
In the world of finance, precision is crucial. Even small miscalculations can lead to significant discrepancies that affect the integrity of reports and decision-making. Recognizing and addressing these mistakes is vital for maintaining the credibility and accuracy of financial data.
Throughout your studies, you’ll encounter various situations where identifying and resolving these inaccuracies is key. Being able to spot potential issues quickly and apply the right techniques to fix them can make a big difference in ensuring that the results are trustworthy and comply with industry standards. The ability to approach these situations with confidence is an essential skill in the field of financial management.
Knowing how to navigate the complexities of financial adjustments not only helps improve your technical skills but also boosts your understanding of how these adjustments shape the bigger picture of business operations. With practice, you can develop a systematic approach to resolving discrepancies and refining your ability to produce precise, reliable reports.
Mastering Accounting Error Correction
Achieving precision in financial reporting requires a strong grasp of how to address discrepancies that may arise during the preparation of financial documents. The process of identifying these inconsistencies and implementing effective solutions is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and credibility of any financial statement. This section will explore strategies for handling common mistakes and provide insights into refining your approach to these challenges.
Key Techniques for Identifying Mistakes
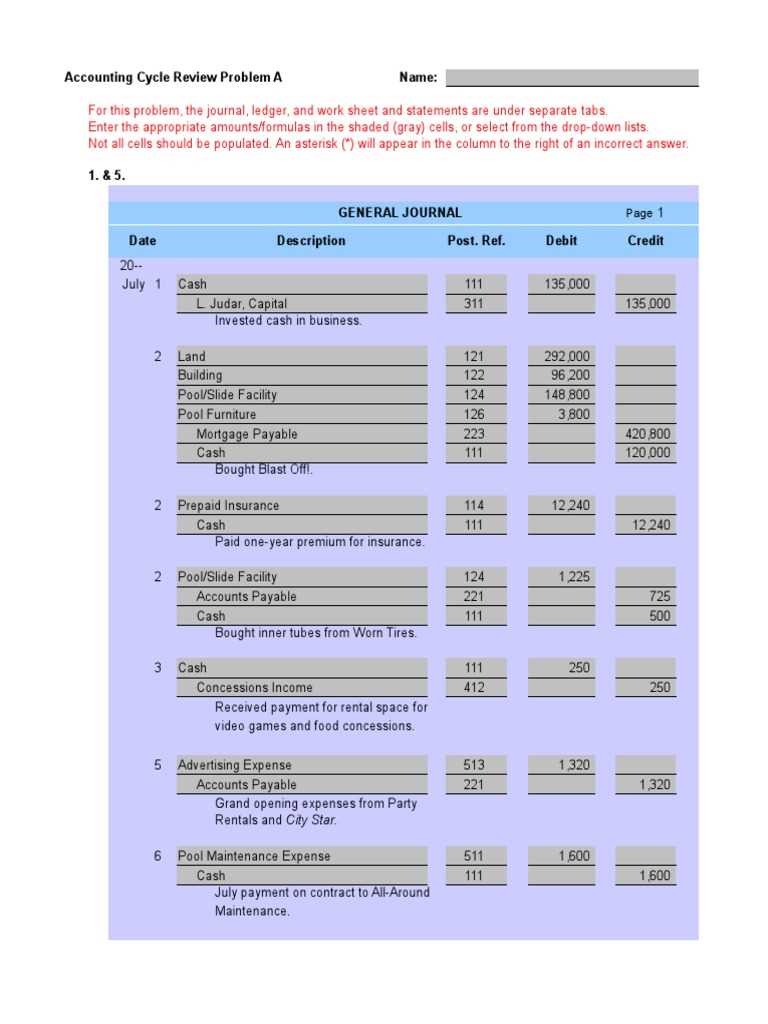
One of the first steps in addressing inaccuracies is recognizing where things have gone wrong. Common pitfalls often occur in calculations, data entry, or misinterpretations of financial rules. Developing a keen eye for spotting these mistakes early on can save considerable time and effort. Utilizing systematic review processes and cross-checking data are effective ways to ensure that every detail aligns with the expected outcomes.
Efficient Approaches for Fixing Discrepancies
Once discrepancies are identified, applying the appropriate methods to resolve them becomes the next critical task. Adjusting entries, revising journal entries, and updating ledgers are some of the common approaches for restoring accuracy in financial documents. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of the steps involved in each method to prevent further complications. Regular practice and exposure to different scenarios help to refine this skill and enhance the overall efficiency of financial processes.
Understanding Common Accounting Mistakes

In the world of financial management, even small mistakes can lead to major discrepancies in reports and financial statements. Understanding the types of missteps that frequently occur is the first step in preventing them. These mistakes can stem from simple oversights or more complex misunderstandings of financial principles, but they all share one thing in common: they undermine the accuracy of financial data.
Typical mistakes in financial documentation often involve issues such as misclassifying transactions, incorrect data entry, or failing to adjust for previous inaccuracies. These miscalculations can distort the financial picture of an organization, leading to misleading conclusions and potentially costly consequences. Being aware of these common pitfalls allows professionals to adopt better practices and avoid them in the future.
Identifying Key Error Types in Accounting
In financial reporting, recognizing the various types of mistakes that can occur is essential for maintaining the integrity of data. These mistakes can manifest in several forms, ranging from minor oversights to more significant misjudgments that affect the overall accuracy of the financial documents. Being able to pinpoint these common missteps early allows professionals to take corrective measures before they lead to larger issues.
Among the most frequent types of mistakes are transposition errors, where numbers are flipped or incorrectly recorded, and omission errors, where essential details are left out of financial records. Additionally, there are issues with incorrect application of accounting principles or misinterpretation of specific transaction details. Understanding these types of mistakes is vital in ensuring that financial statements remain accurate and reliable.
Steps to Correct Simple Accounting Errors

When minor mistakes occur in financial documents, it’s essential to address them quickly and accurately to avoid larger complications. Correcting these mistakes involves a few straightforward steps that can help restore accuracy and maintain the integrity of the financial records. By following a systematic approach, these errors can be rectified with minimal impact on the overall financial statements.
The first step is to identify the source of the mistake, whether it’s a miscalculation, a data entry issue, or a misapplication of financial principles. Once identified, it’s important to document the mistake and the correction method. Next, update the records to reflect the accurate information and ensure all related entries align with the revised data. Lastly, it’s a good practice to double-check the corrected figures to confirm that the changes have been applied correctly and consistently across all relevant documents.
Advanced Techniques for Error Detection

As financial documents become more complex, relying on basic methods of spotting mistakes may no longer be sufficient. Advanced techniques for detecting discrepancies can help identify issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. These methods often involve a more detailed and systematic approach, ensuring that even the smallest inconsistencies are detected and addressed promptly.
Using Data Analysis Tools
One of the most effective ways to detect issues is by leveraging specialized software and data analysis tools. These tools can quickly scan large datasets, highlight inconsistencies, and even provide suggestions for possible mistakes. By automating parts of the review process, accountants can focus on more critical aspects of the financial review while relying on technology to handle routine checks.
Conducting Variance Analysis
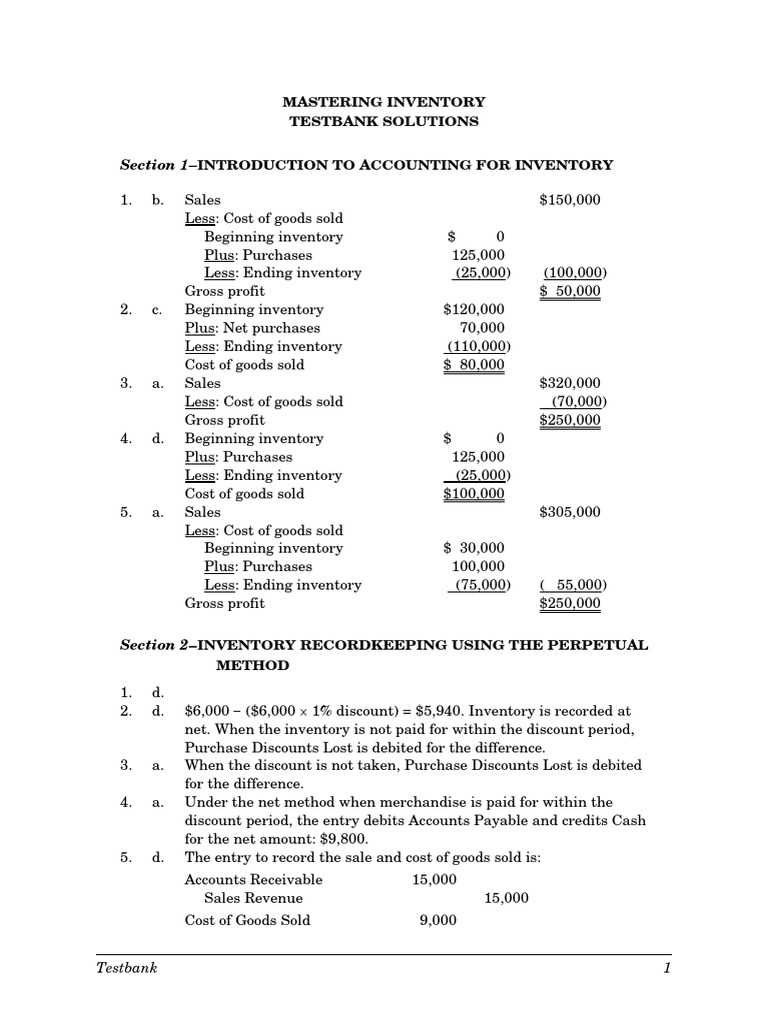
Variance analysis is a technique used to compare actual financial outcomes with expected results. This approach helps to identify areas where discrepancies may have occurred, offering insights into potential mistakes. By analyzing variances across different time periods, departments, or accounts, professionals can pinpoint areas that need further scrutiny and take corrective action before errors escalate.
Common Pitfalls in Financial Statements
When preparing financial documents, there are several common issues that can arise, leading to misleading or inaccurate representations of a company’s financial situation. These pitfalls often stem from misunderstandings, oversights, or incorrect practices. Understanding these potential challenges can help prevent mistakes that could affect decision-making or compliance.
| Common Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Misclassification of Expenses | Expenses may be incorrectly categorized, leading to misrepresentation of the company’s profitability and financial health. |
| Failure to Adjust for Depreciation | Neglecting to account for depreciation can inflate asset values and affect long-term financial projections. |
| Overlooking Revenue Recognition | Improper timing of revenue recognition can lead to discrepancies in income reporting, distorting the financial picture. |
| Inconsistent Application of Accounting Methods | Inconsistencies in applying accounting methods across periods can result in inaccurate comparative financial statements. |
By recognizing these common pitfalls and adopting best practices, professionals can improve the accuracy and reliability of their financial statements, ensuring that they reflect the true financial standing of the organization.
How to Handle Journal Entry Errors
Journal entries are fundamental in maintaining accurate financial records, but mistakes can happen during the process. These mistakes, though common, can distort the overall picture of a company’s finances if not promptly addressed. Knowing how to identify and resolve issues in journal entries is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial reports and ensuring accurate data flow throughout the system.
Identifying the Source of the Mistake
The first step in handling mistakes in journal entries is identifying the source. Common issues include incorrect amounts, misclassified accounts, or duplicate entries. Carefully reviewing the transaction details and ensuring that each entry aligns with the source documentation can help pinpoint where the problem occurred. Once identified, a clear understanding of the mistake will guide the appropriate course of action.
Correcting the Entry and Documenting Changes
After the mistake is identified, the next step is to correct the entry. This often involves reversing the original entry and creating a new, accurate one. It’s essential to document the correction for transparency, especially when dealing with financial audits. This ensures that the adjusted figures are recorded correctly, and the mistake does not reappear in subsequent reports. Regular checks and reconciliations can also help prevent similar issues in the future.
Using Software Tools for Error Correction
In today’s financial landscape, relying on manual processes to identify and fix discrepancies can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Leveraging specialized software tools can greatly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of detecting and addressing issues. These tools are designed to automate parts of the review and adjustment process, ensuring that financial data remains reliable and consistent.
Automation of Common Adjustments
Software tools can automatically detect common mistakes, such as miscalculations or incorrect entries, and suggest adjustments. Features like real-time data validation and built-in error checks help streamline the process, allowing users to correct mistakes before they become larger problems. Automated reports and alerts provide a proactive approach to managing discrepancies, reducing the risk of overlooking key details.
Improving Accuracy with Data Reconciliation
Data reconciliation is a critical step in maintaining accurate financial records, and modern software tools make this task more efficient. By comparing different sets of data, such as bank statements and ledger entries, software can highlight discrepancies that need to be addressed. This process ensures that all financial information aligns, improving the overall reliability of financial statements and reducing the potential for inconsistencies.
Why Accuracy Matters in Accounting

Precision in financial reporting is essential for maintaining trust, ensuring compliance, and making informed decisions. When financial data is inaccurate, it can lead to misguided decisions, missed opportunities, and even legal consequences. Organizations depend on accurate records to guide their strategies, assess performance, and manage risks. Without a solid foundation of trustworthy information, even the best plans can falter.
The Impact on Business Decisions

Financial decisions, whether about investments, budgeting, or expansions, are all based on the integrity of the underlying data. Inaccurate information can result in overestimating or underestimating a company’s financial health, leading to poor decision-making. For example, inaccurate cash flow projections may cause a business to overextend itself or miss opportunities for investment or cost savings.
Compliance and Legal Considerations

Beyond internal decisions, precise financial records are crucial for meeting regulatory and tax requirements. Inaccuracies can lead to fines, legal issues, or even audits, which can damage a company’s reputation. Ensuring that financial statements are accurate and comply with legal standards is vital to maintaining the trust of stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulatory bodies.
| Consequence | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Inaccurate Financial Statements | Misleading data that can lead to poor decision-making and legal issues. |
| Poor Cash Flow Management | Inability to meet obligations or missed opportunities for growth. |
| Non-Compliance | Risk of fines, penalties, or damaged reputation with stakeholders. |
Revising Financial Reports After Mistakes
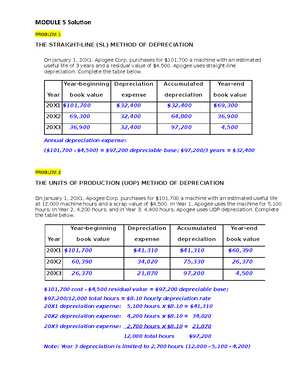
When discrepancies are identified in financial reports, it is crucial to promptly revise the documents to reflect accurate information. The revision process ensures that stakeholders, including investors, auditors, and regulatory bodies, have access to reliable data. Even minor inaccuracies, if left unchecked, can lead to serious consequences, so addressing them swiftly is essential for maintaining trust and transparency.
Revisions should be made carefully, starting with a thorough review of the affected areas. This step involves identifying the root cause of the mistake and adjusting all related figures accordingly. Each correction must be documented and explained to maintain a clear audit trail. By doing so, businesses can ensure that any adjustments made are traceable and justified.
Documenting the Changes

When revising financial documents, it is critical to keep a record of the changes made. This includes noting the original values, the corrected figures, and a detailed explanation of the adjustments. This documentation serves not only as a reference for internal teams but also as a safeguard in case of future audits or reviews. Transparency in the revision process reinforces the integrity of the financial statements and builds confidence in the company’s reporting practices.
Communicating the Adjustments
After making the necessary revisions, it is important to communicate the changes to relevant parties. This can include internal management, external auditors, or even clients who may rely on the information. Clear communication helps to ensure that everyone involved understands the reason for the revisions and the impact on the company’s financial standing. Additionally, it helps maintain consistency in reporting and ensures that stakeholders are aligned with the updated data.
Impact of Mistakes on Financial Health
Small mistakes in financial records may seem insignificant, but they can have a far-reaching impact on the overall financial well-being of a business. When figures are misreported or omitted, the resulting distortions can lead to incorrect assessments of profitability, cash flow, and even solvency. Inaccurate data influences decision-making at every level and can undermine investor confidence, damage reputations, and trigger costly consequences if left unaddressed.
Consequences of Inaccurate Financial Data
- Misleading Profitability Insights: When revenues or expenses are misstated, it can give a false picture of a company’s profitability. This may lead to poor strategic decisions, such as unnecessary cost-cutting or underinvestment in growth.
- Cash Flow Issues: Errors in cash flow reporting can result in liquidity problems. If the company believes it has more available funds than it does, it may overcommit to spending or miss paying important bills on time.
- Regulatory Penalties: Mistakes in financial statements can lead to non-compliance with tax laws and regulations, which may result in fines, legal action, or forced restatements of financial results.
- Lost Investor Confidence: Repeated mistakes can erode trust with shareholders and investors, causing stock prices to drop and making it difficult to raise capital.
How Financial Mistakes Affect Key Stakeholders
- Management: Inaccurate data can lead managers to make poor operational decisions, such as hiring too many staff or investing in the wrong projects.
- Investors: Investors rely on precise financial reports to assess the value of their investments. Mistakes can mislead them about the financial health of the company.
- Regulators: Financial authorities may require companies to submit corrected reports if discrepancies are discovered, which could lead to audits and increased scrutiny.
Best Practices for Preventing Mistakes
Prevention is always better than correction, especially when it comes to managing financial data. By establishing clear procedures and implementing robust controls, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of inaccuracies. Adopting proactive strategies helps maintain the integrity of financial reports, ensures compliance with regulations, and supports informed decision-making across the organization.
Effective Strategies for Error Prevention

- Regular Training and Education: Providing ongoing training for staff ensures they stay updated on best practices and any changes in regulations. Knowledgeable employees are less likely to make mistakes in the first place.
- Automation and Technology: Utilizing financial software to automate calculations and reporting processes minimizes human error. Automation can handle repetitive tasks more accurately and quickly than manual methods.
- Establishing Clear Processes: Clearly defined workflows and procedures for data entry, reconciliation, and reporting make it easier to spot mistakes early in the process and prevent them from escalating.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Scheduling periodic reviews and audits of financial statements helps identify any inconsistencies or areas of concern before they become major issues.
- Segregation of Duties: Ensuring that different individuals are responsible for key tasks such as data entry and review helps prevent oversight and reduces the risk of errors or fraud.
Tools and Technologies for Minimizing Mistakes
- Data Validation Tools: Implementing validation checks during data entry ensures that values are entered correctly, preventing errors before they occur.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Using cloud-based platforms a
Adjusting for Mistakes in Closing Entries
When preparing financial reports at the end of a period, it’s essential to ensure all balances are properly closed to the appropriate accounts. Any discrepancies or miscalculations in this phase can lead to inaccurate results. Adjusting these discrepancies promptly is crucial to ensure that the final figures reflect the true financial position of the business. By carefully reviewing the closing entries and making necessary adjustments, companies can avoid significant issues down the line.
Steps to Correct Closing Entry Mistakes

- Identify the Source of the Mistake: Begin by thoroughly reviewing the entries that were incorrectly closed. This could involve examining account balances or reviewing transaction logs to pinpoint where the discrepancy originated.
- Reverse the Incorrect Entry: If the closing entry has been posted incorrectly, reverse the entry in the books. This action undoes the impact of the mistake, allowing for a fresh adjustment.
- Make the Correct Entry: After reversing the incorrect entry, post the correct closing entry. Ensure that the adjusted amounts reflect the proper balances, taking into account all relevant transactions for the period.
- Verify the Adjusted Balances: Once the adjustment is made, review the updated balances to confirm that the correction has been implemented accurately. It’s vital to double-check the totals to ensure that they align with the expected outcome.
- Document the Changes: It’s important to maintain detailed records of any adjustments made to closing entries. Proper documentation provides an audit trail that can be useful for future reference or in case of an internal review.
Tools to Assist with Entry Adjustments
- Accounting Software: Many accounting platforms offer built-in tools to help identify and adjust closing entry mistakes automatically, reducing the time and effort needed for manual corrections.
- Reconciliation Tools: Using reconciliation tools to compare your adjusted closing balances with previous periods or expected results can help quickly spot any remaining discrepancies.
- Spreadsheet Templates: Templates designed for journal entries and closing entries can also be useful for tracking changes and ensuring the correct amounts are applied to the right accounts.
Examining Ethical Aspects of Adjustment
In the world of financial management, maintaining integrity and transparency is essential, especially when dealing with adjustments to recorded transactions. While it’s crucial to correct discrepancies, the manner in which these changes are handled can have significant ethical implications. Being aware of these concerns and addressing them properly ensures that the financial statements remain accurate and reliable while upholding the trust of stakeholders.
Ethical Principles to Consider
- Transparency: Any adjustments made to financial records should be clearly documented and disclosed. Failing to do so can mislead stakeholders and damage the credibility of the business.
- Accountability: Individuals responsible for making adjustments must take ownership of their actions and ensure that any corrections are fully justified and aligned with established guidelines.
- Fairness: Ensuring that adjustments do not disproportionately benefit or disadvantage any party is a key ethical concern. All stakeholders must be treated equitably, and corrections should not be used to manipulate financial outcomes.
- Confidentiality: Sensitive financial information must remain confidential throughout the process of making adjustments. Any disclosures should be made only to authorized parties and in accordance with company policies and regulations.
Potential Ethical Pitfalls
- Intentional Manipulation: One of the most serious ethical breaches occurs when adjustments are made with the intent to mislead or deceive others, such as inflating profits or hiding losses.
- Failure to Disclose Adjustments: When adjustments are not disclosed, even if they are legitimate, it can create a false representation of a company’s financial situation, leading to a loss of trust.
- Inconsistent Application: Applying adjustments unevenly across periods or accounts, for personal gain or to meet specific targets, violates ethical principles of fairness and integrity.
Mastering Error Reconciliation in Reports
When compiling financial reports, ensuring that all discrepancies between recorded and actual figures are properly addressed is a critical task. Reconciling differences requires careful examination and thorough analysis to align data, guaranteeing that financial statements reflect the true picture of an organization’s fiscal health. This process involves comparing initial records with corrected entries and ensuring that all adjustments are fully documented and justified.
Key Steps for Reconciliation
Reconciliation begins by identifying the source of the discrepancy and determining whether it’s related to a clerical mistake, misclassification, or an overlooked entry. Once identified, the next step is to review supporting documentation such as invoices, receipts, or bank statements to confirm the correct amounts. After verifying the information, any necessary adjustments should be made to ensure the data aligns with the true financial standing.
- Verify Supporting Documents: Always cross-check original records with external sources such as bank statements, contracts, and transaction logs.
- Check for Misclassifications: Sometimes discrepancies arise due to entries being placed in the wrong categories. These need to be corrected promptly.
- Correct and Update Entries: Once discrepancies are identified, ensure that all figures are adjusted accordingly and reflected accurately in the final report.
Common Challenges in Reconciliation
Despite best efforts, reconciling reports can present challenges. One common difficulty arises when historical data is missing or unclear, making it hard to trace the origins of discrepancies. Additionally, ensuring that all adjustments are documented in real-time can sometimes be cumbersome, especially in large organizations with complex financial structures. Regular audits and periodic reviews can help mitigate these issues and streamline the reconciliation process.
How to Avoid Repeating Mistakes
Preventing the recurrence of mistakes requires a proactive approach to both identifying their root causes and implementing strategies to address them effectively. By analyzing past missteps and refining processes, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of repeating the same issues. Creating a system of checks and balances and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are key components in achieving long-term accuracy and consistency.
Review and Reflect
One of the most effective ways to avoid making the same mistakes is to take time to review and reflect on previous actions. After recognizing where the mistake occurred, it’s essential to understand why it happened. Was it a result of rushed decision-making, insufficient information, or a breakdown in communication? Reflecting on these factors can help establish preventative measures to address the root causes.
- Analyze the Situation: Break down the process step by step to identify where things went wrong.
- Seek Feedback: Involve colleagues or supervisors in the review process for different perspectives and insights.
- Develop Actionable Solutions: Based on your findings, create a plan to avoid similar issues in the future.
Implement Preventative Measures
Once the causes are identified, it’s essential to implement changes to avoid repetition. Streamlining workflows, setting up automated processes, or introducing more rigorous verification methods can help ensure that similar mistakes do not reoccur. Additionally, regular training and updates on best practices will help keep everyone involved aware of the latest procedures and tools available to improve accuracy.
- Standardize Procedures: Establish clear guidelines and processes that everyone follows to minimize the chance of mistakes.
- Use Automation: Leverage software tools to automate repetitive tasks, reducing human error.
- Continuous Training: Ensure regular training sessions to keep skills up-to-date and reinforce best practices.
Preparing for an Accounting Final Exam
Effective preparation for any major assessment involves a combination of reviewing key concepts, practicing problem-solving skills, and creating a strategy to approach the test with confidence. In the context of financial recordkeeping and management, it’s essential to grasp both theoretical knowledge and practical application. By organizing study materials, understanding the core principles, and simulating test conditions, students can ensure they are well-equipped for success.
Review Key Concepts and Principles
Start by revisiting the foundational concepts that are likely to appear on the assessment. This includes understanding the various financial reports, methods for tracking transactions, and the rules for balancing ledgers. Make sure you are clear on topics such as:
- Financial Statements: Know the components of income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Trial Balances: Be comfortable preparing and interpreting trial balances.
- Adjusting Entries: Review the process for making adjustments to accounts at the end of an accounting period.
Practice Problem Solving
Working through sample problems is crucial in reinforcing your understanding and building the necessary skills to solve complex tasks during the test. Try to complete practice exercises related to journal entries, ledger posting, and reconciliation tasks. Focus on identifying any areas where you struggle and review the solutions thoroughly to understand your mistakes.
- Work with Mock Problems: Utilize sample questions and practice scenarios from textbooks or online resources.
- Time Yourself: Simulate exam conditions by timing yourself while completing exercises to build speed and accuracy.
- Review Your Mistakes: When you encounter difficulties, spend extra time understanding why your solution was incorrect.
Final Exam Tips for Error Correction
Successfully navigating any major assessment requires more than just memorization; it demands an ability to identify and address mistakes quickly and efficiently. Being able to pinpoint where things went wrong and applying the right solutions can make the difference between a passing and failing grade. Whether you’re facing theoretical questions or practical tasks, having a strategy in place to tackle issues will help you move through the test with greater confidence and precision.
Develop a Systematic Approach
When reviewing your work, it’s crucial to follow a structured approach to identify any discrepancies. Always start by thoroughly reading the instructions and ensuring you understand what is being asked. Then, review your calculations and check each step to see if they align with the principles you’ve studied. This methodical process will help you find and resolve any inconsistencies.
- Check the Fundamentals: Review the basic principles before moving on to more complex problems.
- Work Backwards: When you encounter an issue, try retracing your steps from the conclusion to the beginning.
- Stay Consistent: Use the same methodology for every task, ensuring uniformity in your work.
Manage Your Time Wisely
Time management is essential for dealing with complex questions efficiently. Allocate time for each section based on difficulty and importance, leaving room for review at the end. If you encounter a particularly tricky problem, don’t get stuck–move on to the next one and come back to it later with a fresh perspective.
- Prioritize Tasks: Start with easier questions that you can answer quickly to build confidence.
- Allocate Buffer Time: Make sure to leave time at the end for reviewing and fixing any mistakes you may have missed earlier.
- Don’t Rush: Take your time with each question, as rushing can lead to oversight.