Throughout Earth’s history, there have been several significant events that led to the widespread loss of species, disrupting ecosystems and reshaping the planet. These phenomena have had profound effects on biodiversity and the development of life as we know it. By examining the causes and patterns of these events, we can better understand the dynamics of life on Earth and the importance of preserving biodiversity today.
In this section, we will explore the key factors that contribute to large-scale species disappearance, highlighting the critical role of environmental changes, natural disasters, and other forces. The discussion will also focus on how scientists approach the study of these events, using educational frameworks to analyze their impact. Gaining insight into these past events helps us prepare for the challenges of conserving life in the future.
Mass Extinction Events Explained
Throughout the history of Earth, there have been several catastrophic events that led to the drastic reduction of life forms, permanently altering ecosystems and evolutionary paths. These events, often triggered by sudden environmental shifts, have left lasting marks on the planet’s biodiversity. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for studying the resilience of life and the mechanisms behind such large-scale changes.
These critical events are characterized by rapid environmental shifts that cause widespread destruction of species across various habitats. The causes behind these events are complex, but they generally stem from natural forces that overwhelm the planet’s systems. Some of the most well-known incidents include:
- Climate Change: Sudden shifts in temperature and atmospheric conditions.
- Asteroid Impacts: Large celestial bodies colliding with Earth, leading to global environmental changes.
- Volcanic Activity: Extensive volcanic eruptions that cause significant atmospheric alterations.
- Ocean Acidification: Changes in ocean chemistry that disrupt marine ecosystems.
Each event shares common traits, such as widespread species loss and dramatic shifts in habitat conditions. However, the specific causes and the intensity of their effects vary, making the study of these occurrences vital to understanding past and future environmental shifts. By examining the patterns of these events, we gain insight into how life on Earth adapts to extreme changes, and how the recovery of ecosystems unfolds over time.
The impact of these events is not always immediately apparent, as ecosystems can take millions of years to recover fully. However, by studying the patterns and causes of these events, we can better predict potential risks to current biodiversity and develop strategies to mitigate similar occurrences in the future.
What is Mass Extinction?
Large-scale events that result in the rapid disappearance of a significant proportion of species across the planet are critical moments in Earth’s history. These events are characterized by drastic changes in the environment, leading to the collapse of ecosystems and the loss of numerous life forms in a short period. Understanding the nature of these occurrences helps us appreciate the fragile balance of life and the forces that drive evolutionary change.
Defining Large-Scale Species Loss
When considering such events, it is important to recognize the extent of damage they cause to biodiversity. The loss of species is not a gradual process but a rapid decline due to sudden environmental shifts. The key features of these events include:
- Extensive and widespread species disappearance
- Global environmental disruptions
- Long-lasting effects on ecosystems
Historical Events and Their Impact

Throughout Earth’s history, several such events have drastically altered the course of life. These events are typically linked to catastrophic changes in the environment, such as:
- Climate Shifts: Sudden temperature increases or decreases affecting global habitats.
- Cosmic Collisions: Large objects from space impacting Earth, triggering massive environmental disruptions.
- Geological Activity: Massive volcanic eruptions and tectonic shifts influencing the atmosphere and climate.
The aftermath of these events often leads to new evolutionary opportunities, as remaining species adapt to the changed conditions. However, the process of recovery is slow, often taking millions of years for ecosystems to regain stability and diversity.
Key Causes of Mass Extinction
The widespread loss of species and the collapse of ecosystems are often driven by various catastrophic factors. These events disrupt the balance of life, altering the environment in such a way that many organisms cannot adapt. Understanding the root causes of these large-scale changes is essential for both studying the past and preparing for potential future challenges to biodiversity.
Natural Environmental Shifts
Throughout Earth’s history, many of these events have been triggered by natural forces. These shifts can drastically change the climate, landscape, or atmosphere, making it difficult for many species to survive. The main natural causes include:
- Climate Change: Rapid shifts in temperature, both warming and cooling, can render habitats inhospitable to many species.
- Volcanic Activity: Large-scale eruptions can lead to significant atmospheric changes, reducing sunlight and cooling the planet.
- Sea-Level Fluctuations: Dramatic changes in sea levels can alter coastal and marine ecosystems, displacing numerous species.
Extraterrestrial and Geological Factors
In addition to terrestrial factors, external events have played a significant role in causing massive disruptions to life on Earth. These include:
- Asteroid or Comet Impacts: Collisions with large celestial bodies can trigger widespread environmental changes, including fires, tsunamis, and dust clouds that block sunlight.
- Tectonic Shifts: The movement of Earth’s plates can alter the planet’s surface, creating new landforms and destroying ecosystems.
While these causes vary in intensity and scope, they all have the potential to create conditions where the survival of many species becomes impossible. The recovery from such events is often slow, as new ecosystems take time to evolve and regain biodiversity.
Impact on Earth’s Biodiversity
Catastrophic events that result in the widespread loss of species have profound effects on Earth’s biodiversity. These incidents disrupt the intricate web of life, causing shifts in ecosystems and altering the distribution of organisms. The consequences of such upheavals often lead to the dominance of certain species while others disappear entirely, reshaping the evolutionary trajectory of life on the planet.
The loss of species during these critical events often leads to a reduction in the overall variety of life, creating environments where only a few resilient species thrive. These changes can affect both terrestrial and marine ecosystems, leading to imbalances in food chains and the loss of ecological functions that are vital to the planet’s health.
In some cases, new species emerge to fill ecological niches left vacant by the disappearance of others. However, the recovery of biodiversity is often slow, taking millions of years for ecosystems to stabilize and regain their former richness. The scars left by these events serve as reminders of the fragility of life and the need to preserve the delicate balance that supports diverse ecosystems.
How POGIL Explains Extinction Events
POGIL provides an interactive framework that helps to understand complex biological phenomena, such as the rapid loss of species from ecosystems. By engaging with carefully designed activities, students can explore the various factors that contribute to these significant shifts in biodiversity. This method emphasizes collaborative learning, enabling learners to analyze and discuss various drivers behind the disappearance of species, leading to a deeper understanding of the processes involved.
Through structured exercises, learners identify patterns and connections between environmental changes, biological adaptations, and the resulting effects on life forms. The approach encourages critical thinking and helps participants appreciate how ecosystems evolve and how imbalances can trigger dramatic losses of species over time. By examining historical events and current trends, learners gain insight into the forces that shape the living world and the delicate balance required to maintain biodiversity.
Extinction Theories and Their Relevance
Numerous hypotheses attempt to explain the reasons behind significant biological upheavals that result in the disappearance of species from ecosystems. These theories explore different environmental, biological, and cosmic factors that could disrupt the balance of life. Each theory offers insights into how various elements, such as climate change, natural disasters, or human activity, contribute to these events and how they affect biodiversity across the planet.
Environmental and Climatic Influences
Many theories focus on the role of climate shifts in driving major biological transformations. Sudden changes in temperature, atmospheric composition, or sea levels can create inhospitable conditions for certain species. These shifts often lead to a breakdown in ecosystems, forcing some organisms to adapt, migrate, or face decline. Understanding these processes is vital for predicting potential risks to current biodiversity.
Cosmic and Geophysical Factors
Other hypotheses point to cosmic events such as asteroid impacts or volcanic activity as key drivers. These events can cause rapid environmental changes, like dust clouds blocking sunlight or extreme heat, that disrupt ecosystems. By analyzing these theories, scientists can assess the long-term consequences of such events and their potential to reshape life on Earth.
Fossil Records and Extinction Evidence
Fossils provide invaluable insights into past life forms and the environmental conditions in which they thrived. By studying these remnants, scientists can piece together the story of how species evolved, adapted, and in some cases, disappeared from the planet. Fossil records serve as a critical tool for understanding the forces that led to these significant changes in biodiversity over time.
Uncovering Patterns of Species Decline
Through careful examination of fossil layers, researchers can identify patterns of sudden or gradual decline in specific species. These patterns often correlate with shifts in climate, geological activity, or other external factors that may have created challenging conditions for survival. Fossil evidence helps scientists trace these moments of dramatic change, providing context for how life on Earth has been impacted by environmental factors.
Linking Fossils to Environmental Shifts
Fossils also offer clues about past environmental conditions, such as changes in temperature, sea levels, or the presence of certain gases in the atmosphere. These markers help to establish connections between biological disruptions and the Earth’s changing landscape. By analyzing fossilized remains alongside geological data, scientists gain a clearer understanding of how life forms responded to these shifts and what might have led to their eventual disappearance.
Mass Extinctions in Earth’s History
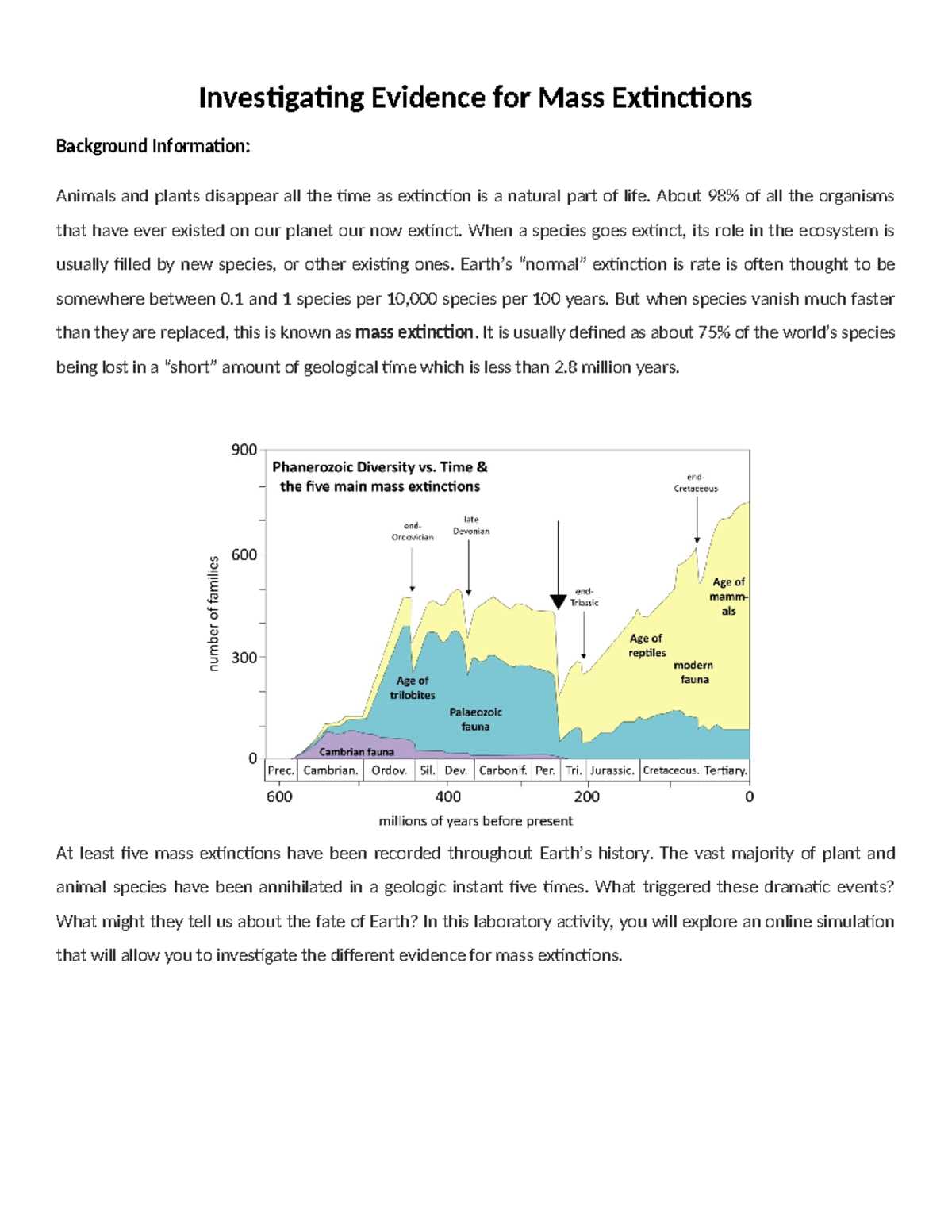
Throughout Earth’s history, several pivotal events have caused widespread loss of biodiversity, reshaping the planet’s ecosystems. These events were marked by significant and rapid changes, affecting a large number of species across different environments. Understanding these moments helps researchers grasp the scale of disruptions that can occur and the factors driving such transformations in life forms.
The Five Major Biological Crises
There have been five major events in Earth’s past that stand out for their immense impact on life. These crises were triggered by various factors, including dramatic climate shifts, volcanic activity, or asteroid impacts. Each event led to a significant reduction in the number of species, with entire ecosystems being altered. By studying these periods, scientists can better understand how life on Earth has evolved in response to sudden and extreme environmental changes.
Rebuilding and Evolution After Catastrophes
Following these large-scale upheavals, Earth’s ecosystems slowly began to recover, with new species emerging and ecosystems evolving to fill the ecological gaps left behind. The process of recovery and renewal reveals the resilience of life and the adaptability of organisms in the face of drastic environmental changes. Fossil evidence from these periods offers a window into how life rebounded and diversified after periods of great loss.
POGIL’s Role in Science Education
Interactive learning methods have become essential in modern science education, enabling students to engage deeply with complex concepts through collaborative exploration. This approach encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, allowing learners to develop a better understanding of scientific principles by actively participating in their discovery rather than passively receiving information.
Enhancing Understanding Through Collaboration
One of the key aspects of this learning model is the emphasis on teamwork. Students work in groups to analyze and discuss scientific problems, which helps them construct knowledge together. By collaborating, they are exposed to diverse perspectives, which strengthens their understanding and encourages them to think more critically about scientific concepts and theories.
Encouraging Active Problem Solving
Another important element is the focus on problem-solving. Instead of simply memorizing facts, students are tasked with applying their knowledge to real-world scenarios. This active involvement in scientific inquiry fosters a deeper understanding of how scientific principles can be applied, making the learning experience more relevant and meaningful.
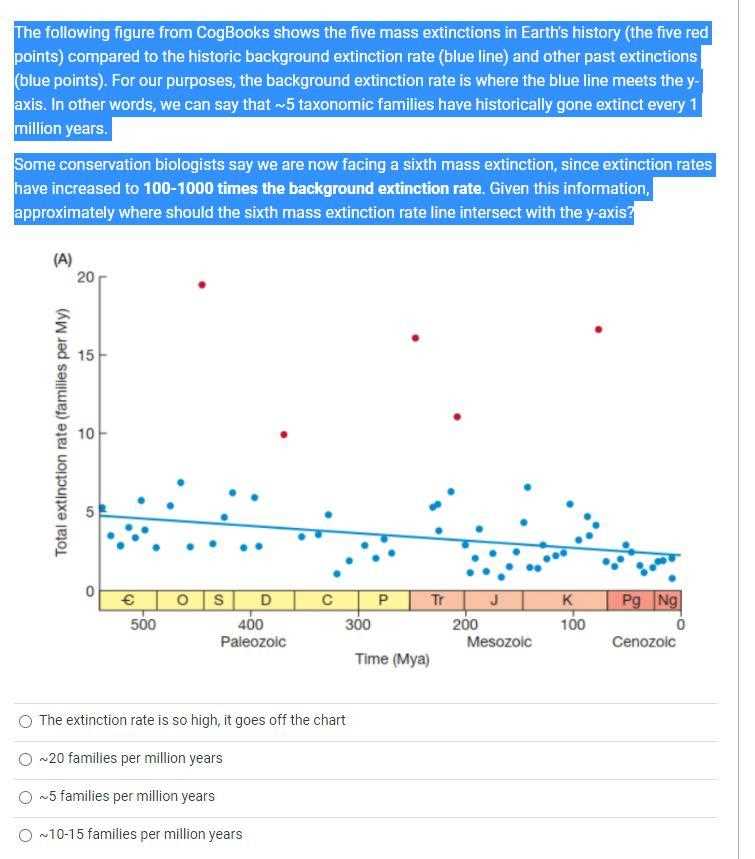
Extinction Event Patterns and Trends
Throughout Earth’s history, there have been recurring patterns and trends in the events that lead to the disappearance of large numbers of species. These events are often triggered by sudden environmental changes, such as shifts in climate, atmospheric composition, or geological activity. By studying these patterns, scientists can better understand the underlying causes and the specific conditions that make ecosystems vulnerable to widespread disruption.
Patterns of Species Loss Over Time
Analyzing the frequency and timing of these events reveals that periods of significant species loss tend to follow certain trends. These events are not random but are often linked to specific triggers, such as volcanic eruptions or asteroid impacts. The following table highlights some of the most notable periods in Earth’s history where large-scale biological changes occurred:
| Event Period | Trigger Factors | Impact on Biodiversity |
|---|---|---|
| End of the Permian | Volcanic activity, climate shift | Mass disappearance of marine and terrestrial life |
| End of the Cretaceous | Asteroid impact, climate change | Loss of dinosaurs and many marine species |
| End of the Triassic | Volcanic eruptions, climate change | Large-scale disappearance of marine life and early dinosaurs |
Identifying Trends in Recovery and Adaptation
After these large-scale disruptions, ecosystems tend to recover gradually. However, the recovery process often follows distinct trends. New species evolve to fill ecological niches left by the lost organisms, and ecosystems adapt to the changing environment. By studying these trends, scientists can better predict how modern-day ecosystems might respond to current environmental pressures.
Human Influence on Modern Extinctions
Human activities have increasingly become a major force shaping the fate of many species on Earth. From habitat destruction to pollution and climate change, the impact of human actions on biodiversity is profound and widespread. These influences often disrupt ecosystems and create conditions that make survival challenging for numerous organisms. Understanding how human behaviors contribute to the decline of species is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate these effects and preserve biodiversity.
Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation
One of the most significant ways humans contribute to the loss of species is through the destruction and fragmentation of natural habitats. As forests are cleared for agriculture, cities expand, and infrastructure grows, many species are left with fewer places to live. The disruption of habitats makes it difficult for species to find food, shelter, and mates, leading to a decline in populations. Habitat loss is considered one of the primary drivers of species decline today.
Climate Change and Its Effects
Human-induced climate change also plays a crucial role in altering the conditions necessary for various species to thrive. Rising temperatures, shifting rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events can force species to migrate or adapt quickly. In many cases, however, species are unable to adjust fast enough, leading to population decreases. Climate change is accelerating the rate of species disappearance, especially for those with specialized habitat needs or slow reproductive cycles.
Extinction’s Effect on Ecosystem Balance
The loss of species has profound consequences on the balance of ecosystems, affecting the delicate interconnections between organisms and their environments. When certain species disappear, it disrupts food webs, alters resource availability, and can trigger a cascade of changes across the entire ecosystem. These disruptions not only impact the affected species but also the broader biological community that depends on them for survival.
Disruption of Food Chains
Every species plays a role in maintaining the stability of its ecosystem. When a key organism disappears, the effects ripple through the food chain:
- Predators may face a shortage of prey, affecting their survival.
- Herbivores may overpopulate in the absence of their natural predators, leading to overgrazing.
- Decomposers may lose a primary source of organic material, disrupting nutrient cycling.
Loss of Ecosystem Services
Species contribute to the functioning of ecosystems in many ways, providing vital services such as pollination, water filtration, and soil regeneration. The disappearance of species can lead to the loss of these essential services, with consequences for both wildlife and human populations:
- Reduced pollination can affect crop production and food supply.
- Loss of soil-building organisms can lead to soil erosion and decreased fertility.
- Disruption of water filtration processes can degrade water quality and availability.
In summary, the loss of species leads to a cascade of impacts, weakening ecosystems and making them more vulnerable to further disturbances. These changes emphasize the importance of maintaining biodiversity for the health and stability of the planet’s ecosystems.
Extinction and Evolutionary Consequences
The disappearance of species has a profound impact on the evolutionary trajectory of life on Earth. When large numbers of organisms vanish, it creates opportunities for other species to fill vacant ecological niches. This process often leads to new forms of adaptation and diversification, which can result in the evolution of entirely new species over time. Understanding the evolutionary consequences of species loss helps scientists grasp how life has adapted to changing conditions throughout history.
Opportunities for Evolutionary Diversification
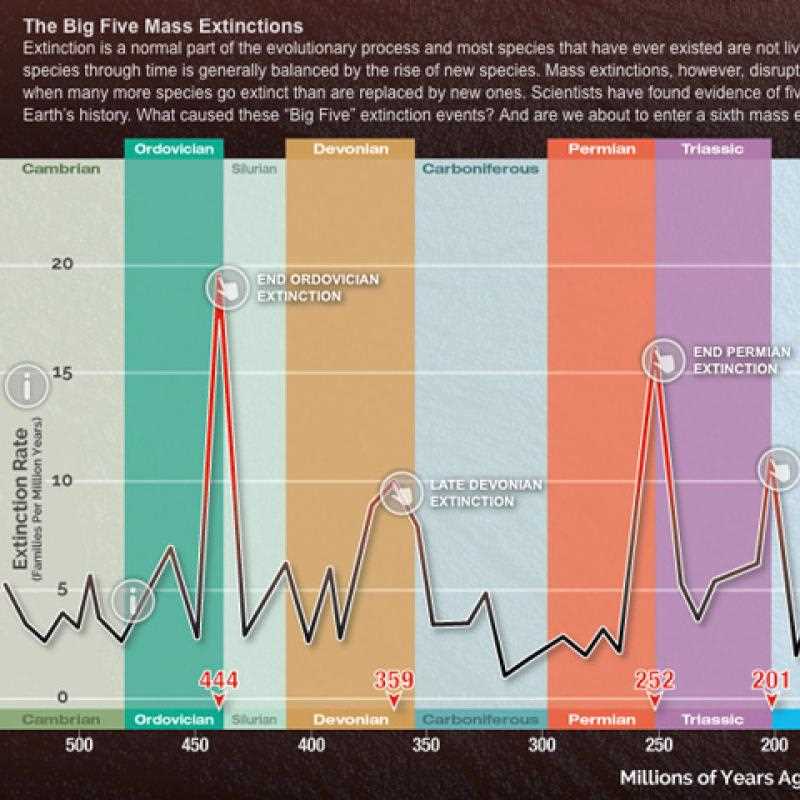
When species disappear, ecological gaps are created, allowing surviving organisms to evolve and adapt to the changing environment. This process of adaptive radiation can lead to the rapid emergence of new species that occupy the available niches. The following table illustrates examples of how past biological upheavals have led to the rise of new life forms:
| Event Period | Vacant Niches | New Species Emerged |
|---|---|---|
| End of the Permian | Marine and terrestrial ecosystems | Rise of dinosaurs and new marine life |
| End of the Cretaceous | Terrestrial ecosystems | Rise of mammals and flowering plants |
| End of the Triassic | Terrestrial ecosystems | Rise of early dinosaurs |
Impact on Evolutionary Rates
Species loss can accelerate the rate of evolution by creating new ecological pressures and challenges. As survivors adapt to these challenges, natural selection plays a more prominent role in shaping the direction of evolutionary development. These shifts can lead to the rapid diversification of surviving species, as they evolve to take advantage of newly available resources and ecological niches.
Current Threats Leading to Extinction
Human activities are increasingly driving the decline of biodiversity across the planet. Various environmental pressures are pushing many species to the brink of disappearance, and these threats are often interconnected. From habitat destruction to climate change, the factors causing this loss of life are complex and have far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation

One of the most pressing challenges species face today is the destruction and fragmentation of their natural habitats. As urbanization, agriculture, and industrial development continue to expand, vast areas of forests, wetlands, and grasslands are being cleared. This disrupts ecosystems and isolates populations, making it harder for species to find food, mates, and shelter. Habitat destruction is a leading cause of biodiversity loss, especially for species that require large, continuous habitats.
Climate Change and Environmental Stress
The rapid pace of climate change is another significant threat to species survival. Rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are altering ecosystems in ways that many organisms cannot adapt to quickly enough. Climate change impacts species in numerous ways, from altering migration patterns to changing the availability of food and water. As a result, species that are already stressed by other factors are becoming increasingly vulnerable to environmental changes.
Global Warming and Biodiversity Loss
The warming of the planet is having a profound effect on the natural world, accelerating the loss of many species. As temperatures rise, ecosystems are undergoing rapid changes, forcing organisms to adapt, migrate, or face significant challenges to their survival. These environmental shifts disrupt established habitats and can lead to the disappearance of species that are unable to cope with the changes.
Effects of Rising Temperatures on Ecosystems
Higher temperatures influence ecosystems in several ways, creating new challenges for species across the globe. These impacts include:
- Disruption of natural habitats, such as coral reefs and forests, leading to loss of shelter and food sources.
- Shifts in migration patterns, causing species to arrive in areas too late or too early for optimal survival.
- Changes in seasonal behaviors, such as breeding cycles, which may not align with the availability of food or other environmental conditions.
Threats to Species Adaptation
While some species are capable of adapting to gradual changes, the rapid pace of climate change makes it difficult for many organisms to keep up. Species that are already living in specialized or vulnerable environments face the greatest risk:
- High-altitude and polar species are particularly vulnerable to temperature shifts as their habitats are limited.
- Species with small populations or limited ranges have less genetic diversity, making them more susceptible to environmental changes.
- Organisms that rely on specific temperature conditions for reproduction, like amphibians, may face reproductive failure.
As the planet continues to warm, the overall impact on biodiversity is expected to grow, stressing the importance of addressing climate change in efforts to conserve life on Earth.
Mass Extinction and Conservation Efforts
The ongoing rapid decline in biodiversity has sparked significant concern worldwide. As many species face the risk of disappearing, various initiatives have been launched to mitigate these threats and protect vulnerable life forms. Conservation efforts are crucial in preserving ecosystems, restoring damaged environments, and ensuring that the remaining species can thrive in a changing world.
Conservation Approaches and Strategies

There are several strategies designed to protect endangered species and their habitats. These approaches aim to reduce human impact on the environment and promote sustainable interactions with nature:
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Protected Areas | Creating reserves and parks to safeguard ecosystems from human activity, offering safe habitats for wildlife. |
| Species Recovery Programs | Efforts to rehabilitate and reintroduce species into the wild, ensuring their long-term survival. |
| Environmental Legislation | Enacting laws to prevent illegal hunting, habitat destruction, and trade of endangered species. |
Barriers to Effective Conservation
Despite the significant progress made, several challenges persist that hinder conservation efforts:
- Insufficient funding for large-scale conservation projects.
- Climate change, which complicates habitat restoration and species adaptation.
- Conflicting interests between economic development and environmental preservation.
While challenges remain, ongoing conservation initiatives and global awareness efforts are vital for the survival of many species and the protection of natural ecosystems.
Future of Biodiversity and Extinction
The future of biodiversity is deeply intertwined with the actions humanity takes today. As environmental pressures continue to grow, the survival of countless species depends on the choices we make in protecting natural habitats and mitigating harmful activities. The trajectory of the planet’s ecosystems will be shaped by ongoing conservation efforts, climate change, and how well societies adapt to the challenges of maintaining balance in the natural world.
Predictions for Biodiversity Loss
Scientists predict that the ongoing changes in climate and human activity could lead to further reductions in biodiversity if left unchecked. Some potential future outcomes include:
- Increased habitat loss due to urban expansion, deforestation, and agricultural development.
- Climate change effects leading to shifts in species distribution, and even extinction of those unable to adapt.
- Pollution poisoning ecosystems, reducing the number of species able to survive in affected areas.
Actions for a Sustainable Future

To prevent further decline, humanity must focus on sustainable practices and proactive measures to protect the natural world. Key actions include:
- Protecting ecosystems through the establishment of protected areas and conservation efforts.
- Implementing policies to curb pollution, reduce carbon emissions, and promote biodiversity conservation.
- Promoting awareness and education to foster global cooperation and commitment to preserving life on Earth.
In conclusion, the future of biodiversity relies on collective action. If we choose to prioritize environmental health, we can reduce the risks that threaten the planet’s diverse life forms and build a more sustainable world for generations to come.