
Assessing an individual’s mental state and cognitive abilities plays a crucial role in understanding various conditions that may affect their daily life. These evaluations help in identifying underlying issues that could be related to mental health or brain function. With such an assessment, healthcare professionals can offer a clearer picture of a person’s condition and guide treatment plans effectively.
Psychological and cognitive assessments aim to evaluate both the mind and brain function. They provide insight into how different factors, such as mood, memory, reasoning, and behavior, are interconnected. These evaluations can highlight specific challenges a person may be facing, whether they are linked to psychological stress or neurological impairments.
The results of these assessments are essential in formulating an accurate diagnosis. By assessing a person’s overall mental health alongside their cognitive abilities, specialists can tailor interventions, treatments, and support systems to suit individual needs. Understanding the full scope of an individual’s condition can make a significant difference in their overall well-being and quality of life.
What is a Mental and Cognitive Assessment
Assessing a person’s mental health and cognitive functioning is essential for understanding the complexities of their well-being. These evaluations focus on various aspects of an individual’s mental state, such as thought processes, behavior, emotional responses, and brain activity. The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of any potential challenges or disorders that could affect how a person thinks, feels, and acts.
Purpose of the Assessment
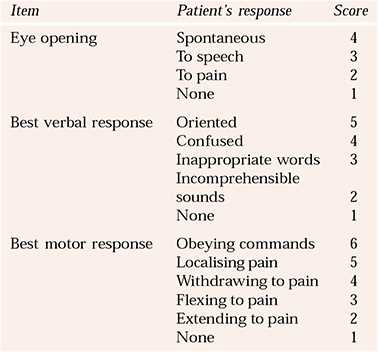
The main objective of such an evaluation is to identify any cognitive impairments or psychological conditions that may be impacting the individual’s daily life. By examining memory, attention, reasoning, and emotional regulation, specialists can form a clearer picture of the person’s condition. This insight can lead to more targeted treatments and interventions designed to address the specific needs of the individual.
What the Evaluation Includes
During this process, a series of tests and interviews are used to assess mental and cognitive functions. These may include tasks designed to measure attention span, memory recall, problem-solving abilities, and emotional responses. Additionally, interviews with the individual allow the healthcare provider to gain a deeper understanding of their personal history and any concerns they may have about their mental health. The combination of these methods provides a holistic view of the person’s condition.
Purpose of Mental and Cognitive Evaluations
The primary goal of assessing mental and cognitive functioning is to identify potential issues that could affect an individual’s mental well-being or brain performance. These evaluations help healthcare professionals understand the underlying causes of symptoms, whether they are related to emotional, psychological, or cognitive factors. By pinpointing specific areas of difficulty, specialists can develop personalized treatment plans to improve overall health and quality of life.
Key Objectives of the Evaluation
Such assessments serve several essential purposes, including:
- Identifying cognitive impairments such as memory loss or trouble with decision-making.
- Diagnosing mental health conditions that affect thinking, emotions, and behavior.
- Providing insight into how an individual’s mental state impacts their daily life.
- Guiding treatment strategies and therapeutic interventions tailored to individual needs.
- Monitoring changes in mental and cognitive function over time, especially in chronic conditions.
How Evaluations Support Diagnosis and Treatment
These evaluations not only help in diagnosing mental and cognitive disorders but also assist in tracking progress during treatment. By comparing baseline results with follow-up assessments, professionals can adjust therapeutic approaches, ensuring the most effective care. This process is especially beneficial for managing long-term conditions, as it provides ongoing insight into how the individual responds to different treatment options.
Common Techniques Used in Cognitive and Emotional Assessments
Understanding mental and cognitive health requires a combination of methods to evaluate how the mind processes information and reacts to different challenges. These techniques are designed to uncover potential areas of difficulty, providing insights into both emotional well-being and brain function. Each approach offers a unique perspective, ensuring a thorough evaluation.
Structured questioning is a foundational method, where specialists ask detailed questions about an individual’s experiences, behaviors, and thought patterns. This helps uncover any underlying issues that might not be immediately apparent. Additionally, performance-based tasks, such as memory recall exercises or problem-solving activities, are used to measure specific cognitive skills and processing speed.
Another common approach involves observing responses to certain scenarios or stimuli. This behavioral analysis can reveal patterns that indicate emotional or cognitive challenges. In some cases, physical tests like coordination or reflex checks are included to assess how well different systems in the body work together with mental functions.
How to Prepare for the Evaluation
Getting ready for a mental and cognitive assessment involves understanding what to expect and taking steps to ensure the process goes smoothly. Proper preparation can help individuals feel more at ease and provide the specialist with the most accurate information possible. It’s important to approach the evaluation with an open mind and a willingness to share details about your experiences.
Gather Relevant Information
Before the assessment, collect any documents that may be helpful, such as medical records, a list of medications, or notes on recent symptoms and changes in behavior. Having this information on hand ensures that the specialist has a complete understanding of your history, which is essential for accurate analysis. Additionally, be prepared to discuss family health history, as it can offer valuable context.
Prepare for the Day
Ensure you get adequate rest the night before, as fatigue can affect your responses during the evaluation. Arrive on time and bring any necessary items, such as identification or previously completed forms. If you have questions or concerns, write them down beforehand so they can be addressed during the session. Staying calm and focused will help you engage fully in the process.
What to Expect During an Evaluation
During a mental and cognitive evaluation, you will go through a series of assessments designed to understand your thinking, memory, emotions, and overall mental functioning. These evaluations are typically structured but can vary based on the specific concerns being addressed. The specialist will guide you through the process, explaining each step along the way.
- Initial Discussion: You will begin with a conversation where the evaluator asks about your health history, daily life, and any symptoms you’ve been experiencing. This helps build a clear understanding of your situation.
- Cognitive Tasks: You will be asked to complete tasks that assess various mental functions, such as problem-solving, attention, memory, and reasoning abilities.
- Behavioral Observation: Throughout the evaluation, the specialist will observe how you react to different situations, paying attention to emotional responses and cognitive processing.
- Physical Checks: Depending on the evaluation’s focus, you may also undergo basic physical tests, like checking reflexes or coordination, to assess how your body and mind work together.
Each step is designed to gather essential information that will help the specialist assess your cognitive health and emotional well-being accurately. The evaluator may take notes throughout the session, but it is an interactive process that encourages your participation and openness.
Key Areas Assessed in Mental and Cognitive Evaluations
A comprehensive mental and cognitive evaluation focuses on several key areas to understand how an individual’s brain and mind function. These areas are crucial for diagnosing potential cognitive impairments or mental health conditions and provide insights into the individual’s overall well-being. The assessment aims to uncover any areas where an individual may be experiencing difficulty, which can inform treatment plans and interventions.
Cognitive Functioning
This area evaluates how well a person can think, reason, and process information. Key aspects include:
- Memory: Short-term and long-term memory are assessed to determine how well an individual can recall information.
- Attention and Focus: Tasks that require sustained attention are used to measure concentration and the ability to stay focused.
- Problem-solving: The ability to approach and solve problems is examined through various tasks.
- Language Skills: An individual’s ability to express themselves and understand language is also evaluated.
Emotional and Psychological Well-being
Understanding the emotional state and mental health of an individual is equally important. This area includes:
- Mood and Affect: Assessing emotional responses and how consistent they are with external events or internal thoughts.
- Thought Patterns: Evaluating how thoughts are structured, and whether any cognitive distortions or irrational thinking occur.
- Behavioral Observations: Monitoring how an individual behaves during the assessment can reveal underlying emotional or psychological issues.
Role of Cognitive Testing in Diagnosis
Cognitive testing plays a critical role in diagnosing various mental and neurological conditions by assessing an individual’s ability to think, remember, reason, and process information. These tests help specialists identify areas where cognitive functioning may be impaired, providing valuable insight into the underlying causes of symptoms. By focusing on specific mental tasks, cognitive tests offer a clear, objective measure of an individual’s strengths and weaknesses in cognitive abilities.
Through the use of standardized tasks and exercises, cognitive testing can uncover subtle changes in brain function that may not be immediately noticeable in daily life. These tests are essential in diagnosing conditions such as dementia, memory disorders, and learning difficulties, as well as in tracking the progression of these conditions over time. The results guide clinicians in making accurate diagnoses, which in turn allows for tailored treatment plans to improve cognitive health and quality of life.
Understanding the Psychological Component
The psychological aspect of assessments focuses on an individual’s emotional state, mental processes, and behavioral patterns. It provides insight into how one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected and how they may impact overall mental health. This component plays a vital role in understanding the underlying causes of emotional distress or mental disorders, helping clinicians identify potential psychological conditions and develop appropriate treatment strategies.
Key Areas of Psychological Assessment

During psychological evaluations, several key areas are assessed to form a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s emotional and mental well-being. These areas include:
| Area of Focus | Description |
|---|---|
| Emotional Regulation | Evaluates the individual’s ability to manage and express emotions in a healthy manner. |
| Stress and Coping | Assesses how a person responds to stress and the strategies they use to cope with challenges. |
| Thought Patterns | Explores how thoughts are organized and whether they contribute to negative emotional states. |
| Social and Interpersonal Functioning | Examines how a person interacts with others and whether social relationships are healthy and functional. |
Importance in Diagnosis
Understanding the psychological component is essential for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, from anxiety and depression to personality disorders. It allows clinicians to identify the mental and emotional factors contributing to the individual’s symptoms. By focusing on both cognitive and emotional aspects, psychological assessments provide a well-rounded view of an individual’s mental health, enabling clinicians to offer more effective and personalized care.
Assessment for Mental Disorders
When individuals experience changes in their thoughts, emotions, or behaviors, a thorough evaluation is essential to understand the root causes of these changes. This process involves assessing cognitive abilities and emotional well-being, providing a comprehensive picture of an individual’s mental health. By examining these areas, healthcare providers can identify potential mental disorders and develop targeted treatment strategies.
Key Disorders Assessed
During the evaluation, a variety of mental health conditions are explored. Common disorders that may be assessed include:
- Anxiety Disorders: Evaluating excessive worry, fear, or nervousness that interferes with daily functioning.
- Depression: Assessing persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest, and low energy levels.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: Identifying recurring, uncontrollable thoughts or behaviors.
- Personality Disorders: Exploring patterns of thinking and behavior that significantly differ from societal norms.
- Psychotic Disorders: Assessing disorganized thinking, delusions, or hallucinations.
Process of Evaluation
The evaluation typically involves a combination of structured interviews, cognitive assessments, and behavioral observations. The clinician will ask detailed questions about the individual’s mental state, history of symptoms, and any recent changes. By gathering this information, they can identify specific symptoms, determine their severity, and consider the possibility of underlying mental disorders. This comprehensive approach is essential in making an accurate diagnosis and planning effective treatment.
Impact of Neurological Conditions on Mental Health
Certain brain disorders and conditions affecting the nervous system can have a profound impact on an individual’s emotional and psychological well-being. These conditions can lead to changes in cognition, mood, behavior, and overall mental health. The connection between neurological function and mental health is complex, and disruptions in one area often affect the other. Understanding this relationship is crucial for providing comprehensive care and support to individuals facing such challenges.
Common Neurological Conditions Affecting Mental Health
Several neurological disorders can contribute to mental health problems, including:
- Stroke: A stroke can cause cognitive impairments, memory loss, and emotional instability, leading to conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Parkinson’s Disease: As the disease progresses, individuals may experience depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline, in addition to motor symptoms.
- Multiple Sclerosis: This condition can affect mood regulation, leading to depression, irritability, and cognitive challenges.
- Dementia: Cognitive decline associated with dementia often leads to confusion, mood swings, and personality changes.
- Epilepsy: Seizure disorders can result in anxiety, depression, and even psychosis due to the impact of the condition on brain function.
Psychological Effects of Neurological Impairments
Individuals living with neurological conditions may experience a range of psychological effects due to the direct impact on brain function. These effects can include:
- Emotional Distress: Feelings of frustration, helplessness, or fear about the progression of the condition can lead to depression and anxiety.
- Social Isolation: Cognitive and behavioral changes can make social interactions difficult, leading to withdrawal and loneliness.
- Increased Stress: Coping with the physical and cognitive challenges of a neurological condition can contribute to heightened stress and anxiety.
Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of neurological conditions is essential for improving the overall well-being of affected individuals. Proper treatment, including medication and therapy, can help manage both the neurological symptoms and the mental health challenges associated with these conditions.
Interpreting Results of Mental Health Assessments
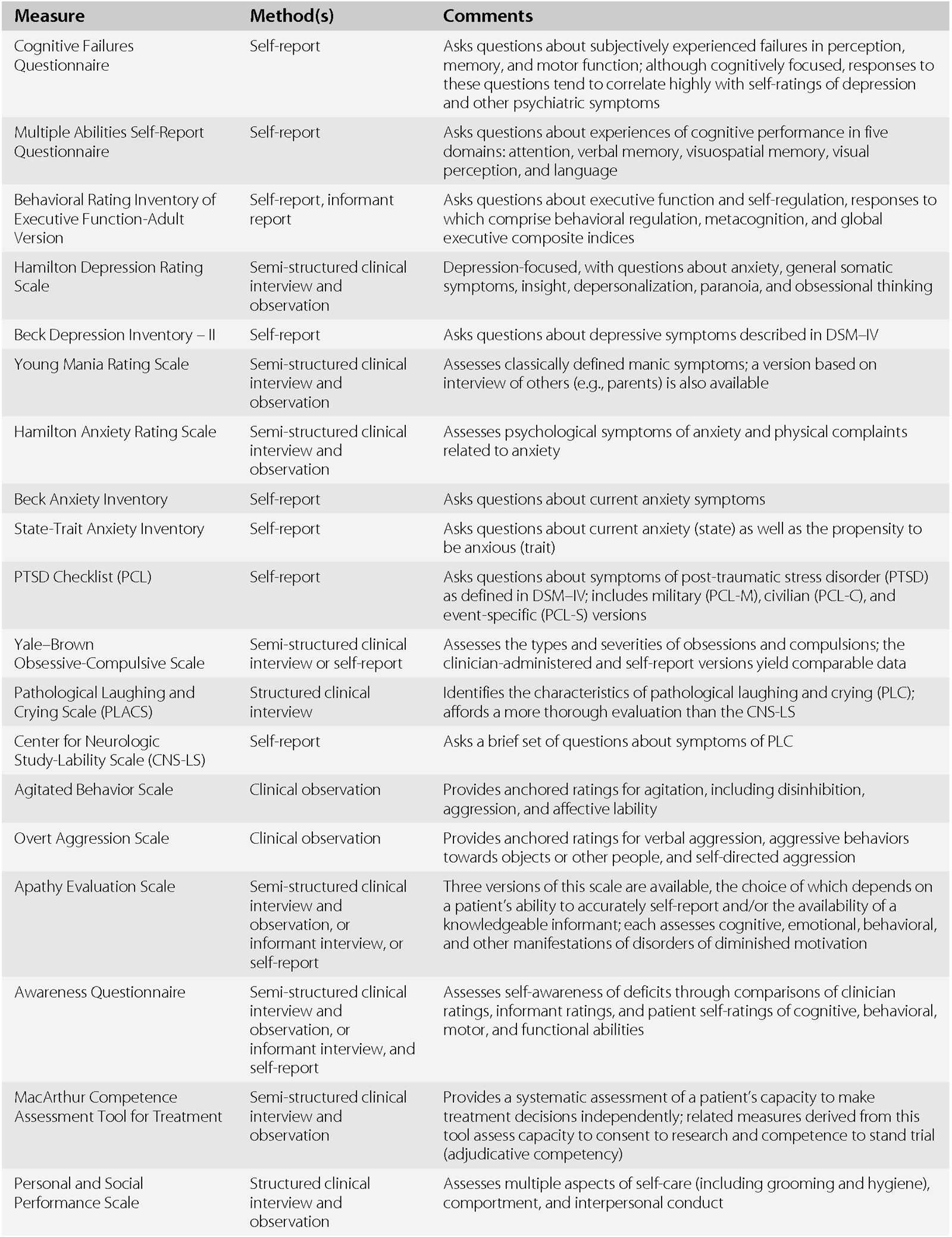
After completing a thorough evaluation of an individual’s cognitive and emotional state, the next crucial step is interpreting the results. These assessments provide insights into the person’s mental and emotional functioning, which can help healthcare providers understand the underlying causes of any difficulties. Proper interpretation is key to developing an effective treatment plan and ensuring that individuals receive the right care and support tailored to their specific needs.
Understanding Cognitive and Emotional Scores
The results of these evaluations often include a series of scores and qualitative observations that reflect different aspects of mental health. Cognitive tests measure areas such as memory, attention, problem-solving abilities, and language skills, while emotional assessments focus on mood, behavior, and stress responses. Both sets of data must be considered together to form a holistic understanding of an individual’s mental state. Common steps in interpreting these results include:
- Comparing Baseline and Current Functioning: Assessing changes from previous evaluations helps to track progress or identify worsening symptoms.
- Identifying Patterns: Patterns in cognitive and emotional responses can indicate the presence of specific conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or cognitive decline.
- Cross-Referencing with Clinical Observations: Test results should be compared with the individual’s medical history, behavior, and other clinical findings to ensure accuracy.
Challenges in Interpretation
While these assessments are valuable, interpreting the results can be challenging due to the complexity of mental health. Various factors, including the individual’s environment, medications, and personal history, can influence the outcome. Additionally, cognitive impairments and emotional distress may affect how individuals respond to questions or tasks, making it difficult to fully assess their abilities. Therefore, healthcare providers must approach the results with careful consideration and seek input from other specialists if necessary to form a complete understanding of the individual’s needs.
When is a Mental Health and Cognitive Assessment Needed
A comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s mental and cognitive functioning becomes necessary when there are noticeable changes or difficulties in their emotional well-being or thought processes. These assessments are used to identify the root causes of symptoms, whether they are linked to psychological, neurological, or physical factors. Early identification through such evaluations helps in determining the right course of treatment and provides valuable insights into the individual’s overall health.
Common situations where these assessments are recommended include:
- Unexplained Memory Problems: Difficulty with memory, concentration, or decision-making may indicate underlying conditions that need further evaluation.
- Changes in Behavior or Mood: Sudden shifts in mood, behavior, or personality can be signs of mental health conditions or neurological disorders.
- Suspected Cognitive Decline: Individuals showing signs of cognitive decline, such as forgetfulness or confusion, may require an assessment to determine the cause.
- After a Traumatic Injury: Following a head injury or other trauma, a detailed evaluation is crucial to assess any cognitive or emotional impacts.
- Difficulty Coping with Life Changes: Challenges such as dealing with stress, major life changes, or anxiety that interfere with daily functioning might require professional evaluation.
In these cases, a structured evaluation can help identify the problem early on and guide individuals towards appropriate treatment or management strategies.
Differences Between Psychological and Cognitive Assessments

While both psychological and cognitive assessments aim to evaluate an individual’s mental state, they focus on different aspects of mental functioning. Psychological assessments primarily investigate emotional health and behavioral patterns, whereas cognitive assessments examine intellectual functions like memory, problem-solving, and reasoning abilities. These evaluations serve distinct purposes, and understanding their differences is essential for addressing the specific needs of the individual.
Focus and Purpose
The primary difference between these two types of evaluations lies in what they seek to measure. Psychological assessments are designed to explore emotional well-being, personality traits, and mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, or trauma. These assessments help identify psychological conditions and guide treatment plans.
- Psychological assessments: Focus on emotional responses, behavior patterns, and mental health conditions.
- Cognitive assessments: Evaluate thinking processes, memory, attention, and intellectual capabilities.
Methods and Tools
Another key distinction is the tools and methods used in each evaluation. Psychological assessments often rely on interviews, questionnaires, and standardized tests to gauge emotions and behavioral traits. Cognitive assessments, on the other hand, involve tests that measure different aspects of mental functioning, such as memory recall, problem-solving, and attention span. These evaluations may include activities or tasks that challenge cognitive skills and help identify areas of concern.
- Psychological methods: Include personal interviews, surveys, and psychological tests designed to explore emotional health.
- Cognitive methods: Focus on tasks and activities that test memory, concentration, and intellectual abilities.
Who Conducts Mental and Cognitive Health Evaluations
Various healthcare professionals are trained to conduct thorough evaluations of mental health and cognitive functioning. These evaluations require expertise in understanding the complexities of both emotional well-being and cognitive processes. Depending on the nature of the assessment, different specialists may be involved to ensure that all aspects of an individual’s health are properly evaluated and addressed.
Professionals Involved in the Process
The individuals who conduct these evaluations typically have specialized training in either psychology, neurology, or psychiatry. Each professional brings their expertise to the evaluation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s mental state and cognitive abilities.
| Specialist | Role in Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Psychologist | Conducts assessments to evaluate emotional health, mental disorders, and behavioral patterns. |
| Neurologist | Assesses cognitive function and brain health, focusing on neurological conditions affecting mental performance. |
| Psychiatrist | Evaluates mental health disorders, prescribes medication, and provides therapeutic treatment for emotional well-being. |
Collaborative Approach
In many cases, these specialists work together to provide a complete and accurate picture of the individual’s health. While one professional might focus on the psychological or emotional aspect, another might evaluate the neurological or cognitive components. This collaborative approach helps to create a well-rounded treatment plan, tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Evaluations for Children and Adults
Assessments of mental health and cognitive functioning are crucial for individuals of all ages. The process may vary depending on the age group, as the way cognitive abilities and emotional health manifest can differ significantly between children and adults. These evaluations are tailored to meet the unique needs and challenges of each age group to provide accurate insights and effective interventions.
Key Differences in Assessments for Children
When conducting evaluations for children, special consideration is given to developmental stages and age-appropriate communication methods. In addition to assessing cognitive functions, the focus is often on understanding behavioral patterns and emotional responses. Common aspects considered in children’s assessments include:
- Developmental milestones: Understanding how well a child is progressing in cognitive, motor, and language skills.
- Behavioral observations: Identifying signs of emotional distress, hyperactivity, or social withdrawal.
- Parental input: Gathering information from caregivers to understand home and school behavior.
Evaluations for Adults
For adults, the assessment focuses more on complex cognitive abilities, mental health conditions, and emotional well-being. Adults may be evaluated for conditions such as depression, anxiety, memory loss, or other cognitive disorders. Key areas in adult evaluations typically include:
- Cognitive testing: Evaluating memory, attention, problem-solving, and executive function.
- Mental health assessments: Screening for mood disorders, anxiety, and other psychological conditions.
- Medical history: Assessing past medical issues or family history that could influence mental health or cognitive function.
In both children and adults, a multidisciplinary approach is often used, combining insights from various specialists to ensure a thorough understanding of the individual’s needs. This approach helps guide appropriate treatment and support strategies, tailored to the specific challenges faced by each person.
Benefits of Assessments for Mental and Cognitive Health
Comprehensive evaluations that examine mental and cognitive health can provide invaluable insights into an individual’s well-being. These assessments serve as an important tool for identifying underlying conditions, developing personalized treatment plans, and tracking progress over time. By offering a detailed understanding of cognitive abilities and emotional health, they can lead to more effective interventions and improved quality of life.
Early Detection of Conditions
One of the primary benefits of these evaluations is their ability to identify mental health or cognitive disorders in their early stages. Early detection can significantly improve the prognosis of conditions such as depression, anxiety, memory disorders, and cognitive impairments. Recognizing symptoms early allows for:
- Timely intervention: Addressing issues before they worsen or cause long-term damage.
- Targeted treatment: Designing treatments that specifically address the identified condition, improving effectiveness.
- Prevention of further complications: Avoiding the escalation of cognitive or emotional problems that could interfere with daily functioning.
Improved Treatment Planning and Support
Through thorough evaluations, healthcare professionals can create customized treatment plans that cater to the individual’s specific needs. These assessments help professionals understand the unique challenges faced by each person, whether they are dealing with cognitive decline, mental health disorders, or emotional distress. The key advantages include:
- Personalized care: Developing a care plan that is suited to the individual’s specific condition and circumstances.
- Holistic approach: Addressing both mental and cognitive health concerns together for a comprehensive treatment strategy.
- Ongoing monitoring: Tracking the progression of conditions and adjusting treatment plans as needed to ensure continuous improvement.
Overall, the benefits of these assessments extend beyond just diagnosing conditions. They play a crucial role in guiding individuals toward a better quality of life by providing valuable insights into their mental and cognitive health, helping both patients and healthcare providers work together for the best possible outcomes.