
In this section, we will focus on essential concepts related to the human body, its various systems, and how they function together. Understanding these complex processes is crucial for mastering this area of study and performing well in assessments. The key to success lies in breaking down each component and grasping its role within the larger framework of human health.
From the circulatory system to the nervous network, each biological mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis. By organizing your study approach and focusing on the core functions of each system, you can gain a deeper understanding and improve recall during tests. Efficient preparation requires not only memorization but also the ability to connect concepts and apply knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Whether you’re reviewing key structures or diving into complex processes, this guide aims to equip you with the tools necessary for mastering the material. Consistent practice and a clear focus on important topics will lead to a more confident and comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Essential Topics for Anatomy and Physiology Exam 3
To succeed in this subject, it’s crucial to focus on the core areas that form the foundation of human biological functions. A solid understanding of how different systems interact and contribute to overall health is key. Mastering these central themes will not only prepare you for assessments but also help you apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios.
Key Systems to Focus On
Each biological system plays a significant role in maintaining balance within the body. Concentrate on understanding the mechanisms, structures, and processes that define these systems. A comprehensive study of the following topics will provide a strong foundation for your understanding:
| System | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Circulatory | Heart function, blood vessels, blood flow, and oxygen delivery |
| Nervous | Neurons, synaptic transmission, brain regions, reflexes |
| Digestive | Enzymes, nutrient absorption, gastrointestinal tract, liver functions |
| Respiratory | Lung structure, gas exchange, breathing mechanisms |
| Endocrine | Hormone regulation, glands, feedback systems |
| Musculoskeletal | Bone structure, muscle function, movement, joint types |
Important Concepts to Grasp

Alongside understanding system functions, it’s vital to grasp the physiological concepts that drive bodily processes. Pay close attention to mechanisms such as homeostasis, cellular communication, and energy production. These concepts will help you connect the dots between different topics and improve your ability to answer application-based questions.
Understanding the Circulatory System
The circulatory system is a complex network that plays a critical role in transporting essential substances throughout the body. It involves a series of interrelated components working together to ensure the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and the removal of waste products. Understanding how each part functions will help clarify its role in maintaining bodily homeostasis.
Key Components of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system consists of several crucial elements, each with a specific function that contributes to the system’s overall efficiency. These components include:
- Heart: The central pump that drives blood through blood vessels.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood throughout the body.
- Blood: The medium that carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
Major Functions of the Circulatory System
The main functions of this system are integral to the body’s ability to function efficiently. These include:
- Oxygen Transport: Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and organs.
- Waste Removal: Blood helps remove carbon dioxide and other waste products from cells.
- Regulation of Body Temperature: Blood flow helps to regulate temperature by distributing heat.
- Nutrient Delivery: Blood supplies essential nutrients to cells to support metabolism and energy production.
A thorough understanding of these components and their functions is essential for mastering the circulatory system in biological studies. This knowledge forms the foundation for tackling more advanced topics related to bodily functions and overall health.
Key Musculoskeletal Structures to Know
The musculoskeletal system is a vital framework that supports body movement and stability. Understanding its major components, such as bones, joints, and muscles, is crucial for comprehending how the body moves and maintains posture. Familiarity with these structures will enhance your understanding of both their individual and collective roles in physical function.
In this section, we will focus on the primary elements of the musculoskeletal system, which are fundamental to your studies. Each structure has unique characteristics that contribute to its function, from enabling movement to providing structural integrity.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Bones | Provide support, protect internal organs, and act as levers for movement. |
| Joints | Allow for movement between bones, varying in type and flexibility. |
| Muscles | Contract to produce movement and maintain posture, either voluntary or involuntary. |
| Tendons | Connect muscles to bones, transmitting force during movement. |
| Ligaments | Stabilize joints by connecting bones to each other. |
Understanding these structures and their interactions is essential for grasping how the body performs complex motions and maintains stability. A clear comprehension of the musculoskeletal system will aid in identifying disorders, understanding movement patterns, and excelling in related assessments.
Nervous System Concepts for Success

The nervous system is central to controlling body functions, enabling communication between different parts of the body and the brain. A thorough understanding of its structure and function is essential for mastering this area of study. This system is responsible for processing sensory information, coordinating movement, and regulating many automatic bodily processes.
Key Components of the Nervous System
To grasp the complexity of the nervous system, it’s important to focus on its major components. These elements work together to ensure rapid and efficient communication throughout the body:
- Brain: The control center that processes information and directs actions.
- Spinal Cord: A conduit for signals between the brain and the body, facilitating reflexes and movement.
- Neurons: Specialized cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body.
- Peripheral Nerves: Networks that connect the brain and spinal cord to limbs and organs.
Critical Functions to Understand
Understanding the main functions of the nervous system will help connect the theoretical concepts with real-life applications:
- Sensory Input: The ability to detect and respond to stimuli from the environment.
- Motor Output: Transmission of signals to muscles and glands for action.
- Integration: Processing information and generating appropriate responses.
Grasping these concepts will help you connect the structural and functional aspects of the nervous system, setting a solid foundation for more advanced topics and assessments.
Important Digestive System Components

The digestive system is responsible for processing food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. It involves a series of organs that work together to break down food, extract essential nutrients, and expel waste. Understanding the key components of this system is crucial for recognizing how the body processes the food we consume.
Major Organs of the Digestive System
The digestive system consists of various organs, each with its own function in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients. Key components include:
- Mouth: The entry point where food is ingested and mechanically broken down by chewing.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: An organ that secretes acids and enzymes to break down food into a semi-liquid form.
- Small Intestine: The primary site for nutrient absorption, where enzymes further digest food particles.
- Large Intestine: Responsible for absorbing water and salts, transforming waste into stool.
- Liver: Produces bile, which aids in the digestion of fats, and processes nutrients absorbed by the intestines.
- Pancreas: Secretes digestive enzymes that break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the small intestine.
Digestive Process Overview
The process of digestion involves several stages that allow the body to extract nutrients efficiently. These stages include:
- Ingestion: The process of taking in food through the mouth.
- Mechanical Digestion: The physical breakdown of food, such as chewing and churning in the stomach.
- Chemical Digestion: The breakdown of food by enzymes and acids, mainly in the stomach and small intestine.
- Absorption: Nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the small intestine into the bloodstream.
- Excretion: Waste products are eliminated from the body via the large intestine and rectum.
Understanding these components and the overall digestive process is essential for recognizing how the body efficiently obtains and processes nutrients while eliminating waste products.
Examining Respiratory System Functions
The respiratory system is essential for providing oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. Its functions are critical for maintaining cellular health and energy production. Understanding how this system operates will help clarify its role in overall homeostasis and physical performance.
Primary Functions of the Respiratory System
The main functions of the respiratory system focus on gas exchange and maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. Key processes include:
- Oxygen Supply: The intake of oxygen from the atmosphere and its delivery to the bloodstream.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: The expulsion of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the external environment.
- Regulation of Blood pH: The respiratory system helps regulate blood acidity by adjusting the levels of carbon dioxide.
- Voice Production: The vocal cords, located in the larynx, vibrate to produce sound during exhalation.
Mechanisms of Breathing

Breathing involves several coordinated actions that allow for efficient gas exchange. The two main phases of breathing are:
- Inhalation: The process of drawing air into the lungs, facilitated by the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- Exhalation: The process of expelling air from the lungs, as the diaphragm and chest muscles relax.
These processes ensure that oxygen is constantly supplied to tissues, while waste carbon dioxide is removed, maintaining a stable internal environment.
In-Depth Review of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a vital network responsible for regulating various bodily functions through the release of hormones. These chemical messengers help control metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood, among other processes. The system works in close coordination with other body systems to maintain overall homeostasis and ensure the proper functioning of physiological processes.
Key Components of the Endocrine System

The endocrine system consists of a variety of glands and organs that secrete hormones. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to target tissues and organs. Important components include:
- Hypothalamus: Controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland and regulates body temperature, hunger, and thirst.
- Pituitary Gland: Known as the “master gland,” it influences other glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs.
- Thyroid Gland: Regulates metabolism and energy production through the secretion of thyroid hormones.
- Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that help the body respond to stress and regulate metabolism.
- Pancreas: Secretes insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels and energy storage.
- Gonads: In males (testes) and females (ovaries), these glands produce sex hormones that control reproduction and secondary sexual characteristics.
Hormones and Their Functions
The hormones released by the endocrine system have a wide range of functions, each essential for maintaining balance in the body. Some key hormones include:
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells.
- Cortisol: Involved in the stress response and helps regulate metabolism and immune function.
- Thyroxine: Controls the rate of metabolism and the use of energy by cells.
- Estrogen: Responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Testosterone: Plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues and secondary sexual characteristics.
Understanding the functions and regulation of these hormones is crucial for recognizing the role of the endocrine system in maintaining bodily functions and responding to internal and external stimuli.
Renal System: Key Terms and Processes
The renal system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and filtering waste from the body. It works to ensure that the body maintains proper hydration levels and eliminates toxins efficiently. Understanding the terminology and processes associated with this system is essential for grasping how it contributes to overall health and homeostasis.
Key Structures of the Renal System
The renal system is composed of several critical organs that collaborate to filter blood, produce urine, and regulate various bodily functions. These key structures include:
- Kidneys: Filter blood to remove waste, excess substances, and toxins, while also regulating fluid balance and electrolyte levels.
- Ureters: Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder for storage.
- Bladder: A muscular sac that stores urine until it is excreted.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine is expelled from the body.
Critical Processes in Renal Function
The renal system’s main function is to regulate the body’s internal environment by filtering blood and producing urine. Some of the key processes involved include:
- Filtration: Blood enters the kidneys, where it is filtered through structures called nephrons. Waste products and excess substances are removed.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients, such as glucose and water, are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream to maintain balance.
- Secretion: Additional waste products and ions are secreted into the urine for excretion.
- Excretion: The final product, urine, is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Each of these processes is vital for the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment and remove waste efficiently. The renal system’s intricate functions are essential for overall well-being and the regulation of homeostasis.
Essential Blood Functions for the Exam
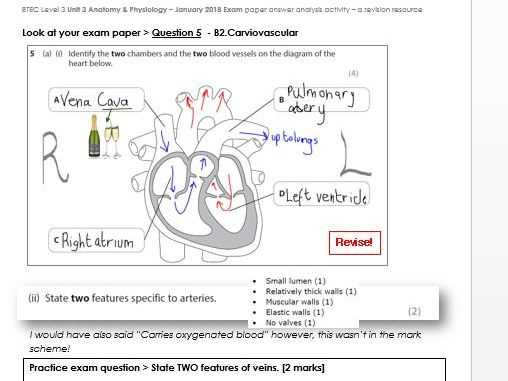
The circulatory system depends on blood to transport critical substances throughout the body. Understanding its core functions is crucial for recognizing how it supports overall health and maintains homeostasis. Blood performs various tasks, each essential for sustaining life and proper organ function.
Primary Roles of Blood
Blood serves multiple vital functions that keep the body functioning smoothly. The key roles of blood include:
- Oxygen Transport: Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs, ensuring energy production at the cellular level.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Blood helps transport carbon dioxide, a waste product, from tissues to the lungs for exhalation.
- Immune Defense: White blood cells protect the body from infections and foreign invaders, playing a major role in the immune system.
- Clotting: Platelets help form clots to stop bleeding when injuries occur, preventing excessive blood loss.
- Hormone Distribution: Blood transports hormones from endocrine glands to target organs, regulating various bodily functions.
Plasma and Cellular Components
Blood is made up of different components that work together to fulfill its functions. The main components include:
- Plasma: The liquid portion of blood, which carries water, nutrients, waste products, proteins, and hormones.
- Red Blood Cells: Cells responsible for oxygen and carbon dioxide transport.
- White Blood Cells: Cells that defend against pathogens and contribute to immune response.
- Platelets: Small cell fragments involved in blood clotting and wound healing.
Each of these components contributes to maintaining homeostasis, ensuring the body functions optimally during stress, rest, or disease.
Understanding the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s immune defenses and fluid balance. It helps protect against infections, remove toxins, and transport immune cells throughout the body. Understanding its components and functions is key to recognizing how the body defends itself against illness and maintains overall health.
Key Components of the Lymphatic System
This system is composed of various structures that work together to protect and nourish the body. Some of the main components include:
- Lymph: A clear fluid that circulates through the system, carrying white blood cells and waste products.
- Lymphatic Vessels: A network of vessels that transport lymph throughout the body, similar to blood vessels.
- Lymph Nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph, trapping harmful particles like bacteria and viruses.
- Spleen: A large organ that filters blood, stores red blood cells, and helps fight infections.
- Thymus: A gland located behind the sternum, where T-cells mature and become active in immune responses.
Primary Functions of the Lymphatic System

The lymphatic system serves several essential functions that help protect the body from disease and maintain fluid balance. These include:
- Immune Response: Lymph nodes and other lymphatic tissues filter pathogens, helping the body fight infections and diseases.
- Fluid Balance: The lymphatic system collects excess fluid from tissues and returns it to the bloodstream, preventing fluid buildup.
- Nutrient Transport: It assists in the absorption and transport of fats from the digestive system to the bloodstream.
- Toxin Removal: By filtering lymph, the system removes waste products and toxins from the body.
Each of these functions contributes to maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the body remains protected from harmful invaders while supporting overall bodily functions.
Strategies for Memorizing Anatomical Terms
Mastering complex terminology related to body structures can be challenging, but effective strategies can help retain key terms more easily. These terms are essential for understanding how different parts of the body function and interact. By adopting a few memorization techniques, you can improve recall and better understand the intricacies of the body’s systems.
Visualization Techniques
One of the most effective ways to remember terms is to visualize them. Associating words with images or diagrams helps reinforce the connections between terms and their meanings. Consider these methods:
- Diagram Labeling: Draw and label diagrams of body structures while learning new terms. This practice helps you visualize where each part is located and how it functions.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards with terms on one side and their definitions or images on the other. Reviewing them regularly strengthens memory recall.
- Color Coding: Color-code diagrams or notes based on categories (e.g., muscles, bones, organs). This adds an extra layer of association that can make terms easier to remember.
Mnemonics and Word Associations
Mnemonics can be a powerful tool for memorizing terms. By creating acronyms or stories, you can make difficult words more manageable. Here are some tips:
- Acronyms: Form acronyms from the first letter of terms. For example, to remember the order of bones in the hand (carpals), you might use the phrase “Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle.”
- Word Associations: Connect terms with familiar words or phrases. For instance, linking the term “humerus” (upper arm bone) to the phrase “Humorous” can help recall the bone’s name.
By incorporating these memorization techniques, you can significantly enhance your ability to recall important terms and their meanings, making studying more effective and efficient.
Common Physiology Questions on the Test
When preparing for tests that cover body functions and processes, certain questions tend to appear more frequently. These questions often focus on fundamental concepts that are critical for understanding how various systems work together to maintain homeostasis. Being familiar with these common topics can help you focus your study efforts and ensure you’re well-prepared for any assessment.
Questions About Body Systems
One area frequently tested involves the major systems of the body and their key functions. Expect questions on the following topics:
- Circulatory System: How does blood flow through the heart, and what role do different blood vessels play in oxygen transport?
- Respiratory System: What are the steps involved in gas exchange, and how does the body regulate breathing?
- Digestive System: How does food move through the digestive tract, and what are the roles of enzymes in nutrient absorption?
Questions on Mechanisms of Regulation
Another area often tested is how the body regulates its internal environment. This includes:
- Homeostasis: How do feedback loops maintain stability in body temperature, pH, and other vital conditions?
- Endocrine Control: How do hormones influence bodily functions, and what are the effects of hormone imbalances?
- Nervous System Regulation: How does the nervous system respond to stimuli and coordinate movements and reflexes?
By focusing on these core topics, you can build a solid foundation to confidently approach questions related to bodily functions and processes.
Preparation Tips for Complex Topics
When tackling challenging subjects, having a structured approach to your studies can make all the difference. Some topics require deeper understanding and the ability to connect various concepts. To master these areas, it’s crucial to break them down into manageable pieces and utilize effective study strategies. Here are several preparation tips to help you succeed with complex content.
Break Down Complex Concepts
The first step to mastering difficult topics is breaking them into smaller, more digestible parts. Focus on understanding one concept at a time before moving on to the next. Consider the following strategies:
- Chunking: Divide large amounts of information into smaller “chunks.” For instance, when studying a process, separate it into steps and learn each one individually.
- Mind Mapping: Use diagrams to visualize connections between different concepts. This will help you see how various ideas fit together.
- Summarizing: After reading a section, summarize it in your own words. This reinforces understanding and highlights key points.
Practice with Real-Life Examples
Applying what you’ve learned to real-life scenarios can help reinforce difficult material. Use practical examples to see how abstract ideas are applied in everyday life. Consider these tips:
- Case Studies: Analyze case studies related to the topic you’re studying. This provides context and deepens your understanding of how complex ideas are used in practice.
- Simulations: Participate in practical exercises or simulations. These activities can help you connect theory with real-world applications.
By breaking down complex topics and applying real-world examples, you can better understand and retain challenging material, making your preparation more effective.
How to Approach Practice Questions

Successfully preparing for any assessment involves more than just reading through the material. Practice questions provide an excellent opportunity to test your understanding and identify areas where you need further study. To make the most of practice questions, it’s important to approach them strategically, ensuring that each one enhances your knowledge and improves your test-taking skills.
Steps to Effectively Tackle Practice Questions
Here are several steps to follow when working through practice questions:
- Read Carefully: Always read each question thoroughly to understand exactly what is being asked. Pay attention to keywords and instructions to avoid misinterpretation.
- Identify Key Concepts: Before answering, identify the core concepts or themes the question addresses. This will help you stay focused on the relevant material.
- Answer First, Then Review: If the question is multiple-choice, try to recall the answer before looking at the options. For other question types, form your answer in your mind and then check for clarity and accuracy.
Reviewing Your Responses
Once you’ve completed the practice questions, reviewing your responses is essential for improvement. Here’s how to make your review process more effective:
- Understand Mistakes: When you get a question wrong, take the time to understand why. Review the material related to the question and make sure you understand the correct answer.
- Track Progress: Keep a record of the questions you’ve missed and revisit them periodically. This will help reinforce weak areas over time.
- Time Yourself: Practice under timed conditions to improve your speed and efficiency. This will help you manage time more effectively during the actual assessment.
By systematically approaching practice questions and reviewing your performance, you can improve both your understanding of the material and your test-taking techniques.
Time Management for Effective Studying
Managing your time wisely is crucial to mastering complex subjects. Effective time management allows you to allocate the right amount of effort to each topic, ensuring that no area is neglected. By planning your study schedule, you can approach the material in an organized and focused manner, which ultimately leads to better retention and understanding.
Steps to Manage Your Study Time
Here are some practical tips to help you manage your study time efficiently:
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions ahead of time. Break down the material into manageable chunks and assign specific time slots for each topic. This prevents procrastination and ensures you cover all areas.
- Prioritize Difficult Topics: Tackle the most challenging subjects first when your energy and focus are at their peak. This allows you to spend more time on areas that require extra attention.
- Use Time Blocks: Study in focused intervals, such as 25 to 30 minutes at a time, followed by a short break. This method, known as the Pomodoro Technique, helps maintain focus while preventing burnout.
Maintaining Consistency and Flexibility
While a structured approach is essential, flexibility is key to staying on track. Adjust your schedule as needed based on your progress and any unforeseen challenges that arise.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is crucial. Study regularly and avoid cramming sessions. Consistent review of the material helps reinforce long-term retention.
- Allow Time for Rest: Don’t neglect breaks and rest. Adequate sleep and relaxation are essential for cognitive function and memory retention.
- Evaluate Your Progress: Regularly assess your understanding of the material. If you find that certain topics are taking more time than expected, adjust your plan accordingly.
By effectively managing your study time, you can approach your preparation in a more balanced, efficient way, leading to better results and reduced stress.
How to Review Lecture Notes Efficiently
Reviewing lecture notes effectively is a key strategy for reinforcing understanding and retaining information. It is essential to approach the review process in a structured manner, focusing on the most important points while ensuring that no critical details are overlooked. By developing a routine for reviewing notes, you can maximize the benefits of each class and improve long-term comprehension.
Organize Your Notes for Clarity
Before diving into review, ensure your notes are well-organized. This will make it easier to find key concepts and link related ideas together.
- Use Headings and Subheadings: Break your notes into clear sections using headings. This structure will make it easier to navigate when revisiting the material.
- Highlight Key Points: Mark important definitions, concepts, or diagrams with a highlighter to draw attention to critical information.
- Use Bullet Points: When reviewing, focus on the most important facts and list them in bullet points for easier memorization.
Review Techniques to Enhance Retention
Once your notes are organized, consider these review techniques to ensure that the material sticks with you.
- Active Recall: Instead of passively reading through your notes, try to recall information from memory. Cover the material and test yourself on the main ideas.
- Spaced Repetition: Review your notes at increasing intervals to improve long-term retention. Start by reviewing them after a day, then after a week, and so on.
- Teach Someone Else: Explaining the material to another person helps reinforce your understanding and highlights any areas that need further attention.
Using Visual Aids for Better Understanding
Incorporate diagrams, charts, and tables into your review process. These visual aids can help clarify complex processes and relationships.
| Visual Aid | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diagrams | Help to visualize structures and processes | Flowchart of a biochemical pathway |
| Charts | Organize related concepts in a clear format | Comparison of cell types |
| Tables | Simplify complex data for easy reference | List of neurotransmitters and their functions |
By organizing your notes, using active recall, and incorporating visual aids, you will make your review sessions more efficient and effective. This approach will deepen your understanding and improve your ability to retain information for future use.
Understanding Diagrams and Visual Aids
Diagrams and visual aids are powerful tools that help simplify complex concepts, making them easier to understand and remember. These visual representations break down intricate ideas into digestible chunks, allowing you to visualize structures, processes, and relationships in a way that text alone may not convey. Whether it’s illustrating systems or showing relationships between different components, mastering the use of these tools can significantly enhance comprehension and retention.
Types of Visual Aids
There are several types of visual tools commonly used to enhance learning. Each serves a unique purpose and can be adapted to different types of content.
- Diagrams: Diagrams help represent structures and their spatial relationships. They are especially useful for illustrating organs, systems, and their connections.
- Flowcharts: These are great for showing processes, such as chemical reactions or cellular functions. They present information in a step-by-step manner, making it easier to follow sequences.
- Tables: Tables organize data and concepts into columns and rows, helping you compare and contrast information quickly. They are ideal for summarizing key details.
- Graphs: Graphs provide a clear way to present statistical or numerical data. Bar, line, and pie charts can illustrate trends and relationships.
Effective Use of Diagrams for Learning
When studying complex subjects, diagrams can significantly boost your understanding. To use them effectively:
- Focus on Key Structures: Pay attention to labeled parts and how they fit into the larger context. This is particularly helpful when studying the relationships between organs or cells.
- Use Color to Enhance Understanding: Color-coding different components or pathways can make diagrams more intuitive, helping to differentiate between structures and their functions.
- Draw Your Own Diagrams: Reproducing diagrams by hand can reinforce memory. This process forces you to engage with the material more deeply.
By integrating diagrams and visual tools into your study routine, you can create a stronger mental map of how various concepts fit together, making complex material easier to retain and recall when needed.
Exam Day Tips for Maximum Performance

The day of an important assessment can be nerve-wracking, but with the right strategies, you can maximize your chances of success. Being prepared is not just about the content you’ve learned, but also about how you manage your time, mental state, and environment on the day itself. Here are several practical tips to help you perform at your best during the test.
Pre-Test Preparation
Setting yourself up for success begins before you even enter the testing room. These steps ensure you are in the best possible state for focusing and recalling the material.
- Get Enough Sleep: Rest is essential for cognitive function. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep the night before.
- Eat a Nutritious Breakfast: A balanced meal with protein, fiber, and healthy fats will keep you energized and alert throughout the test.
- Arrive Early: Getting to the testing location with time to spare reduces stress and gives you a moment to relax before the assessment begins.
During the Test
How you approach the test itself can have a significant impact on your performance. Employing effective strategies during the assessment is key to navigating challenging questions.
- Read Questions Carefully: Take your time to understand what each question is asking before answering. Look for keywords and ensure you know exactly what is required.
- Start with What You Know: Begin with the questions that are easiest for you to answer. This boosts confidence and helps secure early points.
- Manage Your Time: Allocate time for each section or question. Don’t spend too long on any one question–move on and come back later if needed.
- Stay Calm: If you encounter a challenging question, take a deep breath and stay composed. Avoid panic and focus on applying your knowledge systematically.
Post-Test Reflection
After completing the test, it’s important to reflect and review your performance, especially if the results aren’t what you hoped. Identify areas for improvement, but also acknowledge what went well.
| Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Take breaks while studying | Helps maintain focus and prevents burnout |
| Use practice questions | Familiarizes you with the format and types of questions |
| Review notes regularly | Improves retention and deepens understanding |
By applying these strategies, you can ensure that you are not only well-prepared, but also mentally ready to tackle the challenges of the test and perform at your best.