
Preparing for an advanced course in human anatomy and physiology requires a focused approach, as the material can be complex and extensive. To succeed, it is essential to understand key concepts, systems, and processes that shape the human body. This guide will help you navigate the most critical topics, ensuring you are well-equipped to tackle the challenges ahead.
Throughout your studies, you will encounter detailed sections on various body systems, from the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems to the nervous and endocrine systems. Each area plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall function and stability. By mastering these concepts, you will develop a deeper understanding of how the body works as a whole.
By following this structured study plan, you will reinforce your knowledge of important physiological principles and anatomical structures. Strengthen your retention of essential facts, improve your problem-solving skills, and increase your confidence in applying these concepts to real-world scenarios. Whether you are reviewing the basics or diving deeper into complex topics, this guide will help you prepare thoroughly and effectively.
AP 2 Final Exam Review Guide

Successfully mastering the material in advanced anatomy and physiology requires a comprehensive approach that combines theory with practical application. To excel, it is essential to understand how various body systems function and interconnect. This section will guide you through the most important topics to focus on, providing strategies for better retention and understanding.
Key areas of focus include the structure and function of organs and tissues, the physiological processes that sustain life, and the mechanisms that help maintain balance within the body. Each topic is essential to building a holistic understanding of human biology. This guide will also highlight common areas where students typically face difficulties, offering tips on how to overcome them.
By breaking down complex concepts into manageable sections and focusing on core principles, this guide will help you organize your study sessions effectively. Whether reviewing the cardiovascular system, endocrine regulation, or nervous system pathways, a strategic approach will help you achieve a deeper grasp of the material and improve your performance.
Understanding the Anatomy Section
The anatomy portion of this course focuses on the detailed study of the human body’s structures. Understanding how organs, tissues, and systems are organized and interconnected is essential for building a strong foundation. This section requires memorization of key structures and their functions, as well as an understanding of their spatial relationships within the body.
Key Organs and Systems
In this section, you will dive into the specific organs and systems that make up the human body, including the skeletal, muscular, and circulatory systems. Each system plays a vital role in maintaining health and functionality, and knowing the names, locations, and primary functions of these structures is crucial. Focus on the major systems first, then explore their interactions and dependencies for a more comprehensive understanding.
Focus on Body Parts and Regions
Another important aspect of anatomy is understanding the terminology and regions used to describe the body’s layout. Familiarize yourself with directional terms, body planes, and regions to easily navigate through the content. Mastering these basics will help you better visualize how the body is organized, which is essential when studying more complex physiological processes.
Mastering Physiology Concepts
Mastering the principles of human physiology requires a deep understanding of how various body systems function and interact to maintain balance. This section covers the key physiological processes that are essential for life, focusing on the mechanisms that regulate and sustain bodily functions. By grasping these concepts, you will develop a clearer understanding of how the body adapts and responds to internal and external stimuli.
Key Physiological Processes
Physiology revolves around several fundamental processes that control body functions. Here are the most important ones to focus on:
- Homeostasis – The body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external changes.
- Neural Regulation – How the nervous system controls body activities, including reflexes and voluntary actions.
- Endocrine Regulation – The role of hormones in controlling various physiological functions, such as metabolism and growth.
- Cardiovascular Function – How the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
Commonly Tested Concepts
To improve your grasp of physiology, it’s important to focus on the concepts most frequently tested in assessments. These include:
- Membrane Transport Mechanisms – Understanding how substances move across cell membranes through diffusion, osmosis, and active transport.
- Muscle Contraction – The physiological process behind muscle shortening and force generation.
- Respiratory and Circulatory Integration – How the lungs and heart work together to provide oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide.
- Kidney Function – The role of the kidneys in filtering blood, maintaining fluid balance, and regulating electrolytes.
By breaking down these concepts into smaller, more manageable parts, you will be able to study efficiently and build a solid understanding of the body’s physiological functions.
Key Musculoskeletal System Topics
The musculoskeletal system plays a crucial role in providing support, movement, and protection for the body. To excel in this section, it’s essential to focus on the structure and function of bones, muscles, and joints, as well as their interactions. Understanding how these components work together will deepen your knowledge of how the body maintains stability and facilitates movement.
Bone Structure and Function
The skeletal system provides the framework for the body, protecting vital organs and enabling movement. Key concepts to focus on include:
- Bone Types – Understanding the different types of bones: long, short, flat, and irregular.
- Bone Tissue – The distinction between compact and spongy bone and how they contribute to strength and flexibility.
- Osteogenesis – The process of bone formation, including the role of osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts.
- Bone Remodeling – How bones repair themselves and adapt to stress over time.
Muscle Function and Movement
The muscular system enables movement and plays a key role in posture and heat production. Understanding muscle anatomy and physiology is essential for mastering this topic. Key areas include:
- Muscle Types – The differences between skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle, and their respective roles in movement.
- Muscle Contraction – The sliding filament theory, which explains how muscles contract at the microscopic level.
- Lever Systems – How bones and muscles work together as levers to produce movement at joints.
By thoroughly understanding these concepts, you will be well-prepared to tackle the musculoskeletal system’s complexities and its role in overall body function.
Cardiovascular System Review

The cardiovascular system is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, all working in concert to maintain proper circulation and ensure the body’s tissues receive what they need to function. A solid understanding of this system is crucial for recognizing how the body responds to various physiological demands.
Heart Structure and Function

The heart is the central organ of the cardiovascular system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Key areas to focus on include:
- Heart Chambers – The distinction between the left and right atria and ventricles and their roles in circulation.
- Heart Valves – Understanding the function of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves in preventing backflow and ensuring efficient blood flow.
- Electrical System – The role of the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and bundle of His in controlling heart rhythm.
Blood Vessels and Circulation
Blood vessels play a critical role in transporting blood to and from the heart and tissues. Understanding the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries is essential. Focus on:
- Arteries – How they carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart under high pressure.
- Veins – Their role in returning deoxygenated blood to the heart, aided by valves that prevent backflow.
- Capillaries – The site of nutrient and gas exchange between the blood and tissues.
By mastering these concepts, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how the cardiovascular system supports the body’s overall health and function.
Respiratory System Study Tips
Mastering the respiratory system requires a clear understanding of how air is exchanged in the body and how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported between the lungs and tissues. This system plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis and supplying cells with the oxygen they need to function. To grasp the complexities of respiratory processes, focus on both the structure and function of the organs involved, as well as the mechanics behind breathing and gas exchange.
Key Concepts to Focus On
Several fundamental topics should be prioritized when studying the respiratory system. These include:
- Structure of the Respiratory Tract – Familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
- Gas Exchange Mechanisms – Understand how oxygen and carbon dioxide move across alveolar membranes into the bloodstream.
- Breathing Mechanics – Study how the diaphragm and intercostal muscles facilitate inhalation and exhalation.
- Regulation of Respiration – Learn how the brain and chemoreceptors regulate breathing rate in response to blood gases.
Effective Study Strategies
To improve retention and comprehension, use the following study techniques:
- Visual Aids – Diagrams of the respiratory system are invaluable for understanding the structure and function of each organ.
- Practice with Mnemonics – Create memory aids for important physiological processes, like the steps of respiration or the pathway of airflow.
- Relate to Real-Life Examples – Consider how the respiratory system adapts during exercise, high-altitude conditions, or in response to disease.
- Active Recall – Test yourself regularly by recalling key concepts and processes without referring to notes.
By focusing on these topics and using effective study techniques, you will build a comprehensive understanding of how the respiratory system functions and how it integrates with the rest of the body.
Digestive System Focus Areas
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Understanding how this intricate system works requires familiarity with the various organs involved and their specific functions. Focusing on key processes, from ingestion to nutrient absorption, will help clarify how the body processes food and maintains overall health.
Key Organs and Their Functions
Each part of the digestive system plays a critical role in processing food and nutrients. Pay attention to the following organs and their functions:
- Mouth – The entry point for food, where mechanical digestion begins through chewing, and chemical digestion starts with saliva.
- Esophagus – A muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach through peristalsis.
- Stomach – A muscular organ that secretes acid and enzymes to break down food into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
- Small Intestine – The primary site for nutrient absorption, where digestive enzymes further break down food.
- Large Intestine – Responsible for water absorption and the formation of waste products for elimination.
Digestion and Absorption Mechanisms
Understanding how the body breaks down and absorbs nutrients is essential. Key concepts include:
- Enzyme Action – Digestive enzymes catalyze the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules that can be absorbed.
- Absorption in the Small Intestine – Villi and microvilli increase the surface area for nutrient absorption, allowing molecules to enter the bloodstream.
- Role of the Liver and Pancreas – The liver produces bile, which aids in fat digestion, while the pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine.
Focusing on these key areas will help you understand the processes involved in digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination, providing a comprehensive view of how the digestive system supports overall health and well-being.
Endocrine System Exam Preparation
The endocrine system plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions through the release of hormones. To gain a solid understanding of this system, it’s important to focus on how hormones influence metabolism, growth, mood, and more. Each gland and hormone has a specific function, and recognizing how they interact is essential for mastering this topic.
Key Glands and Their Functions
Understanding the major glands and their respective hormones is crucial for mastering the endocrine system. Focus on the following glands and their roles:
- Hypothalamus – A crucial control center that regulates the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary Gland – Known as the “master gland,” it controls other glands like the thyroid, adrenal glands, and gonads.
- Thyroid Gland – Regulates metabolism and energy levels through hormones like thyroxine.
- Adrenal Glands – Produce hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that help manage stress and regulate metabolism.
- Pineal Gland – Responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles through the secretion of melatonin.
Hormonal Pathways and Regulation
To deepen your understanding, study the feedback mechanisms and interactions between different hormones. Important areas to focus on include:
- Negative Feedback Loops – How hormone levels are regulated by feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis.
- Endocrine Disorders – Learn about common disorders such as hypothyroidism, diabetes, and adrenal insufficiency, and how they impact body functions.
- Hormonal Secretion and Action – Understand how hormones like insulin, estrogen, and adrenaline affect their target organs and tissues.
By focusing on these key glands, hormones, and mechanisms, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of how the endocrine system influences overall body function and health.
Neurology and Nervous System Basics
The nervous system is responsible for controlling and coordinating body functions, enabling communication between the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Understanding how signals are transmitted, processed, and interpreted is crucial for grasping how the body responds to internal and external stimuli. A strong foundation in the basic anatomy and physiology of the nervous system will help clarify how it regulates everything from voluntary movement to automatic functions like heartbeat and breathing.
Key Components of the Nervous System
There are two main divisions of the nervous system that work together to maintain communication throughout the body:
- Central Nervous System (CNS) – Composed of the brain and spinal cord, this system processes sensory information and sends signals to the rest of the body.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Consists of all nerves outside the CNS, transmitting information between the CNS and the rest of the body.
Neurons and Signal Transmission
Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical impulses. Key concepts to focus on include:
- Structure of Neurons – Understand the parts of a neuron: dendrites, axons, and synapses, and how they work together to transmit signals.
- Action Potential – Learn how electrical impulses travel along the neuron and how they trigger neurotransmitter release at synapses.
- Neurotransmitters – Study the chemicals involved in transmitting signals between neurons and their effects on body functions.
By understanding these core concepts, you will gain a better appreciation of how the nervous system controls and coordinates the body’s responses, both voluntary and involuntary, to maintain balance and homeostasis.
Urinary System Key Points
The urinary system is essential for maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, filtering waste from the bloodstream, and regulating blood pressure. Understanding its components and how they function together is crucial for comprehending how the body processes and eliminates metabolic waste. Focus on the structure of the kidneys, the filtration process, and the pathways through which waste is removed from the body.
Key Organs and Their Functions
Several organs work in coordination to ensure proper waste filtration and fluid regulation:
- Kidneys – Filter blood, removing waste and excess substances to form urine, while also regulating electrolytes and blood pressure.
- Ureters – Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder for storage.
- Bladder – A storage organ that holds urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
- Urethra – The tube through which urine is excreted from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Filtration and Urine Formation
The process of filtration in the kidneys is key to understanding how waste is eliminated:
- Glomerular Filtration – Blood is filtered in the glomerulus, where water, salts, glucose, and waste products are separated from blood cells and proteins.
- Tubular Reabsorption – Essential substances like water and glucose are reabsorbed into the bloodstream from the renal tubules.
- Tubular Secretion – Additional waste products and excess ions are secreted into the tubules for excretion in the urine.
By understanding these key components and processes, you will have a solid grasp of how the urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s internal environment and removing waste products efficiently.
Reproductive System Overview
The reproductive system is responsible for producing offspring and ensuring the continuation of species. It involves complex structures and processes that support reproduction, including the creation of gametes, fertilization, and the nurturing of developing embryos. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of both male and female reproductive systems is essential for grasping how reproduction is controlled and maintained throughout life.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is designed to produce sperm and deliver it to the female reproductive tract. Key components include:
- Testes – Organs that produce sperm and testosterone, the primary male hormone.
- Epididymis – A coiled tube where sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation.
- Vas Deferens – The duct that transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
- Penis – The external organ used for the delivery of sperm into the female reproductive tract.
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is responsible for producing eggs, supporting fertilization, and nurturing the development of a fetus. Key components include:
- Ovaries – Organs that produce eggs (ova) and secrete hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes – Tubes that transport the egg from the ovaries to the uterus and are the site of fertilization.
- Uterus – The hollow organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops during pregnancy.
- Vagina – The canal that connects the uterus to the outside of the body, used for childbirth and intercourse.
By understanding the roles and functions of these structures, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how the reproductive system supports life and the process of reproduction.
Immune System Study Strategies
The immune system plays a critical role in protecting the body against harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. To effectively understand how the immune system defends the body, it is important to grasp the components involved, the mechanisms of immunity, and how different responses are triggered. A structured approach to studying these concepts will help clarify the complexities of this system and improve retention of key information.
Understand the Key Components
Begin by focusing on the main structures and cells that contribute to immune defense. Some of the key elements to remember include:
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) – These cells are responsible for identifying and neutralizing foreign invaders in the body. Types include T cells, B cells, and macrophages.
- Lymphatic System – This system includes lymph nodes, the spleen, and other structures that store and transport immune cells throughout the body.
- Antibodies – Proteins produced by B cells that specifically target and neutralize pathogens.
- Bone Marrow – The site where immune cells are produced before being sent into circulation.
Focus on Immune Responses
Understanding the different types of immune responses is crucial for mastering this topic. Focus on:
- Innate Immunity – The body’s initial, nonspecific response to pathogens, including physical barriers like the skin and internal defenses such as inflammation.
- Adaptive Immunity – A specific response that involves the activation of T and B cells to target and eliminate pathogens more effectively over time.
- Humoral Immunity – The aspect of adaptive immunity that involves the production of antibodies by B cells to neutralize pathogens.
- Cell-Mediated Immunity – The response where T cells destroy infected cells directly or help other immune cells to do so.
By understanding these strategies and concepts, you can develop a strong foundation in how the immune system functions to protect the body from disease and infections. Reinforcing your knowledge of these processes through active recall and practice questions can further enhance retention and comprehension.
Integumentary System Insights
The integumentary system is a vital part of the body, serving as the first line of defense against environmental threats. It includes various structures that protect, regulate, and sense changes in the external environment. Understanding its components and functions is essential for recognizing its role in maintaining overall health and homeostasis.
Key Structures of the Integumentary System
The system consists of several important structures that work together to perform its functions. These include:
- Skin – The largest organ in the body, acting as a protective barrier against harmful substances, pathogens, and physical damage.
- Hair – Provides insulation, helps with temperature regulation, and serves as a sensory organ.
- Nails – Protect the tips of fingers and toes, enhancing fine motor functions and providing protection from trauma.
- Glands – Include sebaceous glands that produce oil for moisturizing the skin, and sweat glands responsible for regulating body temperature.
Functions of the Integumentary System

The integumentary system serves multiple critical roles in maintaining health. These functions include:
- Protection – Acts as a barrier to prevent injury and entry of harmful pathogens.
- Temperature Regulation – Through sweating and blood vessel constriction or dilation, the skin helps regulate the body’s internal temperature.
- Sensation – The skin contains nerve endings that allow the body to sense touch, temperature, and pain.
- Vitamin D Production – Skin cells produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
By focusing on the anatomical features and functional roles of the integumentary system, you can better appreciate how it protects and supports the body’s overall well-being. Understanding these elements will help you apply this knowledge to various physiological contexts and clinical scenarios.
Important Metabolism Concepts
Metabolism encompasses a wide range of biochemical reactions that occur within living organisms to maintain life. It involves processes that convert food into energy, as well as those that build or break down molecules necessary for cell structure and function. Understanding these processes is crucial for grasping how the body maintains homeostasis and responds to energy demands.
Types of Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways can be divided into two main categories based on their function in the body:
| Pathway Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Anabolic | Builds complex molecules from simpler ones, consuming energy. | Protein synthesis |
| Catabolic | Breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy. | Glycolysis |
Key Energy Molecules
At the core of metabolism are molecules that store and transfer energy within the body. These include:
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) – The primary energy carrier in cells.
- NADH – An electron carrier used in cellular respiration.
- FADH2 – Another electron carrier involved in energy production.
- Glucose – The main source of energy for cells, particularly in anaerobic conditions.
Grasping these basic concepts of metabolism is key to understanding how the body regulates its energy resources and maintains balance under various physiological conditions. This knowledge is also fundamental when exploring more complex metabolic disorders or interventions that target metabolic processes.
Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms
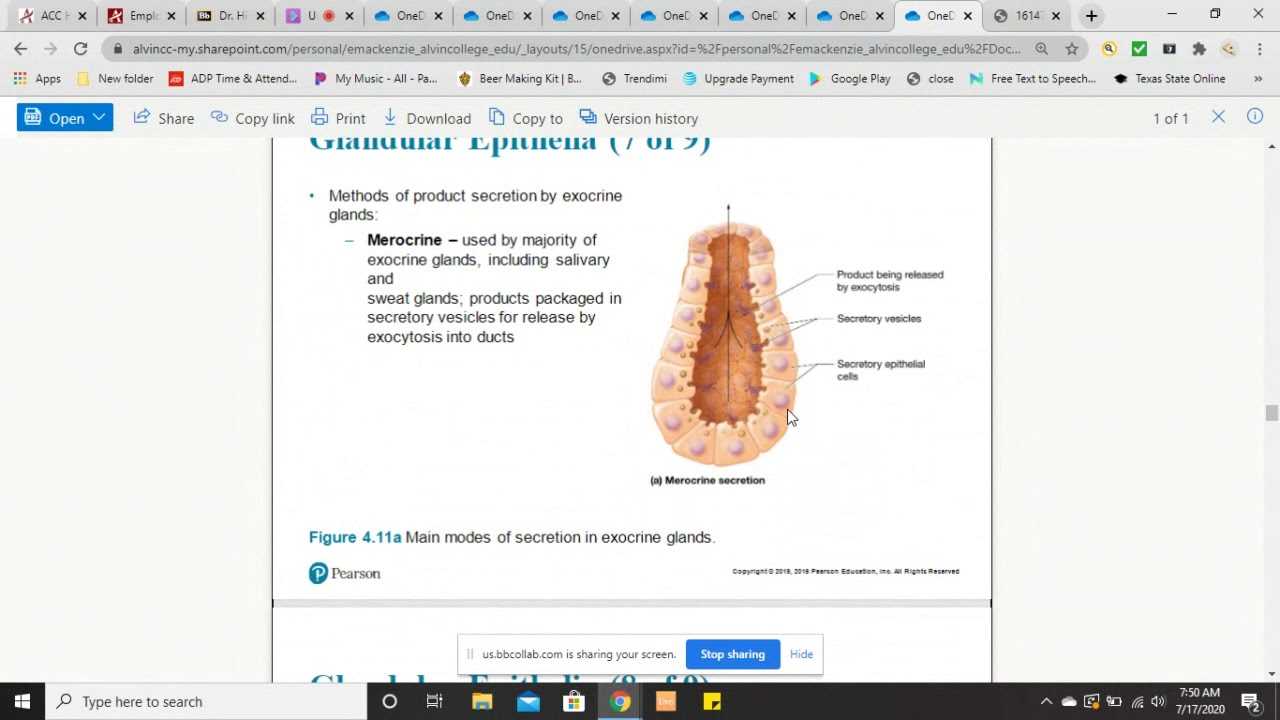
Homeostasis is the process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment despite external changes. This balance is vital for proper functioning and survival. Feedback mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating various physiological systems, ensuring that conditions such as temperature, pH, and blood pressure remain within optimal ranges.
There are two main types of feedback mechanisms in the body: negative feedback and positive feedback. Both types are essential in regulating bodily functions, but they work in different ways to maintain equilibrium.
| Feedback Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Negative Feedback | Works to reverse a change, bringing the system back to its set point. | Temperature regulation (sweating when hot, shivering when cold) |
| Positive Feedback | Amplifies a change, driving the system further away from its set point. | Childbirth (release of oxytocin to increase contractions) |
Negative feedback is the most common mechanism in the body, helping to correct deviations from the set point and restore balance. In contrast, positive feedback is less common and typically occurs in processes that need to be completed rapidly, such as blood clotting or childbirth. Both mechanisms are vital for the proper functioning of physiological processes.
Commonly Tested A&P Disorders
Understanding various disorders of the body systems is crucial for mastering physiological concepts. Certain conditions frequently appear in assessments due to their relevance in maintaining the balance of normal bodily functions. These disorders often highlight the importance of the body’s ability to regulate itself and the consequences when these processes go awry.
Key disorders can affect different systems of the body, ranging from the circulatory to the endocrine systems. Being familiar with their causes, symptoms, and treatments is essential for anyone studying human physiology. Below are some of the most commonly tested conditions across various bodily systems:
Endocrine System Disorders
Disorders related to the endocrine system can disrupt hormone production and regulation, leading to various metabolic and physical issues.
- Diabetes Mellitus: A condition where the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or poor cellular response to insulin.
- Hyperthyroidism: Overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms like weight loss, increased heart rate, and nervousness.
- Hypothyroidism: Insufficient production of thyroid hormones, which can result in fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
Cardiovascular System Disorders
Conditions in the cardiovascular system can have severe impacts on overall health, affecting heart function and blood circulation.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure, often asymptomatic, but a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
- Atherosclerosis: A condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, potentially leading to heart attack or stroke.
- Heart Failure: A condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid retention, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
By understanding these common disorders, students can better anticipate questions related to their causes, symptoms, and treatments. These conditions are critical to the understanding of how the body’s systems interact and the importance of maintaining homeostasis.
Tips for A&P Lab Success

Hands-on laboratory work is an essential part of mastering human physiology and understanding the intricate details of the body’s systems. Success in the lab relies on more than just theoretical knowledge; it requires practical skills, attention to detail, and a methodical approach. By following some key strategies, you can enhance your lab performance and gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Here are some tips to help you excel in your lab sessions:
- Prepare Before Class: Reviewing relevant materials before the lab helps you understand the objectives and key concepts, so you can fully engage during the session.
- Familiarize Yourself with Equipment: Knowing how to use microscopes, models, and other equipment is crucial for conducting accurate experiments and collecting meaningful data.
- Stay Organized: Keep your lab station neat and your materials arranged logically. This minimizes errors and helps you focus on the task at hand.
Active Participation and Collaboration
Lab work often involves teamwork, and collaborating effectively with your peers can enhance the learning experience.
- Ask Questions: If you don’t understand something, don’t hesitate to ask your instructor or classmates. Clarifying doubts in real-time ensures you stay on track.
- Work Well in Groups: Collaboration can bring new insights. Share your observations and listen to others’ interpretations to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the material.
- Take Detailed Notes: Recording observations, measurements, and key findings in a systematic way will help you review the lab later and reinforce the concepts you studied.
Post-Lab Review
After the lab session, it’s important to reinforce what you’ve learned and fill in any gaps in your understanding.
- Review Lab Reports: Go over your notes and finalize your lab reports while the experience is still fresh in your mind. Ensure that all conclusions and findings are well-supported by data.
- Connect with Classmates: Discussing what you learned with your peers can help solidify your understanding and fill in any gaps.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for feedback from your instructor on how you can improve your technique or understanding of specific concepts.
By staying organized, actively participating, and reviewing your work, you can ensure success in the laboratory and gain a deeper, practical understanding of the human body.
How to Handle Final Exam Anxiety
It’s common to feel nervous or stressed when a significant assessment is approaching. The pressure to perform well can often lead to anxiety, making it harder to focus and prepare effectively. However, managing this stress is essential for maintaining mental clarity and maximizing performance. By adopting strategies to cope with anxiety, you can approach your assessment with confidence and composure.
Here are some tips to help you manage anxiety as you prepare for your assessments:
- Plan Your Study Sessions: Instead of cramming at the last minute, break your study material into smaller, manageable chunks. Schedule regular study sessions and give yourself breaks to avoid burnout.
- Stay Organized: Use a study calendar or checklist to track your progress. Knowing exactly what to focus on each day helps reduce feelings of being overwhelmed.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness to calm your mind. These practices help reduce anxiety and improve concentration.
Focus on Positive Thinking
Shifting your mindset from fear to a positive outlook can significantly impact your performance. Instead of focusing on what could go wrong, try to emphasize what you’ve accomplished and what you’ve learned so far.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: When negative thoughts arise, replace them with more balanced ones. Remind yourself of your strengths and how much effort you’ve put into your studies.
- Visualize Success: Picture yourself completing the assessment successfully. Visualization can help calm nerves and enhance your confidence.
Take Care of Your Body and Mind
Physical health plays a key role in how we manage stress. Maintaining your well-being can improve your focus and energy levels during your study sessions.
- Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is crucial for cognitive function. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep a night, especially in the days leading up to the assessment.
- Eat Well: A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, helps maintain energy levels and focus. Avoid excessive caffeine or sugar, as they can contribute to anxiety.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce stress hormones and promotes mental clarity. Even short walks or stretching exercises can be beneficial.
By using these strategies, you can reduce stress and approach your assessment with a clear, focused mind. Remember, preparation and a positive attitude are key to overcoming anxiety and achieving your goals.