
Securing your place as a responsible operator on the water requires a thorough understanding of crucial skills and regulations. This process not only enhances your confidence but also ensures a safer environment for everyone enjoying aquatic activities.
To achieve this goal, you need to familiarize yourself with navigation principles, safety protocols, and operational standards. Each topic plays a vital role in building your expertise and preparing you for real-world scenarios on the water.
This resource offers structured guidance to help you grasp the core concepts effectively. By focusing on critical areas such as vessel control, hazard recognition, and legal compliance, you can approach your certification journey with clarity and determination.
How to Prepare for Boaters Exam
Getting ready to showcase your maritime knowledge involves careful preparation and dedication. By focusing on the most important topics, you can build the confidence and skills needed to excel in this essential certification process.
Study Waterway Traffic Rules
Understanding how to navigate busy waterways is a crucial step in preparation. Learn about right-of-way priorities, signaling systems, and how to safely operate in areas with multiple vessels. Mastery of these rules ensures safe and efficient travel on the water.
Master the Use of Essential Equipment
Familiarity with navigation tools and safety gear is critical. Practice using items such as compasses, life vests, and emergency kits. Knowing how and when to deploy this equipment can make all the difference during real-world scenarios.
Understanding Maritime Rules and Guidelines
Familiarizing yourself with the essential regulations that govern water navigation is crucial to becoming a responsible vessel operator. These rules ensure safety, prevent accidents, and maintain order on busy waterways. A solid understanding of these guidelines will help you navigate with confidence and adhere to legal requirements.
One of the most important aspects of maritime rules is understanding the concept of right-of-way. Knowing when to yield, how to communicate with other vessels, and how to avoid potential collisions is vital for maintaining safety. These practices are not only a matter of law but also of mutual respect and responsibility among those on the water.
In addition to traffic regulations, operators must also be aware of environmental guidelines. These include respecting protected areas, adhering to speed limits, and ensuring that waste disposal is done responsibly. Understanding these rules is essential for preserving waterways and protecting marine life.
By mastering these fundamental maritime rules and guidelines, you can ensure that your time on the water is both safe and enjoyable, while also contributing to the overall safety and preservation of aquatic environments.
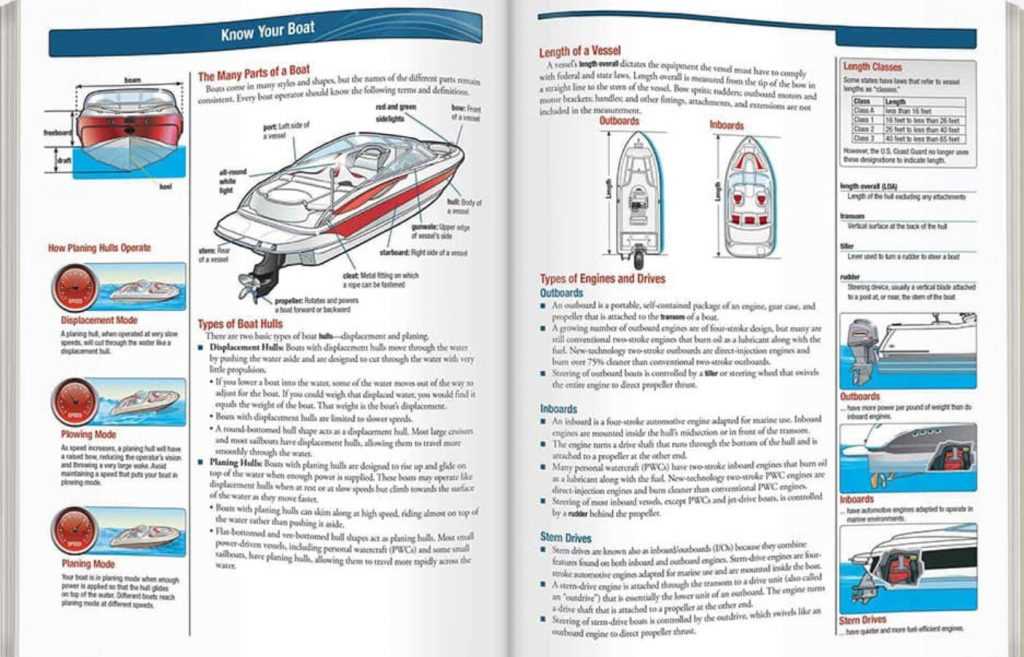
Essential Skills for Safe Boating
Operating a vessel requires a wide range of skills to ensure not only your safety but also that of others on the water. Mastering these essential abilities will help you respond to changing conditions and navigate with confidence. Whether you’re a seasoned navigator or new to the water, these skills form the foundation of safe boating.
Core Skills Every Operator Must Master
- Vessel Handling: Control of the vessel in various conditions, including turns, stops, and maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Emergency Response: Knowing how to react in emergencies, such as when someone falls overboard, how to manage fire hazards, or how to perform basic first aid.
- Navigation: Using charts, GPS, and other tools to safely navigate in unfamiliar or crowded waters.
- Communication: Understanding maritime signaling and radio communication to exchange information with other vessels and shore authorities.
Important Safety Techniques
- Lifejacket Usage: Always wear a lifejacket and ensure all passengers have theirs properly fitted.
- Weather Awareness: Keeping track of changing weather conditions and knowing how to adapt your plans accordingly.
- Pre-departure Checks: Always inspect your vessel before setting out, ensuring that safety equipment and operational systems are functional.
By developing these essential skills, you will be well-prepared to navigate safely and respond to challenges that may arise while on the water.
Identifying Different Types of Watercraft
Understanding the variety of vessels found on waterways is an essential skill for anyone navigating or operating near water. Different types of watercraft serve specific purposes and come with unique design features that influence how they are handled, their speed, and their overall function. Recognizing these distinctions helps improve safety and coordination on the water.
Common Types of Watercraft
Watercraft vary in size, shape, and purpose. Some of the most common include:
- Motorboats: Equipped with engines, these vessels are commonly used for recreational activities like fishing and water sports.
- Sailboats: Powered primarily by sails, they rely on wind to navigate and are popular for leisurely cruises or competitive races.
- Canoes and Kayaks: Small, manually propelled vessels typically used for paddling in calm waters or rivers.
- Personal Watercraft (PWCs): Smaller, jet-powered vessels designed for high-speed rides and quick turns, commonly known by brand names like Jet Ski or Sea-Doo.
Specialized Watercraft
In addition to the common types, there are specialized vessels tailored for specific activities, such as:
- Fishing Vessels: Designed for anglers, these boats are often equipped with specialized storage and equipment for fishing.
- Yachts: Luxury vessels used for long-distance travel or recreation, typically offering extensive amenities.
- Ferries: Large boats used for transporting passengers and vehicles across bodies of water.
Being able to identify these various types of watercraft ensures better decision-making on the water and enhances overall safety for everyone involved.
Mastering Buoy Markings and Signals
Understanding buoy markings and signals is crucial for safe navigation in open waters. These markers serve as important guides, helping mariners identify safe paths, hazards, and other vital information about the waterway. Whether you’re operating a small vessel or a large ship, knowing how to interpret these signals ensures smooth and safe journeys.
Types of Buoy Markings
Buoys come in various shapes, colors, and patterns, each conveying different meanings. Here are the key types:
- Red Buoys: Generally, red markers indicate the right side of the channel when traveling upstream. They are often marked with numbers and may have a conical shape, resembling a “cone” or a “nun”.
- Green Buoys: These markers indicate the left side of the channel when traveling upstream. They are typically cylindrical and are often referred to as “can” buoys.
- Yellow Buoys: These buoys mark caution areas, such as navigation hazards or special conditions like no-wake zones.
- White Buoys: Used to mark navigational hazards like rocks or shallow areas, often paired with other colors for clarity.
Understanding Signals and Their Meaning

Buoy signals are not just visual; they can also be associated with sounds and lights. Here’s how to interpret these signals:
- Flashing Lights: Buoys with flashing lights are often used to mark key locations like rocks or areas of low visibility.
- Day Shapes: Day shapes, such as triangles or squares, are used in conjunction with the buoys to provide additional warning or directions during daylight hours.
- Sound Signals: Buoys may emit sound signals, especially in foggy conditions, indicating their position and warnings of nearby dangers.
By mastering buoy markings and signals, you’ll enhance your ability to navigate safely and avoid potential risks. Understanding these markers ensures that you can make informed decisions while out on the water, contributing to the safety of yourself and others.
Tips for Navigating Crowded Waterways
In busy waterways, maneuvering safely requires heightened awareness and careful planning. When large numbers of vessels are present, it’s crucial to follow best practices for avoiding accidents and ensuring smooth movement. By being mindful of your surroundings and respecting other water users, you can maintain safety and avoid collisions.
Key Practices for Safe Navigation
Here are some important tips to keep in mind when navigating congested areas:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintain a Safe Speed | Always adjust your speed based on the traffic and water conditions. Slower speeds help reduce the risk of accidents and allow you to respond quickly to sudden changes in your surroundings. |
| Keep a Safe Distance | Stay at least a few boat lengths away from other vessels. This gives you time to react to their movements and avoid sudden collisions. |
| Use Your Horn Wisely | Use sound signals when necessary to communicate your intentions, especially in areas of low visibility or when another vessel is too close. |
| Follow Traffic Patterns | In many areas, waterway traffic follows established routes. Stick to designated lanes to avoid confusion and potential collisions. |
Situational Awareness and Responsiveness

Always stay alert and monitor the behavior of other vessels. Here are additional actions to consider:
- Look Ahead: Keep your eyes focused on both immediate and distant areas. Anticipating other boats’ movements gives you more time to respond.
- Monitor Radio Communications: Stay tuned to relevant channels to receive updates on vessel positions and any hazards in the area.
- Plan Escape Routes: Know your surroundings and identify areas where you can maneuver if another vessel approaches too closely.
By applying these strategies, you can navigate crowded waterways confidently and safely, reducing the risk of accidents while ensuring a smoother boating experience for all.
Environmental Protection Rules for Boaters
Protecting water bodies and surrounding ecosystems is a shared responsibility. When operating vessels, it’s essential to be aware of the environmental impact and follow regulations designed to minimize harm. Implementing environmentally friendly practices helps preserve natural habitats and ensure the sustainability of marine environments for future generations.
Here are several key actions and guidelines to follow to contribute to environmental preservation:
- Proper Waste Disposal: Dispose of trash, oil, and other pollutants properly. Never throw garbage or hazardous materials into the water.
- Maintain Your Vessel: Regular maintenance reduces emissions and prevents leaks. Ensuring your vessel is in good condition helps minimize environmental harm.
- Use Biodegradable Products: When possible, choose products that won’t contribute to water pollution, such as biodegradable soaps and cleaners.
- Avoid Disturbing Wildlife: Maintain a respectful distance from wildlife and avoid disturbing sensitive habitats like nesting areas and breeding grounds.
- Limit Noise Pollution: Minimize loud engine noise, especially near wildlife, and during early or late hours when animals are more active.
Complying with Water Quality Standards
In many regions, water quality standards are enforced to protect both the environment and public health. It’s important to stay informed about:
- Wastewater Management: Many areas require that boats be equipped with a waste disposal system, ensuring that wastewater is not discharged into the water.
- Fueling Regulations: Use approved fueling practices to prevent spillage, and avoid fueling near sensitive shorelines or aquatic areas.
- Marine Protected Areas: Some regions restrict boating activities in certain zones to protect wildlife and ecosystems. Always be aware of these areas and comply with any access limitations.
By adopting environmentally responsible practices and adhering to local regulations, you can help safeguard marine ecosystems and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment for everyone.
Safe Loading and Passenger Practices
Ensuring that a vessel is loaded properly and that passengers are safe is essential for preventing accidents and maintaining stability on the water. A well-balanced boat improves its handling and reduces the risk of capsizing or other dangerous situations. Following safe loading guidelines and understanding passenger behavior are key aspects of safe navigation.
When preparing for a trip, consider the following important safety tips:
- Evenly Distribute Weight: Load cargo and passengers in a balanced manner, keeping the weight centered and low. This helps the boat stay stable and maneuver easily.
- Do Not Overload: Always adhere to the vessel’s weight capacity. Overloading can compromise the boat’s performance and increase the risk of accidents.
- Secure Items: Ensure that all gear, equipment, and personal belongings are secured to prevent them from shifting during movement, which could lead to imbalance.
- Keep Passengers Informed: Make sure everyone knows their roles, including the locations of life jackets and emergency equipment. Passengers should be aware of safety protocols in case of an emergency.
- Monitor the Number of Passengers: Maintain a safe number of people aboard, ensuring that everyone has enough space and is properly seated to maintain stability.
By following these practices, you ensure a safer, more enjoyable experience on the water for everyone on board, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall boating safety.
Recognizing and Avoiding Water Hazards
Being aware of potential dangers in the water is crucial to ensure safe navigation and avoid accidents. Water hazards come in many forms, ranging from natural obstacles like rocks and submerged debris to man-made structures. Recognizing these hazards early and taking appropriate actions can prevent damage to the vessel and protect everyone aboard.
Common Types of Water Hazards
Waterways can be unpredictable, and some hazards may not always be visible at first glance. It is important to understand the different types of hazards and how to spot them:
- Submerged Objects: Fallen trees, rocks, and other debris may be hidden below the surface, making it difficult to detect them until it’s too late. Always stay alert in shallow or unknown areas.
- Shifting Sandbars: These underwater mounds of sand can change position, especially during tides or after storms. Navigating too close to sandbars can cause the vessel to run aground.
- Buoys and Navigation Aids: Pay attention to these markers, as they indicate safe channels and warn of dangerous areas like reefs or shallow waters.
- Weather Conditions: Fog, storms, and high winds can drastically reduce visibility and maneuverability, making the water more hazardous. Always check weather forecasts before heading out.
Effective Strategies for Avoiding Hazards
Taking preventive measures and practicing caution can help avoid dangerous encounters while navigating:
- Stay Informed: Use charts, GPS, and local knowledge to familiarize yourself with the waterway before setting out.
- Reduce Speed: Slowing down gives you more time to react to unexpected obstacles, particularly in areas with limited visibility or unknown conditions.
- Maintain Safe Distance: Always keep a safe distance from marked hazards such as buoys, rocks, and other watercraft to avoid collisions.
- Monitor Water Conditions: Stay aware of changing tides, currents, and water levels, especially when navigating in areas prone to rapid changes.
By recognizing these common hazards and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure a safer journey and minimize the risk of accidents on the water.
Communication Methods Used on the Water
Effective communication on the water is essential for ensuring safety, coordinating activities, and avoiding accidents. Whether interacting with other vessels, shore-based personnel, or emergency services, there are several methods used to communicate in the maritime environment. Understanding these communication channels helps prevent misunderstandings and enhances the overall safety of everyone on the water.
Common Communication Methods
There are a variety of tools and systems in place that allow individuals to stay in touch while out on the water. These include:
- VHF Radio: The most widely used form of communication on the water. It allows boat operators to communicate with other vessels, marinas, and coast guard units over a long range. The VHF radio operates on specific channels and is especially useful for emergency situations.
- Hand Signals: In situations where verbal communication may not be possible, hand signals can be used between crew members or other vessels. These are essential for maneuvering and signaling intentions, such as turning or stopping.
- Sound Signals: Horns, bells, and whistles are often used to communicate in noisy environments or when visibility is low. Different sound signals indicate different actions, such as altering course or requesting assistance.
- Cell Phones: Though not the primary method, cell phones can be useful when navigating near the shore or in areas with good reception. They allow direct contact with emergency services or other parties on land.
Effective Use of Communication Tools
To ensure safety and clarity, it’s important to use communication tools correctly:
- Know the Channels: Each communication tool has specific channels for different types of communication. Familiarizing yourself with these channels helps ensure you are using the correct one for the situation.
- Maintain Proper Etiquette: When using a VHF radio, always identify yourself and your vessel clearly. Keep messages brief and to the point, especially in emergency situations where every second counts.
- Monitor the Environment: Always be aware of background noise, weather conditions, and other factors that may impact communication. Ensure you can hear and be heard in critical moments.
- Stay Calm in Emergencies: In an emergency, staying calm and composed when communicating can make a significant difference. Ensure the message is clear and the need for help is well understood.
Mastering communication methods on the water is vital for maintaining a safe and efficient maritime experience. Whether in normal conditions or emergencies, knowing how and when to use the appropriate tools can make all the difference in preventing accidents and ensuring quick response when needed.
Checklist for Boating Safety Equipment
Ensuring the proper safety equipment is aboard is a crucial step in preventing accidents and handling emergencies on the water. Having the right gear can make a significant difference in maintaining safety and readiness. This checklist outlines the essential items every vessel should have to meet legal requirements and ensure the well-being of everyone on board.
Essential Safety Gear
Before setting out on any water trip, ensure the following equipment is available and in good working condition:
- Life Jackets: Every person on board must have a personal flotation device (PFD). Ensure each one is the correct size and type for the individual’s weight and age group.
- Fire Extinguisher: A marine-rated fire extinguisher is essential for controlling fires, especially near fuel sources. Check that it is charged and easily accessible.
- First Aid Kit: A well-stocked first aid kit is necessary for addressing injuries and medical needs while on the water. Ensure it includes bandages, antiseptics, and any personal medications that might be required.
- Visual Distress Signals: These include flares, distress flags, or signaling mirrors. These tools are vital in case of emergencies to attract attention.
- Sound-Producing Devices: A horn or whistle is required to signal distress or communicate intentions, especially in reduced visibility conditions.
Additional Important Items
While the essential items are non-negotiable, additional equipment can enhance safety and preparedness:
- Anchor and Line: An anchor is vital for securing the vessel in a stationary position, especially in adverse weather conditions.
- Navigation Lights: Proper lighting is required for operating at night or in low-visibility conditions. Ensure all lights are functioning properly.
- Bilge Pump or Bailers: These tools help remove water from the vessel in case of a leak or heavy rain.
- Tools and Spare Parts: A small toolkit, including basic repair items such as duct tape and spare parts, can be invaluable in case of equipment failure.
- Weather Radio: A battery-powered or hand-crank weather radio allows you to stay informed of changing weather conditions and warnings.
Regularly check the condition and availability of all required safety equipment. Proper preparation reduces risk and enhances the safety of everyone on the water, helping to ensure a smooth and secure journey.
Rules for Nighttime Boating Activities
Operating a vessel after dark presents unique challenges that require heightened awareness and adherence to specific regulations. Navigating in low visibility conditions demands extra caution, as it’s essential to avoid accidents and ensure the safety of everyone on board. This section covers the rules and guidelines designed to promote safe nighttime travel on the water.
Navigation Lights and Signals
When operating at night, it is mandatory to display appropriate lighting to signal your vessel’s presence and intentions. These lights help prevent collisions and make it easier for other operators to determine the position and movement of nearby vessels.
- Red and Green Bow Lights: A red light should be displayed on the left (port) side, and a green light on the right (starboard) side of the vessel.
- White Stern Light: A white light is required at the stern of the boat, visible from behind and to indicate that the boat is moving away from the observer.
- All-Around White Light: A 360-degree white light is required for non-motorized vessels and as an additional safety light on motorized vessels when stationary.
Speed Limits and Vigilance
At night, reducing speed is crucial to allow more time to react to unexpected obstacles or other vessels. Most regions enforce stricter speed limits during nighttime hours to minimize risks.
- Speed Restrictions: Adhere to the posted speed limits, which are often lower after dark, to improve reaction time and reduce wake.
- Increased Vigilance: Be extra alert when navigating in poorly lit or unfamiliar areas. Watch for potential hazards such as buoys, floating debris, and other vessels.
Proper lighting, maintaining a safe speed, and staying vigilant can significantly reduce the risks associated with nighttime boating. Following these guidelines helps ensure a safe and enjoyable experience on the water during evening hours.
Responsibilities of a Boat Operator
Operating a vessel involves a wide range of duties aimed at ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone on board and those in the surrounding environment. It is crucial to be fully aware of the rules and practices that guide responsible navigation and emergency preparedness. The role of the boat operator is not only about controlling the vessel but also managing safety protocols, equipment, and adhering to laws.
Safety Measures
The first and foremost responsibility of an operator is to ensure a safe environment for all passengers and those on the water. This includes the following tasks:
- Check Safety Equipment: Before departing, ensure all required safety equipment is onboard and in good condition. This includes life jackets, fire extinguishers, signaling devices, and first aid kits.
- Adhere to Speed Limits: Maintain safe speeds appropriate to the water conditions, visibility, and local regulations.
- Monitor Weather Conditions: Stay informed about weather forecasts and be prepared to alter plans if conditions become unsafe.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Each operator is expected to be knowledgeable about and follow the local and national maritime laws, including those related to waterway access, vessel registration, and environmental protection.
- Vessel Registration: Ensure the vessel is properly registered with the appropriate authorities and display registration numbers as required.
- Observe Navigation Rules: Follow the established rules of the road for vessels to avoid collisions, including right-of-way laws and safe boating practices.
- Respect Environmental Guidelines: Avoid actions that harm aquatic ecosystems, such as littering or discharging pollutants into the water.
Being a responsible operator not only protects individuals on board but also ensures the safety and preservation of the marine environment. Proper knowledge and diligence in following these responsibilities contribute to a safe and enjoyable boating experience for everyone involved.
Emergency Situations and How to Respond
Unexpected events on the water can arise at any moment, and being prepared to handle them is essential for the safety of all onboard. Knowing how to recognize and appropriately react to various emergency situations can mean the difference between a quick resolution and a serious disaster. Proper training and a calm, methodical approach are key in these scenarios.
Common Emergency Scenarios

When emergencies occur, a swift and efficient response is critical. Below are some common situations and how to effectively handle them:
| Situation | Action |
|---|---|
| Capsizing | Stay calm, assess the situation, and help all passengers into the watercraft or onto floating objects. Ensure everyone wears a life jacket and signal for help if necessary. |
| Man Overboard | Immediately throw a life buoy or other floatation device to the person. Turn the vessel around carefully, keeping the person in sight, and approach from downwind if possible. |
| Fire Onboard | Extinguish the fire using a fire extinguisher if it is small and manageable. If the fire spreads, evacuate the vessel safely and call for help. |
| Engine Failure | Check the fuel supply, battery, and connections. If the issue is not easily resolved, use the emergency radio or flares to signal for assistance. |
| Severe Weather | Seek shelter immediately. Reduce speed and head to the nearest safe harbor or area of protection, keeping an eye on weather alerts. |
General Emergency Tips
In any emergency situation, follow these steps to increase your chances of a safe outcome:
- Stay Calm: Panic can hinder decision-making. Take a deep breath, assess the situation, and then act.
- Call for Help: Use the vessel’s radio or distress signals (like flares) to contact emergency services or nearby vessels.
- Assist Others: Ensure all passengers are accounted for and assist them as needed, especially in high-stress situations.
- Follow Protocols: Know and practice emergency drills and procedures, so everyone onboard understands their role during a crisis.
Proactively preparing for emergencies by knowing these response protocols and equipping your vessel with the necessary safety gear can significantly improve outcomes in critical moments. Always remain vigilant and prioritize safety above all else when navigating the waterways.
Fueling Procedures to Prevent Accidents
Fueling a vessel requires careful attention to ensure safety and avoid accidents. Improper fueling can lead to dangerous situations such as spills, fires, and explosions. Following correct procedures and taking necessary precautions are vital steps to reduce risks and ensure the safety of everyone onboard. Understanding the proper steps can help maintain a secure environment while refueling.
Before starting the fueling process, make sure the vessel is anchored or secured to prevent movement. Always turn off the engine, electrical devices, and any other sources of ignition. Keep the fueling area well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes. Always use a fueling nozzle that is properly designed for marine fuel systems, ensuring a secure fit to prevent spills.
During fueling, never leave the nozzle unattended, and maintain a clear view of the tank’s fill level to avoid overfilling. If any fuel spills, clean it immediately using proper spill containment equipment. Do not attempt to handle any electrical components or devices until the area is clear of fuel vapors. After fueling, ensure the cap is securely tightened, and check for any leaks before starting the engine.
Lastly, it’s essential to dispose of any used materials, such as rags or spill kits, properly. Never dispose of them in the water, as they can cause environmental harm. By following these procedures, you can minimize the risks associated with fueling and contribute to a safer environment on the water.
Basic Maintenance to Ensure Boat Safety
Proper maintenance is crucial to the longevity and safety of any watercraft. Regular upkeep ensures that all components function as intended and minimizes the risk of malfunctions while on the water. By conducting routine inspections and performing necessary repairs, boat operators can maintain a safe environment for everyone onboard.
Key Maintenance Tasks
- Engine checks: Regularly inspect the engine for any leaks, corrosion, or wear. Change the oil and replace fuel filters as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Hull inspection: Check the hull for any cracks or damage. Ensure there are no signs of leaks and that the boat is watertight.
- Battery maintenance: Inspect the battery for corrosion and ensure it is fully charged. Clean the terminals and replace any worn-out cables.
- Safety equipment: Verify that life jackets, flares, fire extinguishers, and first-aid kits are in good condition and easily accessible.
Additional Tips

- Clean the boat regularly to remove dirt, salt, and grime that may cause long-term damage.
- Ensure all lights and navigation systems are functioning properly, especially if boating at night.
- Test bilge pumps and ensure that they are clear of debris.
- Keep an eye on weather conditions, as extreme weather can cause stress on boat components and systems.
By following these basic maintenance steps, boat operators can reduce the likelihood of accidents and improve the overall performance of their vessel, ensuring a safe boating experience every time.
How Weather Conditions Affect Boating
Weather plays a significant role in determining the safety and overall experience on the water. From strong winds to unpredictable temperature changes, each element can impact the way a vessel handles, its speed, and its ability to navigate safely. Being aware of how different weather conditions affect boating activities is crucial for ensuring a smooth and secure journey.
Key Weather Factors and Their Impact
| Weather Condition | Impact on Boating |
|---|---|
| Wind | Strong winds can cause rough waves and difficulty in steering, especially for smaller vessels. Wind direction also affects how a boat moves and its stability on the water. |
| Rain | Heavy rain reduces visibility and can make navigation more challenging. It also increases the likelihood of slippery decks, making movement more hazardous for passengers. |
| Temperature | Extreme heat or cold can affect the performance of the boat’s engine and other components. Colder water temperatures also increase the risk of hypothermia if someone falls overboard. |
| Fog | Fog severely limits visibility and can make it difficult to spot obstacles or other vessels. Boaters should reduce speed and use navigation lights when encountering foggy conditions. |
Preparing for Weather Changes
- Check weather forecasts regularly before setting out on the water.
- Ensure that the vessel is equipped with weather-resistant gear and safety equipment.
- Adjust boating speed and course to accommodate adverse weather conditions.
- Be prepared to return to shore or find shelter if weather conditions worsen suddenly.
Understanding how weather influences boating can help operators take appropriate precautions to avoid accidents and enjoy a safer experience on the water.