
Preparing for a comprehensive assessment in the field of earth sciences requires a solid understanding of key concepts and a strategic approach to studying. The vast array of topics covered in this subject can make it overwhelming, but with the right methods, success is achievable. The key to excelling lies in identifying critical areas of focus and effectively reviewing them.
Strategic study techniques and familiarization with the types of questions you might face can help reduce stress and increase confidence. From foundational knowledge about Earth’s composition to more complex theories about its dynamic processes, grasping the essential principles will serve as a strong foundation for any test.
Planning your revision wisely and practicing with relevant material will give you a competitive edge, enabling you to approach the challenge with clarity and competence. Whether it’s understanding how to interpret rock layers or applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, this preparation will set you on the path to success.
Geology Final Exam Answer Key
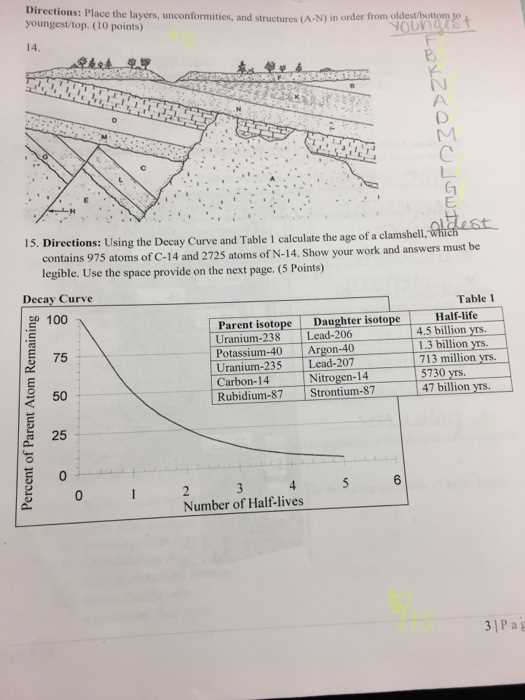
Having a clear reference guide is essential for understanding the correct responses to various questions related to Earth sciences. By reviewing a detailed key, students can verify their knowledge, ensuring that they grasp the important concepts required for success. This section provides a comprehensive outline of typical questions and their corresponding solutions, helping you sharpen your understanding and improve performance.
| Question | Correct Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the process of rock formation? | Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic processes |
| Which mineral is hardest on the Mohs scale? | Diamond |
| What is the primary cause of tectonic plate movement? | Convection currents in the mantle |
| What type of rock is formed from volcanic lava? | Igneous rock |
| What is the outermost layer of the Earth? | Crust |
| What is the difference between an earthquake and a volcano? | An earthquake is caused by tectonic shifts, while a volcano erupts due to molten rock from beneath the Earth’s surface. |
Understanding Common Geology Exam Topics
In any test covering the study of Earth’s structure, materials, and processes, there are certain subjects that consistently appear. Familiarizing yourself with these core concepts is crucial for effective preparation. Key topics often include various types of rocks, mineral identification, plate tectonics, and the dynamic forces shaping our planet. Recognizing and mastering these areas will provide a solid foundation for tackling related questions.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Rock Types | Understanding the differences between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks and their formation processes. |
| Plate Tectonics | The study of Earth’s lithosphere, including tectonic plate movements and their role in earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain formation. |
| Minerals | Identifying key minerals based on their physical properties, including hardness, color, and cleavage. |
| Volcanic Activity | Understanding the causes and effects of volcanic eruptions, as well as the types of volcanoes and lava flows. |
| Earthquakes | Studying seismic waves, fault lines, and the measurement of earthquakes using the Richter scale and seismographs. |
| Geological Time Scale | Familiarity with the divisions of Earth’s history, including eras, periods, and epochs. |
Top Strategies for Studying Geology

Effective preparation for any assessment in Earth sciences requires a mix of focused study techniques and practical application. To retain complex concepts and perform well, it is important to adopt strategies that not only improve recall but also deepen your understanding of the subject matter. Combining regular practice with targeted review will help solidify key principles and reduce study stress.
Active Learning Techniques
Rather than passively reading through materials, engage actively with the content. Use flashcards, quizzes, and self-made summaries to reinforce what you’ve learned. Active learning helps retain information and connects theory to practical examples, which is critical for applying knowledge to questions.
Time Management and Planning
Setting a structured study schedule is essential for mastering all the key topics. Break down the material into manageable sections and allocate specific time slots for each area. Consistent study habits, along with periodic reviews, will ensure you’re well-prepared for any challenge.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Recall | Testing yourself regularly on core concepts to strengthen memory retention. |
| Mind Mapping | Creating visual diagrams to connect related ideas and understand concepts holistically. |
| Group Study | Collaborating with peers to discuss difficult topics and reinforce learning through teaching. |
| Practice Questions | Solving sample problems and past questions to familiarize yourself with exam-style queries. |
| Breaks and Rest | Taking regular breaks to avoid burnout and allow your brain to process information effectively. |
Important Geological Terms to Know
Understanding key terms is essential when studying the Earth’s composition and processes. These terms form the foundation of any discussion regarding the planet’s structure, dynamics, and history. Being familiar with the vocabulary will not only help in answering questions accurately but also aid in understanding complex theories and systems.
Core Concepts
- Plate Tectonics: The theory explaining the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere.
- Seismic Waves: Waves of energy that travel through the Earth’s layers, often caused by earthquakes.
- Fossils: Preserved remains of ancient organisms, often used to understand past environments.
- Minerals: Naturally occurring, inorganic substances that make up rocks.
Key Rock Types
- Igneous Rock: Formed from cooled and solidified magma or lava.
- Sedimentary Rock: Created from layers of sediment compressed over time.
- Metamorphic Rock: Rock that has been changed by heat and pressure.
- Basalt: A dark-colored, fine-grained igneous rock.
How to Approach Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions are common in assessments, and while they can seem straightforward, they often require a strategic approach. The key is to carefully evaluate each option and use your knowledge to eliminate incorrect answers. With the right techniques, you can improve accuracy and reduce the likelihood of making mistakes.
Step-by-Step Strategy
- Read the question carefully: Understand what is being asked before looking at the options.
- Eliminate obviously incorrect choices: Narrow down the options by removing answers that are clearly wrong.
- Consider all choices: Avoid jumping to conclusions. Review each option even if one seems right at first glance.
- Look for clues in the wording: Sometimes, keywords or phrases in the question can hint at the correct answer.
- Make an educated guess: If unsure, choose the most logical option based on your knowledge.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overthinking: Don’t get stuck in doubt. Stick to your initial, well-considered choice.
- Choosing the longest option: The correct answer is not always the most complex or lengthy one.
- Skipping questions: If you are uncertain, make a note to return to them later, but don’t leave them unanswered.
- Misreading options: Be cautious of negative words like “not” or “except” that can change the meaning of the question.
Effective Techniques for Geology Test Prep
Preparing for an assessment in Earth sciences requires a focused approach that maximizes learning while minimizing stress. By using the right study techniques, you can ensure that you are well-prepared for the various types of questions you may encounter. These strategies help reinforce your understanding, enhance retention, and boost overall performance.
Active Learning Methods

- Practice Quizzes: Regularly test yourself on key concepts to strengthen recall and identify weak areas.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to memorize important definitions, processes, and diagrams. The repetitive nature of this method aids retention.
- Concept Mapping: Create visual diagrams linking related ideas and terms to better understand their relationships.
- Teach Others: Explaining concepts to peers can deepen your own understanding and help reinforce the material.
Time Management and Planning
- Set a Study Schedule: Break down the material into manageable sections and allocate specific times for each topic.
- Prioritize Weak Areas: Focus on the subjects where you feel least confident and dedicate more time to those areas.
- Use Timed Practice Sessions: Simulate test conditions by setting a timer and working through questions within the given time limit.
- Take Regular Breaks: Avoid burnout by incorporating short breaks to refresh your mind and maintain focus.
Reviewing Key Geological Processes
Understanding the processes that shape the Earth’s surface and internal structure is fundamental to mastering Earth sciences. These dynamic activities involve the movement of materials within the planet, the formation of natural structures, and the constant reshaping of landscapes. A solid grasp of these processes is essential for answering questions related to how the Earth evolves over time.
Important Processes to Focus On
- Plate Movements: The shifting of large sections of the Earth’s outer layer, which causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.
- Rock Cycle: The continuous transformation of rocks through various stages including formation, alteration, and destruction.
- Weathering: The breakdown of rocks into smaller particles due to natural forces like wind, water, and temperature changes.
- Erosion: The removal and transportation of rock fragments and soil by forces like rivers, glaciers, and wind.
Processes That Influence Earth’s Surface
- Volcanic Activity: The eruption of molten rock from the Earth’s interior, shaping landscapes and releasing gases into the atmosphere.
- Earthquakes: The sudden release of energy along fault lines that results in shaking and surface deformation.
- Glacial Movement: The slow movement of glaciers, which carve valleys and deposit sediment as they advance or retreat.
- Hydrological Cycle: The continuous movement of water within the Earth’s systems, including evaporation, precipitation, and runoff.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on Exams
During assessments, it’s easy to make simple mistakes that can cost valuable points. Being aware of common pitfalls and knowing how to avoid them is crucial for maximizing your performance. By approaching the questions carefully and following best practices, you can reduce errors and increase your chances of success.
Frequent Errors to Watch Out For
- Rushing Through Questions: Taking too little time to read and understand the question can lead to misinterpretation and incorrect answers.
- Skipping Instructions: Failing to follow specific guidelines, such as word limits or required steps, can result in incomplete or disqualified answers.
- Overlooking Keywords: Missing important terms like “except,” “not,” or “always” can completely change the meaning of the question.
- Changing Answers Without Reason: Frequently second-guessing your initial responses can lead to errors, as first instincts are often correct.
How to Prevent These Mistakes
- Read Carefully: Take your time to read every question and answer choice thoroughly, paying attention to all details.
- Stay Organized: Mark questions you are unsure about and come back to them later. This prevents you from wasting time on difficult questions early on.
- Practice Time Management: Allocate time to each section and avoid spending too long on any one part. Practice under timed conditions to improve speed.
- Double-Check Your Work: If time permits, review your answers to ensure accuracy and completeness before submitting.
Time Management Tips for Exam Day

Effective time management is one of the most important factors in performing well during any assessment. Managing your time wisely helps reduce stress, ensures that you complete all sections, and gives you the opportunity to review your work. Having a plan for how to approach the test can make a significant difference in your overall performance.
Planning Your Time Wisely
- Familiarize Yourself with the Format: Know the structure of the test before you start, including the number of questions and how much time is allocated to each section.
- Set Time Limits for Each Section: Determine a reasonable amount of time to spend on each part and stick to it. This helps you avoid spending too much time on any one section.
- Prioritize Easier Questions: Start with the questions that you feel most confident about to build momentum and save time for more challenging ones.
- Leave Time for Review: Reserve the last 10-15 minutes for reviewing your answers, checking for mistakes, and ensuring that no questions were left unanswered.
Staying Focused and Efficient
- Avoid Overthinking: If you are unsure about a question, move on and return to it later. Spending too much time on one question can take away from others.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: If time is running out, focus on completing the questions you know first. Don’t panic, and keep a steady pace.
- Keep Track of Time: Use a watch or clock to monitor your progress. Keep an eye on how much time you have left for each section.
Geology Exam Sample Questions and Answers
Practicing with sample questions is an essential part of preparing for any assessment. By working through examples, you can familiarize yourself with the types of questions you might encounter and develop strategies for answering them accurately. Below are some sample questions that cover key topics, along with their corresponding solutions to help guide your preparation.
Sample Question 1

Question: What is the primary difference between sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks?
Answer: The main difference lies in their formation processes. Sedimentary rocks form from the compaction of sediments, igneous rocks crystallize from cooling magma or lava, and metamorphic rocks result from the transformation of existing rocks due to high pressure or temperature.
Sample Question 2
Question: Describe the process of plate tectonics and its impact on Earth’s surface.
Answer: Plate tectonics is the movement of large slabs of Earth’s lithosphere on the more fluid asthenosphere beneath them. This movement leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. The shifting of plates causes the continuous reshaping of Earth’s surface over geological time.
Sample Question 3

Question: What is the rock cycle, and how does it influence the Earth’s surface?
Answer: The rock cycle is the continuous process by which rocks are created, altered, and destroyed. It involves the transformation of one type of rock into another through processes like melting, cooling, erosion, and sedimentation. This cycle plays a key role in the dynamic changes on Earth’s surface, as rocks are constantly being formed and recycled.
How to Interpret Geological Diagrams
Understanding diagrams is a critical skill when studying Earth’s processes. These visual representations can convey complex information, such as rock layers, faults, and mineral compositions, in a concise format. Learning how to interpret these diagrams accurately can significantly enhance your comprehension and ability to analyze geological data.
Identifying Key Features
When examining a diagram, it’s important to first identify the key elements. This may include the type of diagram, such as a cross-section, map, or stratigraphic chart. Pay attention to labels, scales, and symbols, which help explain the data being presented. For example, a cross-sectional view of Earth’s crust may show the relationship between different rock layers, faults, or folds.
Understanding Relationships and Processes
Focus on the relationships between different features. For instance, a diagram showing sedimentary layers will often indicate the relative age of these layers through their position (older layers typically lie beneath younger ones). Identify processes such as erosion, deposition, and faulting that might be occurring. For example, tilted layers in a diagram might suggest tectonic activity, while smooth, horizontal layers could indicate periods of calm deposition.
Use the diagram context: Always take note of the accompanying notes, legends, and explanations that give context to the diagram. This will help you connect the visual data to theoretical concepts, making it easier to understand the geological processes represented.
Understanding Geology Formulas and Equations
Formulas and equations are essential tools for analyzing and solving problems related to Earth processes. These mathematical expressions help quantify relationships between physical properties, such as density, pressure, and temperature, and are used to model various phenomena like rock formation, mineral composition, and structural behavior. Understanding how to apply these equations is crucial for accurate interpretation of geological data.
Key Equations to Know
One of the most important formulas in Earth sciences is the density equation:
Density = Mass / Volume. This equation helps to determine the density of rocks and minerals, which is critical for understanding their composition and behavior under different conditions. Another essential equation is related to pressure and volume changes in materials, particularly in the study of tectonic forces and metamorphism:
P1 × V1 = P2 × V2, known as Boyle’s Law, which describes the relationship between pressure and volume in a closed system.
Applying Equations in Practical Scenarios
When applying formulas, it’s important to understand the context of the problem. For example, when calculating the stress or strain on geological materials, you may use the equation Stress = Force / Area. This helps in understanding how materials respond to external forces, such as tectonic shifts. Similarly, using equations for heat transfer, such as Fourier’s law, is essential in studying volcanic activity and geothermal energy. Recognizing the proper equation for a specific scenario ensures more accurate results and better decision-making in Earth sciences studies.
Memorization Techniques for Geological Concepts
Memorizing complex concepts related to Earth’s processes can be challenging, but effective strategies can make it easier. By using memory aids, visualization techniques, and structured study methods, you can enhance your retention and understanding of critical ideas. These approaches help in recalling important terms, processes, and relationships when needed, especially during assessments.
One of the most effective methods is the use of mnemonics, which are memory devices that simplify information by associating it with something more familiar. For example, creating a phrase using the first letter of a series of terms can help you remember the sequence of events in a process or the steps involved in an analysis. Another useful technique is chunking, where you break down large amounts of information into smaller, more manageable parts. This can be especially useful for remembering long lists or complex processes.
Visualization is also a powerful tool for memorization. By visualizing diagrams, maps, or physical models, you can create a mental image that strengthens your understanding of abstract concepts. Repeatedly reviewing these visuals and associating them with key terms or ideas can significantly improve memory recall. Additionally, active recall–testing yourself on the material regularly–ensures that you don’t just passively review but actively engage with the content, reinforcing it in your memory.
Commonly Tested Geological Layers and Rocks
Understanding the various layers of the Earth and the types of rocks found within them is crucial for grasping the fundamental concepts of Earth sciences. These layers and rocks are frequently discussed due to their role in shaping the planet’s structure and the processes that occur within it. Recognizing key characteristics of these layers and rock types is essential for accurate analysis and interpretation of Earth processes.
The crust, the outermost layer, is often the first point of focus. It consists primarily of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, each with distinct properties and formation processes. Basalt and granite, for instance, are common igneous rocks, formed from cooling molten material. Sedimentary rocks like sandstone and limestone are created from the deposition and compression of materials over time, while metamorphic rocks such as schist and marble are formed through heat and pressure from existing rock types.
Another key focus is the mantle, which lies beneath the crust and contains materials like peridotite, an ultramafic rock rich in minerals like olivine and pyroxene. The mantle plays a vital role in tectonic movements and volcanic activity. Lastly, the core, made up of a liquid outer layer and solid inner core, is composed mainly of iron and nickel, affecting the planet’s magnetic field and overall dynamics. By familiarizing oneself with these layers and rocks, it becomes easier to understand the physical changes and forces at work within the Earth.
How to Handle Essay-Type Questions

Essay-type questions test your ability to articulate knowledge in a structured and comprehensive manner. To approach these questions effectively, it’s important to understand the key concepts and express them clearly, while also demonstrating critical thinking and depth of understanding. Preparing for these questions requires both thorough knowledge and a methodical approach to writing.
Breaking Down the Question
The first step is to carefully read the question and break it down into manageable parts. Identify the key terms and concepts that the question is asking for, and make sure you understand what is being required. For example, if the question asks you to describe a process, you should first explain the sequence of events involved, and then discuss its significance. If it asks you to compare or contrast, focus on the similarities and differences between the elements in question.
Organizing Your Response
Once you understand the question, it’s time to plan your answer. An organized response not only helps you stay on track but also makes your points clearer to the reader. Use bullet points or a brief outline if needed, ensuring that each point follows logically from the previous one. This approach helps in maintaining a coherent flow of ideas, which is crucial for essay questions.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Read and analyze the question |
| 2 | Identify key terms and concepts |
| 3 | Plan your answer with an outline |
| 4 | Write a clear introduction and conclusion |
| 5 | Review and revise your response |
In addition to structure, your answer should be clear and concise. Avoid overly complex sentences and jargon, as these can detract from your argument. Focus on answering the question directly while supporting your points with relevant examples. After writing, review your essay to ensure that it flows logically, and check for any spelling or grammatical errors. These steps will help you tackle essay-type questions with confidence and clarity.
Last-Minute Revision Tips
When time is running short before an important assessment, it’s essential to focus your efforts on the most crucial topics. Effective last-minute preparation involves prioritizing key concepts, reviewing core materials, and utilizing efficient study strategies to maximize retention. With the right approach, you can make the most of your limited time and boost your confidence going into the test.
Prioritize Key Topics
Instead of trying to cover everything, focus on the areas that are most likely to appear on the test. Review any study guides, previous practice questions, or class notes that highlight major themes. By identifying and focusing on high-yield topics, you can improve your chances of recalling relevant information during the assessment. It’s also helpful to quickly review any definitions, formulas, or diagrams that might be important.
Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
Active recall is one of the most effective ways to enhance memory retention under time pressure. Test yourself regularly on the material you’ve studied, rather than just passively reviewing notes. Try using flashcards or summarizing concepts aloud to reinforce key points. Spaced repetition, where you revisit material at increasing intervals, can also be a helpful technique to reinforce your understanding in the final hours before the assessment.
Stay Calm and Focused
As the clock ticks down, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. However, maintaining a calm and focused mindset is crucial for effective revision. Take short breaks during your study sessions to stay refreshed. Deep breathing exercises or a quick walk can also help clear your mind. A positive attitude and staying calm will help you approach the assessment with confidence.
Finally, ensure you get a good night’s rest before the test. A well-rested mind performs better than a fatigued one, so avoid staying up late cramming. With these last-minute revision tips, you can give yourself the best possible chance of success, even when time is limited.
Using Study Groups for Exam Preparation
Collaborating with peers in study groups can be a powerful way to enhance your understanding and retention of key material. By discussing concepts with others, you can gain new perspectives, clarify doubts, and reinforce your knowledge in ways that solitary study may not allow. Study groups also help create a structured environment where you can focus on the most important topics and share helpful resources.
Benefits of Group Study
Study groups provide an excellent opportunity to break down complex subjects into manageable chunks. Each group member can take responsibility for specific topics, and then teach those concepts to others. This approach benefits everyone, as teaching material helps deepen understanding. Additionally, hearing explanations from different people can offer insights or shortcuts that you might not have considered. Group study also encourages accountability, as you’re more likely to stick to a schedule when others are involved.
How to Make the Most of Group Study

To ensure the study group is effective, it’s important to set clear goals and expectations from the start. Agree on the topics to cover and stick to a study schedule. Make use of diverse resources, such as textbooks, notes, or online materials, and encourage discussion to reinforce concepts. It’s also helpful to quiz each other on key points, as this practice of active recall can significantly improve memory retention. Lastly, keep the group size manageable–too many people can lead to distractions and less focus on the material.
When used correctly, study groups can greatly enhance your learning process, helping you feel more prepared and confident going into the assessment.