
Understanding key principles related to equal opportunity in living spaces is essential for anyone involved in property management, real estate, or legal professions. This area of law ensures that all individuals have access to safe and fair living conditions, regardless of personal characteristics. As such, it is crucial to prepare thoroughly for any evaluations or certifications in this field, as they test your grasp on these significant regulations.
To succeed, candidates must familiarize themselves with various concepts, rules, and regulations that safeguard individuals from discriminatory practices. Emphasizing the importance of inclusivity, these assessments cover essential material on what constitutes illegal practices, as well as the rights of both tenants and landlords. The focus is on developing an in-depth understanding that goes beyond surface-level knowledge, ensuring that professionals are well-equipped to apply these laws effectively in real-world situations.
Effective preparation requires careful attention to the key elements that define the regulatory framework. Whether you are reviewing essential case laws or going over specific policies, a strategic approach will help you identify and address the most important topics. Mastering this subject not only supports your professional growth but also contributes to a fairer and more equitable community.
Fair Housing Exam Answers Guide
Mastering the essential concepts of equal living opportunities is vital for professionals involved in real estate and property management. Understanding the regulations that govern this area of law is key to ensuring that everyone has the right to safe and fair accommodations. This guide will provide you with practical insights and tips to excel in assessments focused on these topics, helping you build a solid foundation of knowledge.
Core Topics to Focus On
When preparing for an evaluation in this field, it’s important to focus on the fundamental principles that underpin equal access to housing. These include the laws protecting individuals from discrimination based on race, gender, disability, and other personal attributes. Additionally, you should familiarize yourself with specific acts that support these regulations and the various case studies that have shaped current practices. Being well-versed in these areas will enable you to answer questions confidently and accurately.
Study Tips for Success

Effective preparation involves more than just memorizing definitions. It’s essential to understand how these laws apply in real-world scenarios. Practice with sample questions, review case law, and engage in discussions about the legal framework. Focus on areas that are commonly tested, such as identifying discriminatory practices and understanding the responsibilities of landlords and tenants. With the right approach, you can ensure that you are fully prepared for any assessment on this topic.
Understanding Fair Housing Laws
Equal access to residential properties is a fundamental right, and various regulations have been established to protect individuals from discrimination in this area. These laws are designed to ensure that all people, regardless of background or personal characteristics, can secure a place to live without facing unjust barriers. Understanding the core principles of these regulations is essential for anyone working in property management, real estate, or related fields.
At the heart of these laws are rules that prevent unfair treatment based on factors such as race, gender, disability, and familial status. These protections apply to both renters and potential homeowners, ensuring that everyone is treated equitably in the process of securing living accommodations. Familiarizing yourself with these legal provisions helps in recognizing what constitutes discriminatory practices and how they can be avoided in everyday interactions within the housing market.
Common Questions on Housing Discrimination
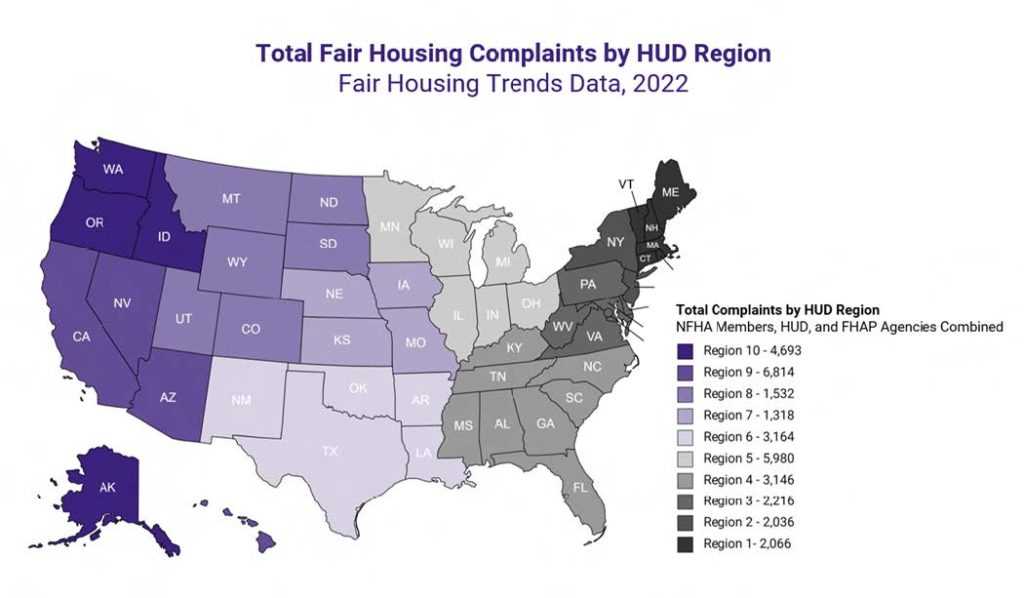
When it comes to ensuring equal access to residential properties, many questions arise regarding what constitutes discrimination and how to identify it. Understanding the most common scenarios and concerns related to unfair treatment can help clarify the key issues at stake. These questions often address what practices are prohibited and how they can be avoided in the housing market.
One common question revolves around the legality of refusing to rent or sell a property based on a person’s race, disability, or other protected characteristics. Another frequent query involves understanding what actions constitute discriminatory advertising or biased rental practices. Clarifying these and similar concerns is essential for those who wish to comply with legal standards and promote equal opportunities for all individuals seeking housing.
Preparing for Your Fair Housing Test
Getting ready for an assessment on residential equality laws requires a clear understanding of the key principles and regulations that govern this area. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the legal protections, prohibited practices, and the rights of both tenants and landlords. A focused approach to your preparation will not only help you pass but also deepen your knowledge of critical legal concepts.
Key Areas to Focus On
To excel, it’s important to concentrate on the most relevant topics. These include understanding protected classes, the types of discrimination prohibited in the residential sector, and the legal responsibilities of property owners. Additionally, you should be prepared to answer questions related to specific acts and how they apply to real-world situations. Reviewing case studies and common scenarios will help solidify your understanding.
Effective Study Techniques

Use a variety of study methods to ensure a thorough grasp of the material. Practice with mock questions, engage in group discussions, and review key legal texts. Creating a study schedule and breaking down complex topics into smaller, manageable parts will also make your preparation more efficient. The more actively you engage with the material, the more confident you will feel during the test.
Key Concepts to Study for the Exam
To succeed in a test on residential equality and anti-discrimination laws, it’s crucial to understand the foundational principles and regulations that govern the rights of individuals seeking living spaces. Mastering these concepts will ensure you can confidently answer questions about legal protections, prohibited behaviors, and the responsibilities of both property owners and renters.
Some of the most important topics include understanding the concept of protected classes, which refers to groups of people who cannot be discriminated against based on characteristics such as race, gender, disability, and family status. Additionally, you should be familiar with various key laws and acts that provide these protections, such as the Civil Rights Act and the Americans with Disabilities Act. Knowing how these laws apply in practical situations is also essential for success in your assessment.
Understanding Protected Classes in Housing
In the context of residential laws, certain groups of people are granted special legal protections to prevent discrimination in acquiring living spaces. These protections ensure that individuals are not denied access to housing based on specific personal characteristics or status. Understanding which groups are covered under these legal safeguards is essential for both property managers and tenants alike.
What Constitutes a Protected Class
A protected class refers to a group of people who are legally shielded from discrimination. These classes typically include race, color, national origin, gender, disability, familial status, and religion. In some jurisdictions, additional groups may be protected, such as sexual orientation or gender identity. It’s crucial to understand the scope of these protections and how they apply to various aspects of the rental and sales process.
Legal Implications of Discriminatory Practices
Any action that unfairly limits access to housing based on a person’s belonging to a protected class is considered illegal. Discriminatory practices can include denying a rental application, offering less favorable terms, or providing misleading information based on someone’s membership in a protected class. Property owners, managers, and agents must be aware of these laws to avoid legal consequences and ensure equitable treatment for all individuals seeking housing.
How to Identify Discriminatory Practices
Recognizing unfair treatment in the rental and property market is essential for ensuring equal access to accommodations for everyone. Discriminatory practices can take many forms, ranging from overt actions to more subtle behaviors. Identifying these practices involves understanding the various ways that individuals or groups might be treated unequally based on protected characteristics.
Common Forms of Discrimination
Discriminatory practices can be subtle or explicit. The following are some of the most common forms of unlawful discrimination in the housing sector:
- Refusal to Rent or Sell: Denying housing to individuals based on characteristics such as race, gender, or disability.
- Unequal Terms or Conditions: Offering different rental terms or prices based on a person’s background or family status.
- Steering: Directing potential tenants to certain areas of a property or neighborhood based on their race or ethnicity.
- Discriminatory Advertising: Advertisements that specify certain preferences, such as only renting to a specific gender or age group.
- Harassment: Creating a hostile environment through actions or comments based on someone’s protected status.
Signs of Discriminatory Behavior
It’s important to be alert to behaviors that may suggest discrimination. Here are some indicators to look out for:
- Vague or Inconsistent Responses: If an individual is given unclear or conflicting information about property availability, it may indicate discriminatory practices.
- Inquiries about Personal Information: Asking questions unrelated to the rental process, such as marital status or childbearing plans, can be a red flag.
- Unequal Treatment during Showings: When a landlord or agent offers different levels of service or attention based on a person’s race, gender, or family status, it may signal bias.
Key Fair Housing Acts to Know
Various laws have been enacted to ensure that all individuals have equal access to residential properties without facing discrimination. These key statutes form the backbone of anti-discrimination efforts in the real estate and rental markets. Understanding these acts is crucial for anyone involved in property management, real estate, or legal fields, as they provide the framework for protecting tenants’ rights.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964
One of the foundational pieces of legislation in the fight against discrimination, the Civil Rights Act, particularly Title VII, addresses discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. While primarily aimed at employment, it laid the groundwork for broader anti-discrimination measures in various sectors, including housing. Title VIII, also known as the Fair Housing Act, specifically addressed equal access to housing opportunities.
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Enacted in 1990, the ADA prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in many aspects of life, including housing. This law mandates that property owners and managers make reasonable accommodations for tenants with disabilities, such as accessible units and common areas. The ADA also ensures that individuals with disabilities can enjoy the same rights to housing and related services as those without disabilities.
Test Strategies for Success
Achieving success in any assessment requires a combination of preparation, time management, and a strategic approach to answering questions. Whether you’re facing a written or online assessment, having a solid strategy can make a significant difference in your performance. It’s essential to focus on understanding key concepts, practicing regularly, and approaching each question with a clear plan in mind.
Preparation Tips
Effective preparation begins with understanding the scope of the material. Focus on key legal concepts, important regulations, and practical examples. Create a study schedule and break down the material into manageable sections. Regular practice with sample questions and mock tests will help you familiarize yourself with the format and question types, making you more comfortable when the real test arrives.
Time Management and Focus
During the test, time management is crucial. Allocate enough time to each section based on its complexity and point value. If you encounter a difficult question, don’t get stuck; move on and come back to it later. Stay focused on the task at hand, and avoid overthinking. Prioritize clarity and accuracy over rushing through questions. By maintaining a calm and organized approach, you can maximize your chances of success.
Common Pitfalls in Fair Housing Exams
When preparing for an assessment on residential equality and anti-discrimination laws, it’s easy to overlook certain areas that can lead to mistakes. Many candidates fall into common traps, such as misinterpreting the law or confusing key terms and concepts. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid errors and approach the test with greater confidence and precision.
| Common Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Confusing protected classes | Review all groups that are legally protected to ensure you don’t miss any, such as familial status or disability. |
| Misunderstanding the scope of discrimination | Focus on what constitutes discrimination in the context of rental practices and ownership rights. |
| Overlooking key legal protections | Familiarize yourself with relevant legislation, including the Civil Rights Act and the Americans with Disabilities Act, to know their specific applications. |
| Incorrectly applying exceptions to the law | Understand when exceptions exist (e.g., religious organizations, private rentals) and how they are applied within the law. |
By being aware of these common pitfalls, you can avoid confusion and ensure a more successful approach to your preparation and test-taking strategies.
Reviewing Fair Housing Case Studies
Analyzing real-world case studies is an effective way to understand how laws related to discrimination are applied in practice. These examples provide insight into common issues that arise in the property rental and sales sectors, as well as the decisions made by courts and regulatory bodies. By reviewing these cases, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of what constitutes unlawful discrimination and how to handle similar situations in the future.
Notable Cases and Key Takeaways
Case studies can highlight a range of discriminatory practices, from overt bias to subtle forms of exclusion. Here are some key cases to consider:
- Case 1: Discriminatory Rental Practices – In this case, a landlord was found guilty of refusing to rent to applicants based on their race. The court ruled in favor of the applicants, affirming the importance of fair treatment during the leasing process.
- Case 2: Accessibility Violations – A property owner was sued for failing to provide adequate accessibility for tenants with disabilities. The ruling emphasized that landlords must ensure their properties meet accessibility requirements.
- Case 3: Familial Status Discrimination – A tenant was denied housing because of her children. The court ruled that discrimination based on familial status is illegal, reinforcing that families with children have the same rights as others.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
From these case studies, several important lessons can be derived:
- Understanding Protected Classes: Ensure you are fully aware of the groups protected under anti-discrimination laws, such as race, religion, gender, and disability.
- Recognizing Subtle Forms of Discrimination: Discrimination can take many forms, including steering or providing unequal terms and conditions. It is essential to identify these actions and address them appropriately.
- Importance of Legal Compliance: Property owners and agents must follow all legal requirements related to equal opportunity in housing. Non-compliance can result in serious legal consequences.
Reviewing case studies helps to clarify the complexities of discrimination laws and reinforces the importance of creating inclusive and equitable practices in real estate. By learning from these examples, individuals can be better equipped to prevent and address discriminatory practices.
What to Expect During the Exam
When taking an assessment related to anti-discrimination laws in the real estate sector, it’s important to know what to expect during the process. These tests are designed to evaluate your understanding of legal principles and practical applications. Preparing for the format and type of questions can help you approach the test with confidence and clarity.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Test Format | The test may consist of multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, and scenario-based queries that require you to apply knowledge to specific situations. |
| Time Limit | You will typically have a set amount of time to complete the test. Be sure to pace yourself and manage your time effectively to avoid rushing through the questions. |
| Topics Covered | The test will focus on key legal concepts related to discrimination, including protected classes, unlawful practices, and required practices in property transactions. |
| Difficulty Level | The questions may range from basic concepts to more complex scenarios requiring careful thought and application of legal knowledge. |
Understanding the structure of the assessment allows you to approach it methodically, focusing on each section with the appropriate attention. The key is to stay calm, pace yourself, and rely on your preparation. With the right mindset, you will be able to navigate the questions confidently.
Impact of Fair Housing on Communities
The implementation of anti-discrimination laws in the property market has had a significant influence on the way communities are structured. By ensuring equal access to housing opportunities, these regulations have fostered a more inclusive and diverse environment. The positive outcomes of these laws extend beyond the individual level, benefiting the broader society and contributing to the social and economic well-being of entire neighborhoods.
When individuals are not subjected to discrimination based on factors like race, religion, gender, or disability, they have the freedom to choose where to live based on personal preferences and needs. This increases mobility, leading to a more balanced distribution of people across various communities. As a result, areas that were once segregated or homogenous have become more integrated, leading to richer cultural diversity.
Moreover, creating a more equitable environment in terms of property access has long-term positive effects on local economies. When everyone, regardless of background, can access quality housing, there is an increase in consumer spending, a boost in community investment, and a reduction in social inequalities. This, in turn, enhances the stability and cohesion of neighborhoods, making them more resilient to economic downturns and social challenges.
Furthermore, ensuring that all individuals have equal access to housing opportunities helps build stronger, more interconnected communities. It encourages mutual respect, understanding, and cooperation among residents, fostering a sense of belonging and shared responsibility. This creates a more harmonious environment where individuals from diverse backgrounds can thrive together.
Legal Responsibilities of Housing Providers
Property managers, landlords, and other individuals involved in property transactions have specific legal obligations to ensure that all potential residents are treated fairly and equally. These responsibilities are established to protect individuals from discriminatory practices and ensure that everyone has the opportunity to access housing without bias or prejudice. Understanding and complying with these legal duties is essential for maintaining an inclusive and equitable living environment for all members of society.
One of the primary responsibilities is to avoid any form of discrimination based on race, color, nationality, gender, familial status, disability, or religion. This includes ensuring that no one is denied housing, subjected to unfair terms, or harassed because of their protected status. Property providers must also provide reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities and make necessary modifications to ensure accessibility.
Furthermore, housing providers are required to display non-discriminatory policies in their advertisements, rental agreements, and during tenant interactions. They must also ensure that their practices, whether it be screening tenants or managing leases, align with equal opportunity laws. This means consistently applying the same criteria to all applicants and tenants, avoiding any form of preferential treatment or exclusion.
In addition to these requirements, housing providers must respond promptly to complaints regarding discrimination or harassment. They are obligated to investigate any claims thoroughly and take appropriate action if a violation is found. Failure to comply with these legal duties can result in significant legal and financial consequences, including fines and lawsuits.
Resources for Fair Housing Exam Prep
Preparing for a property-related certification or qualification test requires access to quality resources and study materials. To succeed, it is crucial to use up-to-date guides, practice questions, and reliable study aids that cover the essential concepts and regulations. These resources help individuals familiarize themselves with the topics that will be tested, boosting their confidence and performance during the assessment.
One of the best ways to prepare is through comprehensive study guides that outline key principles and provide clear explanations of complex topics. Many of these guides are available both in print and online, offering a flexible way to study. Additionally, practice tests are an invaluable tool. They allow individuals to simulate the actual test environment and become accustomed to the types of questions that may appear, helping to identify areas of strength and weakness.
Other valuable resources include official websites and training programs offered by professional organizations in the property management field. These platforms often provide tutorials, webinars, and interactive materials designed to deepen understanding and enhance retention of critical knowledge. Many organizations also offer certification courses that provide in-depth training and expert insights into the laws and regulations governing property management.
Finally, forums and discussion groups can offer peer support and a place to ask questions or clarify doubts. Engaging with a community of learners can provide additional perspectives and tips from others who have successfully navigated the same process. Using a combination of these resources ensures a well-rounded preparation experience, leading to greater success in achieving certification.
How Fair Housing Relates to Real Estate
The principles of equality and non-discrimination are fundamental when it comes to real estate transactions. Real estate professionals, including agents, brokers, and property managers, must ensure that all individuals are given equal access to property opportunities. These principles impact various aspects of the real estate industry, from buying and selling homes to rental agreements and property management.
Real estate professionals are responsible for ensuring that the practices they use in marketing, leasing, and selling properties do not discriminate based on protected categories. This ensures that all potential clients have the same opportunities to secure housing regardless of their background or personal characteristics.
Here are key ways in which real estate is directly impacted by non-discrimination standards:
- Marketing and Advertising: Property listings must be designed to reach a wide audience, without excluding any groups based on race, gender, religion, or other protected characteristics.
- Tenant Screening: Screening procedures should be consistent for all applicants, applying the same criteria to evaluate financial stability, rental history, and other qualifications without bias.
- Leasing Practices: Real estate professionals must ensure that terms and conditions in rental agreements are equally available to all tenants, with no unfair clauses or restrictions based on protected traits.
- Fair Treatment During Transactions: Every individual should be treated respectfully, without preference or discrimination during the home buying or renting process.
Understanding how non-discrimination regulations intersect with real estate helps professionals maintain ethical standards and ensure that all parties, regardless of background, are treated with fairness. This fosters a more inclusive industry and protects individuals’ rights to secure housing without bias or obstacles.
Real-Life Applications of Fair Housing Laws
Understanding the practical impact of non-discrimination regulations is essential for anyone involved in the property sector. These laws are designed to ensure that individuals have equal access to housing opportunities and are not subjected to unfair treatment based on their identity or background. In real-world scenarios, these laws shape how housing providers, agents, and property managers interact with potential tenants and buyers, ensuring that everyone is given a fair opportunity to secure housing.
Here are some real-life examples of how non-discrimination regulations are applied in the housing sector:
1. Rental Practices and Lease Agreements
Property owners and managers must ensure that the rental process is fair and transparent. They must avoid discriminatory actions in screening tenants, such as:
- Discriminating against potential tenants: Rejecting applicants based on race, religion, disability, or family status is illegal. All applicants must be evaluated based on the same objective criteria, such as financial standing or rental history.
- Offering different terms: Housing providers cannot offer different rental terms, such as higher rents or more restrictive conditions, based on an individual’s protected class.
- Accessibility in housing: Properties must be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes physical accommodations in the building and ensuring that rental terms do not exclude those with mobility challenges.
2. Homeownership and Sales

In the home-buying process, these regulations ensure that all individuals, regardless of their background, can access properties they can afford. Real-life applications include:
- Non-discriminatory marketing: Property listings must not exclude any group or target only certain demographic segments. This includes language used in advertisements that might inadvertently discourage certain groups from applying.
- Loan practices: Lenders must ensure that mortgage applications are reviewed based on the applicant’s financial qualifications, not their race, ethnicity, or any other protected characteristic.
- Equal treatment during showings: Real estate agents and brokers must treat all clients equally, providing them with the same opportunities to view homes and negotiate terms, without bias or favoritism.
By applying these non-discrimination laws, individuals in the housing industry help create a more equitable and inclusive environment where everyone has the same opportunity to secure a home, regardless of their personal characteristics or background.
Improving Fair Housing Knowledge for Career Growth

Mastering the principles and regulations surrounding equal opportunity in the property sector can significantly enhance your professional prospects. By gaining a deeper understanding of non-discrimination laws and their applications, individuals can not only meet the legal requirements but also build a reputation for ethical practices. This knowledge opens up diverse career opportunities in areas such as property management, real estate, and development, where legal compliance is a cornerstone of successful business operations.
1. Enhancing Professional Expertise

By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in equal opportunity regulations, you can ensure that your professional expertise is highly valued. Understanding these laws and their practical applications gives you an edge in the competitive property market. Key areas of focus should include:
- Regulatory changes: New laws and amendments can impact how properties are managed and sold. Continuously updating your knowledge helps you stay compliant and avoid costly legal issues.
- Ethical decision-making: A deep understanding of ethical standards in property dealings sets you apart as a trusted professional who values fairness and transparency.
- Problem-solving in practice: Recognizing subtle signs of discrimination and knowing how to address them can strengthen your problem-solving abilities in complex situations.
2. Career Opportunities and Growth
Professionals who are well-versed in equal opportunity practices in the property sector have access to a wide range of career opportunities. Being knowledgeable in this area can help you:
- Advance in real estate: Positions such as real estate agents, brokers, and developers require a strong understanding of legal compliance. Mastery of these principles can make you an attractive candidate for senior roles.
- Transition into new fields: If you’re interested in property management or urban development, knowledge of these laws is crucial for success. It allows you to manage projects effectively while respecting the rights of all involved.
- Become a trainer or consultant: Professionals with deep knowledge of property law may choose to guide others, offering training, advice, or legal consultation services within the industry.
By continuously improving your understanding of non-discrimination laws, you position yourself as a knowledgeable and reliable professional, prepared for greater responsibilities and career advancement in the property sector.