
The study of how belief systems shape and influence cultures offers a fascinating glimpse into the interconnectedness of human societies. From daily practices to large-scale movements, these systems play a critical role in determining the values, behaviors, and structures that define different groups. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping how people interact with each other and their environment over time.
Across the world, these frameworks manifest in diverse forms, each influencing local customs, politics, and interactions. The spread of ideologies and their transformation through history has had profound effects on the development of civilizations. Key concepts related to these systems help illuminate the complex ways in which they impact communities and individual identities.
As we dive deeper into this topic, it is crucial to examine not only the origins and practices of these systems but also their role in shaping global patterns. Through exploration of major movements and trends, one can better understand how belief structures continue to evolve and influence societies worldwide.
AP Human Geography Chapter 6 Religion Overview
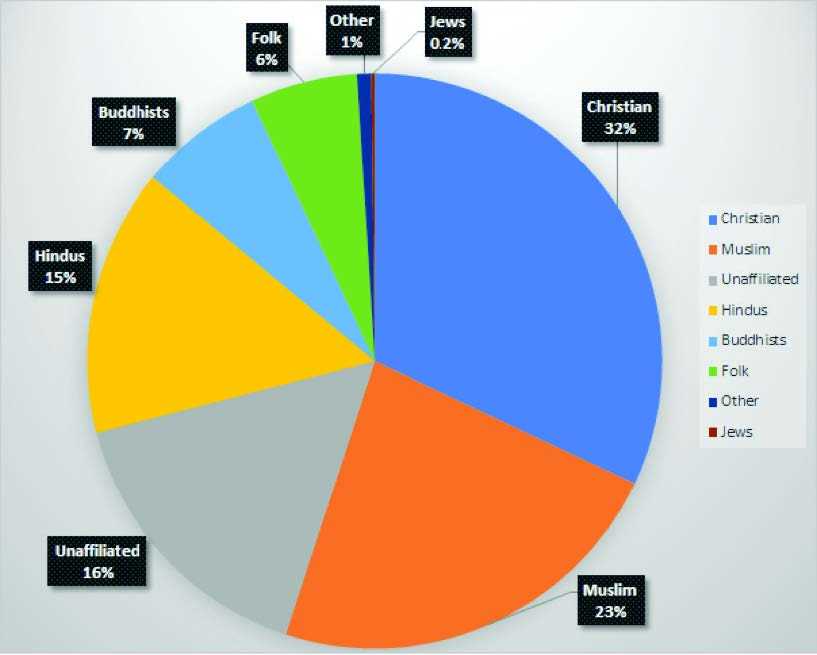
In this section, we explore the significance of belief systems and how they shape the cultural and social landscapes of different societies. The influence of such systems can be seen in everything from daily routines to global movements. Understanding their role is essential for recognizing how they impact various aspects of human life, from politics to individual identity.
Key Elements of Belief Systems
Belief systems can manifest in multiple forms, influencing the way communities organize themselves and interact with their surroundings. These systems often dictate not only personal practices but also societal structures, values, and conflicts. From sacred texts to oral traditions, the core principles of these systems are passed down through generations, shaping cultural norms and expectations.
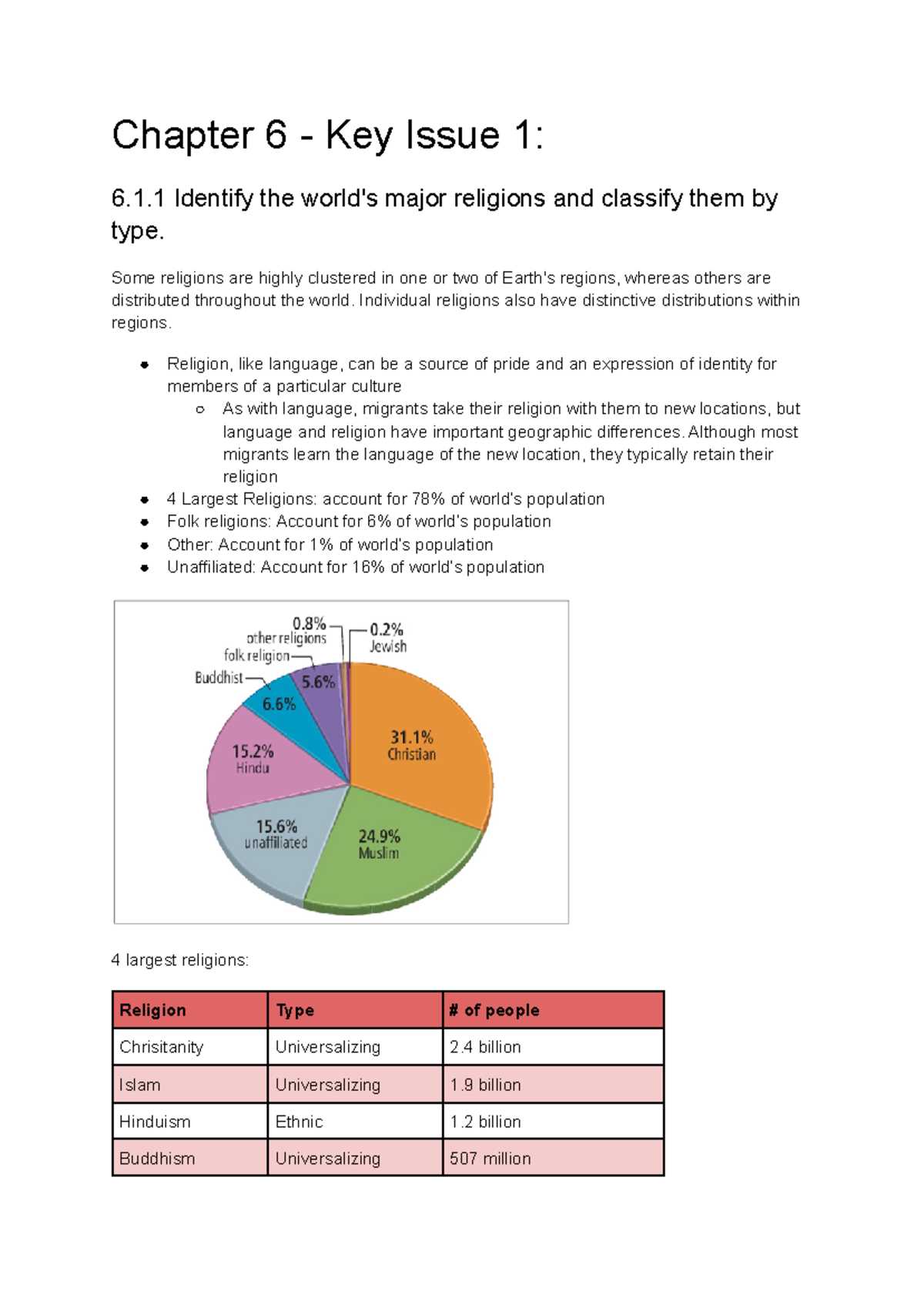
Global Distribution and Influence
The spread of belief systems across the world has led to a variety of cultural landscapes, each influenced by unique ideologies. Some systems are concentrated in specific regions, while others have transcended geographic boundaries, impacting societies on a global scale. Understanding these patterns of diffusion helps explain the diversity of practices and their impact on the development of human civilizations.
Key Concepts in Religious Geography
Understanding the influence of belief systems on space and society requires knowledge of several key principles. These concepts help explain how such systems shape human interactions and the world around us. By exploring their reach and impact, we can better understand the diverse ways these systems manifest in different regions and cultures.
- Diffusion: The process through which belief systems spread across regions, influencing new areas and cultures. This can occur through migration, trade, or conquest.
- Sacred Spaces: Locations that are considered holy or significant within a belief system, such as temples, churches, or pilgrimage sites.
- Cultural Landscape: The physical and cultural imprint left on the environment by belief systems, including places of worship, monuments, and religious landmarks.
- Syncretism: The blending of different belief systems or practices, often resulting from cultural interaction or exchange.
- Secularization: The decline or shift away from the influence of belief systems in public life, often in favor of more secular or scientific worldviews.
These concepts form the foundation for analyzing how belief systems shape cultures and regions. By examining their application, one can better understand the intricate relationships between society and ideology, as well as how such systems evolve and influence one another.
Religious Distribution Across the Globe
Belief systems are not distributed equally across the planet, with certain ideologies concentrated in specific regions. The spread of these systems has been influenced by historical, cultural, and environmental factors, shaping the cultural landscapes of different areas. Understanding where these belief systems are most prevalent and how they have expanded over time provides valuable insight into global patterns and relationships.
The distribution of belief systems is often linked to geography, with specific practices and traditions emerging in particular areas based on historical migrations, trade routes, or conflicts. For instance, some ideologies are deeply rooted in specific regions, while others have spread worldwide due to migration, conquest, and globalization. As a result, the distribution reflects both historical trajectories and contemporary trends.
- Christianity: Predominantly found in Europe, the Americas, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, though it has a significant presence in other regions due to migration and missionary work.
- Islam: Concentrated in the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of South Asia, with growing communities in Europe and North America.
- Hinduism: Primarily practiced in India and Nepal, with diaspora communities in various parts of the world.
- Buddhism: Predominantly in East and Southeast Asia, with pockets of influence in the West, particularly in the United States and Europe.
- Judaism: Concentrated in Israel and Jewish communities worldwide, particularly in North America and parts of Europe.
The movement and spread of these systems demonstrate how cultural exchanges, conflicts, and trade have played a crucial role in shaping global religious landscapes. As such, understanding these patterns provides a deeper understanding of the world’s diverse cultural fabric.
Major World Religions and Beliefs
The world is home to a variety of belief systems that shape the values, practices, and daily lives of billions of people. These systems provide a framework for understanding the world, offering answers to life’s big questions and influencing everything from personal behavior to societal norms. While some belief systems are deeply rooted in specific regions, others have spread globally, adapting to different cultures along the way.
| Belief System | Primary Location | Key Beliefs | Followers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Christianity | Europe, Americas, Sub-Saharan Africa | Monotheism, belief in Jesus Christ as the savior, salvation through faith | 2.3 billion |
| Islam | Middle East, North Africa, South Asia | Monotheism, belief in Allah, Prophet Muhammad as the final messenger, Five Pillars of Islam | 1.9 billion |
| Hinduism | India, Nepal | Polytheism, karma, reincarnation, moksha, caste system | 1.2 billion |
| Buddhism | East and Southeast Asia | Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path, meditation, Nirvana | 500 million |
| Judaism | Israel, North America, Europe | Monotheism, covenant with God, importance of Torah, waiting for Messiah | 14 million |
These major systems have shaped global history and continue to influence cultural, social, and political dynamics around the world. Understanding the core beliefs and practices of each system is essential for gaining insight into the diverse spiritual traditions that coexist on Earth.
The Impact of Belief Systems on Culture
Belief systems have a profound effect on shaping the customs, values, and social structures within societies. These systems provide frameworks that influence not only personal behavior but also collective identity and societal norms. Their impact is seen in various aspects of culture, including art, law, education, and social organization.
Influence on Social Norms and Practices
Belief systems often dictate the moral and ethical codes that govern behavior. They guide what is considered acceptable or taboo in different societies, shaping everything from daily activities to complex social roles. Some key areas where belief systems impact culture include:
- Family and Social Structure: Expectations about marriage, gender roles, and community life.
- Festivals and Rituals: Religious ceremonies, holidays, and observances that mark important events in life.
- Law and Governance: Legal systems influenced by moral teachings and divine principles.
Artistic and Intellectual Contributions
Belief systems also leave a lasting mark on artistic expression and intellectual pursuits. From architecture to literature, music, and philosophy, these systems have inspired some of the world’s most significant cultural achievements. The influence can be seen in:
- Religious Architecture: Temples, mosques, churches, and other sacred structures that embody the principles of a belief system.
- Literature and Philosophy: Sacred texts and philosophical works that explore existential questions and provide moral guidance.
- Visual Arts: Religious symbols, motifs, and stories depicted in paintings, sculptures, and other art forms.
The cultural footprint of belief systems is vast, affecting how people see themselves, their communities, and the world around them. Through both tangible and intangible expressions, these systems shape the way societies evolve and maintain their identity across generations.
Religious Practices and Sacred Spaces
Belief systems often include specific practices and rituals that are integral to the spiritual lives of their followers. These practices are expressions of devotion, designed to strengthen the connection between individuals and their higher power, community, or nature. In addition to these practices, certain locations are considered sacred, holding deep spiritual significance and acting as centers for worship, reflection, and pilgrimage.
The activities performed by followers vary greatly depending on the system and its traditions, but they often include acts of prayer, fasting, meditation, and communal celebrations. These rituals are not only personal but often serve to unite communities and reinforce shared values. Sacred spaces play a crucial role in these practices, providing a physical environment where individuals and groups can come together to express their beliefs.
Examples of sacred spaces include:
- Temples: Often dedicated to a deity or spiritual figure, these structures are places for meditation, worship, and ceremonies.
- Churches and Mosques: Central locations for communal prayer, these spaces hold great significance in many traditions, offering a space for spiritual gatherings.
- Pilgrimage Sites: Locations of historical or divine importance that attract visitors seeking spiritual enlightenment or fulfillment of vows.
These sacred sites and practices are powerful manifestations of faith, shaping the cultural identity of communities and contributing to the continuity of traditions across generations. They provide a sense of belonging and purpose, marking significant moments in the lives of individuals and society as a whole.
Historical Evolution of Global Belief Systems
The development of belief systems over time is deeply intertwined with human history. From their origins in ancient cultures to their spread across continents, these systems have continuously evolved, shaped by social, political, and environmental forces. Understanding their historical evolution helps us recognize the ways in which these systems have adapted to different societies and influenced global cultures.
Early Beginnings and Foundations
The earliest belief systems were often animistic, rooted in the reverence for nature and the forces believed to govern the world. As societies grew more complex, these belief systems began to take on structured forms, often with a focus on a pantheon of gods or the worship of a single divine figure. Early agricultural societies, such as those in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley, developed religious practices that were deeply connected to their environments, marking the beginnings of organized spiritual traditions.
Spread and Global Influence
As civilizations expanded, so did the influence of their belief systems. Trade, migration, and conquest played significant roles in the dissemination of ideas. For example, the spread of monotheism in the Middle East through figures like Moses and Muhammad had a profound impact on regions far beyond their origins. Similarly, Eastern traditions such as Buddhism and Hinduism traveled across Asia, reaching new lands and adapting to different cultures along the way.
The process of diffusion continued through empires, missionary efforts, and the movement of people across continents, especially during the period of European colonial expansion. Today, these belief systems have reached every corner of the globe, often intertwining with local customs and practices to form unique cultural identities.
Belief System Diffusion and Expansion
The spread of belief systems across regions and continents has shaped the social, cultural, and political landscapes of the world. As people moved, traded, and interacted with others, ideas and practices related to spirituality traveled beyond their places of origin. This process, known as diffusion, has been crucial in the development of global communities and the establishment of shared values and practices across diverse cultures.
Mechanisms of Diffusion

Belief systems have expanded in various ways, with some spreading through peaceful means, while others were driven by conquest or migration. The diffusion of these systems often follows certain patterns, influenced by historical events, social interactions, and cultural exchanges. Key mechanisms include:
- Missionary Activity: The intentional efforts to spread spiritual teachings to new areas, often through dedicated missionaries or religious movements.
- Trade and Commerce: Economic exchanges between regions facilitated the movement of people and ideas, allowing spiritual practices to reach distant places.
- Conquest and Empire Building: The expansion of empires often brought with it the imposition of a dominant belief system on conquered peoples.
Examples of Expansion
Several belief systems have undergone significant expansion, reaching areas far from their places of origin. Notable examples of diffusion include:
- Christianity: Spread from the Middle East through the Roman Empire and later through European exploration and colonialism.
- Islam: Expanded rapidly from the Arabian Peninsula through conquest, trade, and missionary work into Africa, Europe, and Asia.
- Buddhism: Traveled across Asia, first from India to Central and East Asia through merchants and monks.
The global spread of belief systems has not only transformed societies but also led to the formation of diverse religious landscapes, blending practices and traditions from different cultures. As a result, the diffusion of spiritual ideas continues to influence the way people interact with the world and each other today.
The Role of Belief Systems in Conflict
Throughout history, belief systems have played both unifying and divisive roles in societies. While they can bring people together with shared values and goals, they have also been a source of tension, division, and even violence. The role of spirituality in conflict is complex, as it often intertwines with political, economic, and cultural factors, influencing the course of disputes both within and between nations.
Factors Contributing to Conflict
Belief systems can contribute to conflict in several ways. When groups with differing spiritual views come into contact, the potential for misunderstandings and hostilities can arise. The following factors are key in understanding how these systems can escalate tensions:
- Religious Differences: Contrasting beliefs about divine authority, sacred texts, or practices can lead to mistrust and violence, particularly when one group seeks to assert dominance over the other.
- Political Power: Religious ideologies often become entangled with political ambitions, leading to the use of belief systems to justify wars or territorial expansion.
- Ethnic and Cultural Identity: Religion is frequently tied to ethnic or cultural identities, and conflicts can emerge when these identities clash or are threatened by external forces.
Examples of Religious Conflicts
History is replete with examples where spiritual beliefs have played a central role in conflict. These include:
- The Crusades: A series of religious wars fought between Christians and Muslims in the Middle Ages, driven by territorial and spiritual motives.
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: A long-standing dispute with deep religious, cultural, and political roots, involving Jewish, Muslim, and Christian communities.
- Religious Persecution: The persecution of religious minorities, such as during the Spanish Inquisition or the partition of India, where conflict arose due to differences in belief.
Despite the divisive potential of belief systems, many individuals and groups also use spiritual teachings to promote peace, reconciliation, and social justice. The role of belief in conflict is therefore not absolute; it depends on how people interpret and act upon their spiritual principles in the context of their broader social and political realities.
Religious Landscapes and Patterns
Belief systems shape the physical and cultural landscapes in profound ways, leaving lasting marks on the way people live and interact with their environment. The distribution of sacred places, the construction of worship spaces, and the cultural practices tied to spirituality can reveal much about the values and history of different communities. As these belief systems spread, they create distinct patterns that reflect both historical movements and ongoing influences.
In various regions, the physical environment is transformed to reflect spiritual significance. Sacred sites, places of pilgrimage, and structures of worship not only serve religious functions but also become symbols of identity and power. These patterns are influenced by many factors, including geography, population density, and cultural practices.
Patterns of Sacred Spaces
The layout of sacred spaces can vary greatly depending on the belief system and the needs of the community. Some common features of religious landscapes include:
- Churches and Temples: In many Christian, Hindu, and Buddhist traditions, places of worship are central to community life. The architectural style and layout often reflect the hierarchy and theological principles of the belief system.
- Cemeteries: Burial sites are often organized around religious principles, with certain areas reserved for the faithful or for specific groups within society.
- Pilgrimage Routes: Journeys to sacred sites, such as the Hajj in Islam or the pilgrimage to Mecca, create physical patterns across landscapes, linking various religious communities.
Table: Distribution of Major Sacred Sites Around the World
| Region | Sacred Sites | Key Belief Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Mecca, Jerusalem | Islam, Judaism, Christianity |
| South Asia | Varanasi, Bodh Gaya | Hinduism, Buddhism |
| East Asia | Mount Fuji, Kiyomizu-dera | Shinto, Buddhism |
| Europe | Santiago de Compostela, St. Peter’s Basilica | Christianity |
These landscapes often reveal not only religious devotion but also the historical and cultural forces that have shaped the development of these belief systems. As societies evolve, these sacred spaces continue to influence the way people relate to their environment, each other, and their own spiritual practices.
Secularism and Its Influence Worldwide

As societies evolve, the influence of spiritual practices on daily life has seen significant shifts, with many nations experiencing a rise in secularism. This phenomenon, where religious beliefs and institutions play a reduced role in public and governmental affairs, has reshaped cultural, social, and political landscapes. Secularism has become a defining characteristic of modern states, influencing everything from laws and education to personal freedoms and ethical norms.
The rise of secular thought has challenged traditional views, leading to debates on the proper role of belief systems in governance and societal structures. While some countries maintain a strong connection between their spiritual heritage and state functions, others have embraced secularism as a means of ensuring equal treatment for people of all beliefs and promoting a more inclusive, diverse society.
Secularism in Practice
Secularism manifests in various ways around the world, influencing everything from legal systems to cultural norms. Some key aspects include:
- Separation of Church and State: In many countries, laws are designed to keep religious institutions from influencing governmental decisions. This principle ensures that policies are created without religious bias.
- Freedom of Belief: Secularism often leads to greater religious tolerance, allowing individuals to freely choose their beliefs without fear of persecution or discrimination.
- Impact on Education: Secular societies often implement educational systems that teach science, history, and other subjects without religious interpretation, focusing on critical thinking and empirical evidence.
Table: Secularism’s Impact by Region
| Region | Secular Influence | Examples of Secular Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Western Europe | High influence in public policy and law | Separation of religion from government, secular education systems |
| North America | Secularism in government and schools, but with significant religious diversity | First Amendment protections, secular laws, diverse faiths |
| Middle East | Secularism is less widespread, though some nations are adopting secular policies | Secular laws in Turkey, limited secular practices in the Gulf states |
| Asia | Varied levels of secularism depending on the country | Secular education in Japan, limited religious interference in governance in China |
While secularism has fostered advancements in human rights and governance, it also raises important questions about the role of spiritual and cultural traditions in modern life. The balance between secular values and religious identities continues to evolve, shaping the future of societies around the world.
Religion and Politics in Human Geography
The interplay between belief systems and political structures is a defining characteristic of many societies. In numerous regions, spiritual values shape governmental policies, laws, and social norms. Conversely, political decisions can influence how people practice their faith or even dictate the level of religious freedom within a country. This dynamic relationship often leads to tension and transformation, especially as cultural and political landscapes evolve.
The role of spiritual beliefs in politics varies across the world, with some nations embracing a closer union between church and state, while others champion the separation of the two. Understanding how belief systems influence politics helps explain the complex interactions between individual freedoms, societal norms, and governmental powers.
Religious Influence on Political Systems
In many countries, the impact of belief systems on politics can be seen in both the creation of laws and the governance of citizens. Some ways in which faith influences political systems include:
- Theocratic Rule: In some nations, religious authorities hold significant political power, dictating laws based on spiritual doctrines.
- Policy Making: In many democratic nations, belief systems often shape debates on issues like marriage, abortion, and education.
- Religious Freedom Laws: Political systems may create legislation to protect individuals’ rights to practice their beliefs freely, or conversely, impose restrictions based on religious ideologies.
Political Influence on Religious Practices

On the other hand, political powers also affect how religions are practiced, where they are permitted, and the freedom of expression they enjoy. Key factors include:
- Religious Restrictions: Governments may limit or control the practice of certain faiths, sometimes outlawing religious groups they deem a threat to national unity or political stability.
- Religious Toleration and Persecution: While some governments foster a climate of religious pluralism, others may oppress specific religious groups, leading to persecution or forced conversions.
- Secular Policies: In some political systems, a push for secularism can influence laws to limit the role of religion in public spaces and governmental affairs.
While the relationship between belief systems and politics can vary greatly between regions, it remains a critical aspect of how societies function and evolve. The ongoing interaction between spiritual practices and political structures continues to shape the future of nations worldwide.
Religion and Social Structures
Belief systems play a fundamental role in shaping the social fabric of societies around the world. From family units to broader community organizations, spiritual values often influence social hierarchy, roles, and norms. These belief systems create frameworks through which individuals understand their position in society and their relationships with others. Whether reinforcing traditional norms or challenging societal structures, these values have a deep impact on the dynamics within a culture.
Social systems are not merely influenced by political or economic factors but are equally shaped by spiritual and moral beliefs that define acceptable behavior and social expectations. These belief systems provide the foundation for laws, ethical standards, and even personal identities, creating a blueprint for how people interact and organize themselves within society.
Social Hierarchy and Belief Systems
Many societies are structured based on principles derived from belief systems. These structures often define roles within families, communities, and larger social systems. Some key aspects include:
- Class and Caste Systems: In some cultures, spiritual beliefs determine an individual’s status and social position, with certain roles or castes considered more prestigious based on religious principles.
- Gender Roles: Spiritual doctrines may also dictate traditional gender roles, prescribing specific duties and responsibilities for men, women, and other gender identities within the community.
- Social Norms: Many societies use spiritual values to define acceptable behaviors, from dietary restrictions to dress codes, thereby influencing social interaction.
Religion as a Unifying and Dividing Force
While belief systems can foster unity and a sense of shared purpose, they can also contribute to divisions within society. The ways in which they shape group identities and social cohesion are diverse:
- Community Bonding: Shared beliefs often create strong bonds between individuals, fostering a sense of belonging and collective responsibility.
- Social Inequality: In some cases, the hierarchy reinforced by spiritual beliefs may contribute to social stratification and discrimination, marginalizing certain groups based on their perceived lack of spiritual or social value.
- Conflict and Division: Differing spiritual beliefs can lead to conflicts between groups, as differing values and practices often lead to tensions or even violence within societies.
Overall, the relationship between belief systems and social structures is complex. While these values can foster harmony, they also shape societal norms and can influence the inclusivity or divisiveness of social systems. Understanding these connections helps clarify how spiritual frameworks mold the way people live together, interact, and organize their communities.
Globalization and Religious Change
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected through trade, technology, and communication, cultural practices and belief systems are undergoing significant transformations. The spread of ideas and lifestyles across national borders has led to a blending of traditions, creating new forms of expression and adaptation. This process of global integration affects how spiritual practices are perceived and practiced, leading to both the preservation of ancient customs and the emergence of new ones.
Globalization can foster the exchange of religious ideas, facilitating the growth of new communities while challenging traditional practices. In some regions, local customs may be influenced or even replaced by dominant global ideologies, reshaping spiritual landscapes. The interaction between local beliefs and global influences leads to a dynamic relationship where cultures and practices continuously evolve.
The impact of this global shift is not limited to the spread of certain faiths or practices; it also shapes how individuals engage with spirituality, creating new opportunities for personal expression while sometimes leading to tensions between tradition and modernity. While some groups embrace the global flow of ideas, others resist these changes, seeking to protect their traditional ways of life.
Religious Tolerance and Diversity
The coexistence of various belief systems within a society presents both challenges and opportunities for fostering mutual understanding and respect. As cultures and societies become more interconnected, the need for tolerance and acceptance of diverse worldviews becomes increasingly important. People are exposed to a variety of spiritual practices, philosophies, and traditions, each offering unique perspectives on life, values, and human existence. Promoting an environment of tolerance allows for peaceful coexistence and enriches societies by creating spaces where different viewpoints can be shared and appreciated.
Despite the potential for harmony, religious diversity can also lead to conflict when beliefs clash or when intolerance emerges. Differences in practices, rituals, and doctrines can sometimes become sources of division, but with effective communication and open-mindedness, these challenges can be overcome. It is essential for communities to recognize the importance of respecting differences and finding common ground, fostering peace and stability in an increasingly pluralistic world.
Understanding the role of tolerance in managing diversity is key to building a society where all individuals can freely express their beliefs without fear of discrimination or persecution. Encouraging dialogue and cooperation between different groups can lead to greater social cohesion, ensuring that diversity is celebrated rather than feared.
Future Trends in Religious Geography
The patterns of belief systems around the world are continuously evolving as societies change and interact on a global scale. As globalization accelerates, the movement of people, ideas, and technologies is reshaping spiritual landscapes. Emerging trends indicate a shift in the geographical distribution of practices, with some gaining prominence in new regions while others face challenges in their traditional strongholds.
Migration and Mobility play a crucial role in the diversification of religious practices. As individuals migrate across borders, they bring their beliefs and traditions with them, often leading to the blending of cultures and spiritual expressions. This movement has the potential to introduce new forms of religious syncretism, where elements from various traditions combine to form new practices.
Technological Advances also contribute to the changing nature of belief systems. The rise of digital platforms and social media allows individuals to access spiritual content from all over the world, fostering cross-cultural exchanges and sometimes challenging traditional structures. The internet provides a space for the spread of non-traditional beliefs and encourages virtual communities that transcend geographical boundaries.
As the world continues to evolve, it is likely that the future will see even greater interconnectedness among different belief systems, potentially leading to both greater harmony and new challenges. Understanding these shifts and their impact on cultural landscapes will be key to navigating the complexities of a pluralistic world.