
In this section, we explore the vital components that contribute to overall well-being and vitality. By examining the relationship between food and body functions, we gain a deeper understanding of how specific substances support various aspects of physical performance, energy levels, and growth.
Proper intake of key substances plays a fundamental role in maintaining optimal bodily functions. From enhancing daily energy to promoting a strong immune system, each nutrient serves a distinct purpose. Whether it’s the role of macronutrients or micronutrients, the body relies on a variety of elements to stay balanced.
Achieving a harmonious approach to daily eating is essential for supporting long-term wellness. By integrating essential elements into one’s lifestyle, it becomes easier to boost vitality, prevent deficiencies, and manage individual health goals effectively.
Key Insights on Essential Dietary Elements
This section delves into the critical factors that influence bodily functions and overall well-being. By understanding the role of different components in the foods we consume, we can better appreciate how they contribute to energy levels, vitality, and optimal bodily performance.
Each substance plays a unique role in supporting specific processes, from strengthening the immune system to improving muscle function. The balance between various types of macronutrients and micronutrients is key to maintaining stability and preventing deficiencies that could compromise well-being.
Adopting a thoughtful approach to meal planning allows individuals to meet their personal goals, whether it’s managing weight, enhancing physical endurance, or supporting mental clarity. Tailoring one’s intake to meet individual needs helps achieve sustainable results over time.
Understanding Key Nutrients for Health
In this section, we explore the essential elements that the body requires to function at its best. From providing energy to supporting cellular repair, each nutrient plays a vital role in maintaining overall bodily performance and well-being. These elements are not just a source of fuel but are involved in numerous biochemical processes that sustain life.
Each type of nutrient, whether it be protein, fat, carbohydrate, vitamins, or minerals, has a specific function in promoting physical strength, cognitive function, and immune defense. Achieving the right balance of these substances ensures that the body operates efficiently and effectively in both daily tasks and long-term health goals.
Importance of Balanced Diet for Wellness
A well-rounded eating plan is the cornerstone of maintaining optimal physical and mental well-being. It ensures that the body receives all the essential elements it needs to function effectively, while also preventing potential health issues caused by deficiencies or imbalances. Striking the right balance between various food groups is crucial to supporting long-term vitality and energy levels.
A diverse intake of foods provides a broad spectrum of essential components, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each plays a unique role in ensuring the body operates at peak efficiency. Maintaining this balance contributes to a stronger immune system, improved mood, better cognitive function, and overall vitality.
| Nutrient | Function | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Primary source of energy | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables |
| Proteins | Builds and repairs tissues | Lean meats, legumes, nuts |
| Fats | Supports brain function and energy | Olive oil, avocado, fatty fish |
| Vitamins | Boosts immune system, supports growth | Leafy greens, citrus fruits, dairy |
| Minerals | Supports bone health and fluid balance | Leafy vegetables, dairy, nuts |
How Nutrition Affects Physical Performance
The quality and composition of what we consume play a pivotal role in how the body performs during physical activities. From enhancing endurance to supporting muscle recovery, the right dietary choices can significantly influence overall fitness levels and athletic capabilities. The body relies on specific nutrients to fuel muscles, maintain energy, and repair tissue after exertion.
Energy and Endurance
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy during exercise. When consumed in adequate amounts, they are converted into glucose, which is stored in muscles as glycogen. During intense physical activities, the body taps into this reserve to fuel prolonged performance. Without sufficient carbohydrates, the body may run out of energy quickly, leading to fatigue.
Muscle Repair and Growth
Proteins are essential for repairing muscle fibers broken down during physical exertion. Consuming the right amount of protein supports muscle growth and helps recover strength after exercise. Additionally, healthy fats play a role in reducing inflammation and supporting joint health, which can be crucial for preventing injuries during intense workouts.
Vitamins and Their Role in Health
Vitamins are essential compounds that support numerous functions within the body, ensuring proper metabolic processes, immune function, and overall well-being. These micronutrients are required in small amounts, but they play an indispensable role in maintaining good physical and mental health. Without an adequate intake of vitamins, various body functions may become compromised, leading to deficiencies or health issues.
Key Functions of Vitamins

Each vitamin has a specific role in the body, contributing to different physiological processes. Here are some essential functions:
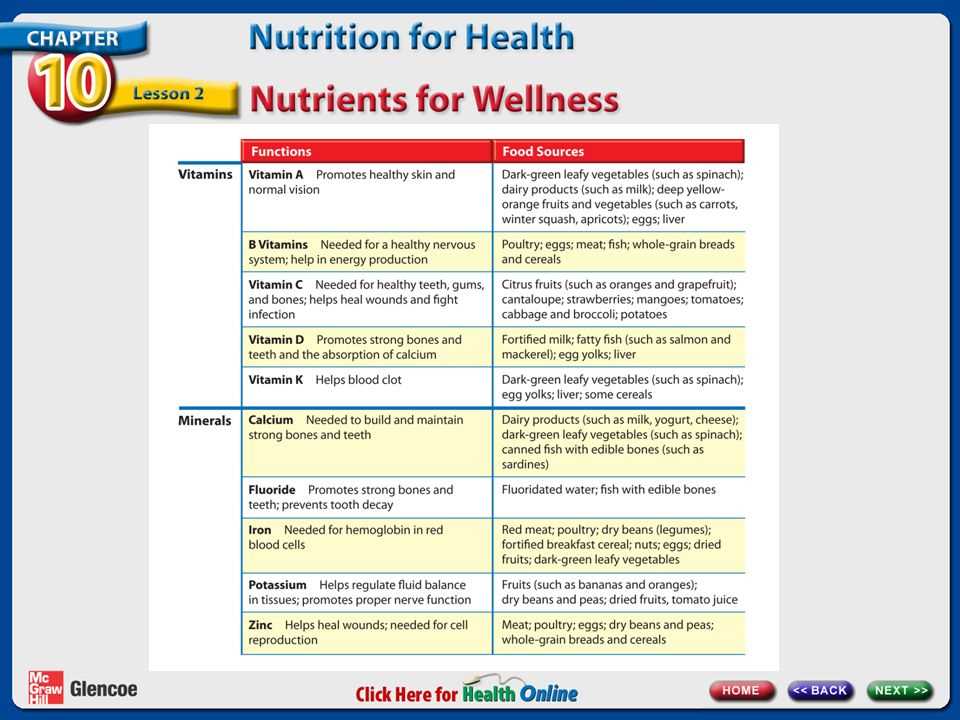
- Vitamin A: Supports vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin C: Promotes wound healing, boosts immunity, and acts as an antioxidant.
- Vitamin D: Aids in calcium absorption and supports bone health.
- Vitamin E: Protects cells from oxidative damage and supports skin health.
- Vitamin K: Crucial for blood clotting and bone health.
Sources of Essential Vitamins
To ensure adequate vitamin intake, it is important to include a variety of foods in the diet. Here are some common sources:
- Vitamin A: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach.
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries.
- Vitamin D: Fatty fish, fortified dairy products, sunlight.
- Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables.
- Vitamin K: Leafy greens, broccoli, Brussels sprouts.
The Impact of Proteins on Body Functions
Proteins are fundamental building blocks for the body, involved in a wide range of essential processes that support growth, repair, and overall function. From forming the structure of muscles to producing enzymes and hormones, these macronutrients play a crucial role in maintaining bodily health and ensuring optimal performance in daily activities. A balanced intake of protein is key to supporting tissue regeneration and sustaining energy levels.
Key Roles of Proteins
Proteins contribute to many vital processes in the body. Some of their most important functions include:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Proteins are essential for repairing and rebuilding muscle tissue after physical exertion or injury.
- Enzyme Production: Proteins help produce enzymes that regulate metabolic processes, such as digestion and energy production.
- Immune Function: Certain proteins are involved in the formation of antibodies that help defend the body against infections and illnesses.
- Hormone Regulation: Proteins are involved in the synthesis of hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and mood.
- Transport and Storage: Proteins transport nutrients, such as oxygen, through the bloodstream, and store important minerals in cells.
Sources of High-Quality Protein
Incorporating a variety of protein-rich foods into the diet is essential for meeting the body’s needs. Common sources of high-quality protein include:
- Animal-based Proteins: Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Plant-based Proteins: Legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, and whole grains.
- Protein Supplements: Whey protein, plant-based protein powders, and other protein-rich shakes can be convenient options for those with higher protein demands.
Healthy Fats and Their Benefits
Fats are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. While they are often misunderstood, not all fats are harmful. Healthy fats contribute to various bodily functions, including hormone regulation, brain health, and energy production. Including the right types of fats in the diet can have long-term positive effects on physical and mental performance.
Functions of Healthy Fats
Healthy fats provide a wide range of benefits that are vital for bodily function:
- Energy Source: Fats are a concentrated source of energy, providing more calories per gram than carbohydrates or proteins.
- Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids found in certain fats are essential for brain function and may help improve memory and cognitive function.
- Cellular Structure: Fats are a key component of cell membranes, helping maintain their integrity and fluidity.
- Absorption of Vitamins: Certain vitamins, such as A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble and rely on fats to be absorbed and utilized by the body.
- Inflammation Control: Healthy fats, particularly omega-3s, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Sources of Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet can be simple by choosing the right food sources. Some excellent options include:
- Monounsaturated Fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fish oil, algae, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
Carbohydrates and Their Role in Energy
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of fuel, providing essential energy for daily activities and physical exertion. When consumed, these nutrients are broken down into glucose, which is used by the body to power muscles, brain functions, and various metabolic processes. Understanding the role of carbohydrates in maintaining energy levels can help optimize performance and overall well-being.
How Carbohydrates Provide Energy
Once consumed, carbohydrates are converted into glucose, a simple sugar that circulates in the bloodstream. Glucose is then used by cells to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the body. This process supports everything from basic bodily functions to intense physical activity. The body stores excess glucose as glycogen in muscles and the liver for later use during high-energy demands, such as exercise or physical labor.
Types of Carbohydrates
Not all carbohydrates are created equal, and their effects on energy levels can vary. There are two main types of carbohydrates:
- Simple Carbohydrates: Found in sugary foods and drinks, these are quickly digested and provide a rapid burst of energy, but they may cause energy crashes afterward.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, these are digested more slowly and provide a steady, sustained release of energy over time.
Minerals Essential for Healthy Growth
Minerals play a critical role in supporting growth, development, and overall bodily functions. These micronutrients are vital for numerous physiological processes, from maintaining bone strength to supporting the immune system. A well-balanced intake of essential minerals ensures that the body can perform optimally, aiding in tissue repair, energy production, and maintaining proper fluid balance.
Key Minerals and Their Functions
Each mineral has a unique role in the body, contributing to various processes necessary for growth and health. Below are some key minerals and their benefits:
| Mineral | Function | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Supports strong bones and teeth, aids in muscle function and nerve signaling. | Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified plant milk. |
| Iron | Essential for oxygen transport in the blood and energy production. | Red meat, legumes, spinach, fortified cereals. |
| Magnesium | Important for muscle and nerve function, bone health, and regulating blood pressure. | Whole grains, nuts, seeds, leafy vegetables. |
| Zinc | Supports immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis. | Meat, shellfish, legumes, seeds, nuts. |
| Potassium | Helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve function. | Bananas, potatoes, spinach, beans. |
Ensuring Adequate Mineral Intake
A well-rounded diet that includes a variety of whole foods can help provide the essential minerals the body needs. It is important to include a mix of animal-based and plant-based sources to meet the body’s mineral requirements. In cases of deficiency, supplements may be recommended by a healthcare professional, but natural food sources are typically the best way to maintain balance.
Hydration and Its Effect on Health
Maintaining proper fluid balance is essential for optimal bodily function. Water is involved in virtually every process within the body, from temperature regulation to nutrient absorption and waste elimination. Dehydration can lead to a range of health issues, affecting both physical and mental performance. Understanding the importance of staying adequately hydrated can greatly improve overall well-being.
Hydration plays a vital role in many bodily functions, including the transportation of nutrients, regulation of body temperature, and the removal of waste products. Proper fluid intake ensures that the cells, tissues, and organs function effectively. It is particularly important for maintaining energy levels, supporting the digestive system, and enhancing cognitive function.
While water is the most common and essential fluid, other beverages and foods can contribute to hydration. However, it is important to be mindful of the types of fluids consumed, as sugary drinks or excessive caffeine can lead to dehydration in some cases. Regular intake of water, along with a balanced diet rich in hydrating foods such as fruits and vegetables, helps maintain healthy fluid levels in the body.
Nutrition Tips for Better Digestion

Proper digestion is essential for overall wellness, as it ensures the body effectively absorbs nutrients from food. A balanced approach to eating can promote smoother digestion, reduce discomfort, and enhance nutrient uptake. By making mindful food choices and adopting specific habits, it’s possible to support digestive health and avoid common issues like bloating, constipation, and indigestion.
Several dietary strategies can help improve the digestive process. These include consuming fiber-rich foods, staying hydrated, and including fermented items in the diet. A balanced meal structure and mindful eating habits can also reduce stress on the digestive system and improve gut health over time.
Effective Food Choices for Digestion
The foods you eat play a crucial role in how efficiently your digestive system operates. Below is a table of some key foods that promote digestive health:
| Food | Benefits for Digestion |
|---|---|
| Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables | Help regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and promote gut health. |
| Whole grains | Provide complex carbohydrates that aid digestion by promoting regularity and feeding beneficial gut bacteria. |
| Fermented foods | Support the growth of good bacteria, improving gut flora balance and digestion. |
| Ginger | Stimulates digestion and alleviates nausea or bloating. |
| Water | Hydrates the digestive system, helping to break down food and prevent constipation. |
Healthy Habits for a Better Digestive Process
In addition to the right food choices, certain eating habits can further enhance digestion. Eating slowly, chewing food thoroughly, and avoiding overeating are simple strategies that can minimize digestive strain. Additionally, incorporating stress-reducing practices like mindfulness or regular physical activity can positively impact digestion by promoting a more relaxed gut environment.
The Relationship Between Diet and Immunity
The foods we consume have a profound effect on our body’s ability to fight off infections and maintain overall well-being. A strong immune system relies on a variety of nutrients that help defend against harmful pathogens. By making mindful food choices, we can support and enhance our body’s natural defenses, ensuring it is better equipped to protect itself from diseases.
A well-rounded diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote immune function. Nutrients such as vitamin C, zinc, and probiotics play a direct role in boosting immunity by enhancing the activity of immune cells and supporting the body’s response to infections. Eating a diverse range of whole foods ensures that the body receives a wide spectrum of nutrients necessary for optimal immune performance.
In addition to specific nutrients, healthy dietary habits also support immune function. A balanced approach to eating, rich in plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins, can help reduce inflammation and maintain a healthy gut microbiome. The gut plays a critical role in immunity, as a large portion of the immune system is found there. Therefore, prioritizing gut health through diet can have a significant impact on overall immune strength.
Weight Management through Proper Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy weight is not solely about reducing calorie intake but rather about choosing the right types of foods that support the body’s needs. A balanced approach to eating, with a focus on whole foods, can help regulate body weight and improve overall well-being. Proper meal planning and mindful eating are key to achieving and sustaining an ideal weight over time.
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods, such as vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains, can support weight control by providing the body with essential vitamins and minerals. These foods are often lower in calories but rich in fiber, which helps to keep you full longer and prevent overeating. When the body receives the proper nutrients, it can maintain a healthy metabolism and effectively regulate weight.
Key Principles for Effective Weight Management

Several strategies can help guide a balanced approach to weight management through food choices. These include:
- Portion control: Eating in moderation helps prevent excess calorie intake and supports a sustainable approach to weight maintenance.
- Balanced macronutrients: A mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for keeping energy levels stable while supporting metabolic health.
- Fiber-rich foods: High-fiber options, like vegetables and whole grains, support digestion and help keep hunger at bay.
Foods to Include in Your Diet
Choosing foods that are both filling and nutritious can make weight management easier. Here are some examples of foods that can support your goals:
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and legumes
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice
- Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil
Incorporating these foods into your daily meals can help provide the right balance of nutrients while supporting weight management efforts in a sustainable way.
Mindful Eating for Long-Term Health
Adopting a mindful approach to eating can profoundly impact overall well-being and longevity. By paying attention to the food we consume, as well as how and when we eat, we can foster a healthier relationship with food. This practice encourages awareness of hunger and fullness cues, allowing the body to guide consumption while enhancing digestion and enjoyment of meals.
Mindful eating focuses on being present during meals, making conscious choices about the types of foods and their nutritional value. It also involves slowing down and savoring each bite, which can help improve digestion and prevent overeating. By tuning into the body’s signals, individuals are more likely to make healthier food choices, maintain a balanced diet, and achieve long-term well-being.
Key Principles of Mindful Eating
To incorporate mindful eating into your routine, consider these foundational principles:
- Focus on the present moment: Eat without distractions such as phones or television to fully enjoy your food and recognize when you are satisfied.
- Eat slowly: Take the time to chew thoroughly, allowing your body to register fullness before overeating.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to hunger and satiety cues, which can help avoid unnecessary calorie intake.
- Appreciate food: Cultivate gratitude for the food on your plate and its ability to nourish your body.
Benefits of Mindful Eating
When practiced regularly, mindful eating can offer a variety of benefits for both physical and mental well-being:
- Improved digestion: Eating slowly allows the digestive system to function more efficiently and reduces the likelihood of digestive discomfort.
- Better weight management: Mindful eating helps prevent overeating by encouraging individuals to recognize when they are full, leading to more balanced eating habits.
- Enhanced emotional well-being: Being more connected with food can reduce stress around eating, leading to a more positive attitude toward meals and body image.
By embracing mindful eating practices, individuals can build healthier habits that not only improve physical health but also promote a deeper connection to the food they consume, contributing to a more balanced and fulfilling life in the long run.
How to Avoid Common Nutritional Deficiencies
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial to ensuring the body receives all the essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients it needs. Many individuals struggle with deficiencies in specific nutrients, which can lead to various health complications. The key to avoiding such deficiencies is understanding which nutrients are most commonly lacking and how to incorporate them into your daily meals.
Several nutrients are vital for optimal function, and missing out on them can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakened immunity, and poor bone health. A well-rounded diet that includes a variety of food groups is the best way to prevent these issues. By being mindful of what you eat and ensuring you’re getting enough of the necessary nutrients, you can protect your body from deficiencies.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies
The following are some of the most common deficiencies and how to address them:
- Iron: Often lacking in individuals who do not consume enough red meat or plant-based sources such as legumes and spinach. Incorporate iron-rich foods into your meals, such as beans, lentils, and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin D: A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to weak bones and a compromised immune system. Spending time in sunlight, consuming fortified dairy, and eating fatty fish like salmon can help.
- Vitamin B12: Essential for energy production and nervous system health, B12 is typically found in animal products. Vegans and vegetarians can consider fortified foods or supplements.
- Calcium: Crucial for bone health, calcium is often insufficient in those who do not consume dairy products. Leafy greens, fortified plant milks, and tofu are great alternatives.
Tips to Prevent Nutrient Deficiencies
To ensure you’re not falling short on essential nutrients, consider these strategies:
- Eat a varied diet: Include a wide range of foods from all food groups to cover all your nutritional needs.
- Monitor your intake: Track what you eat to identify any potential gaps in your diet and take action to fill them.
- Consider supplements: If certain nutrients are hard to obtain from food, speak with a healthcare provider about appropriate supplements.
- Focus on whole foods: Fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provide a rich source of the vitamins and minerals your body requires.
By being proactive about your dietary choices and incorporating nutrient-rich foods, you can effectively avoid common deficiencies and support your overall well-being. The key is to maintain variety in your meals and listen to your body’s signals, ensuring you’re nourishing it with what it needs to function at its best.
Nutrition Guidelines for Special Health Conditions
People with specific medical conditions often require tailored dietary plans to manage their symptoms, support recovery, and enhance overall well-being. Certain conditions may affect nutrient absorption, metabolism, or the body’s ability to process certain foods, making it crucial to adjust one’s eating habits accordingly. Adopting a personalized approach to food choices can help individuals better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Dietary guidelines vary greatly depending on the nature of the condition. Whether dealing with diabetes, heart disease, digestive disorders, or autoimmune conditions, understanding which foods to prioritize and which to avoid is essential. A well-balanced diet, rich in the right nutrients, can alleviate symptoms and contribute to better long-term outcomes for those with specialized health needs.
Guidelines for Managing Common Health Conditions
Here are some dietary recommendations for individuals with specific health concerns:
- Diabetes: Focus on low-glycemic foods to regulate blood sugar levels. Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and lean proteins are excellent choices. Limit sugary snacks and refined carbohydrates.
- Heart Disease: Incorporate heart-healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish like salmon. Reduce saturated fats and avoid trans fats. Aim for plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support cardiovascular health.
- Digestive Disorders: For conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or celiac disease, it’s essential to avoid gluten-containing foods and choose easily digestible options. High-fiber foods can support gut health, but they should be introduced gradually.
- Autoimmune Diseases: A diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods can help manage inflammation. Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids (from fish or flaxseeds), colorful vegetables, and fruits to support immune function.
General Tips for Special Conditions
In addition to condition-specific guidelines, here are general tips for adapting your diet:
- Consult a professional: A dietitian or healthcare provider can help create a meal plan tailored to your specific needs and health goals.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is key for managing many health conditions. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support bodily functions.
- Monitor portion sizes: Portion control can help prevent overeating and manage conditions like diabetes or obesity.
- Avoid processed foods: Processed foods often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives that can exacerbate health issues. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods when possible.
By following these personalized dietary recommendations and consulting healthcare providers for guidance, individuals with special health conditions can better manage their condition, enhance their well-being, and lead healthier lives.
How to Create a Nutritional Plan
Creating a personalized eating strategy is essential for maintaining overall well-being and meeting specific health goals. A well-structured plan helps ensure the body receives the right balance of essential nutrients, supports physical and mental performance, and promotes long-term vitality. Whether the objective is weight management, improving energy levels, or addressing specific health concerns, a tailored dietary approach is key to success.
To develop an effective eating plan, it’s important to consider several factors, such as activity levels, dietary preferences, and specific goals. Taking a thoughtful approach ensures that the body gets the necessary fuel while minimizing the risk of deficiencies or overeating. A balanced approach can also improve digestion, strengthen the immune system, and promote a positive relationship with food.
Steps to Create a Personalized Eating Plan
- Set Clear Goals: Begin by defining what you want to achieve. Are you looking to lose weight, build muscle, improve overall energy, or manage a specific condition? Your goals will guide the choices you make regarding food types and portions.
- Assess Your Current Eating Habits: Take note of your current dietary patterns. Identify areas where you could improve, such as consuming more fruits and vegetables, reducing processed foods, or incorporating healthy fats.
- Balance Macronutrients: Ensure your meals contain a balanced mix of proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. This will provide sustained energy, support muscle repair, and help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate Micronutrients: Don’t forget about vitamins and minerals, which are essential for various bodily functions. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure adequate intake of these micronutrients.
Key Considerations for an Effective Eating Strategy
- Portion Control: Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if eaten in excess. Learn to control portion sizes and avoid overeating by paying attention to hunger cues.
- Meal Timing: The timing of your meals can impact energy levels and metabolism. Aim to eat regular meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is crucial for digestion, detoxification, and overall bodily functions. Aim to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Be Flexible: Your plan should be adaptable to your lifestyle. If something isn’t working or you experience cravings, make adjustments rather than being too rigid.
With a clear plan in place, you can begin taking practical steps toward healthier eating. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and staying mindful of portion sizes, you can make lasting changes that improve your quality of life and help you achieve your personal wellness goals.