
When it comes to acquiring critical life-saving skills, practical knowledge and preparation are essential. Being equipped to handle emergency situations can make a significant difference in saving lives. The process of learning these vital procedures includes understanding key techniques, knowing how to apply them, and ensuring proficiency in high-pressure scenarios. This guide will explore the most important aspects of mastering these skills and provide useful insights for those looking to succeed in their certification journey.
Through structured learning and comprehensive tests, individuals are assessed on their ability to respond effectively to emergencies. Whether it’s assisting someone who has stopped breathing or offering help in other urgent health situations, knowing the right actions can be life-changing. This section will highlight the most commonly tested areas and provide a deeper understanding of what is expected during assessments, offering tips to help you feel confident and prepared.
American Red Cross CPR Final Exam Answers
Completing a certification course in life-saving procedures involves both learning the techniques and demonstrating competence through practical assessments. These evaluations ensure that individuals are fully prepared to act in emergency situations, applying the right skills to save lives. The assessments often focus on various scenarios, testing knowledge and ability to perform correctly under stress. Understanding what is expected in these tests can help you feel more confident and ensure a higher level of success.
Key Areas of Focus During Assessments
To prepare effectively, it’s crucial to know the primary topics that are commonly covered in evaluations. These areas are designed to test both theoretical understanding and practical application of skills. Below are the key components you should focus on:
- Chest compressions and proper depth
- Effective airway management techniques
- Proper use of defibrillation equipment
- Recognizing signs of distress in various individuals (adults, children, infants)
- Clear communication in emergency scenarios
Study Tips for Success
Preparing for the certification assessment requires a combination of practical practice and theoretical study. Here are some tips to help you get ready:
- Review all course materials thoroughly before attempting the test.
- Practice hands-on techniques regularly to improve muscle memory.
- Use simulation tools or mock assessments to simulate real-life situations.
- Stay calm and focused during the evaluation to ensure accuracy in each step.
- Ensure you are familiar with all required equipment and how to use it efficiently.
With these tips and focused preparation, you’ll be ready to pass your certification and gain the necessary skills to help in emergency situations confidently.
Overview of CPR Training Program

Life-saving skill courses are designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and practical abilities to respond effectively to emergencies. These programs focus on critical techniques that can make the difference between life and death, such as performing chest compressions, using defibrillators, and maintaining clear airways. The training is structured to offer both theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience, ensuring that participants are prepared for real-world situations.
The program is typically divided into multiple stages, each focusing on specific skills and techniques. Participants learn to identify the signs of a medical emergency, such as cardiac arrest, and apply appropriate interventions based on the victim’s condition. With a blend of instruction and practice, learners gain the confidence they need to act quickly and effectively in high-pressure situations.
Courses often cater to different levels, from basic to advanced, allowing individuals to choose the right program based on their needs. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a first responder, or someone interested in learning life-saving techniques for personal or community use, these training sessions provide invaluable knowledge that could help save lives in critical moments.
Key Concepts Covered in CPR Exam
The process of evaluating proficiency in life-saving procedures involves several critical concepts that participants must understand and demonstrate. These concepts ensure that individuals are capable of responding to emergencies in the most effective way possible. Mastery of these core ideas is essential for successful completion of the assessment and for confidently managing emergency situations.
The topics covered in the assessment range from basic life support to more advanced techniques. They focus on the correct methods for performing chest compressions, maintaining airflow, and recognizing various medical conditions that require immediate attention. Understanding these key principles will help ensure that participants are fully prepared for the challenge of a real emergency.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Proper technique for performing compressions to maintain blood circulation in a person experiencing cardiac arrest. |
| Airway Management | Techniques for opening and maintaining the airway to ensure the victim can breathe properly. |
| Use of Defibrillators | How to properly use an automated external defibrillator (AED) to restore normal heart rhythm. |
| Breathing Techniques | Effective methods for delivering rescue breaths when necessary to assist with breathing. |
| Recognizing Cardiac Arrest | Signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest that require immediate intervention. |
Understanding these foundational concepts is crucial for success in the evaluation. They ensure that individuals are prepared to make life-saving decisions under pressure, ultimately leading to better outcomes in emergencies.
Understanding the CPR Certification Process
The process of obtaining a life-saving procedure certification involves several key steps designed to ensure participants are fully prepared to respond to emergencies. This structured approach includes learning the essential techniques, practicing hands-on skills, and demonstrating proficiency through a formal evaluation. Each stage is intended to build confidence and ensure that individuals can effectively manage critical situations when necessary.
Steps to Obtain Certification
The certification process is typically divided into a few clear phases, each focusing on different aspects of emergency care. Below are the main steps involved:
- Enrolling in a course that covers essential life-saving techniques
- Participating in both theoretical lessons and practical training sessions
- Completing required assignments or quizzes to test knowledge
- Demonstrating competence in performing the procedures correctly
- Receiving a certification upon successful completion of the course and test
Maintaining Certification
Once certified, it is important to keep your skills current. Most certifications require periodic renewal to ensure that individuals remain up-to-date with the latest guidelines and techniques. Here are the general steps for maintaining certification:
- Complete any required refresher courses within the designated time frame.
- Attend regular training sessions to practice and reinforce skills.
- Stay informed about updates or changes in emergency response procedures.
By understanding the certification process and committing to continued learning, you ensure that you are always prepared to act effectively in any emergency situation.
Commonly Asked Questions in CPR Test
When preparing for an assessment in life-saving techniques, it’s helpful to anticipate the types of questions that may arise. These questions typically focus on critical concepts such as identifying emergency conditions, performing necessary interventions, and understanding proper protocols. Knowing what to expect can help build confidence and ensure that you’re fully prepared to demonstrate your knowledge and skills during the evaluation.
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions during these assessments:
- What is the correct depth and rate for chest compressions in adults?
- How do you recognize when a person is in cardiac arrest?
- What steps should you take when performing rescue breaths?
- When is it appropriate to use a defibrillator?
- What are the key differences between performing life-saving procedures on adults and children?
- How can you assess whether someone is breathing normally?
- What should you do if you encounter an unresponsive individual with no pulse?
These questions test both theoretical understanding and practical knowledge. To succeed, it’s important to not only memorize the steps but also to understand the rationale behind each action, as this will allow you to respond effectively in any emergency situation.
How to Prepare for CPR Exam
Preparing for a life-saving procedures assessment requires a combination of studying key concepts and practicing hands-on skills. The goal is to ensure you understand the necessary steps and can perform them under pressure. By familiarizing yourself with the techniques and understanding the scenarios likely to be tested, you’ll be better equipped to handle the evaluation successfully.
Here are several effective strategies to help you prepare:
- Review the Course Material: Thoroughly read through all training materials, including guidelines and instructional books. Focus on understanding each step in the process.
- Practice Hands-On Skills: Actively practice the physical techniques, such as chest compressions and using defibrillators, to build muscle memory and confidence.
- Take Mock Tests: Participate in practice scenarios to simulate the evaluation conditions. This will help you get used to performing under pressure.
- Understand Key Concepts: Make sure you grasp the theory behind each procedure, such as the importance of chest compression depth or airway management.
- Ask for Feedback: Get feedback from instructors or peers to identify areas where you might need improvement.
- Stay Calm and Focused: During the test, focus on each task step by step and avoid rushing. Staying calm will help ensure better performance.
By following these strategies, you’ll not only be prepared for the assessment but also be confident in your ability to act in real-life emergencies when needed.
Steps to Perform Effective Chest Compressions
Chest compressions are one of the most crucial life-saving interventions in emergency situations, especially when someone is experiencing a cardiac arrest. Properly performing compressions helps maintain blood circulation and provides oxygen to vital organs until advanced medical help arrives. Understanding and mastering the correct technique is essential to increasing the chances of survival for the person in distress.
Here are the essential steps to perform effective chest compressions:
- Position Your Hands: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, just below the breastbone. Then, place your other hand on top of the first and interlock your fingers.
- Body Position: Ensure your shoulders are directly above your hands and your elbows are fully extended. Keep your arms straight to allow your body weight to assist in the compressions.
- Compression Depth: Press down hard and fast, compressing the chest at least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults. Ensure the chest fully recoils between compressions.
- Compression Rate: Perform compressions at a rate of about 100 to 120 compressions per minute, which is roughly the tempo of the song “Stayin’ Alive” by the Bee Gees.
- Allow Full Recoil: After each compression, let the chest return to its normal position. Do not lean on the chest between compressions.
- Minimize Interruptions: Avoid pausing compressions unless absolutely necessary, such as to check for breathing or administer rescue breaths.
By following these steps, you can effectively maintain circulation and increase the likelihood of a positive outcome for the person in need of urgent help. Proper chest compressions are vital in any emergency where cardiac arrest is suspected, and performing them correctly can make a life-saving difference.
Recognizing Cardiac Arrest Symptoms

Recognizing the signs of cardiac arrest is crucial for taking immediate action to save a person’s life. Cardiac arrest occurs suddenly and can lead to death if not treated quickly. Knowing the symptoms and understanding when immediate intervention is required can make a significant difference in the outcome. Prompt recognition allows for faster response and increases the chances of survival through proper intervention.
Common Symptoms of Cardiac Arrest
The symptoms of cardiac arrest are often very sudden and may not show any prior warning signs. Recognizing these signs immediately is vital for initiating life-saving measures. The following are the most common indicators:
- Sudden Collapse: The person may collapse unexpectedly and lose consciousness.
- No Breathing: The individual may stop breathing or breathe abnormally, such as gasping for air.
- Unresponsiveness: The person will not respond to verbal or physical stimuli, such as shaking or tapping their shoulder.
- Pale or Bluish Skin: The skin may turn pale or develop a bluish tint, especially around the lips and face, due to lack of oxygen.
- No Pulse: A pulse will be absent or extremely weak when checked.
Steps to Take After Recognizing Symptoms
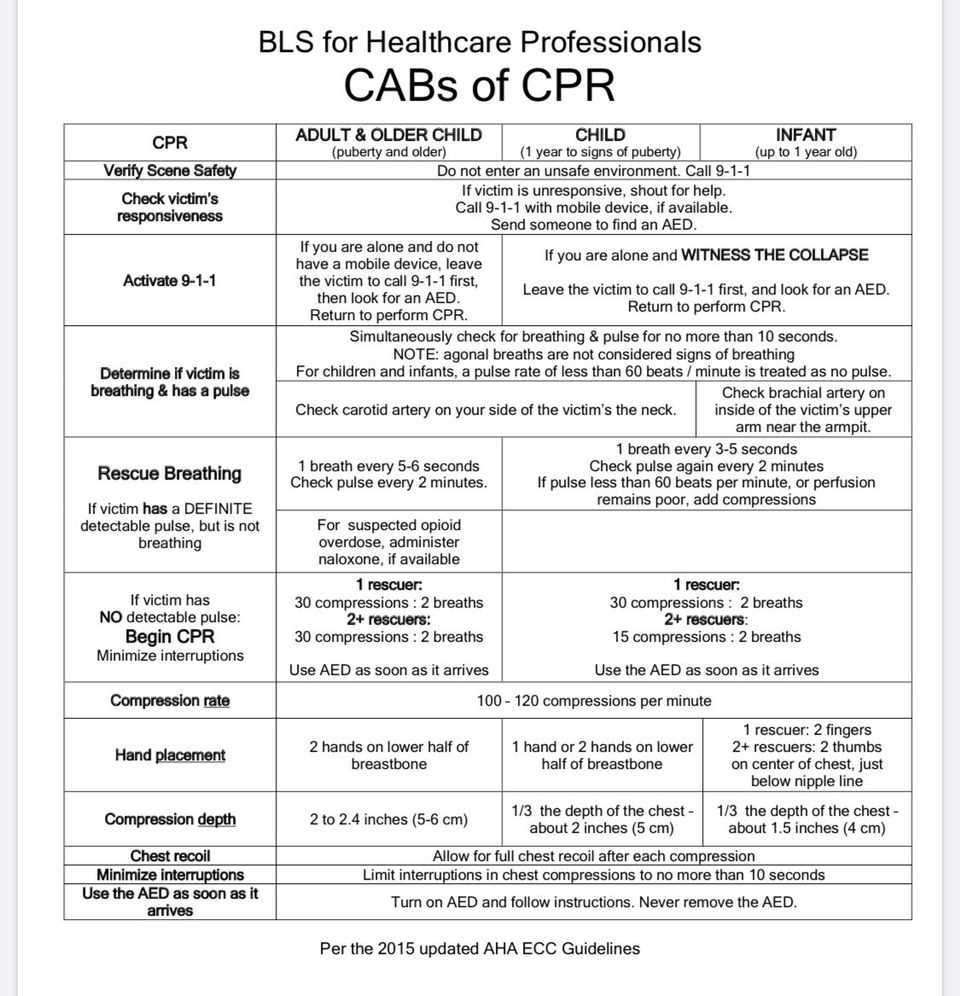
If you notice these signs, it is crucial to act quickly. Follow these steps to provide the best chance of survival:
- Check for responsiveness and call for help immediately.
- Start chest compressions to maintain circulation and oxygen flow.
- If available, use a defibrillator to shock the heart back into a normal rhythm.
- Continue life-saving measures until emergency medical professionals arrive.
Understanding these symptoms and knowing what to do in such situations can drastically improve the chances of recovery. Acting quickly and correctly is essential in any case of suspected cardiac arrest.
Airway Management in CPR Situations
In any emergency where someone is unconscious or not breathing properly, managing their airway is a critical step in ensuring that oxygen can reach the lungs and vital organs. Proper airway management helps maintain oxygen flow to the brain and heart, which is essential for survival. Knowing how to clear and open the airway effectively can be the difference between life and death in many situations.
There are several key techniques for managing the airway during an emergency:
- Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift: This is the most common method for opening the airway. By tilting the head back and lifting the chin, the tongue is moved away from the back of the throat, opening the airway and allowing air to flow freely.
- Jaw-Thrust Maneuver: In cases where there may be a neck injury, the jaw-thrust maneuver is used. By pushing the jaw forward without tilting the head, the airway can be opened while minimizing the risk of exacerbating any neck or spine injuries.
- Supraglottic Airways: In more advanced situations, specialized devices such as supraglottic airways may be used to secure the airway and ensure proper ventilation. These are typically used by trained medical professionals.
In addition to opening the airway, it’s also important to monitor the victim for any signs of obstruction. If there is a blockage in the airway, it must be cleared as soon as possible. In cases where the individual is unresponsive and not breathing, it’s essential to proceed with rescue breathing or chest compressions while maintaining the airway.
Proper airway management is an essential part of any life-saving response, as it ensures that the body gets the oxygen it needs to function properly, particularly when other vital organs are at risk due to lack of breathing. Whether you’re performing basic or advanced procedures, having a clear and open airway is one of the first steps toward stabilizing the individual until professional help arrives.
Importance of Early Defibrillation
In critical situations such as cardiac arrest, the heart’s electrical activity can become irregular, preventing the heart from pumping blood effectively. Early intervention is key to restoring a normal rhythm and increasing the chances of survival. Defibrillation is a crucial procedure that involves delivering an electrical shock to the heart in order to reset its rhythm, allowing it to return to normal function. The sooner defibrillation occurs, the greater the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Why Timing is Crucial
The effectiveness of defibrillation is highly dependent on how quickly it is administered. The longer the heart remains in an abnormal rhythm, the less likely it is that the individual will survive. Immediate defibrillation can significantly improve survival rates and reduce the risk of long-term damage to vital organs.
- Faster Restoration of Heart Rhythm: Early shock can quickly restore the heart’s normal rhythm, preventing further complications.
- Improved Survival Rates: Studies show that when defibrillation is performed within the first few minutes of cardiac arrest, survival rates increase dramatically.
- Reduced Risk of Brain Damage: By restoring circulation quickly, early defibrillation helps prevent brain damage due to lack of oxygen.
How to Administer Defibrillation
Defibrillation can be performed using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED), which is designed to be used by individuals with minimal training. AEDs are user-friendly and provide clear instructions on how to proceed. Here’s how to administer the shock:
- Turn on the defibrillator and follow the prompts.
- Attach the electrode pads to the individual’s chest as indicated on the device.
- The AED will analyze the heart rhythm and determine if a shock is needed.
- If a shock is recommended, the AED will instruct you to press a button to deliver the shock.
- Continue following the AED’s instructions for further care until emergency personnel arrive.
In conclusion, early defibrillation is a vital component of emergency response. The faster it is administered, the better the chances of a positive outcome. Whether by trained professionals or bystanders, using an AED can save lives and make the difference between recovery and tragedy.
CPR Guidelines for Children and Infants
When providing life-saving care to young children or infants, it is essential to understand the differences in their physiology compared to adults. The approach to resuscitation in these cases must be adjusted to meet the unique needs of their smaller, more fragile bodies. Knowing the correct methods for performing chest compressions and rescue breathing can significantly improve the chances of survival and recovery in an emergency situation.
Key Differences in Pediatric Resuscitation
Children and infants require a more gentle touch and different techniques due to their size and developmental stage. For example, compression depth and the force applied are much less than in adults. Understanding these key distinctions is critical when responding to emergencies involving younger individuals.
- Infants (under 1 year old): When performing chest compressions on infants, use two fingers placed just below the nipple line in the center of the chest. Compress the chest about 1.5 inches (4 cm) deep at a rate of about 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Children (1 year to puberty): For children, use one or two hands depending on the child’s size. Compress the chest about 2 inches (5 cm) deep. The compression rate should remain around 100-120 per minute.
Rescue Breathing for Children and Infants
Rescue breathing for younger individuals requires careful attention to avoid overinflating their lungs. The amount of air provided during breaths should be just enough to make the chest rise visibly. For infants, a gentle puff of air is sufficient, while for children, you may need to provide slightly more forceful breaths.
- Infants: Cover both the infant’s nose and mouth with your mouth to provide gentle breaths. Give 1 breath every 3 seconds during resuscitation.
- Children: Seal your mouth around the child’s mouth and nose (for smaller children) or just their mouth (for older children). Provide 1 breath every 3 seconds.
It’s important to remain calm and focused when providing care to children and infants. Rapid action, combined with the right techniques, can make a life-saving difference. Be sure to follow appropriate guidelines and seek professional medical assistance as soon as possible.
Difference Between CPR and First Aid
While both resuscitation techniques and basic emergency care are essential for handling medical emergencies, they serve different purposes and involve distinct approaches. Understanding the key differences between these two life-saving methods can help individuals respond appropriately to various situations and provide the right care at the right time.
What is Resuscitation?
Resuscitation, or life-saving techniques, is focused on restoring vital functions such as breathing and circulation in individuals who are in critical conditions, like cardiac arrest or severe breathing difficulties. It typically involves specific actions like chest compressions and rescue breaths, aimed at restoring blood flow and oxygen to the body.
- Purpose: Primarily intended to restart heart function or maintain oxygen flow to vital organs.
- Procedure: Involves chest compressions, rescue breathing, or the use of a defibrillator to shock the heart back into a regular rhythm.
- When to Use: Used during medical emergencies like heart attacks, respiratory failure, or when an individual is unresponsive and not breathing.
What is Basic Emergency Care?
On the other hand, basic emergency care, also known as first aid, includes a wide range of techniques designed to manage injuries or health conditions until professional help arrives. First aid focuses on stabilizing the individual and preventing further harm, rather than restoring vital functions like resuscitation techniques do.
- Purpose: Aims to stabilize an individual and manage injuries or illnesses before medical professionals take over.
- Procedure: Involves actions such as dressing wounds, applying pressure to stop bleeding, helping with choking, and providing comfort to those in distress.
- When to Use: Used in situations like cuts, burns, sprains, fractures, and other non-life-threatening conditions.
In essence, while both methods are vital in emergencies, resuscitation focuses on life-saving techniques for critical cases, while first aid addresses a broader range of injuries and medical concerns. Knowing when and how to apply each can be the difference between life and death or preventing a condition from worsening.
Essential CPR Tools and Equipment
When performing life-saving procedures, having the right tools and equipment at hand can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. These tools are designed to support the responder in performing critical interventions, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the care provided. Understanding the essential items that should be readily available in any emergency situation is crucial for effective response.
Basic Tools for Immediate Intervention
In many emergency scenarios, a few simple tools can make a significant difference. These items help stabilize the individual and enable the responder to perform necessary actions efficiently.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Gloves, face shields, and masks are essential to protect both the victim and the responder from potential contamination and transmission of infections.
- CPR Mask: A mask with a one-way valve is used to provide rescue breaths while minimizing direct contact, reducing the risk of exposure to bodily fluids.
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED): This portable device analyzes the heart rhythm and delivers a shock if needed to restore a normal heartbeat in the event of cardiac arrest.
Advanced Tools for Specific Emergencies
In addition to basic tools, advanced equipment is required in certain situations, particularly in cases of severe medical emergencies. These items are typically used by trained professionals but may also be available for use by trained bystanders.
- Oxygen Tank: For individuals who are not breathing or require supplemental oxygen, an oxygen tank can be used to provide necessary air until emergency medical personnel arrive.
- Airway Management Devices: Tools like oral and nasal airways or advanced airway management devices may be used to maintain an open airway, particularly in cases of severe airway obstruction.
Having access to the right tools is not only vital for performing the required steps efficiently but also for ensuring the safety of both the responder and the individual receiving care. Proper training in using these tools can increase confidence and effectiveness when responding to emergencies.
How to Stay Calm During CPR

In emergency situations, staying composed is critical for effective intervention. The stress of dealing with someone who is unresponsive or not breathing can be overwhelming, but maintaining a calm demeanor is essential for both your effectiveness and the safety of the person in need. Having a clear plan and staying focused can help ensure the best possible outcome in these high-pressure moments.
Here are some practical strategies to help you stay calm while performing life-saving procedures:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Focus on the Task | Concentrating on the immediate actions that need to be taken, such as chest compressions or using a defibrillator, can help redirect your mind away from panic and ensure you’re providing care effectively. |
| Control Your Breathing | Take deep, steady breaths to calm your nervous system. Controlled breathing will help you maintain focus and stay energized during the intervention. |
| Trust Your Training | If you have completed a training course, trust in the knowledge and skills you’ve acquired. This confidence will help reduce anxiety and allow you to act decisively. |
| Stay Organized | Having a clear structure in your mind (e.g., assess the scene, call for help, begin chest compressions, use AED) can help you stay on track and reduce feelings of uncertainty. |
| Delegate Tasks | If there are others nearby, delegate tasks to them. Having someone call emergency services or assist with other actions can relieve some of the pressure and help you focus. |
By applying these strategies, you can stay focused, maintain clarity of thought, and provide the best possible care in an emergency situation. Remember, staying calm is not just beneficial for you–it also increases the likelihood of a successful outcome for the person in need.
Post-CPR Care and Recovery Procedures
After performing life-saving interventions, it is essential to provide proper follow-up care to ensure the person’s recovery and well-being. While the immediate focus is on restoring breathing and circulation, post-resuscitation care plays a crucial role in minimizing complications and promoting a smooth recovery. This phase involves monitoring the individual’s vital signs, providing emotional support, and preparing for professional medical care.
The following steps outline the procedures to follow after performing emergency life-support actions:
- Monitor Vital Signs: After stabilizing the person, closely observe their heart rate, breathing, and responsiveness. It’s important to ensure that the person remains stable until medical professionals arrive.
- Keep the Person Comfortable: If the individual is conscious, help them stay calm and comfortable. Reassure them and keep them warm to prevent shock.
- Administer Oxygen (if available): If you have access to oxygen or breathing equipment, administer it as needed. This is especially important if the person shows signs of difficulty breathing or if they remain unresponsive.
- Prepare for Medical Personnel: When emergency responders arrive, provide them with detailed information about the event, including the time of collapse, interventions performed, and the person’s current condition.
- Avoid Giving Food or Water: Refrain from offering food, water, or drinks until the person has been thoroughly evaluated by a medical professional.
Important Considerations: Even if the person regains consciousness and appears stable, they still require a full medical assessment. Emergency medical teams will provide the necessary care, including monitoring for potential complications and deciding on any further interventions.
In some cases, individuals may experience psychological distress after an emergency, so it’s vital to offer emotional support. Encourage the person to seek counseling if needed, as traumatic events can sometimes have long-term effects on mental health.
By following these recovery procedures, you ensure the individual receives comprehensive care after an emergency, increasing their chances for a full recovery.
CPR Test Scoring and Evaluation Criteria
When assessing proficiency in life-saving techniques, it is essential to have clear guidelines to measure how well individuals perform under pressure. The scoring and evaluation process is designed to ensure that each candidate demonstrates the necessary skills, knowledge, and judgment required in emergency situations. The criteria used in this assessment focus on the candidate’s ability to follow protocol, apply correct techniques, and respond effectively to different scenarios.
The evaluation typically includes both practical skills and theoretical knowledge, and candidates are scored based on their ability to execute each step accurately. Below are the key areas evaluated during the assessment:
- Technique Accuracy: The candidate is assessed on their ability to perform essential maneuvers, such as chest compressions, rescue breaths, and other critical steps in the life-saving process. Proper hand placement, compression depth, and rhythm are key factors in scoring.
- Response Time: Speed and efficiency are important when performing life-saving techniques. The candidate is evaluated on how quickly they recognize the need for intervention and how promptly they begin administering assistance.
- Decision-Making and Judgment: Evaluators look at the candidate’s ability to make correct decisions under pressure. This includes recognizing signs of distress, determining when to call for help, and choosing the right intervention for the situation.
- Adherence to Protocols: Following established guidelines is critical for effective emergency response. Candidates are evaluated on their adherence to safety protocols, including checking the surroundings, ensuring the person is unresponsive, and calling emergency services.
- Communication Skills: In emergency situations, clear communication is vital. Candidates are assessed on how well they communicate with bystanders, emergency responders, and other individuals involved in the situation.
Evaluation Scoring: Typically, a pass or fail evaluation system is used. Each candidate’s performance is assigned a score based on the accuracy and effectiveness of their actions. Some programs may also include additional factors such as teamwork or leadership skills when working in group scenarios.
By maintaining these standards of assessment, the goal is to ensure that individuals are fully prepared to handle real-life emergencies. These evaluations also provide constructive feedback for participants, helping them improve their skills for future life-saving situations.
What to Do After Passing the Exam
After successfully completing the certification process and demonstrating your ability to perform essential life-saving techniques, there are several important actions to take. The journey does not end with the certificate; staying updated, regularly practicing, and knowing how to apply your skills in real-life situations are crucial to maintaining proficiency. Below are the key steps to follow once you’ve received your certification.
1. Receive Your Certification and Documentation
Once you pass the assessment, you will receive an official certification recognizing your competency in critical life-saving skills. This certificate is typically valid for a specific period, such as two years, after which you may need to retake the training or attend a refresher course. Make sure to keep the certificate in a safe location, as it may be required for various professional or volunteer roles.
2. Keep Your Skills Up to Date
It’s important to remember that learning these techniques is an ongoing process. Over time, skills can become rusty, so it’s essential to refresh your knowledge and practice regularly. Here are some ways to stay sharp:
- Review techniques and principles periodically to reinforce your knowledge.
- Attend refresher courses or training sessions to stay current with updated protocols.
- Participate in community-based activities or practice groups to keep your skills fresh.
3. Understand Recertification Guidelines
Many organizations require recertification after a certain period. Be sure to understand the recertification process and requirements, as they vary between different certifying bodies. Plan ahead to ensure you remain certified and can continue to use your skills when needed.
4. Apply Your Skills in Real-Life Situations
Now that you’re certified, it’s time to feel empowered to use your knowledge when an emergency occurs. Whether at home, at work, or in public spaces, the ability to act quickly and confidently is vital. Volunteering for community organizations or emergency response teams is an excellent way to gain practical experience and further develop your skills.
Table: Key Post-Certification Actions
| Action | Details | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receive Certification | Obtain the official certificate, which may be used for personal or professional purposes. | ||||
| Review and Practice | Continue practicing regularly and review key skills to maintain your proficiency. | ||||
| Understand Recertification | Be aware of the expiration date and requirements for recertification. | ||||
| Apply Knowledge | Seek out opportunities to use your skills in real-life situations, whether through volunteering or other means. |
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Check Expiration Date | Review your certification’s expiration date and plan for renewal in advance. |
