
When preparing for a high-stakes healthcare qualification, it is crucial to understand not only the theoretical aspects but also the practical application of life-saving techniques. This section focuses on essential topics and challenges that healthcare professionals encounter during training, ensuring readiness for real-world situations.
In-depth understanding of key procedures, medications, and patient assessments plays a critical role in successful outcomes. By mastering various critical care protocols, practitioners gain the confidence needed to perform under pressure and make informed decisions in emergencies.
Throughout this guide, you’ll encounter detailed scenarios that mirror the complexity of actual healthcare environments. Analyzing and practicing these situations helps solidify concepts and prepares candidates for immediate application during high-intensity moments. Each section is designed to improve both knowledge retention and practical performance, setting you up for success when it’s needed most.
Overview of Advanced Life Support Qualification
This section introduces the core structure and objectives of the advanced life support qualification process. It is designed to assess an individual’s ability to perform critical interventions in high-pressure, emergency situations, ensuring that healthcare professionals are equipped to provide immediate, life-saving measures.
Participants are evaluated on their understanding of various medical procedures, protocols, and treatment guidelines, as well as their ability to respond effectively to different emergency scenarios. Successful completion of this qualification indicates proficiency in handling complex life-threatening situations.
- Assessing cardiovascular emergencies and treatment protocols
- Administering medications in acute situations
- Managing airway and ventilation in critical conditions
- Performing high-quality chest compressions and defibrillation
- Recognizing and addressing arrhythmias and other cardiac irregularities
To prepare for this qualification, candidates must be familiar with a broad range of medical concepts, from basic life support to advanced therapeutic interventions. The process typically includes a combination of written assessments and hands-on practical evaluations, testing both knowledge and technical skills.
Successful candidates are expected to demonstrate not only theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply their learning under pressure, making quick decisions that can have a significant impact on patient outcomes.
Key Components of Advanced Life Support Evaluation

When preparing for this high-level qualification, understanding the core areas of focus is essential. The assessment tests both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring candidates can effectively manage complex, life-threatening emergencies. The key components cover a broad range of medical interventions, emphasizing rapid decision-making and technical proficiency.
Core Areas of Focus
- Initial patient assessment and prioritization
- Recognition and management of cardiac arrest
- Advanced airway management and ventilation
- Pharmacological interventions in critical conditions
- Defibrillation and cardioversion techniques
Practical Skills and Protocols
Beyond theoretical knowledge, candidates must demonstrate proficiency in performing life-saving procedures. These practical skills are assessed in scenarios that simulate real-life emergencies, where prompt and accurate actions can mean the difference between life and death.
- Performing high-quality chest compressions
- Correctly using a defibrillator in various settings
- Effective drug administration based on patient condition
- Team coordination and communication during critical moments
The ability to make sound decisions quickly and maintain composure under pressure is central to success in this qualification process. Candidates are expected to demonstrate both knowledge and the capability to act decisively in urgent situations.
Common Advanced Life Support Questions and Answers

Understanding the types of questions commonly encountered during advanced life support assessments can significantly improve preparedness. These questions often focus on practical scenarios that require both theoretical knowledge and the ability to apply concepts in real-world emergency situations. Below are some frequently asked questions and their answers, providing insight into critical care decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the first step in managing a patient in cardiac arrest?
- How should a healthcare provider assess airway patency?
- What medication is typically administered during an arrhythmic event?
- When should defibrillation be used in a patient with ventricular fibrillation?
- What is the appropriate compression-to-ventilation ratio for an adult during CPR?
Sample Answers and Explanations
- The first step in managing a patient in cardiac arrest is to ensure the safety of both the patient and the responder, followed by assessing the patient’s responsiveness and starting chest compressions immediately.
- Airway patency can be assessed by checking for visible obstructions, listening for breath sounds, and performing a head-tilt, chin-lift maneuver to ensure the airway is open.
- During arrhythmic events, such as bradycardia, medications like atropine may be administered to help increase heart rate, while other medications such as epinephrine are used in cases of severe cardiac arrest.
- Defibrillation should be performed immediately when a patient is in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, as these conditions are not survivable without prompt defibrillation.
- The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio for adults during CPR is 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths, ensuring adequate blood flow while preventing fatigue.
Mastering these questions and answers is essential for efficient response during high-stress situations. Familiarity with common scenarios ensures that candidates are ready to make the right decisions in real emergencies.
Critical Concepts for Advanced Life Support Success
To succeed in high-stakes healthcare assessments, it is essential to grasp key principles that govern patient care during emergencies. Mastering these core concepts ensures that healthcare professionals are well-prepared to make quick, accurate decisions in critical situations. A deep understanding of protocols, medications, and patient assessments lays the foundation for effective intervention.
First and foremost, recognizing the signs of life-threatening conditions is crucial. Early detection allows for timely interventions, greatly improving patient outcomes. Understanding how to prioritize patient needs based on severity and urgency is a vital skill that ensures resources are used efficiently.
- Airway management: Ensuring that the airway is clear and maintaining ventilation is the top priority in any critical situation.
- High-quality chest compressions: Proper technique during CPR can significantly increase the likelihood of survival.
- Medication administration: Knowing which drugs to administer based on the patient’s condition is essential for stabilization.
- Defibrillation: The use of defibrillators in cases of cardiac arrhythmias can restore normal heart rhythm and save lives.
- Team communication: Effective collaboration and clear communication between healthcare providers are critical during emergencies.
By mastering these critical concepts, professionals can confidently respond to medical crises, knowing they have the necessary skills to save lives. Each concept contributes to a structured approach that ensures rapid, decisive action when every second counts.
Understanding Advanced Life Support Protocols and Guidelines

Mastering the protocols and guidelines for critical care is essential for healthcare professionals tasked with managing emergencies. These protocols provide a structured approach to diagnosing and treating life-threatening conditions, ensuring that each intervention is timely, accurate, and effective. They are designed to standardize care while allowing flexibility based on individual patient needs.
Clear, evidence-based guidelines outline the best practices for handling common medical emergencies such as cardiac arrest, stroke, and respiratory distress. These guidelines offer a step-by-step approach, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions under pressure and deliver appropriate treatments swiftly.
- Cardiac Arrest Management: Recognizing the rhythm and promptly applying defibrillation, if needed, is critical for increasing survival chances.
- Airway and Breathing Support: Ensuring proper airway management and ventilation can prevent further complications and provide life-saving support.
- Medication Guidelines: Specific medications are used for certain conditions, and knowing the right drug and dosage is vital for patient recovery.
- Post-Resuscitation Care: Following successful resuscitation, it’s essential to provide ongoing monitoring and interventions to stabilize the patient.
- Team-Based Approach: Effective communication and coordination within the healthcare team are crucial during emergencies to ensure that each task is executed efficiently.
By understanding and adhering to these protocols, healthcare providers can ensure they are ready to respond effectively in high-pressure situations. These guidelines serve as a blueprint for the most common and critical medical interventions, offering clear steps to follow in times of crisis.
Heart Rhythm and Advanced Life Support Treatment Plans

Understanding the various types of heart rhythms and how to manage them is crucial for healthcare professionals handling cardiac emergencies. Different arrhythmias require specific treatment strategies to restore normal rhythm and improve patient outcomes. Recognizing the rhythm and promptly applying the appropriate intervention can significantly affect the patient’s survival chances.
Common Heart Rhythms and Their Treatment Plans

| Heart Rhythm | Treatment Approach | Medications and Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) | Immediate defibrillation | Defibrillation (shock), Epinephrine administration |
| Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) | Defibrillation if no pulse, antiarrhythmic drugs | Amiodarone, Lidocaine, Magnesium sulfate |
| Atrial Fibrillation (AF) | Rate or rhythm control | Beta-blockers, Calcium channel blockers, Anticoagulants |
| Bradycardia | Atropine administration, pacing if necessary | Atropine, Dopamine, Epinephrine |
| Tachycardia | Vagal maneuvers, synchronized cardioversion | Adenosine, Beta-blockers |
Key Interventions and Medications
Each rhythm has specific protocols for treatment, and the timely use of medications and interventions can help stabilize the patient. For instance, in cases of ventricular fibrillation, immediate defibrillation is necessary, while medications like epinephrine are used to improve the chances of survival. In cases of bradycardia, atropine can be administered to increase the heart rate, and if necessary, pacing is employed to support heart function.
Familiarity with these rhythms and their corresponding treatments is essential for effective response in emergency settings. Understanding these heart rhythms and their associated therapies ensures that medical professionals are prepared to intervene quickly and effectively in life-threatening situations.
Top Tips for Advanced Life Support Preparation
Preparing for a critical care assessment requires a focused approach that combines theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills. Success in such evaluations depends not only on understanding medical concepts but also on being able to apply them under pressure. By following specific strategies, candidates can increase their chances of performing well and feeling confident during the process.
- Review Core Protocols: Familiarize yourself with the key protocols for handling emergencies, including cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, and arrhythmias. Understanding the steps to take in each situation will help guide your actions during practical assessments.
- Practice Scenario-Based Skills: Engage in simulations or practice scenarios that mimic real-life emergencies. This helps reinforce your ability to think quickly and act decisively when every second counts.
- Understand Medication Usage: Be clear on which medications are used in specific conditions, their dosages, and how they affect the body. Knowing when and how to administer the right drugs is crucial for patient care.
- Stay Updated with Guidelines: Medical guidelines and protocols are updated regularly, so ensure that you are using the most current information when studying and preparing.
- Focus on Teamwork: Many scenarios require collaboration, so practice effective communication and leadership skills. Coordinating well with others is key to delivering optimal care during emergencies.
By consistently reviewing materials, practicing practical skills, and staying informed about the latest updates, you can improve your preparedness and approach the assessment with confidence. The ability to apply what you know under stressful conditions is what sets successful candidates apart.
How to Master Advanced Life Support Scenarios
Mastering critical care scenarios requires a combination of theoretical understanding and hands-on practice. Being able to respond effectively in high-pressure situations is essential for saving lives. By becoming familiar with the most common emergency situations and their appropriate responses, healthcare professionals can build confidence and improve their performance in real-life settings.
Key Steps to Master Scenarios

1. Understand the Protocols: Every emergency situation follows a specific set of protocols. Knowing these steps inside and out helps ensure that you don’t miss critical actions during a high-stress event. Review and memorize the guidelines for managing cardiac arrest, strokes, and respiratory failure.
2. Practice Simulation Scenarios: Participating in simulated scenarios mimicking real-life emergencies is one of the best ways to prepare. These exercises help you apply what you’ve learned in a controlled environment, allowing you to practice your decision-making, communication, and technical skills. Repetition will reinforce your ability to stay calm under pressure.
Key Focus Areas for Mastery
- Airway Management: Practice securing the airway and ensuring adequate ventilation in different situations. Airway compromise is often the most immediate threat in emergencies.
- Effective Chest Compressions: High-quality chest compressions are essential in any cardiac arrest scenario. Consistent practice will help you deliver compressions with the correct depth, rate, and recoil.
- Medications and Doses: Familiarize yourself with the medications used for each scenario, including when and how to administer them. Understanding their effects on the body will help you make better clinical decisions.
- Team Dynamics: Effective teamwork is crucial in managing emergencies. Work on your communication skills, learn to delegate tasks, and ensure everyone on the team knows their role.
Mastering these critical skills and scenarios will help you handle real-world emergencies with confidence and competence. Regularly practicing these scenarios in a realistic setting can drastically improve your ability to act decisively when it matters most.
Key Pharmacology for Advanced Life Support
Pharmacological knowledge plays a crucial role in managing critical care situations, particularly during emergencies that involve life-threatening conditions. Understanding which medications to administer, their dosages, and their effects on the body can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. In such high-stress environments, the ability to make quick, informed decisions regarding drug therapy is essential for healthcare professionals.
- Epinephrine: Used for cardiac arrest, this drug helps increase heart rate, contractility, and blood flow to vital organs. It is often administered during situations such as ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
- Amiodarone: A key antiarrhythmic used for life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. It helps restore normal heart rhythm by blocking abnormal electrical signals.
- Lidocaine: Another antiarrhythmic that can be used in cases of ventricular arrhythmias. It works by stabilizing the heart’s electrical activity.
- Atropine: Administered to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate), this drug works by blocking vagal effects and increasing the heart rate.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Used to treat specific arrhythmias like torsades de pointes, a rare form of ventricular tachycardia. It helps stabilize the heart’s electrical activity.
- Adenosine: A drug used to treat certain types of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). It works by slowing down the electrical signals in the heart, allowing it to return to a normal rhythm.
- Furosemide: A diuretic used in cases of heart failure or pulmonary edema to help reduce fluid overload and relieve pressure on the heart.
Having a solid understanding of these medications and knowing when and how to administer them is essential for anyone working in advanced life support settings. Healthcare professionals must be well-versed in the indications, dosages, and side effects of these medications to provide the best possible care during critical emergencies.
Effective CPR Techniques in Advanced Life Support

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a critical life-saving intervention used in emergency situations when a patient’s heart has stopped beating. Performing high-quality CPR is essential for maintaining circulation to vital organs and increasing the chances of survival. Understanding the correct techniques and applying them effectively is key to providing optimal care during cardiac arrest scenarios.
Key Elements of Effective CPR
Effective CPR is more than just performing chest compressions. It involves a series of actions that must be executed in a specific order to maximize the likelihood of a successful outcome. Here are the core elements:
- Compression Depth: Chest compressions should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) deep to ensure adequate blood flow to the heart and brain. Avoiding shallow compressions is critical.
- Compression Rate: Compressions should be delivered at a rate of 100-120 per minute, providing consistent pressure to circulate blood throughout the body.
- Allow Full Recoil: Ensure the chest fully recoils between compressions to allow the heart to refill with blood. Incomplete recoil can reduce the effectiveness of the compressions.
- Minimize Interruptions: Minimize any interruptions to chest compressions, especially during rhythm analysis or defibrillation. The goal is to maintain continuous circulation as much as possible.
- Ventilations: After every 30 compressions, provide 2 rescue breaths to supply oxygen to the lungs. Proper technique for delivering breaths helps improve oxygenation and circulation.
Table of CPR Compression Ratios and Techniques
| Age Group | Compression Depth | Compression Rate | Rescue Breaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | At least 2 inches (5 cm) | 100-120 compressions/min | 2 breaths after 30 compressions |
| Child | About 2 inches (5 cm) | 100-120 compressions/min | 2 breaths after 30 compressions |
| Infant | About 1.5 inches (4 cm) | 100-120 compressions/min | 2 breaths after 30 compressions |
Maintaining high-quality CPR is essential in all cases of cardiac arrest. Healthcare providers must be well-practiced in these techniques to respond quickly and effectively. Consistent and efficient CPR increases the chances of survival and helps stabilize the patient until further medical interventions are available.
Managing Airway and Breathing in Advanced Life Support
Effective management of the airway and breathing is essential during critical care situations, particularly when the patient is unable to breathe or maintain an adequate oxygen supply. Securing the airway and ensuring proper ventilation can significantly improve survival chances and prevent further complications. Understanding the techniques and devices used to support the airway is vital for healthcare providers working in emergency settings.
Techniques for Securing the Airway
During a medical emergency, promptly securing the airway is the first priority. Several methods are available to ensure the patient can breathe effectively, depending on the severity of the situation and the patient’s condition:
- Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift: A basic technique used to open the airway by positioning the patient’s head and neck to clear any obstruction, particularly in unresponsive patients.
- Jaw-Thrust Maneuver: Often used for patients with suspected spinal injury, this technique helps open the airway without moving the neck, reducing the risk of exacerbating spinal damage.
- Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Airways: These devices are inserted into the mouth or nose to keep the airway open, particularly when the patient is unconscious but has no gag reflex.
- Endotracheal Intubation: A more advanced technique used for patients who cannot maintain their airway independently. A tube is inserted into the trachea, providing a secure airway for ventilation.
Effective Breathing Support Methods

Once the airway is secured, it is crucial to ensure the patient is receiving adequate ventilation. Below are methods used to support breathing:
- Bag-Valve Mask (BVM) Ventilation: This technique uses a mask and a self-expanding bag to deliver positive pressure ventilation, ensuring the patient receives sufficient oxygen.
- Advanced Airway Devices: In cases of severe respiratory distress, healthcare providers may use advanced devices such as laryngeal mask airways (LMA) or endotracheal tubes to facilitate ventilation.
- Rescue Breathing: For patients who are breathing but in respiratory distress, rescue breathing may be necessary. This involves giving mouth-to-mouth ventilation or using a mask to deliver breaths manually.
- Oxygen Therapy: Administering oxygen is a critical step in stabilizing patients, particularly those experiencing respiratory failure or shock. Oxygen can be delivered through a mask, nasal cannula, or more advanced devices depending on the patient’s needs.
Proper airway management and ventilation are fundamental in ensuring that the body receives adequate oxygen. Every healthcare provider should be proficient in these techniques to effectively respond in emergency situations and improve patient outcomes. Consistent and timely interventions can prevent complications and enhance survival chances during life-threatening medical events.
Assessing Cardiac Arrest During the Evaluation
Recognizing and assessing cardiac arrest is crucial in any emergency medical scenario. Immediate and accurate identification of this life-threatening condition is essential for initiating the correct interventions to improve the chances of survival. In clinical practice, particularly during structured evaluations, healthcare providers must demonstrate their ability to quickly assess a patient’s condition and initiate appropriate treatment based on the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest.
Key Indicators of Cardiac Arrest
When assessing a patient for cardiac arrest, it is important to focus on several key clinical signs:
- Unresponsiveness: The patient will not respond to verbal or physical stimuli, indicating a severe impairment of brain function.
- Absence of Pulse: One of the hallmark signs of cardiac arrest is the absence of a detectable pulse. Providers must assess the carotid or femoral pulse for at least 10 seconds.
- Irregular or Absent Breathing: The patient may not breathe at all or exhibit abnormal gasping breaths, known as agonal breathing, which requires immediate intervention.
- Skin Changes: The skin may appear pale, cyanotic, or mottled, indicating poor circulation and oxygenation.
Steps to Take When Cardiac Arrest is Suspected
Upon recognizing the signs of cardiac arrest, it is important to take immediate action. The following steps are crucial in managing the situation:
- Call for Help: Alert emergency services and initiate the chain of survival as soon as possible.
- Begin Chest Compressions: High-quality chest compressions should be started immediately. Ensure the chest is compressed at a depth of at least 2 inches and at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Deliver Rescue Breathing (if trained): If trained and able, give rescue breaths in conjunction with chest compressions to maintain oxygenation.
- Use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED): If available, an AED should be applied to assess the need for defibrillation. Follow the AED prompts carefully to deliver a shock if indicated.
Effective and prompt assessment of cardiac arrest is essential for initiating life-saving interventions. Demonstrating proficiency in recognizing and responding to cardiac arrest is a critical skill for healthcare providers, ensuring better outcomes in emergency situations.
Strategies for Handling Mock Practice Assessments
Preparing for high-stakes medical evaluations requires more than just theoretical knowledge. Mock practice tests are essential tools that simulate real-world scenarios, helping to build confidence and refine critical skills. By approaching these mock tests strategically, you can improve your performance, identify areas for improvement, and enhance your overall readiness for the actual assessment.
Effective Strategies for Practice Tests
To maximize the benefit of mock practice assessments, implement the following strategies:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Format: Before taking a mock test, understand the structure and types of questions that will be asked. This will help you feel more comfortable and focused during the practice.
- Time Management: Mock assessments often have strict time limits. Practice answering questions quickly but accurately. Being mindful of time will help you manage your pacing during the real evaluation.
- Review Correct and Incorrect Answers: After completing each mock test, go over both the questions you answered correctly and the ones you missed. Understanding why a particular answer is correct or incorrect helps reinforce learning.
- Simulate Real-Life Conditions: Treat mock assessments like the actual evaluation. Minimize distractions and create a realistic testing environment to replicate the pressure of the actual event.
Analyzing Mock Test Results
Once you’ve completed several mock practice tests, analyzing your performance becomes key to improving your skills. The following approach will help you track progress and fine-tune your abilities:
| Category | Action to Take |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Focus on understanding why certain questions were missed and address knowledge gaps. |
| Speed | Practice answering questions more quickly without compromising accuracy. |
| Confidence | Identify patterns in your strengths and weaknesses to boost confidence in your abilities. |
Mock practice assessments are a vital part of preparation. By strategically tackling them and carefully analyzing your performance, you can enhance both your skills and your confidence in readiness for the real test.
Time Management Tips for Medical Assessments
Effective time management is essential when preparing for any high-pressure medical evaluation. With a limited amount of time to answer questions, demonstrate critical skills, and apply knowledge, how you manage your time can significantly impact your performance. By using strategic planning and honing efficient decision-making skills, you can ensure that you complete the test within the allotted time while maintaining accuracy.
Prioritize Critical Tasks
During any medical assessment, some tasks will require more immediate attention than others. It’s important to focus on the most crucial aspects first to avoid spending too much time on less urgent elements. Here’s how:
- Identify High-Yield Topics: Some areas of knowledge are more heavily weighted than others. Prioritize studying high-yield topics that are likely to be tested more frequently.
- Focus on Key Skills: When dealing with practical scenarios, prioritize interventions that could make a significant impact, such as chest compressions, airway management, or administering vital medications.
- Know When to Move On: If you’re unsure about a particular question or scenario, don’t spend too much time dwelling on it. Make an educated guess, move on, and return to it if time allows.
Practice Under Time Pressure

To develop a sense of how long tasks should take and to improve your speed, it’s crucial to practice under timed conditions. Incorporate the following strategies:
- Simulate Real Testing Conditions: Set aside dedicated time to complete mock tests or practical drills within the designated time limits. This will help you get comfortable with the pace.
- Set Time Milestones: Break the test into smaller segments, and aim to complete each section within a certain timeframe. This helps ensure that you stay on track and avoid spending too long on any one task.
- Use a Timer: During practice sessions, use a timer to get used to the time pressure. It will help you gauge how long you typically take to answer questions and allow you to adjust your pacing.
Mastering time management is critical to performing well on any high-stakes medical test. By focusing on high-priority tasks, practicing under time constraints, and refining your pacing, you can improve both your speed and accuracy, leading to a more successful outcome.
Exam Tips for Non-Healthcare Professionals
For individuals without a healthcare background, preparing for a medical assessment can seem overwhelming. However, with the right approach and understanding of essential concepts, it’s possible to excel in these evaluations. This section provides strategies specifically designed for non-medical professionals to effectively navigate through assessments that require medical knowledge and practical skills.
First, it’s important to break down complex topics into manageable sections. Focusing on understanding the core principles, such as basic life-saving procedures, recognizing emergency symptoms, and responding appropriately in critical situations, will allow you to gain confidence and improve your test performance.
Start with the Basics
For those new to medical knowledge, begin by mastering the most fundamental concepts. This will form a solid foundation that you can build upon. Key areas to focus on include:
- Understanding Vital Signs: Knowing how to assess heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure is crucial. These indicators can help you assess the condition of a patient in emergency scenarios.
- Basic First Aid: Learn the essential techniques for performing first aid, such as CPR and wound care. These are fundamental skills that are often tested in various formats.
- Recognizing Common Medical Emergencies: Familiarize yourself with the signs of common emergencies like heart attacks, strokes, and choking. Understanding what to look for can improve your response time and accuracy.
Utilize Study Aids and Resources

There are numerous resources available that can help simplify the learning process for non-healthcare professionals. Make use of these tools to reinforce your knowledge:
- Practice Tests: Taking practice assessments can help you get comfortable with the format and timing. This will also give you a sense of what areas require more focus.
- Visual Learning Tools: Use videos, diagrams, and interactive tools to visualize emergency procedures. Seeing these actions performed can make them easier to understand and remember.
- Study Groups: If possible, join a study group with peers or colleagues who are also preparing. This collaborative approach can make learning more engaging and offer diverse perspectives on complex topics.
By focusing on the essentials, utilizing available resources, and practicing regularly, non-healthcare professionals can build the necessary skills and confidence to succeed in medical assessments. Stay patient and persistent, and remember that even without a healthcare background, mastery of fundamental procedures can greatly enhance your performance.
Post-Exam Review and Self-Assessment

After completing a medical-related assessment, it is essential to reflect on your performance to identify areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. A thorough review of the completed test can enhance your learning and ensure that you are better prepared for future challenges. This section outlines strategies for self-assessment and ways to effectively review your performance following an evaluation.
Once the assessment is over, take time to analyze your results and review the questions that posed difficulty. Understanding where mistakes were made and why they occurred will provide valuable insights into your current level of knowledge and ability. This self-reflection process is crucial for continuous improvement and long-term success in similar scenarios.
Steps for a Productive Review
To maximize the benefits of your post-assessment review, consider the following steps:
- Examine Incorrect Responses: Carefully go over each question you answered incorrectly. Understand the reasoning behind the correct answers and the rationale for your mistakes.
- Identify Knowledge Gaps: Take note of topics where you struggled. These areas need further study to improve your grasp of the concepts.
- Seek Clarification: If there were questions that you didn’t fully understand, make sure to seek clarification from a trusted source, such as instructors or reliable study materials.
- Practice Time Management: Evaluate how effectively you managed your time during the assessment. Were there any sections that took longer than expected? Adjust your strategy for future practice or evaluations.
Engage in Self-Assessment
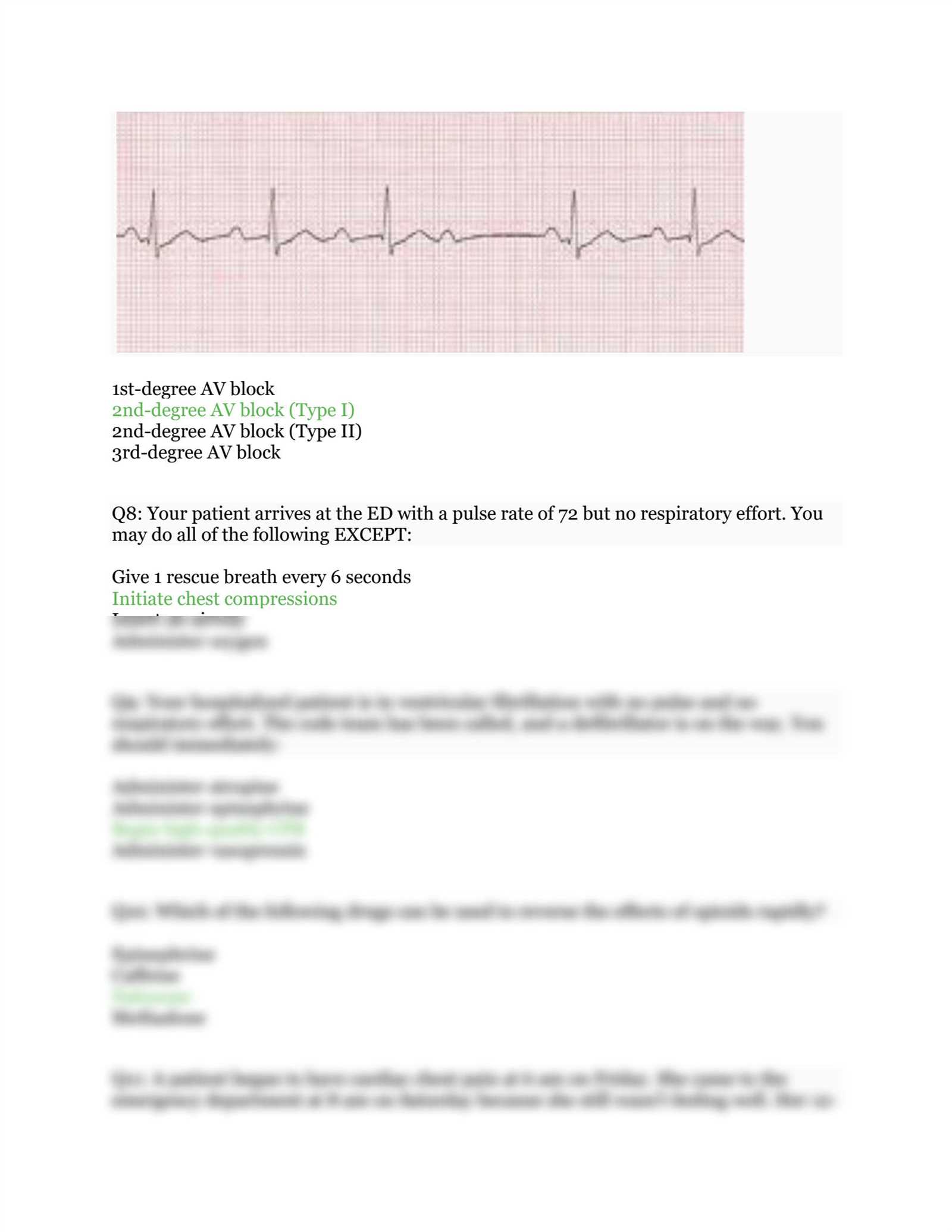
In addition to reviewing incorrect answers, self-assessment involves critically analyzing your overall approach to the test:
- Self-Reflection: Consider your overall performance and mindset during the test. Did you feel confident in your decision-making? Were there any moments of hesitation? Recognizing these aspects helps you to build mental resilience for future challenges.
- Continuous Improvement: Based on your findings, create an action plan for ongoing study and practice. Focus on areas where improvement is necessary, and incorporate new strategies into your study routine.
- Evaluate Preparation Techniques: Reflect on your preparation methods leading up to the assessment. Were they effective, or do you need to adapt your approach? Try using different resources, such as practice tests or group study, to see what works best for you.
Incorporating post-assessment review and self-assessment into your routine is key to building confidence and expertise. With each review, you gain the insight needed to perform better in future evaluations and real-world situations. Keep a positive mindset and use your reflections as a tool for growth and improvement.