
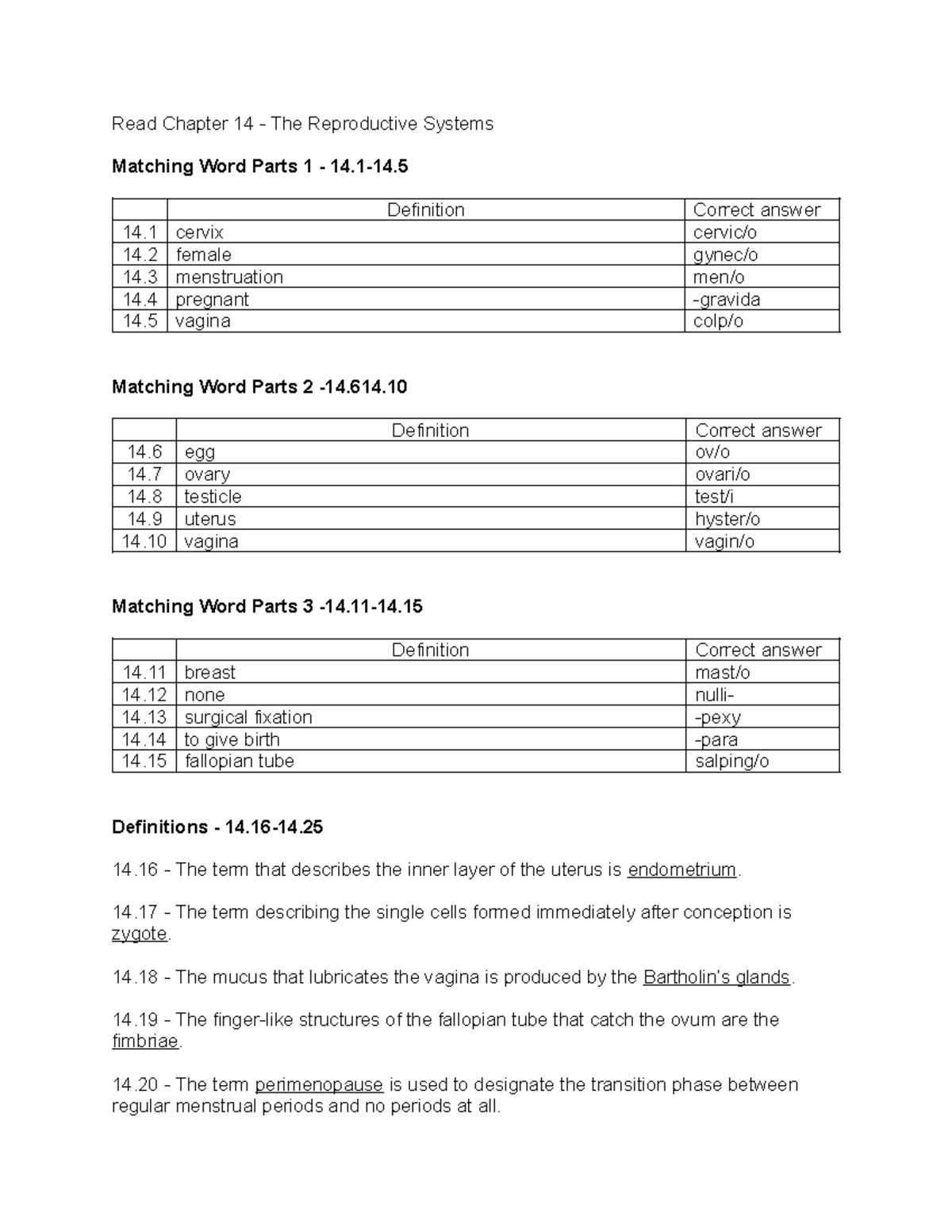
In this section, we explore essential concepts and terms related to the field of healthcare, focusing on their meanings and how they are used in daily practice. Gaining a strong grasp of these terms is vital for both professionals and students who are navigating the complexities of this field.
By familiarizing yourself with common prefixes, suffixes, and root words, you will develop a deeper understanding of how various conditions, procedures, and body systems are described. This foundational knowledge is critical for interpreting clinical documentation and communicating effectively in a healthcare setting.
Through detailed examples and explanations, we will break down complex vocabulary into manageable pieces, helping you master the language used in medical discussions and ensure clarity in all forms of medical communication.
Understanding Key Concepts in Healthcare Vocabulary
This section delves into the core elements that form the foundation of healthcare language. By breaking down complex words and expressions, we can better understand how they relate to various conditions, procedures, and treatments. The ability to interpret these terms is crucial for professionals and students alike, helping to navigate the vast landscape of healthcare communication.
Breaking Down Complex Words
Healthcare vocabulary often combines multiple parts to convey specific meanings. Root words, prefixes, and suffixes play a crucial role in this process. Understanding these components helps simplify complex terms, making it easier to interpret their full meaning and use them effectively in clinical practice.
Common Prefixes and Suffixes
Prefix and suffix combinations are key to deciphering the meaning behind many healthcare terms. Knowing their definitions allows for faster recognition and understanding of unfamiliar words in different contexts.
| Prefix | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hyper- | Excessive or above normal | Hypertension (high blood pressure) |
| Hypo- | Below normal | Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) |
| Brady- | Slow | Bradycardia (slow heart rate) |
| Tachy- | Fast | Tachycardia (fast heart rate) |
Mastering the use of these building blocks can greatly enhance comprehension and improve overall efficiency in understanding healthcare documentation and discussions.
Understanding Key Terms in Medicine

In healthcare, accurate and clear communication is essential for providing quality care. The use of specific words and phrases allows professionals to describe conditions, treatments, and bodily functions precisely. Understanding these terms is crucial for anyone working in or studying this field, as it ensures effective interaction and accurate interpretation of clinical information.
Core Concepts in Healthcare Vocabulary
Several key terms are commonly used to describe various aspects of patient care. These terms can be grouped into different categories, each focusing on a particular area of healthcare. Familiarity with these categories helps in understanding the larger picture of medical practice.
- Diseases and Conditions: Descriptive words used to identify and categorize illnesses, infections, and disorders.
- Procedures and Treatments: Terms that describe actions taken to diagnose or treat specific health issues.
- Anatomy and Physiology: Vocabulary related to the structure and function of the human body.
- Diagnostic Terms: Words used in the identification of specific health problems, often through tests or evaluations.
Common Prefixes and Suffixes in Healthcare
Prefixes and suffixes are integral parts of many medical terms. These affixes help form words that are easier to understand and remember. Below are some common prefixes and suffixes used in healthcare language:
- Prefix: Hypo- (meaning below or under), as in hypotension (low blood pressure).
- Prefix: Hyper- (meaning above or excessive), as in hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Suffix: -itis (meaning inflammation), as in arthritis (inflammation of the joints).
- Suffix: -ectomy (meaning removal), as in appendectomy (removal of the appendix).
Mastering these elements is essential for anyone looking to improve their understanding of healthcare language and enhance their ability to communicate effectively in medical settings.
Common Prefixes in Medical Terminology
Prefixes are essential components in healthcare vocabulary, as they modify the meaning of root words to provide more specific details. By understanding the role of these prefixes, it becomes easier to interpret complex terms related to conditions, treatments, and procedures. Knowing common prefixes helps both professionals and students grasp the full meaning of medical terms quickly and accurately.
Prefixes often convey important information such as size, location, time, or intensity. Learning these prefixes allows for a deeper understanding of how medical terms are constructed and how they relate to various aspects of healthcare.
| Prefix | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hypo- | Below normal, insufficient | Hypotension (low blood pressure) |
| Hyper- | Above normal, excessive | Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) |
| Brady- | Slow | Bradycardia (slow heart rate) |
| Tachy- | Fast | Tachycardia (fast heart rate) |
| Neo- | New | Neonatal (newborn) |
By mastering these common prefixes, healthcare professionals can quickly deduce the meanings of unfamiliar terms, making communication more efficient and precise in clinical environments.
Suffixes and Their Medical Significance
In healthcare vocabulary, suffixes play a vital role in shaping the meaning of terms. These word endings provide additional context, often indicating conditions, procedures, or the status of a particular aspect of health. Understanding suffixes is crucial for interpreting complex healthcare terms, as they help to narrow down the focus of a word, making it easier to understand its specific context.
Suffixes are often used to describe various aspects of patient care, from the identification of diseases to the naming of procedures and treatments. By recognizing common suffixes, healthcare professionals can quickly grasp the core meaning of unfamiliar terms.
Common Suffixes in Healthcare Vocabulary
- -itis – Refers to inflammation. Example: Arthritis (inflammation of the joints).
- -ectomy – Refers to the surgical removal of a body part. Example: Appendectomy (removal of the appendix).
- -ology – The study of a specific branch of knowledge. Example: Cardiology (the study of the heart).
- -pathy – Refers to a disease or disorder. Example: Neuropathy (disease or damage of nerves).
- -algia – Refers to pain. Example: Myalgia (muscle pain).
- -emia – Refers to a condition of the blood. Example: Anemia (a deficiency of red blood cells).
Understanding Suffix Usage in Healthcare
By learning the meanings and applications of these common suffixes, individuals can improve their ability to decode medical terms, enhancing both comprehension and communication in clinical settings. Mastery of these suffixes is essential for professionals dealing with complex documentation and terminology on a daily basis.
Breaking Down Complex Medical Words
Complex healthcare terms can often seem overwhelming, but understanding how they are constructed makes it easier to break them down into simpler components. Many of these terms are formed by combining root words, prefixes, and suffixes, each contributing specific meaning. By learning how to deconstruct these words, you can quickly grasp their full meaning and apply them in practice.
Key Elements of Complex Terms
The structure of most healthcare terms follows a predictable pattern. Knowing the basic components helps in recognizing the meaning of unfamiliar words. Here’s how complex words are typically formed:
- Root words: The core part of the term, often referring to a body part or system.
- Prefixes: Added at the beginning of a word to modify its meaning (e.g., “hypo-” meaning below).
- Suffixes: Placed at the end of a word to indicate a condition or procedure (e.g., “-itis” meaning inflammation).
Examples of Breaking Down Complex Terms
Here are a few examples of how to break down common healthcare terms:
- Osteoarthritis: “Osteo-” (bone) + “-arthritis” (inflammation of the joints).
- Cardiomyopathy: “Cardio-” (heart) + “-myo-” (muscle) + “-pathy” (disease).
- Dermatitis: “Derm-” (skin) + “-itis” (inflammation).
By recognizing and understanding these components, you can gain a better understanding of complex healthcare vocabulary, making it easier to comprehend and use these terms accurately in medical discussions.
Abbreviations Used in Healthcare
In the healthcare field, abbreviations are widely used to streamline communication and improve efficiency. These shortened forms of words or phrases help professionals quickly document and share critical information. Understanding these abbreviations is essential for anyone involved in patient care, as they ensure clarity and prevent errors in clinical settings.
Abbreviations can refer to medical conditions, procedures, medications, and various aspects of patient care. Learning to recognize and use these abbreviations properly allows healthcare workers to communicate more effectively and reduce the risk of misunderstanding in a fast-paced environment.
Commonly Used Abbreviations
Here are some of the most frequently encountered abbreviations in healthcare:
- BP – Blood Pressure
- HR – Heart Rate
- IV – Intravenous
- PRN – As Needed (from the Latin “pro re nata”)
- AC – Before Meals (from the Latin “ante cibum”)
- PO – By Mouth (from the Latin “per os”)
- Dx – Diagnosis
- Sx – Symptoms
Using Abbreviations Safely
Although abbreviations enhance efficiency, it is crucial to use them correctly to avoid confusion. For example, some abbreviations might be interpreted differently depending on the context, leading to errors. Healthcare professionals should always ensure that the meaning of an abbreviation is clear to everyone involved in the patient’s care to maintain safety and accuracy.
Medical Root Words and Their Meanings
Root words form the foundation of many healthcare terms. These core components provide the basic meaning of a word, often referring to body parts, conditions, or functions. By understanding the root word, it becomes easier to interpret the full meaning of a complex term. Root words are frequently combined with prefixes and suffixes to create terms with more specific meanings related to diagnosis, treatment, and anatomy.
Recognizing these root words is essential for anyone in the healthcare field, as it allows for a deeper understanding of medical language and aids in clear communication. Here are some common root words and their meanings:
Common Root Words in Healthcare
- Cardi- – Refers to the heart. Example: Cardiology (study of the heart).
- Derm- – Refers to the skin. Example: Dermatitis (inflammation of the skin).
- Gastr- – Refers to the stomach. Example: Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining).
- Hemat- – Refers to blood. Example: Hematology (study of blood and its disorders).
- Osteo- – Refers to bones. Example: Osteoporosis (condition of weak bones).
- Neuro- – Refers to nerves or the nervous system. Example: Neurology (study of the nervous system).
By mastering these root words, healthcare professionals can more easily understand and communicate complex terms, ensuring clearer and more effective interactions in clinical environments.
Diagnostic Terms and Their Definitions
In healthcare, diagnostic terms are used to describe conditions, diseases, and illnesses that affect patients. These terms often represent the results of tests, symptoms, or evaluations conducted by healthcare professionals. Understanding these terms is crucial for making accurate diagnoses and determining the most effective course of treatment. By familiarizing oneself with common diagnostic terms, it becomes easier to navigate medical records, communicate with other professionals, and understand the clinical language used in healthcare settings.
Common Diagnostic Terms
Here are some widely used diagnostic terms, along with their meanings:
- Acute – A condition that develops suddenly and is typically severe in nature. Example: Acute pain (sharp, intense pain that comes on suddenly).
- Chronic – A long-lasting condition that persists over time. Example: Chronic illness (an ongoing health issue, such as diabetes).
- Benign – A condition that is not harmful or cancerous. Example: Benign tumor (a non-cancerous growth).
- Malignant – A condition that is harmful, often used to describe cancerous tumors. Example: Malignant melanoma (a dangerous form of skin cancer).
- Symptomatic – Refers to a condition that shows clear symptoms. Example: Symptomatic treatment (treatment aimed at alleviating symptoms rather than curing the condition).
Understanding Diagnostic Terminology
Diagnostic terms help healthcare providers describe and categorize patient conditions, which in turn guides treatment and management strategies. Proper use of these terms ensures better communication between patients and providers, helping to create a more accurate medical record and leading to better patient outcomes. Knowing the meanings behind diagnostic labels can also empower patients to become more involved in their healthcare decision-making process.
Medical Conditions and Their Terminology
Healthcare professionals use specific language to describe various health issues, diseases, and disorders. These terms provide clarity and precision, helping to accurately communicate the nature of a patient’s condition. Understanding these terms is essential for anyone involved in patient care or healthcare administration, as it facilitates clear discussions, effective treatment plans, and proper documentation.
Many health conditions are named based on their symptoms, affected areas, or underlying causes. By familiarizing oneself with these terms, individuals can better comprehend diagnoses and the treatment options available. Below are some commonly used terms related to specific health conditions:
Common Health Conditions
- Hypertension – A condition characterized by consistently high blood pressure, which can lead to serious complications like heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes – A chronic condition where the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels effectively, leading to high glucose levels.
- Asthma – A respiratory condition that causes difficulty in breathing due to inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
- Arthritis – Inflammation of the joints, often leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Common forms include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Influenza – A viral infection that attacks the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue.
Understanding the Terminology
The names of medical conditions often provide key insights into their nature and impact. For example, “arthritis” combines the Greek word “arthron” (joint) with the suffix “-itis” (inflammation), indicating inflammation of the joints. Similarly, “diabetes” comes from the Greek word “siphon,” referring to the frequent urination seen in people with this condition. Recognizing these roots, prefixes, and suffixes can help individuals decipher unfamiliar terms and gain a better understanding of various health problems.
Understanding Medical Procedures and Terms
In healthcare, specific language is used to describe various procedures and interventions designed to diagnose, treat, or manage health conditions. These terms are crucial for ensuring clear communication between healthcare professionals and patients, as well as for accurate documentation. Understanding these terms allows individuals to navigate the complex healthcare system and better comprehend the treatments they may undergo.
Medical procedures can vary widely, from simple diagnostic tests to complex surgeries. The terminology used to describe these procedures often reflects the method, purpose, or body part involved. Familiarity with these terms can help patients understand what to expect and make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Common Medical Procedures
- Endoscopy – A minimally invasive procedure used to examine the interior of a body cavity or organ using a flexible tube with a camera.
- Biopsy – A procedure where a small sample of tissue is removed for examination to diagnose diseases such as cancer.
- Colonoscopy – A procedure used to examine the colon for abnormalities or signs of disease using a long, flexible tube with a camera.
- Radiography – The use of X-rays to view the inside of the body, commonly used to diagnose fractures, infections, or tumors.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – A non-invasive imaging technique that uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body.
Breaking Down Procedure Terminology
Many healthcare terms are derived from Latin or Greek roots, which often describe the procedure’s purpose or the body part involved. For example, “endoscopy” comes from the Greek words “endon” (inside) and “skopein” (to look), indicating a procedure to look inside the body. Similarly, “biopsy” is derived from the Greek word “bios” (life) and “opsis” (view), referring to the examination of living tissue.
By understanding these roots and terms, patients and healthcare professionals can communicate more effectively, ensuring better care and a clearer understanding of procedures.
Body Systems and Related Terminology
In healthcare, understanding the different systems of the human body and the language used to describe them is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Each system has its own set of functions, structures, and related terms that help professionals communicate clearly about the body’s processes and conditions. These terms provide a common ground for discussing everything from basic physiological functions to complex disorders affecting specific organs or structures.
The human body is made up of several interconnected systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining health and supporting life. Knowing the key terminology related to these systems allows healthcare providers to identify and address issues effectively. Below, we explore some of the primary systems of the body and common terms associated with them.
Common Body Systems
- Circulatory System – Involves the heart and blood vessels, responsible for transporting blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes throughout the body. Example: Cardiovascular (relating to the heart and blood vessels).
- Respiratory System – Includes the lungs and airways, enabling the intake of oxygen and expulsion of carbon dioxide. Example: Pulmonary (relating to the lungs).
- Digestive System – Comprises organs that process food, absorb nutrients, and expel waste. Example: Gastrointestinal (pertaining to the stomach and intestines).
- Nervous System – Consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, controlling bodily functions and responding to stimuli. Example: Neurology (the study of the nervous system).
- Musculoskeletal System – Includes muscles, bones, and joints that support movement and structure. Example: Orthopedic (related to the correction of deformities in bones and muscles).
Understanding System-Specific Terminology
Each body system is associated with a set of specific terms, often derived from Latin or Greek roots, that help healthcare professionals describe conditions, treatments, and procedures. For example, “cardiology” refers to the study of the heart, with “cardio” meaning heart and “logy” meaning study. Similarly, “pulmonology” pertains to the study of the lungs, from “pulmo,” meaning lung, and “logy,” meaning study.
Familiarity with these terms allows healthcare providers to communicate effectively, ensuring clarity in diagnosis, treatment plans, and patient education.
How to Learn Medical Terminology Effectively
Mastering the specialized language used in healthcare requires dedication, practice, and a strategic approach. Understanding how different terms are constructed and familiarizing oneself with their meanings can significantly improve comprehension and recall. Whether you are a student or a healthcare professional, adopting a systematic learning method is crucial for success in this field.
The key to effective learning lies in breaking down complex terms into their components. Most healthcare terms consist of prefixes, root words, and suffixes that can be understood individually, making it easier to decipher unfamiliar words. By practicing with these building blocks, learners can expand their vocabulary and enhance their ability to understand and use the language accurately.
Practical Strategies for Learning
- Focus on Root Words – Understanding the core part of a term is the foundation of learning. Root words often indicate the main concept or function, such as “cardio” for heart or “pulmo” for lungs.
- Learn Common Prefixes and Suffixes – Recognizing common prefixes (like “hyper-” meaning excessive) and suffixes (like “-itis” meaning inflammation) helps you quickly interpret terms.
- Use Flashcards – Create flashcards with terms and their meanings to test your knowledge and reinforce memory.
- Practice with Real-Life Examples – Apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios, such as reading healthcare articles, watching medical videos, or engaging in practice exams.
Utilizing Resources for Success
Effective learning also depends on the resources you use. Textbooks, online courses, and apps can provide structured content, while peer study groups can offer collaborative opportunities for practicing new terms. It’s also helpful to regularly review and self-test to assess progress and identify areas for improvement.
| Resource | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Textbooks | Provide comprehensive explanations and examples |
| Online Courses | Offer structured lessons and quizzes |
| Apps | Allow for interactive and on-the-go learning |
| Study Groups | Encourage discussion and shared knowledge |
By combining these strategies and utilizing the right resources, learning the language of healthcare becomes a more manageable and rewarding process. With consistent practice, you can build a strong foundation and improve your ability to navigate the complex world of healthcare terminology.
Common Mistakes in Medical Terminology
When learning specialized vocabulary used in the healthcare field, it is easy to make certain errors that can lead to confusion or misunderstanding. These mistakes typically arise from misinterpreting terms, using them incorrectly, or confusing similar-sounding words. Recognizing these common pitfalls is essential for improving your understanding and communication within the medical environment.
One of the most frequent issues is the misuse of prefixes, suffixes, or root words. These components form the backbone of most terms, and a small error in applying them can change the entire meaning of a word. For instance, confusing the prefixes “hypo-” (meaning below normal) and “hyper-” (meaning above normal) can lead to misdiagnosis or incorrect treatment planning. Similarly, mixing up suffixes like “-itis” (inflammation) and “-osis” (abnormal condition) can result in improper descriptions of diseases or conditions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing Prefixes and Suffixes: Misunderstanding the meaning of common prefixes or suffixes can lead to inaccurate descriptions. For example, “pre-” (before) and “post-” (after) may be used incorrectly in medical documentation.
- Mixing Similar Terms: Words that sound similar but have different meanings can be easily confused, such as “cirrhosis” (a liver condition) and “cystic fibrosis” (a genetic disorder affecting the lungs).
- Incorrect Plurals: Many medical terms have irregular plural forms. For example, “bacterium” becomes “bacteria,” not “bacteriums,” and “diagnosis” becomes “diagnoses,” not “diagnosises.”
- Misunderstanding Word Components: Failing to break down complex terms into their individual components (prefix, root, suffix) can lead to incorrect interpretations. For example, “gastroenteritis” refers to inflammation of the stomach and intestines, not just one organ.
- Overgeneralizing Terms: Using terms too broadly can lead to errors, such as using “infection” when a specific condition like “viral infection” or “bacterial infection” is meant.
Tips to Avoid Mistakes
- Familiarize Yourself with Word Components: Understand the meaning of common prefixes, roots, and suffixes. This will help you better understand and use terms accurately.
- Practice Regularly: Reinforce your knowledge by reviewing terms and practicing their usage through flashcards, quizzes, or practical examples.
- Consult Reliable Resources: Always refer to trusted dictionaries or medical reference materials to ensure the correct usage of terms.
- Ask for Clarification: If you’re unsure about a term, don’t hesitate to ask colleagues or instructors for clarification to prevent mistakes.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and taking proactive steps to avoid them, you can enhance your accuracy and confidence when working with specialized healthcare language. Developing a strong grasp of these terms will ensure clearer communication and help prevent misunderstandings in a medical setting.
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professionals
For individuals working in the healthcare field, understanding and using specialized vocabulary is essential for clear communication and effective patient care. Professionals in this sector must be familiar with the language used to describe diseases, procedures, anatomy, and treatments. Mastering these terms allows healthcare workers to communicate accurately, avoid misunderstandings, and provide the highest level of care to their patients.
Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other medical staff, are regularly required to understand and apply a wide range of complex terms. These terms are often derived from Latin and Greek roots, and mastering them can help streamline documentation, patient assessments, and treatment protocols. Understanding how to correctly use these terms is crucial for patient safety and effective team collaboration.
Key Areas of Focus
- Anatomical Terms: These terms are used to describe the body’s structures and their locations. Examples include terms such as “proximal,” “distal,” and “superficial.”
- Conditions and Diseases: Healthcare professionals must be familiar with the names and definitions of various conditions, such as “diabetes mellitus,” “hypertension,” and “asthma.”
- Procedures and Treatments: Many medical professionals use specific terms to describe treatments, such as “laparotomy” for surgical opening of the abdomen or “chemotherapy” for cancer treatment.
- Drug Names and Dosages: Understanding pharmaceutical terminology, including generic and brand names, dosages, and routes of administration, is essential for prescribing and administering medications.
- Diagnostic Terms: Professionals use specialized terms to describe diagnostic processes and outcomes, such as “biopsy,” “X-ray,” and “MRI.”
Why Mastering This Language is Crucial
- Clear Communication: Precise use of terms helps prevent misunderstandings between medical teams, ensuring that the right treatment is provided to patients.
- Efficient Documentation: Accurate documentation using the proper vocabulary improves medical records, facilitating better care and avoiding errors in treatment or diagnosis.
- Patient Understanding: Explaining conditions and procedures in layman’s terms, based on the medical language, helps ensure patients understand their diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Professionalism: A solid understanding of specialized terms enhances credibility and professionalism in interactions with colleagues, patients, and their families.
Mastering specialized vocabulary not only enhances communication but also improves the overall functioning of healthcare systems. By consistently learning and applying the correct terms, healthcare professionals can ensure better patient outcomes and maintain a high standard of care. As the medical field evolves, ongoing education and familiarity with new terms remain essential to staying effective in the ever-changing landscape of healthcare.
Learning Through Medical Terminology Practice
Mastering the specialized vocabulary used in healthcare requires consistent practice and application. Engaging with new terms regularly not only improves retention but also enhances understanding of how these words are used in real-life contexts. Whether you’re studying for exams or preparing for a healthcare career, hands-on practice is essential for gaining fluency in the language of healthcare.
By practicing with terminology in various scenarios, learners can deepen their knowledge and apply it more effectively. This process often involves breaking down complex terms into their components, reinforcing their meanings, and using them in context. Regular exercises, quizzes, and discussions allow students and professionals to internalize the language, making it second nature in clinical settings.
Techniques for Effective Learning
- Flashcards: Creating flashcards for terms and definitions is an excellent way to reinforce knowledge through active recall. By regularly testing yourself, you can better remember and understand the meaning of terms.
- Case Studies: Analyzing real-life case studies helps learners see how specific terms are used in context. This practical approach solidifies the connection between theoretical knowledge and its application in the medical field.
- Interactive Exercises: Online quizzes and interactive exercises allow students to practice their knowledge in a dynamic way. These exercises often simulate clinical scenarios, providing valuable hands-on experience.
- Peer Discussions: Engaging in discussions with peers or mentors helps reinforce understanding. Explaining terms to others and answering questions about them boosts comprehension and retention.
The Benefits of Practice
- Increased Confidence: Regular practice helps build confidence in using complex terms, which is essential when interacting with patients and colleagues in a clinical setting.
- Enhanced Understanding: Applying new terms in different contexts helps learners gain a deeper understanding of their meanings and relationships to other terms.
- Better Retention: Repetition is key to mastering healthcare language. The more you encounter and use terms in practice, the more likely they are to stay in long-term memory.
- Improved Communication: With practice, learners can communicate more effectively with colleagues and patients, using accurate terms to describe symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments.
Whether through self-study or structured practice, continuous engagement with healthcare vocabulary is crucial for success. The more you practice, the more natural and intuitive the language becomes, ultimately helping you to provide better care and excel in your healthcare profession.
Resources for Mastering Medical Terms
Gaining proficiency in healthcare vocabulary requires access to quality resources that support both learning and practical application. Various tools and materials can help individuals at different stages of their education or career journey. These resources allow learners to build a solid foundation, expand their knowledge, and reinforce their skills through continuous exposure and practice.
From textbooks and online courses to apps and flashcards, there is a wide array of learning tools available for those looking to master this essential language. The key is to choose resources that fit your personal learning style and provide comprehensive coverage of key terms. Leveraging these tools consistently will not only improve vocabulary retention but also enhance the ability to use terms effectively in real-life scenarios.
Books and Textbooks
- Comprehensive Textbooks: Books that cover basic and advanced vocabulary are indispensable for building a strong foundation. Look for textbooks that break down terms into their components and provide practical examples.
- Specialized Dictionaries: A medical dictionary is an invaluable reference for looking up unfamiliar words. Many dictionaries also include pronunciation guides and examples of usage.
- Study Guides: Guides that focus on preparing learners for exams often include summaries, quizzes, and review questions. These can be a helpful way to test knowledge and ensure a deeper understanding.
Online Platforms and Apps
- Interactive Learning Platforms: Websites and platforms like Quizlet or Anki offer customizable flashcards and spaced repetition systems, ideal for reinforcing vocabulary over time.
- Healthcare Apps: Apps designed for healthcare professionals or students can provide quizzes, mini-courses, and flashcards. These often include visual aids and examples to make learning more engaging.
- Video Tutorials: Video content on platforms such as YouTube or specialized learning sites offers visual explanations and in-depth breakdowns of terms. Watching these videos can help solidify your understanding of complex concepts.
Practice and Peer Interaction
- Study Groups: Forming study groups with peers allows for collaborative learning. Explaining terms to each other and discussing their meanings in-depth can deepen understanding.
- Online Forums: Participating in online communities, such as Reddit or dedicated healthcare forums, provides an opportunity to ask questions, share knowledge, and learn from others’ experiences.
- Clinical Exposure: Practical experience, such as internships or clinical shadowing, allows learners to apply terms in a real-world setting, reinforcing theoretical knowledge.
Utilizing a combination of these resources will enhance your ability to understand, retain, and effectively use healthcare language. Whether you prefer self-study through books, interactive learning with apps, or collaborative practice with peers, consistent use of these tools will ensure mastery of essential vocabulary.
Tips for Retaining Medical Terms
Mastering complex vocabulary, especially in healthcare, can be a challenging task. However, there are effective strategies that can help improve retention and ensure long-term recall. The key to success lies in consistent practice, creative approaches to learning, and methods that cater to your individual strengths. With the right techniques, you can increase your ability to remember and apply the terms effectively in various contexts.
Developing a deep understanding of the components of each term–such as roots, prefixes, and suffixes–can significantly improve recall. Regular exposure through repetition and practical usage is crucial to reinforcing what you’ve learned. Additionally, breaking down large amounts of information into smaller, manageable chunks can make studying feel less overwhelming and more effective.
Use Mnemonics and Associations
- Mnemonics: Creating memory aids such as acronyms or rhymes can simplify complex terms. For example, you can create a phrase to help remember the parts of a term, making it easier to recall when needed.
- Association: Link new terms to something familiar. For example, associating the term “cardi” (relating to the heart) with the word “cardio” (as in cardiovascular exercise) can create a mental connection that reinforces your understanding.
Regular Practice and Review
- Spaced Repetition: Use flashcards or apps that incorporate spaced repetition algorithms to revisit terms at increasing intervals. This technique helps reinforce terms before they are forgotten.
- Active Recall: Instead of passively reviewing notes, actively quiz yourself on terms and their meanings. The process of trying to recall information strengthens memory pathways.
- Daily Practice: Set aside time each day to review terms and test yourself. Short, frequent study sessions are often more effective than longer, infrequent ones.
Engage with the Material in Context
- Real-World Application: Try using new terms in conversations or writing. This can help solidify your understanding and ensure that you can apply terms correctly in various scenarios.
- Teach Someone Else: Teaching is one of the best ways to reinforce your own understanding. Explain new terms to a peer or study partner to deepen your knowledge.
- Visual Aids: For terms that are particularly difficult to remember, use visual aids such as diagrams or infographics. These tools can make abstract concepts more tangible and easier to recall.
By incorporating these strategies into your study routine, you can improve both your retention and practical use of healthcare-related terms. Remember, the goal is not only to memorize but also to understand the meanings behind each term and how they relate to the broader concepts in the field.
The Importance of Accurate Terminology
Using precise language is essential in any field, but it is especially critical in healthcare. Inaccurate or imprecise terms can lead to misunderstandings, misdiagnoses, and improper treatments. Clear communication ensures that everyone, from patients to healthcare providers, is on the same page, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing the quality of care. When professionals use the correct words to describe conditions, treatments, and procedures, they promote safety, efficiency, and trust within the healthcare system.
Inaccurate or vague language can result in confusion or misinterpretation, which may affect patient outcomes. The ability to use precise and consistent terminology enables professionals to make informed decisions and deliver optimal care. Moreover, it enhances the collaboration among various medical specialists, allowing for a unified approach to patient care.
Key Reasons for Accuracy
- Patient Safety: Accurate language helps to avoid mistakes that could lead to harm, ensuring that procedures, dosages, and treatments are correctly understood.
- Clear Communication: It fosters effective collaboration among different professionals, from doctors to nurses, reducing the chance of errors and misunderstandings.
- Legal and Ethical Implications: Inaccurate terms can have legal consequences, potentially jeopardizing patient care and the credibility of the healthcare provider.
- Efficient Record-Keeping: Proper use of terms ensures that patient records are clear and precise, making it easier to track progress and make decisions.
Examples of Critical Terms
| Term | Meaning | Example of Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | High blood pressure, a condition that can lead to severe complications if untreated. | The patient was diagnosed with hypertension and prescribed medication to manage it. |
| Myocardial Infarction | A heart attack, a condition where the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. | The patient was admitted with a myocardial infarction and received immediate care. |
| Neurodegenerative Disorder | A group of conditions that involve the progressive degeneration of the nervous system. | The neurologist suspected a neurodegenerative disorder and recommended further testing. |
In summary, the importance of using accurate and well-understood language cannot be overstated. For both patient safety and the effectiveness of care, clarity is key. It allows healthcare professionals to convey critical information efficiently, ensuring that treatment is timely and appropriate. By adhering to proper terminology, healthcare workers contribute to a safer, more reliable healthcare environment for everyone involved.