
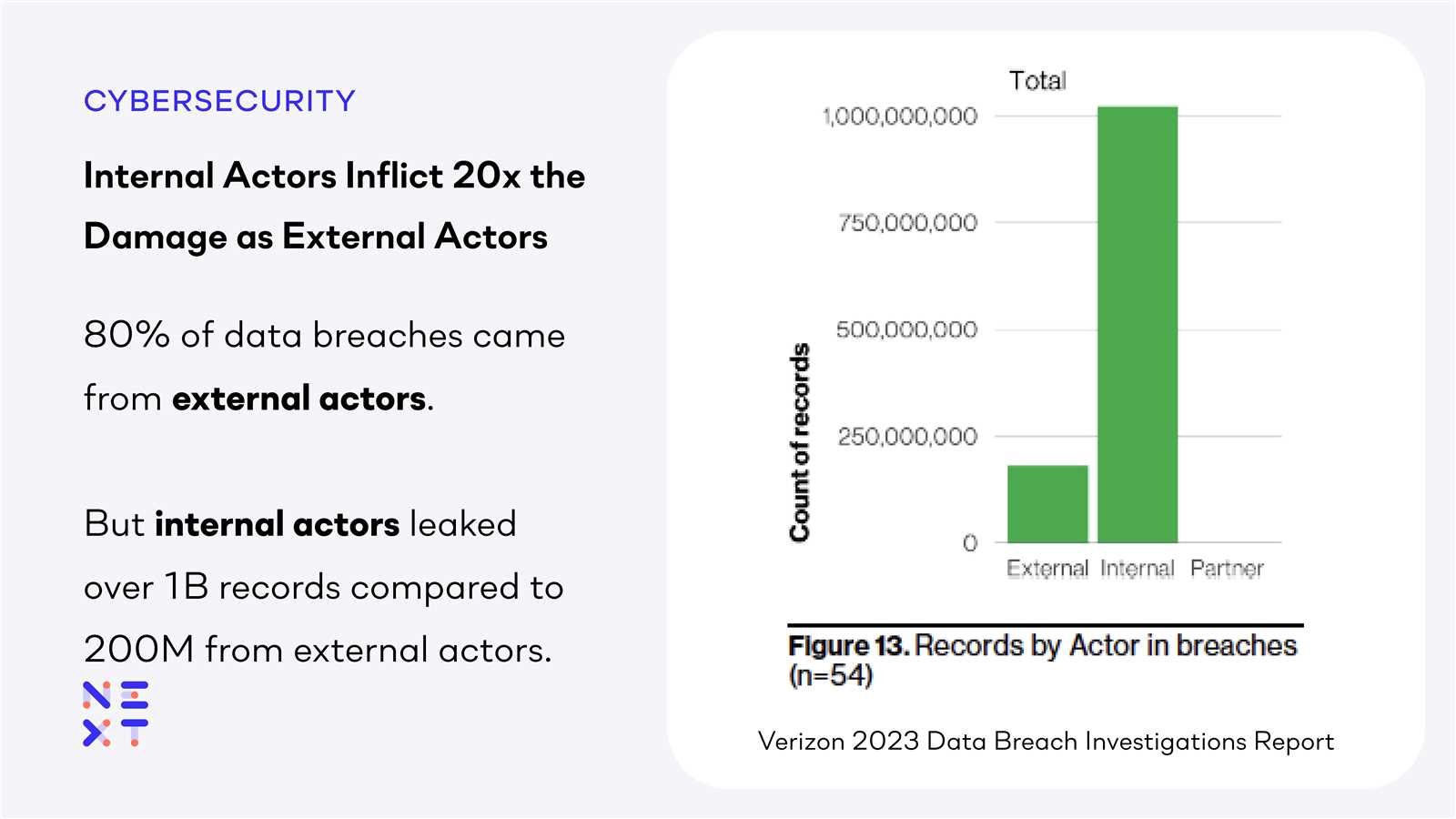
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, protecting an organization from internal disruptions is crucial. Employees and trusted personnel can unintentionally or deliberately compromise sensitive information, posing significant risks. Recognizing potential vulnerabilities within an organization’s environment is essential for maintaining a secure and efficient workplace.
By identifying warning signs and implementing effective prevention measures, organizations can reduce the likelihood of security breaches. Training staff to detect unusual activities and understand the importance of safeguarding confidential data plays a vital role in minimizing these risks. Strong security practices not only protect valuable assets but also foster a culture of responsibility and vigilance.
Proactive steps in mitigating internal security issues involve recognizing patterns that deviate from normal operations and creating clear protocols for responding to suspicious activities. With a combination of awareness and the right tools, businesses can strengthen their defenses and ensure a safe operational environment.
Insider Threat Awareness Exam Overview
As businesses and organizations face increasingly sophisticated security challenges, understanding the risks posed by individuals within the company becomes more critical. It’s essential to equip employees with the knowledge needed to identify and address potential vulnerabilities that could arise from trusted personnel. This section provides a broad overview of the process designed to assess knowledge in managing internal security risks.
Key Areas Covered
The focus is placed on recognizing behaviors and actions that may compromise company assets. Employees are trained to identify irregular activities that fall outside normal procedures. Key concepts include spotting early indicators of potential security breaches, understanding the motives behind internal risks, and knowing how to respond effectively.
Objectives and Benefits

Participation in this learning process helps individuals understand the importance of safeguarding sensitive information. It emphasizes the development of a proactive mindset that can prevent or mitigate potential damage before it escalates. Knowledge gained through this training allows teams to create a more secure environment, protecting both the organization’s integrity and its reputation.
Understanding Insider Threats in Security
Protecting organizational assets from internal risks is a critical part of any security strategy. Employees, contractors, and trusted individuals within an organization have access to sensitive information and systems, making them potential sources of risk. These internal risks can emerge from unintentional mistakes or deliberate actions, both of which can have severe consequences for the company’s safety and operations.
Types of Internal Risks
Understanding the various forms of internal risks is essential to building a robust defense plan. These risks can come from individuals with legitimate access who misuse their privileges, or from individuals who intentionally exploit their position for personal gain or harm. The table below highlights common types of internal risks and their characteristics.
| Risk Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Unintentional Actions | Errors or negligence that lead to security breaches. | Accidental sharing of sensitive data via email. |
| Malicious Intent | Deliberate actions to harm the organization or steal valuable data. | Stealing confidential company information for financial gain. |
| Disgruntled Employees | Employees who use their access to damage the organization out of revenge. | Sabotaging systems after resignation or dismissal. |
Identifying and Preventing Risks
Proactive measures to identify and prevent internal risks involve monitoring system activity, implementing access controls, and fostering a culture of security awareness. With clear protocols in place, companies can mitigate the impact of these risks and reduce the likelihood of significant disruptions or data losses. Regular training and security audits are essential to keeping employees vigilant and informed about the dangers posed by internal vulnerabilities.
Key Concepts in Threat Detection
Effective detection of potential risks within an organization is vital to maintaining a secure environment. Identifying unusual behavior or suspicious activities early can prevent significant damage. This section highlights the core principles involved in recognizing and addressing these risks before they escalate.
One of the most important aspects of detecting risks is monitoring activities that fall outside of typical operational patterns. By establishing a baseline of normal behavior, organizations can quickly spot anomalies that may indicate a problem. Proactive monitoring combined with automated tools enhances an organization’s ability to detect risks in real-time.
Behavioral analysis plays a crucial role in understanding what constitutes normal operations versus what may signal a potential issue. By analyzing actions, access patterns, and system usage, teams can identify individuals whose behavior diverges from the norm. This approach requires constant refinement to stay ahead of evolving tactics used to bypass detection methods.
Common Signs of Insider Misconduct
Identifying warning signs of inappropriate actions within an organization is key to preventing potential security breaches. Certain behaviors or patterns can indicate that an employee or trusted individual is engaging in activities that may compromise the safety and integrity of company resources. Recognizing these early signs allows teams to address issues before they escalate into serious incidents.
One of the most noticeable signs is unauthorized access to sensitive information or systems. Employees accessing data or areas outside their scope of work, especially when it involves confidential materials, is a red flag. This can include viewing records they don’t need for their role or attempting to bypass security measures.
Changes in behavior are also an important indicator. Individuals who suddenly exhibit a lack of interest in their tasks, display unusual emotional responses, or show frustration with internal procedures may be displaying signs of discontent or potential misconduct. Such shifts in attitude could indicate underlying motives or dissatisfaction that could affect their actions in the workplace.
Types of Insider Threats Explained
Internal security risks can manifest in several ways, depending on the individual’s motives and level of access. Understanding the different types of risks posed by employees, contractors, or other trusted personnel is essential to developing an effective security strategy. These risks range from unintentional mistakes to deliberate malicious actions, and each type requires a unique approach to prevention and mitigation.
Unintentional Actions occur when employees unknowingly compromise sensitive data or systems. These mistakes can happen due to lack of knowledge, carelessness, or failure to follow established protocols. For example, an employee might accidentally send confidential information to the wrong person or fail to securely log off from their workstation, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access.
Malicious Intent involves deliberate actions taken to harm the organization, often driven by personal gain, revenge, or ideology. Employees with access to sensitive systems may misuse their privileges to steal data, damage company assets, or undermine operational effectiveness. This type of misconduct can be especially damaging as it is often planned and executed with a clear purpose.
Another category is disgruntled employees who, due to dissatisfaction with their job or the organization, may engage in actions designed to cause harm. Whether through sabotage, theft, or the leaking of confidential information, their actions are typically motivated by personal grievances rather than external influence. These individuals can pose a significant risk, as their knowledge of internal systems allows them to exploit vulnerabilities with ease.
Importance of Security Awareness Training

Training employees to recognize potential risks and take appropriate actions is a vital component of any organization’s security strategy. By equipping staff with the knowledge and tools to identify security vulnerabilities, companies can significantly reduce the likelihood of incidents that may compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations. A well-trained workforce is often the first line of defense against both accidental and intentional security breaches.
Effective training programs teach employees how to spot unusual behavior, understand company protocols, and follow best practices for maintaining a secure environment. This not only helps prevent errors caused by lack of knowledge but also empowers individuals to take proactive steps in protecting company assets. Regular training ensures that security measures stay relevant and that employees remain vigilant in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
How to Identify Suspicious Behavior
Recognizing unusual actions or behavior within an organization is crucial for preventing potential security incidents. Employees or trusted personnel who act outside of their normal patterns can indicate an elevated risk to the organization’s security. Identifying such behavior early allows teams to take preventive measures before issues escalate.
Here are some common indicators that may suggest suspicious behavior:
- Accessing Unnecessary Information: Individuals who frequently seek out data or systems that are irrelevant to their job responsibilities may be attempting to gather sensitive information without authorization.
- Unusual Working Hours: Employees working outside of standard hours, especially without a clear need, could be trying to access systems undetected.
- Frequent System Logins: Excessive login attempts or frequent access to multiple systems in a short period can suggest an attempt to manipulate or gather sensitive data.
- Changes in Behavior: A sudden shift in attitude or work habits, such as increased secrecy, isolation, or agitation, can sometimes indicate internal dissatisfaction or malicious intent.
- Use of Unauthorized Devices: Connecting personal or unapproved devices to company networks can lead to vulnerabilities and potential data leaks.
By keeping an eye on these behaviors, organizations can create a more vigilant environment and respond promptly to potential risks, ensuring that any suspicious activity is addressed before it can cause harm.
Impact of Insider Threats on Organizations
Risks stemming from trusted individuals within an organization can have far-reaching consequences. When employees or contractors engage in activities that compromise company resources, the effects can be severe, affecting not only the organization’s bottom line but also its reputation, trust, and operational continuity. Understanding the potential impact of these actions is crucial for developing effective preventive measures.
Financial and Operational Consequences
One of the most immediate impacts is the financial damage caused by data loss, intellectual property theft, or system disruptions. The cost of recovering from such incidents often involves significant monetary resources, as companies may need to invest in investigation, legal fees, and technology upgrades. Furthermore, internal disruptions can halt business operations, causing delays, loss of productivity, and potentially even regulatory penalties.
Damage to Reputation and Trust
Beyond the financial losses, a security breach involving trusted personnel can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Clients, customers, and partners may lose trust in the company’s ability to protect sensitive data, which can result in a loss of business and long-term damage to relationships. Regaining trust after such an incident requires considerable effort, transparency, and often a public commitment to strengthening security measures.
Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
Mitigating risks posed by internal actors requires a combination of proactive strategies, technological tools, and a well-defined organizational culture. By establishing clear security policies and promoting responsible behaviors, companies can reduce vulnerabilities and prevent incidents from occurring. Below are some of the most effective practices for reducing internal risks.
- Regular Security Training: Ensure that all employees understand the importance of security and are equipped with the knowledge to spot potential risks. This includes recognizing suspicious activities and understanding company policies on data handling and access.
- Least Privilege Access: Restrict access to systems and sensitive information based on an individual’s role. Employees should only have access to the resources they need to perform their jobs effectively, minimizing the potential for misuse.
- Strong Authentication Measures: Implement multi-factor authentication and strong password policies to ensure that unauthorized individuals cannot gain access to systems or sensitive data.
- Behavioral Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track user activities and identify deviations from normal behavior. This helps quickly detect unusual actions that may indicate a potential security risk.
- Clear Incident Response Plan: Develop and communicate a well-defined plan for addressing security breaches. Ensure that all employees know how to report incidents and that the organization can respond swiftly and effectively when issues arise.
By following these best practices, organizations can strengthen their defenses and reduce the likelihood of costly incidents that result from internal actions. Regular review and adaptation of these strategies are necessary to stay ahead of evolving risks and challenges.
Building a Strong Security Culture
Creating a robust security culture within an organization is essential for minimizing risks and protecting critical assets. A security-focused culture goes beyond policies and tools; it involves fostering a mindset where every individual understands their role in safeguarding the company’s data and systems. When security is ingrained in the organization’s values, employees are more likely to adopt best practices and remain vigilant to potential vulnerabilities.
Promoting Leadership Support

For a security culture to take hold, it must start at the top. Leadership should actively promote and model secure behaviors, ensuring that security is prioritized at all levels of the organization. Leaders who lead by example set the tone for employees, encouraging them to take personal responsibility for maintaining a secure environment. This includes supporting security initiatives, allocating resources, and maintaining transparency in security efforts.
Engaging Employees at All Levels
Employees play a pivotal role in upholding a secure environment, and their engagement is crucial for a strong security culture. Providing regular training, open communication channels, and a system for reporting concerns ensures that security remains a continuous priority. Rewarding employees for recognizing and addressing risks can also reinforce positive security practices and promote awareness across the organization.
By creating a culture where security is part of the organization’s DNA, companies can significantly reduce risks and ensure that all employees are active participants in maintaining a safe and secure environment.
Tools for Detecting Internal Risks

To mitigate potential risks posed by trusted personnel, organizations rely on a variety of tools that help detect unusual activities and behaviors. These tools enable monitoring of digital environments, tracking employee actions, and analyzing patterns that may indicate malicious or negligent actions. By leveraging the right technology, businesses can identify early warning signs and take appropriate measures to prevent harm.
The following table highlights some of the key tools used to detect and mitigate internal risks:
| Tool | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Monitors and controls the movement of sensitive data within the network. | Real-time alerts, content filtering, and data encryption |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Aggregates and analyzes security event logs to detect suspicious activities. | Event correlation, log management, real-time alerts |
| User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) | Analyzes user behavior and identifies deviations from normal patterns. | Machine learning, anomaly detection, predictive analytics |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Monitors endpoints for signs of compromise and enables quick response to incidents. | Real-time monitoring, threat detection, incident response |
By employing these tools, organizations can more effectively identify and address internal risks, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure and operations run smoothly.
Legal Considerations for Security Teams
When it comes to protecting sensitive information and maintaining a secure environment, security teams must be mindful of various legal obligations and constraints. The actions taken to prevent unauthorized access or investigate potential misconduct must align with local, national, and international laws. Understanding the legal framework surrounding security measures ensures that teams can act swiftly and effectively without violating employees’ rights or jeopardizing the organization’s standing.
Privacy Laws and Regulations
One of the most important legal considerations is privacy. Security teams must ensure that any monitoring, data collection, or surveillance does not violate privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU or California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. It is crucial to obtain proper consent from employees where necessary, and to handle data in accordance with privacy policies to avoid legal repercussions.
Employee Rights and Due Process
Security teams must also be cautious when investigating employee activities. It is vital to respect employees’ rights, including their right to privacy and fair treatment. Any action taken, such as surveillance or disciplinary measures, should be based on legitimate business needs and conducted in a manner consistent with company policies and labor laws. Engaging legal counsel before taking significant actions can help ensure compliance with employment laws and reduce potential liabilities.
By adhering to legal guidelines and maintaining clear communication about security policies, organizations can protect themselves while fostering a culture of trust and transparency. Balancing security measures with legal compliance is key to mitigating risks effectively without infringing on individual rights.
Handling Internal Investigations
When an organization suspects that a trusted individual has engaged in harmful actions, it’s critical to conduct a thorough and fair investigation. The process should be methodical, ensuring that all facts are gathered objectively and that the privacy and rights of individuals are respected. A well-executed investigation can help identify the scope of the issue, prevent further damage, and allow for informed decisions regarding corrective actions.
The first step in handling such investigations is to establish a clear protocol. Security teams should follow a defined procedure that includes documenting every action, from initial suspicion to resolution. Gathering all relevant evidence, including system logs, emails, and any other records, is essential for building a comprehensive case. Ensuring that this information is collected in a way that maintains its integrity is also crucial for any legal considerations that may arise later.
Another important aspect is communication. Throughout the investigation, it’s essential to maintain confidentiality to prevent unnecessary panic or damage to the reputations of those involved. Informing only those with a direct need to know helps protect the integrity of the investigation and prevents bias from affecting the outcome. Once the investigation is concluded, the results should be reviewed by legal and HR departments to ensure compliance with company policies and applicable laws.
Finally, handling internal investigations requires a careful balance between acting quickly to mitigate risks and ensuring that any actions taken are justified and lawful. By following a structured approach and respecting legal and ethical guidelines, organizations can protect their assets while ensuring fairness and transparency in addressing potential misconduct.
Preventive Measures Against Internal Attacks
To safeguard an organization from potential damage caused by trusted individuals, implementing proactive security measures is essential. Prevention is often more effective than responding to incidents, as it helps minimize risks and ensures that the organization remains secure even when faced with potential internal vulnerabilities. By creating a robust framework for mitigating these risks, organizations can foster a secure environment while maintaining trust among employees.
Security Policies and Access Control
Establishing clear policies regarding data access and usage is crucial in reducing the likelihood of unauthorized actions. These policies should cover the following:
- Role-based access: Ensure employees have access only to the information necessary for their job functions.
- Regular audits: Monitor and audit access logs to detect any unusual or unauthorized activities.
- Least privilege principle: Limit the permissions granted to employees to the minimum necessary for their tasks.
Employee Training and Awareness

Training employees on the risks of internal misconduct and the importance of maintaining security practices is a key preventive measure. Regular training sessions can help employees recognize warning signs and understand their role in protecting the organization. In addition, establishing clear channels for reporting suspicious activities fosters a proactive security culture.
- Cybersecurity education: Equip staff with the knowledge to recognize phishing attempts, weak passwords, and other common security issues.
- Clear reporting mechanisms: Encourage staff to report any suspicious behavior or anomalies they observe.
By combining clear security protocols, controlled access to sensitive data, and comprehensive employee education, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of harmful actions from within. Preventive measures not only enhance security but also promote a culture of accountability and vigilance among all members of the organization.
Responding to an Internal Security Incident
When an organization faces an event where an employee or trusted individual compromises security, a structured and timely response is essential. The immediate goal is to mitigate potential damage, secure sensitive data, and understand the nature of the incident. A well-defined response plan enables quick action and ensures that the organization can recover swiftly while maintaining confidence in its ability to handle such situations.
Initial Incident Assessment
The first step in responding to any security breach is to assess the situation. This involves gathering all relevant information about the event and determining its scope. Key actions include:
- Confirming the breach: Verify whether the event is a legitimate security issue or a false alarm.
- Containment: Quickly limit access to affected systems and data to prevent further damage.
- Documentation: Record all actions taken, including the time of the incident, involved systems, and initial findings.
Investigation and Analysis
Once the immediate danger has been contained, a thorough investigation must take place. This phase aims to uncover the root cause, evaluate the impact, and determine the motives behind the incident. Steps include:
- Forensic analysis: Review logs, data access patterns, and system activity to track the origin and progression of the incident.
- Employee interviews: Speak with relevant staff members to gather insights about the event and identify any potential gaps in security practices.
- Impact assessment: Determine the damage caused to systems, data integrity, and the organization’s reputation.
Communication and Recovery
During and after an incident, transparent communication is critical. Both internal and external stakeholders must be informed about the situation, while also ensuring that steps are taken to restore normal operations.
- Internal notifications: Inform relevant employees and departments about the breach and the actions being taken.
- Public disclosure: If necessary, communicate the incident to external parties, including customers or regulators, with transparency about the issue and the corrective mea
Effective Communication in Security Management

Effective communication is essential for managing risks and ensuring the safety of an organization’s resources. Clear and consistent messaging across teams allows for swift responses to potential incidents, while also helping to build a culture of security that everyone in the organization contributes to. Without effective communication, even the best security strategies can fail, leaving the organization vulnerable. It is crucial that all team members, from frontline employees to top management, understand their roles and how they can contribute to maintaining a secure environment.
Key Elements of Security Communication

In the context of managing security, several important elements help ensure communication is both effective and efficient:
- Clarity: Ensure that all communications are clear and easy to understand, avoiding complex jargon that may confuse recipients.
- Timeliness: Prompt communication is vital, especially in cases where quick action is required to minimize risks.
- Relevance: Only share information that is directly applicable to the recipients to avoid information overload.
- Consistency: Maintain regular updates so that all parties are continuously informed of any new developments or potential concerns.
Tools for Facilitating Effective Communication
Choosing the right communication channels and tools is also crucial in maintaining an effective security strategy. Here are some common tools used to support security communication:
Tool/Channel Purpose Email Used for formal updates, incident notifications, and important alerts across teams. Instant Messaging Ideal for quick, real-time communication during incidents or for immediate alerts. Incident Management Systems Centralized systems that help track incidents, assign tasks, and provide documentation of events. Security Dashboards Real-time platforms used to monitor security status and provide live updates to teams and stakeholders. By integrating these communication tools and maintaining clear, timely messaging, organizations can ensure they are prepared to address risks swiftly and effectively. Strong communication is not only about responding to incidents but also about building trust within the organization, promoting a proactive security culture that helps to minimize potential risks before they escalate.