assessment, healthcare professionals can identify areas where gas is present, which can indicate normal bowel function or potential issues like obstruction or bloating.
Gas in the intestines produces a distinct sound during tapping, known as tympany. This high-pitched, drum-like tone is typically heard over areas where the intestines contain air or gas. The presence of tympany can be a sign of normal bowel activity, but when combined with other symptoms, it may point to conditions such as gastrointestinal obstruction or excessive gas production.
By evaluating the distribution and intensity of tympany, clinicians can gauge the overall function of the bowel and detect abnormal gas accumulation. If the sound is overly pronounced or absent in certain regions, it may suggest underlying issues that require further investigation or treatment.
Role of Percussion in Liver Enlargement
Detecting changes in the size of internal organs is an important part of a thorough physical examination. In the case of liver enlargement, sound-based assessment is a helpful tool in identifying abnormal increases in size, which can signal conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver tumors.
Identifying Dullness Over the Liver
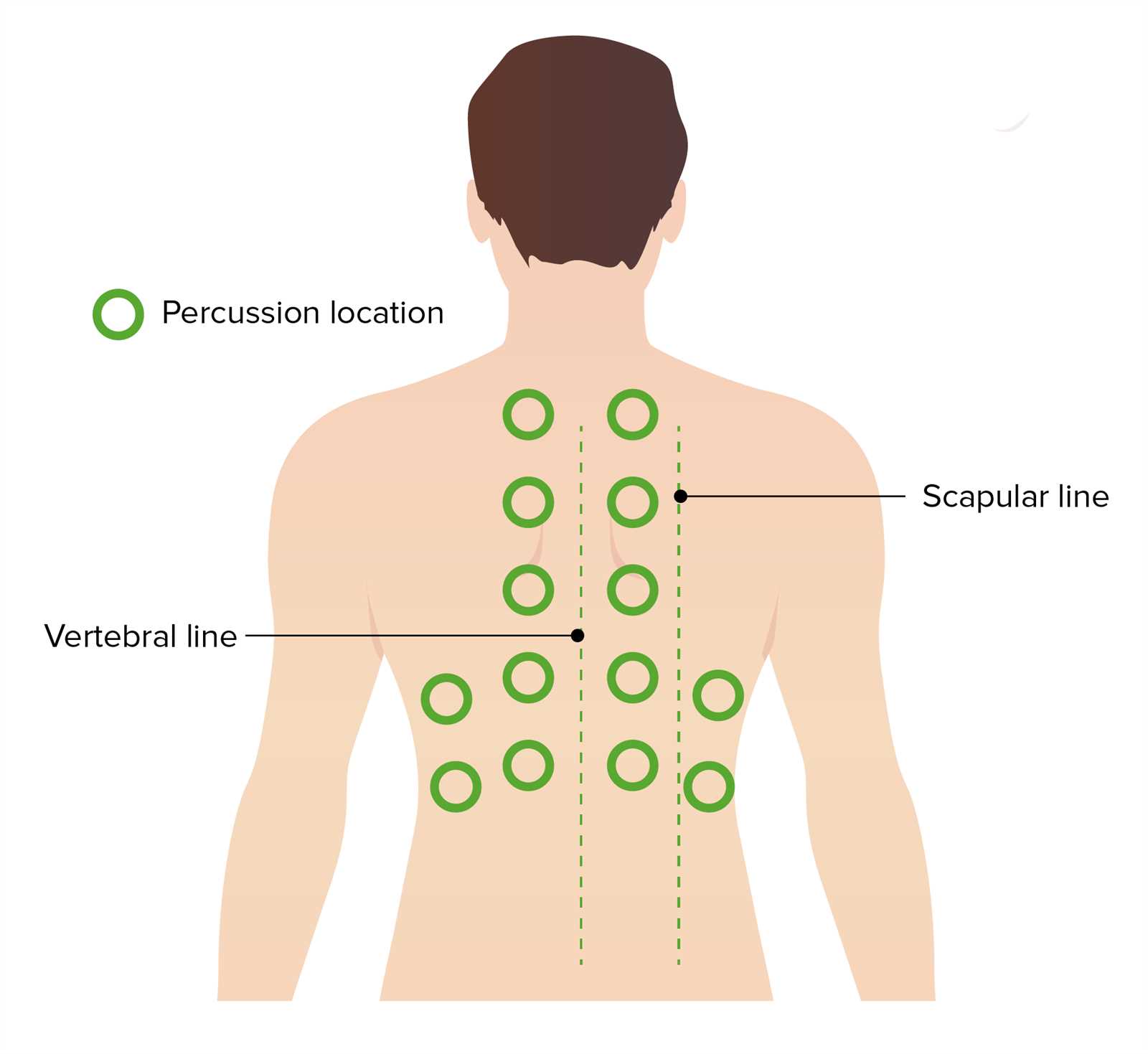
When the liver enlarges, it can alter the sounds heard when tapping over the abdominal area. Normally, the liver produces a dull sound, but when it becomes enlarged, the dullness may extend further beyond its usual borders. This increase in the dull area can suggest that the liver is swollen or enlarged, which warrants further investigation.
Confirming Findings with Physical Techniques
Sound assessment can be used alongside other techniques, such as palpation, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of liver size. By tapping in specific regions, a clinician can map out the edges of the liver and assess whether it extends beyond the normal range. This method is non-invasive, simple, and effective in identifying potential liver problems that may need more detailed imaging or diagnostic procedures.
Differences in Percussion for Children and Adults
Sound-based diagnostic methods can vary significantly when applied to children and adults, due to differences in anatomy, body composition, and the development of internal organs. Understanding these differences is crucial for obtaining accurate results and ensuring a proper evaluation of the patient’s condition.
- Anatomical Variations: Children have smaller, more flexible bodies, which can affect the way sounds travel through tissues. The abdominal cavity is smaller, and organs are in different relative positions compared to adults, which can lead to variations in how sound is produced and heard.
- Amount of Air and Gas: Children generally have a higher amount of intestinal gas due to faster metabolic rates, which can make tympanic sounds more pronounced. In adults, gas patterns may be more variable and influenced by diet, health conditions, or age-related changes.
- Thickness of Tissue: Children’s tissues tend to be thinner and less fatty than adults, which can influence the clarity and volume of sounds. In adults, thicker layers of fat and muscle can dampen the sounds, making them harder to interpret.
Given these differences, it is important for healthcare professionals to adjust their technique when evaluating children. A more gentle touch, combined with a deeper understanding of developmental stages, helps ensure that the results are accurate and relevant to the patient’s age and condition.
Percussion for Detecting Abnormal Masses
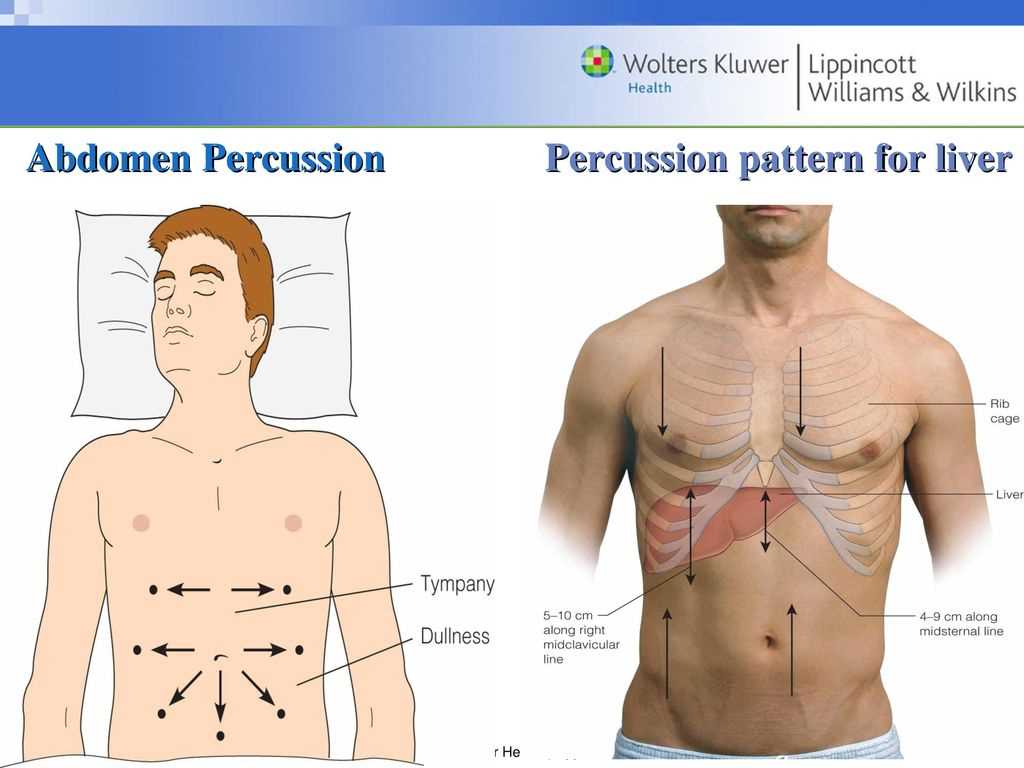
Sound-based techniques are highly effective for identifying abnormal masses within the body. By tapping over different areas and listening for changes in the tone or intensity of the sound, healthcare professionals can detect areas where solid or fluid-filled masses may be present. This method is particularly useful for identifying tumors, cysts, or other growths that may not yet be palpable.
When a mass is present, it often alters the normal sounds heard during assessment. For example, a solid mass may produce dull, thudding sounds, while a fluid-filled mass may result in a similar dullness but with a different tone or intensity. In contrast, areas filled with air or gas will produce a higher-pitched, tympanic sound.
Identifying the Location and Size of Masses
By systematically tapping different regions, clinicians can identify the location, size, and consistency of a mass. This helps in distinguishing between benign conditions and those that may require further investigation, such as imaging or biopsy. The ability to detect changes in sound provides valuable insights, particularly in the early stages of diagnosing abnormalities.
Common Errors in Abdominal Percussion
When using sound-based techniques to assess internal conditions, there are several common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results. These errors can stem from improper technique, external factors, or misinterpretation of the sounds produced. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring reliable and consistent findings.
Improper Technique
- Inconsistent Pressure: Applying too much or too little pressure can distort the sound. It is important to use a consistent, gentle touch to ensure clear and accurate results.
- Poor Hand Placement: Incorrect positioning of the tapping finger or applying pressure to the wrong area of the body can lead to unreliable sounds, making it difficult to assess the underlying condition.
- Failure to Tap Systematically: Skipping areas or tapping too quickly without following a consistent pattern can result in missed findings or incomplete assessments.
Environmental and Patient Factors
- External Noise: Background noise in the examination room can interfere with the ability to hear subtle changes in sound, leading to misinterpretation of results.
- Patient Positioning: The patient’s body position can significantly affect the sounds heard. Incorrect positioning may alter the distribution of gas or fluid, resulting in inaccurate readings.
- Inadequate Relaxation: If the patient is tense, it can affect the consistency of the sounds, especially in areas that are more sensitive, such as the diaphragm or lower abdomen.
Avoiding these common errors will help ensure that the results are more accurate and reliable, allowing for better clinical decisions and patient care.
Integrating Percussion with Other Techniques
Sound-based assessments are a valuable tool, but when combined with other diagnostic techniques, they can provide a more complete picture of a patient’s condition. Integrating this method with physical exams, imaging, and patient history allows healthcare providers to make more informed decisions and develop effective treatment plans.
Combining with Palpation
- Confirming Findings: While sound assessments can reveal areas of interest, palpation helps confirm the presence of masses, tenderness, or organ enlargement. Together, these methods can provide a clearer understanding of underlying conditions.
- Refining the Diagnosis: Percussion can highlight potential problem areas, which can then be further explored through palpation to assess the exact location, size, and consistency of abnormalities.
Pairing with Imaging Techniques
- Initial Screening: Sound assessments can serve as an initial screening tool to identify potential issues, prompting the need for further imaging such as ultrasound or CT scans.
- Complementary Data: While imaging provides detailed views of the internal structures, sound-based methods offer real-time data about organ function, fluid accumulation, and gas distribution.
By integrating sound-based techniques with other clinical approaches, healthcare providers can enhance their diagnostic accuracy and ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition.
Training for Effective Percussion Practice
Mastering sound-based diagnostic techniques requires practice, attention to detail, and proper training. The skill of accurately identifying and interpreting the different tones and sounds produced during the assessment of internal structures can significantly impact diagnostic accuracy. Healthcare professionals need to develop both technical and perceptual skills to use this method effectively in clinical settings.
Developing the Right Technique
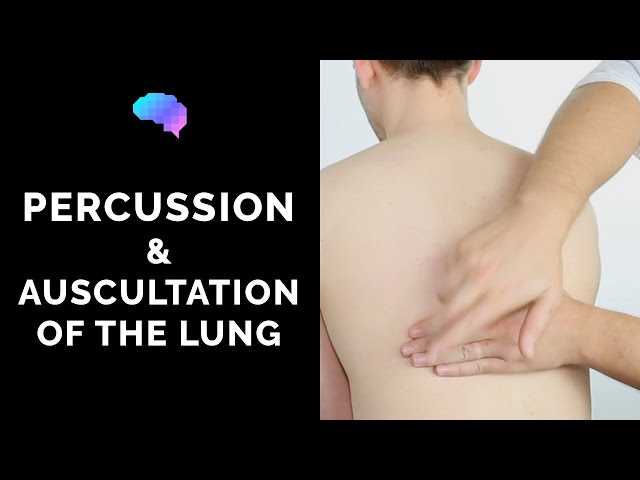
Effective technique is essential for obtaining reliable results. Proper hand positioning, consistent pressure, and systematic tapping are key elements to ensure that the sounds produced are clear and informative. Practicing these techniques on both healthy individuals and patients with known conditions helps to refine the ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal findings.
Enhancing Perceptual Skills
Beyond technique, the ability to interpret sounds accurately is equally important. Training should focus not only on producing the right tones but also on developing a keen ear for subtle differences in sound. Differentiating between tympany, dullness, and resonance requires an understanding of how various tissues and fluids affect sound transmission.
| Focus Area | Importance | Training Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Placement | Ensures consistent sound production | Practice on various body areas with feedback |
| Pressure Control | Prevents distortion of sounds | Gradual adjustments while practicing |
| Sound Differentiation | Helps identify normal vs. abnormal findings | Training with audio examples of various tones |
Ongoing training, whether through practical sessions, feedback from experienced clinicians, or simulation exercises, is critical for mastering these skills and applying them effectively in patient care.