
Preparing for an important evaluation can often feel like a daunting task. Whether you’re revising fundamental principles or refining specific skills, having a clear understanding of the essential material is crucial. This section is designed to provide guidance on what to focus on and how to approach the different types of questions you may face.
To succeed, it’s not just about memorizing facts but also understanding the core ideas behind them. By honing your ability to analyze and apply concepts effectively, you can navigate various challenges with confidence. From market dynamics to the role of government, each topic has its unique approach, and mastering these will give you a strong foundation for the upcoming test.
Effective preparation requires not only reviewing key topics but also developing a strategy that aligns with your strengths. By practicing and focusing on areas where improvement is needed, you can approach the test with clarity and assurance.
Economics Unit 2 Exam Answers
When preparing for a major assessment, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the material. This section focuses on how to approach different types of questions and provides key insights that will help strengthen your response strategies. Mastering both theoretical knowledge and practical applications will ensure you’re well-equipped to tackle the challenge.
Critical Topics to Focus On
Pay attention to the fundamental principles such as market behavior, government intervention, and cost structures. These concepts are often the backbone of many questions and are crucial for forming well-rounded answers. A deep understanding of supply and demand, as well as price elasticity, will allow you to break down complex scenarios and answer questions with confidence.
How to Tackle Analytical Questions
Analytical questions require more than just knowledge–they require the ability to interpret data and apply theory. When dealing with these types of queries, it’s important to structure your responses clearly. Focus on identifying key variables and making logical connections between theory and real-world situations. Practice with past questions to refine this skill and ensure your answers are both accurate and insightful.
Key Concepts for Unit 2 Exam
Understanding the core ideas and their interconnections is vital when preparing for a challenging assessment. Focus on grasping the essential principles that define various economic models and frameworks. Recognizing how these concepts apply to real-world situations will give you an edge in answering questions effectively.
| Concept | Definition | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Market Structures | The different types of markets, such as perfect competition and monopoly. | Helps in understanding pricing strategies and market efficiency. |
| Supply and Demand | The relationship between the quantity of a good or service and its price. | Fundamental in determining market equilibrium and price fluctuations. |
| Elasticity | The responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price. | Important for understanding consumer behavior and pricing strategies. |
| Government Intervention | The role of government policies such as taxes, subsidies, and regulations. | Crucial for analyzing the impact on market efficiency and social welfare. |
| Cost Structures | The different types of costs businesses incur, such as fixed and variable costs. | Key to understanding profitability and production decisions. |
Effective Study Strategies for Economics

To prepare effectively for any significant assessment, it’s crucial to adopt strategies that not only cover all necessary topics but also enhance retention and application of knowledge. A focused approach, combining active recall with strategic practice, can make a substantial difference in performance. The following methods will help you maximize your study sessions and tackle the material with confidence.
Organize Your Study Sessions
Begin by breaking down the content into manageable sections. This allows for focused study on individual concepts without feeling overwhelmed. Consider using the following techniques:
- Prioritize Key Areas: Identify the most heavily tested topics and concentrate on them first.
- Use Active Recall: Rather than passively reading, test your knowledge by recalling key points from memory.
- Practice Past Questions: Familiarize yourself with the format of questions you are likely to encounter.
Utilize Different Learning Resources

Mix up your study materials to reinforce different types of learning. Combining textbooks, online resources, and interactive tools can provide a more comprehensive understanding of each topic.
- Textbooks and Notes: Use these as your primary source of information for detailed explanations.
- Video Tutorials: Visual aids and video lectures can help clarify complex ideas.
- Discussion Groups: Join study groups to exchange ideas and test each other’s knowledge.
Understanding Microeconomics for Success
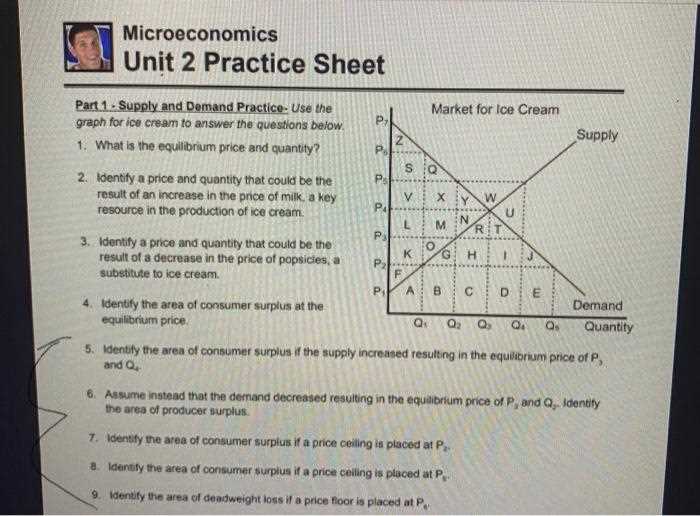
Grasping the fundamental concepts of individual decision-making and market interactions is key to performing well in assessments. This area of study focuses on how smaller economic entities, such as consumers and firms, make choices and how these decisions impact prices, resources, and production. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be able to approach real-world scenarios with clarity and insight.
The Role of Consumers and Firms
One of the core aspects of understanding microeconomics is recognizing the behaviors of both consumers and producers. Consumers aim to maximize utility, while firms seek to maximize profit. By analyzing these goals, you can better understand supply-demand dynamics and price determination.
Market Dynamics and Efficiency
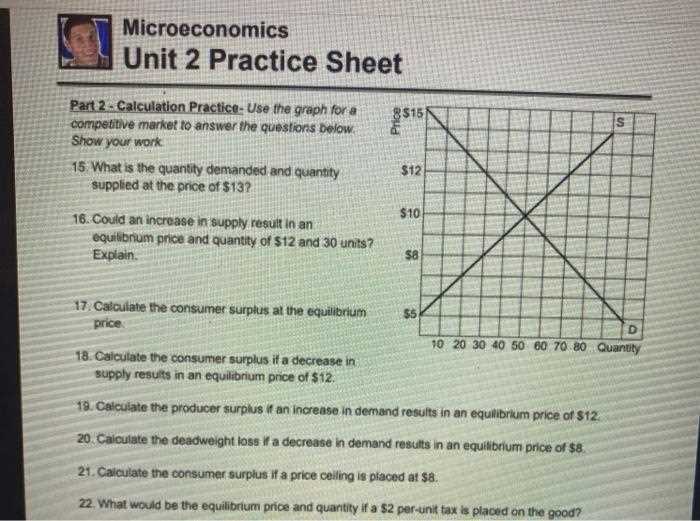
Markets are driven by the interaction of buyers and sellers. Understanding how markets reach equilibrium, the factors that can shift supply and demand curves, and the role of competition is crucial. This knowledge provides a solid foundation for analyzing the efficiency of various market outcomes and the effects of external forces.
How to Analyze Supply and Demand
Understanding how supply and demand interact is essential for interpreting market behavior. The relationship between the amount of a good or service available and the desire for it determines pricing, availability, and resource allocation. By analyzing these forces, you can predict how changes in the market will affect both producers and consumers.
Identify Key Variables: To start, recognize the two main components: the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded. These variables will often change in response to shifts in factors such as price, income levels, or consumer preferences.
Assess Shifts in the Curves: A shift in the supply or demand curve indicates a change in the overall market conditions. An increase in demand, for example, might lead to higher prices, while an increase in supply could push prices lower. Understanding these shifts helps you anticipate how markets will adjust to external factors.
Understand Equilibrium: The point where supply equals demand is known as market equilibrium. Analyzing this equilibrium helps identify when a market is stable and when it might be experiencing a shortage or surplus of goods.
How to Analyze Supply and Demand
Understanding how supply and demand interact is essential for interpreting market behavior. The relationship between the amount of a good or service available and the desire for it determines pricing, availability, and resource allocation. By analyzing these forces, you can predict how changes in the market will affect both producers and consumers.
Identify Key Variables: To start, recognize the two main components: the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded. These variables will often change in response to shifts in factors such as price, income levels, or consumer preferences.
Assess Shifts in the Curves: A shift in the supply or demand curve indicates a change in the overall market conditions. An increase in demand, for example, might lead to higher prices, while an increase in supply could push prices lower. Understanding these shifts helps you anticipate how markets will adjust to external factors.
Understand Equilibrium: The point where supply equals demand is known as market equilibrium. Analyzing this equilibrium helps identify when a market is stable and when it might be experiencing a shortage or surplus of goods.
Role of Government in Economics
The government plays a crucial role in shaping the financial and social landscape of a nation. Its involvement impacts both the functioning of markets and the welfare of individuals. Through various actions, the government influences the overall economic health, ensuring stability and equitable growth for all sectors of society.
One of the key responsibilities of the government is to regulate markets to prevent monopolies, ensure fair competition, and protect consumers. By establishing rules and guidelines, it creates a level playing field where businesses can thrive while safeguarding the interests of the public.
Additionally, governments provide essential public services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure, which are often not adequately supplied by private entities. These services contribute to the well-being of citizens, helping to reduce inequality and promote social cohesion.
Taxation and redistribution are also powerful tools in the government’s arsenal. By collecting taxes from individuals and businesses, the state can redistribute wealth to support vulnerable populations, fostering greater economic balance and reducing disparities.
In times of crisis, governments can step in to stabilize the economy through fiscal and monetary policies. These interventions help manage inflation, stimulate growth, and mitigate the effects of unemployment, ensuring that the nation can recover and continue to progress.
Mastering Cost and Revenue Calculations
Understanding the financial dynamics of a business involves accurately assessing both the expenses and income generated from its operations. Mastery of these calculations is essential for evaluating performance, setting prices, and making informed decisions about resource allocation and growth strategies.
Costs are typically divided into fixed and variable categories. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of output, while variable costs change with production levels. On the other hand, revenue is driven by sales, and calculating the relationship between price and quantity sold is key to determining profitability.
Below is a simplified breakdown of cost and revenue components:
| Cost/Revenue Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Costs | Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales. | Rent, Salaries |
| Variable Costs | Costs that vary in direct proportion to the level of production. | Raw materials, Packaging |
| Total Revenue | Income generated from selling goods or services. | Price per unit x Quantity sold |
| Total Costs | The sum of fixed and variable costs. | Fixed Costs + Variable Costs |
By mastering these concepts, individuals can assess the financial health of a business and make decisions that lead to profitability and sustainable growth.
Understanding Economic Efficiency Measures
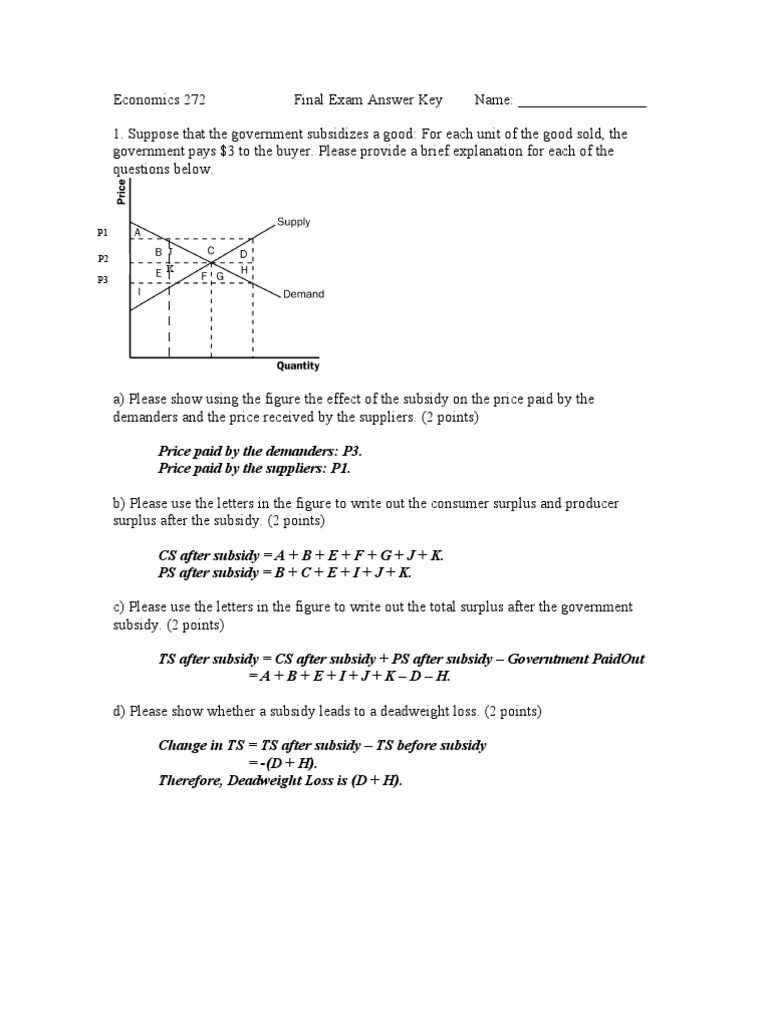
Assessing how well resources are utilized within a system is crucial for determining its overall performance. Efficiency measures provide valuable insights into how effectively inputs are transformed into outputs, and how well a system balances cost with the value produced. Achieving high efficiency is key for optimizing production and maximizing societal welfare.
At the core of measuring efficiency is the concept of productive efficiency, which occurs when resources are used in such a way that no additional output can be produced without increasing inputs. This means that the system operates at the lowest possible cost, without wasting any resources.
Another important aspect is allocative efficiency, which focuses on how well resources are distributed across different sectors to meet the needs and wants of society. Allocative efficiency is achieved when the value derived from the output is equal to the cost of the resources used to produce it, ensuring that resources are not over-allocated or under-utilized in any area.
Measuring these efficiencies requires detailed analysis of input-output relationships, cost structures, and the responsiveness of producers and consumers to market signals. By evaluating these factors, policymakers and businesses can identify areas for improvement and make adjustments that promote better utilization of available resources.
Common Mistakes in Unit 2 Exam
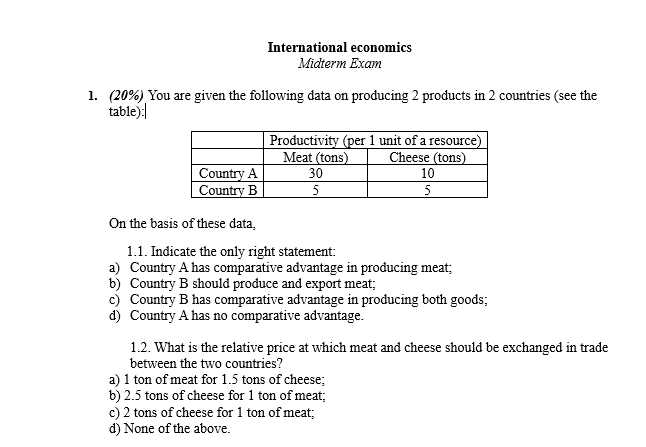
Many individuals face challenges when attempting to apply key concepts in assessments. These challenges often stem from misunderstandings or misinterpretations of questions, as well as failure to fully grasp the underlying principles. Identifying common pitfalls can help improve performance and increase confidence in answering related queries.
One frequent mistake is misreading questions, particularly when they involve multiple parts or require specific definitions. It’s easy to overlook important details that affect the overall answer, leading to incomplete or irrelevant responses. Paying close attention to wording and breaking down each question into smaller segments can help avoid this issue.
Another common error is failing to show all calculations or reasoning. Simply providing an answer without demonstrating the steps taken to arrive at that conclusion can lead to lost marks, especially in cases where partial credit is awarded. Ensuring that all necessary workings are clearly presented is crucial for achieving maximum points.
Additionally, a lack of time management during the assessment can result in rushed answers or incomplete responses. Allocating time effectively to each section ensures that all aspects of the test are addressed thoughtfully and thoroughly. Practicing time constraints beforehand can significantly improve exam performance.
Tips for Writing Clear Essays
Writing a well-structured and coherent essay requires careful planning, clarity in expression, and logical flow of ideas. Ensuring that each argument is supported by relevant evidence and articulated clearly is key to crafting a compelling response. The following guidelines will help sharpen your writing and enhance the effectiveness of your work.
Planning and Organizing Your Thoughts


Before starting, it’s essential to outline your main ideas and the order in which they will be presented. This will prevent the essay from becoming disjointed and will help ensure that your arguments are built upon a solid foundation. Organizing your thoughts into clear sections will allow for smoother transitions between points.
Clarity and Precision in Writing

Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentences that might confuse the reader. Simplicity and precision are key in making your points clear. Use specific examples to support your arguments, and always explain complex terms or concepts to ensure that they are accessible to a broad audience.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Provide a clear overview of the topic and the direction of your argument. |
| Body Paragraphs | Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or argument, supported by evidence and explanation. |
| Conclusion | Summarize your key points and restate the importance of your argument in a broader context. |
By following these tips, you can write essays that are not only well-organized and informative but also engaging and easy to follow.
Tips for Writing Clear Essays
Writing a well-structured and coherent essay requires careful planning, clarity in expression, and logical flow of ideas. Ensuring that each argument is supported by relevant evidence and articulated clearly is key to crafting a compelling response. The following guidelines will help sharpen your writing and enhance the effectiveness of your work.
Planning and Organizing Your Thoughts
Before starting, it’s essential to outline your main ideas and the order in which they will be presented. This will prevent the essay from becoming disjointed and will help ensure that your arguments are built upon a solid foundation. Organizing your thoughts into clear sections will allow for smoother transitions between points.
Clarity and Precision in Writing
Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentences that might confuse the reader. Simplicity and precision are key in making your points clear. Use specific examples to support your arguments, and always explain complex terms or concepts to ensure that they are accessible to a broad audience.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Provide a clear overview of the topic and the direction of your argument. |
| Body Paragraphs | Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or argument, supported by evidence and explanation. |
| Conclusion | Summarize your key points and restate the importance of your argument in a broader context. |
By following these tips, you can write essays that are not only well-organized and informative but also engaging and easy to follow.
Commonly Tested Theories and Models

Key theories and models serve as essential tools for analyzing various phenomena within markets and decision-making processes. These frameworks help explain how individuals, businesses, and governments interact within complex systems. Familiarity with the most relevant concepts allows for better understanding and application in both theoretical and practical scenarios.
Important Theories
Several fundamental theories frequently appear in assessments, providing insights into behavior and outcomes across different sectors. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing economic activity and guiding decision-making:
- Law of Demand – Suggests that as the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases, assuming all other factors remain constant.
- Marginal Utility Theory – Focuses on how the value of each additional unit of a good or service decreases as consumption increases.
- Opportunity Cost – Refers to the value of the next best alternative that is forgone when a decision is made.
Frequently Referenced Models
Models simplify real-world complexities, offering a structured way to predict and interpret behavior. Some widely tested models include:
- Market Structure Models – Describes different market forms such as perfect competition, monopoly, and oligopoly, each with distinct characteristics and outcomes.
- Aggregate Demand and Supply Model – Shows the total demand and supply in an economy, highlighting how shifts affect output and price levels.
- Phillips Curve – Illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment in the short run.
Understanding these key theories and models is essential for analyzing real-world scenarios, making predictions, and evaluating economic policies effectively.
How to Approach Multiple-Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions require a strategic approach to ensure that each option is carefully considered before selecting an answer. While these questions may seem straightforward, they often include distractors designed to test your understanding. A systematic method can help you avoid common pitfalls and improve your chances of selecting the correct response.
Here are some steps to effectively tackle multiple-choice questions:
- Read the Question Carefully – Before looking at the answer choices, fully understand what is being asked. Pay attention to keywords and phrases that clarify the requirements.
- Analyze All Options – Do not settle for the first answer that seems correct. Consider all the options and eliminate those that are clearly wrong.
- Use Process of Elimination – If you are unsure, cross out the answers that don’t fit. Narrowing down your choices increases the likelihood of selecting the right one.
- Watch for Qualifying Words – Words like “always,” “never,” “most,” or “least” can significantly affect the meaning of the question. Be cautious with absolutes, as they are often incorrect in many cases.
- Make an Educated Guess – If after considering all options you are still uncertain, make an educated guess based on what you know. It’s better to attempt than to leave a question blank.
By following these strategies, you can approach multiple-choice questions with more confidence and improve your ability to choose the correct answers under pressure.
Reviewing Past Papers for Insights
Reviewing previous assessments is an essential strategy for enhancing performance in future tests. By analyzing past questions, you can gain a deeper understanding of recurring themes, question formats, and specific areas that require more focus. This approach helps streamline your study efforts and increases your chances of success.
Why Reviewing Past Papers is Valuable
There are several key reasons why revisiting past tests is beneficial. By studying them carefully, you can:
- Identify Key Topics: Certain concepts tend to appear regularly, making them vital to your preparation.
- Understand Question Structure: Familiarizing yourself with the typical phrasing and style of questions allows you to better anticipate what will be asked.
- Improve Time Management: Practicing with previous papers enables you to gauge how much time to allocate for each question or section.
Effective Strategies for Analyzing Past Papers

To make the most of your review sessions, it is important to analyze past papers strategically. Here are some effective methods:
- Organize by Topic: Sort questions by subject or difficulty to pinpoint areas that require more attention.
- Focus on Challenging Questions: Mark questions that were difficult and revisit those topics to reinforce your understanding.
- Examine Marking Criteria: If available, review the grading guidelines to understand what examiners are looking for in responses.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Practice answering questions within a set time frame to mimic real testing conditions.
By systematically reviewing and analyzing past assessments, you can sharpen your skills, build confidence, and optimize your study approach for future success.